FLAT is a web-based linguistic annotation environment based around the FoLiA format (https://proycon.github.io/folia), a rich XML-based format for linguistic annotation. Flat allows users to view annotated FoLiA documents and enrich these documents with new annotations, a wide variety of linguistic annotation types is supported through the FoLiA paradigm.
Project description

FLAT - FoLiA Linguistic Annotation Tool
FLAT is a web-based linguistic annotation environment based around the FoLiA format (http://proycon.github.io/folia), a rich XML-based format for linguistic annotation. FLAT allows users to view annotated FoLiA documents and enrich these documents with new annotations, a wide variety of linguistic annotation types is supported through the FoLiA paradigm. It is a document-centric tool that fully preserves and visualises document structure.
The project is in its early stages but already quite functional and in practical use in an academic setting.
FLAT is written in Python using the Django framework. The user interface is written using javascript with jquery. The FoLiA Document Server (https://github.com/proycon/foliadocserve) , the back-end of the system, is written in Python with CherryPy and is used as a RESTful webservice.
Features
Web-based, multi-user environment
Server-side document storage, divided into ‘namespaces’, by default each user has his own namespace. Active documents are held in memory server-side. Read and write permissions to access namespaces are fully configurable.
Concurrency (multiple users may edit the same document similtaneously) [not completed yet]
Full versioning control for documents (using git), allowing limitless undo operations. (in foliadocserve)
Full annotator information, with timestamps, is stored in the FoLiA XML and can be displayed by the interface. The git log also contains verbose information on annotations.
Annotators can indicate their confidence for each annotation
Highly configurable interface; interface options may be disabled on a per-configuration basis. Multiple configurations can be deployed on a single installation
Displays and retains document structure (divisions, paragraphs, sentence, lists, etc)
Support for corrections, of text or linguistic annotations, and alternative annotations. Corrections are never mere substitutes, originals are always preserved!
Spelling corrections for runons, splits, insertions and deletions are supported.
Supports FoLiA Set Definitions to display label sets. Sets are not predefined in FoLiA and anybody can create their own.
Supports Token Annotation and Span Annotation
Simple metadata editor for editing/adding arbitrary metadata to a document
Architecture
The FLAT architecture consists of three layers:
The FoLiA Document Server (https://github.com/proycon/foliadocserve)
The FLAT server
The user-interface
At the far back-end is the FoLiA Document Server, which loads the requested FoLiA documents, and passes these as JSON and HTML to the middle layer, the FLAT server, this layer in turn passes edits formulated in FoLiA Query Language (FQL) to the Document Server. The user-interface is a modern web-application interacting with the FLAT server and translates interface actions to FQL.
FLAT distinguishes several modes, between which the user can switch to get another take of a document with different editing abilities. There are currently two modes available, and a third one under construction:
Viewer - Views a document and its annotations, no editing abilities
Editor - Main editing environment for linguistic annotation
Structure Editor - Editing environment for document structure (rudimentary version, not done)
In the viewer and editor mode, users may set an annotation focus, i.e. an annotation type that they want to visualise or edit. All instances of that annotation type will be coloured in the interface and offer a global overview. Moreover, the editor dialog will automatically present fields for editing that type whenever a structure element (usually a word/token) is clicked.
Whereas the annotation focus is primary, users may select what other annotation types they want to view locally, i.e. in the annotation viewer that pops up whenever the user hovers over a structural element. Similarly, users may select what annotation types they want to see in editor, allowing the editing of multiple annotation types at once rather than just the annotation focus.
FoLiA distinguishes itself from some other annotation formats by explicitly providing support for corrections (on any annotation type, including text) and alternative annotations. In FLAT these are categorized as edit forms, as they are different forms of editing; the user can select which form he wants to use when performing an annotation.
The site administrator can configure in great detail what options the user has available and what defaults are selected (for annotation focus for instance), as a full unconstrained environment (which is the default) may quickly be daunting and confusing to the end-user. Different tasks ask for different configurations, so multiple configurations per site are possible; the user chooses the desired configuration, often tied to a particular annotation project, upon login.
Installation
Setting up a web application is often a fairly complex endeavour. We provide instructions in this sections.
FLAT runs on Python 3 (the document server requires Python 3, the rest can also work on Python 2). We recommend installation in a Python virtualenv, create one as follows:
$ virtualenv --python=python3 env
Activate the virtual environment as follows (you will need to do this every time you want to access the virtual environment):
$ . env/bin/activate
FLAT can then simply be installed through the Python Package Index:
$ pip install FoLiA-Linguistic-Annotation-Tool
Or alternatively from the cloned git repository:
$ pip install -r requires.txt #(to install the dependencies) $ python3 setup.py install
If you are the system administrator and opt for a global installation instead of using a virtualenv, then just add sudo on most Linux distributions.
The following dependencies will be pulled in automatically if you follow either of the above steps:
foliadocserve (https://github.com/proycon/foliadocserve)
pynlpl (https://github.com/proycon/pynlpl) (contains the FoLiA and FQL library)
django (https://www.djangoproject.com)
Updating
To update your existing instalation of flat, run:
$ pip install -U FoLiA-Linguistic-Annotation-Tool
In production environments, you will then also need to update your configuration to point to the right version.
FLAT Configuration
Copy the settings.py that comes with FLAT (or grab it from https://github.com/proycon/flat/blob/master/settings.py) to some custom location, edit it and add a configuration for your system. The file is heavily commented to guide you along with the configuration. It is here where you specify what your users will see and what function are enabled..
Database Configuration
FLAT uses a database to store user accounts. In your settings.py you refer to this database. Multiple backends are supported (MySQL, PostgreSQL and others). Make sure you create the desired database and user, with proper rights to access and modify the database, in your database management system.
Before you start FLAT for the first time, this database needs to be populated. Set PYTHONPATH to the directory that contains your settings.py and initialise the database:
$ export PYTHONPATH=/your/settings/path/ $ django-admin syncdb --settings settings
Starting the Document Server
FLAT constantly talks to a document server running in the background. We need to start the FoLiA document server prior to starting FLAT, it is a required component that needs not necessarily be on the same host. Your copy of settings.py should point to the host and port where FLAT can reach the document server, start it as follows:
$ foliadocserve -d /path/to/document/root -p 8080
The document path will be a directory that will contain all FoLiA documents. Create a root directory and ensure the user the foliadocserve is running under has sufficient write permission there. The document server needs no further configuration. Note that it does not provide any authentication features so it should run somewhere where the outside world can NOT reach it, only FLAT needs to be able to connect to it. Often, FLAT and the document server run on the same host, so a localhost connection is sufficient.
Starting FLAT (development server)
After all this is done, the development server can be started now using your settings.py by setting PYTHONPATH to the directory that contains it:
$ export PYTHONPATH=/your/settings/path/ $ django-admin runserver --settings settings
FLAT will advertise the host and port it is running on (as configured in your settings.py), and you can access it in your browser.
Tests
FLAT has integration and automatic interface tests for the annotation editor, point your browser to http://127.0.0.1:8000/editor/testflat/testflat to execute all tests.
Deployment in Production
The development server is not intended for production use. In production environments, you will want to hook up FLAT to a webserver such as Apache2 or nginx. First ensure that you completed all previous steps and you manage to run the development server properly, as this mode is by definition more suited for debugging any problems that may occur. After all that works, you can consider deployment in a production setting.
For Apache2, you can use either mod_wsgi or mod_uwsgi_proxy. For both, you need a wsgi script, so the first step is to copy the provided template.wsgi (or grab it from https://github.com/proycon/flat/blob/master/template.wsgi) and edit it for your situation, this script will be referenced from your web server’s configuration. It is commented to guide you in the setup.
Apache 2.4 with mod_wsgi:
1) Install and enable the mod_wsgi module for Apache (corresponding also to the Python version you intend to use). On Debian/Ubuntu systems, install the package libapache2-mod-wsgi (python 2) or libapache2-mod-wsgi-py3 (python 3). 2) Configure Apache2 for FLAT. We assume you use a dedicated subdomain for FLAT, so a configuration with a dedicated VirtualHost directive. Create a file flat in /etc/apache2/sites-available/ (or similar) to this end. The configuration within should look as follows, but make sure all paths and Python and FLAT version numbers correspond exactly to your setup:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName flat.yourdomain.org
WSGIScriptAlias / /path/to/your_copy_of_template.wsgi
Alias /static/ /path/to/virtualenv/lib/python3.4/site-packages/django/contrib/admin/static/
Alias /style/ /path/to/virtualenv/lib/python3.4/site-packages/FoLiA_Linguistic_Annotation_Tool-0.4.2-py3.4.egg/flat/style/
<Directory /path/to/virtualenv/lib/python3.4/site-packages/FoLiA_Linguistic_Annotation_Tool-0.4.2-py3.4.egg/flat/style/>
Options All
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
<Directory /path/to/virtualenv/lib/python3.4/site-packages/django/contrib/admin/static/>
Options All
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>If you did not use a virtualenv but installed everything globally then /path/to/virtualenv/ is usually /usr/ or /usr/local/. The FLAT directory may also reside in dist-packages/flat/ on some installations.
Enable the configuration using sudo a2ensite flat and restart Apache after this.
Screenshots
The login screen:
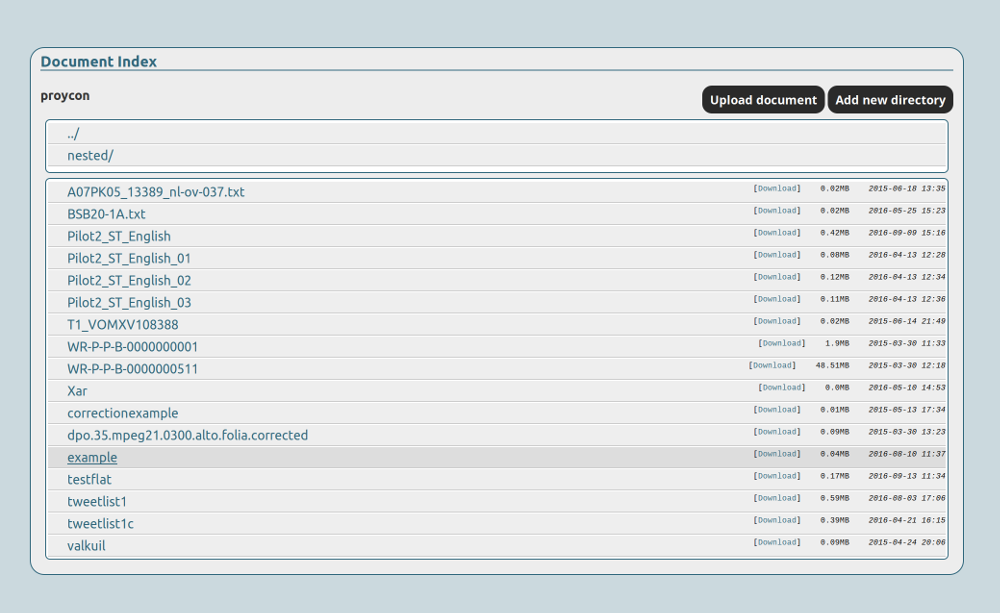
Document index, showing namespaces accessible to the user and the documents within.
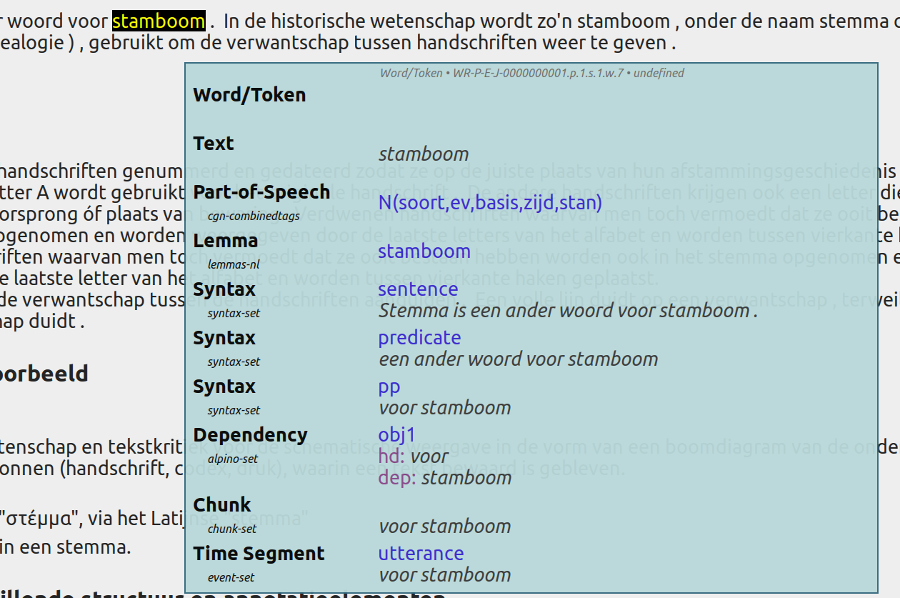
Hovering over words reveals annotations:
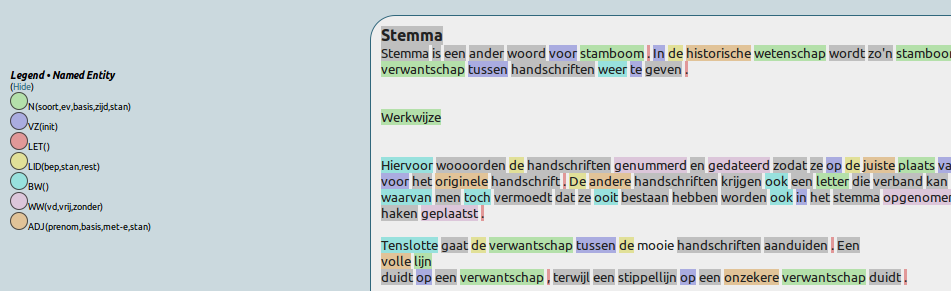
A particular annotation focus can be set to highlight the most frequent classes in that set:

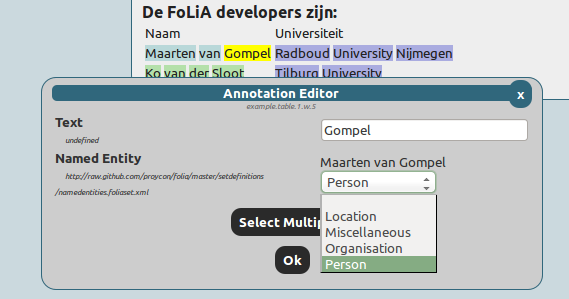
Editing a named entity in a set for which a set definition is available:
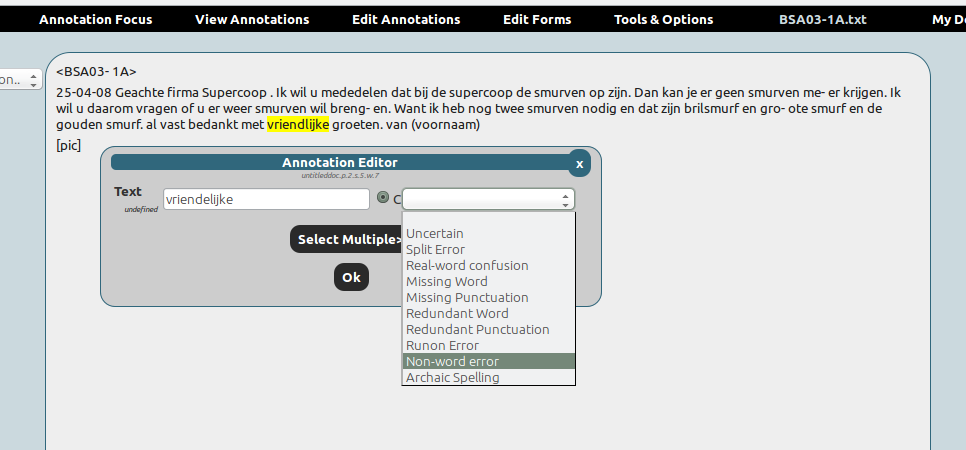
Correcting a word in a spelling-annotation project:
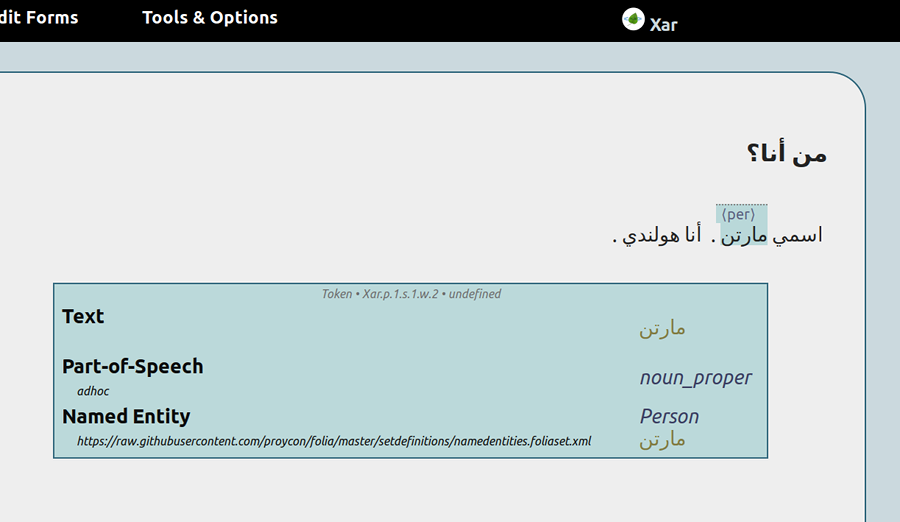
Proper right-to-left support for languages such as Arabic, Farsi and Hebrew. This relies on the FoLiA document having either a metadata attribute direction set to rtl, or a properly set language field in the metadata.
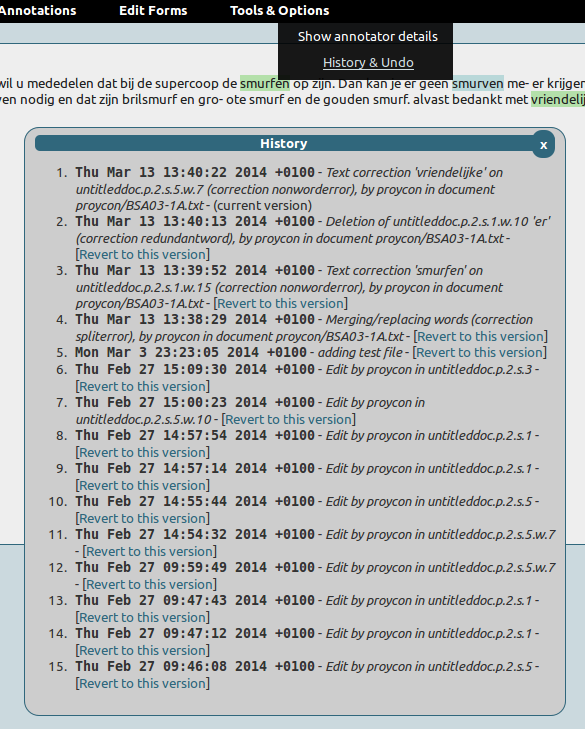
Extensive history with limitless undo ability, git-based:
FoLiA & Set Definitions
We urge people wanting to set up FLAT to familiarise themselves with FoLiA, as the tool is specifically designed for this format. Characteristic of FoLiA is the class/set paradigm and the distinction of a large number of specific annotation types, such as for example part-of-speech, lemma, dependencies, syntax, co-references, semantic roles, and many more…
The values of annotations, of whatever type, are known as classes, which in turn are the elements of sets. A set thus defines what classes exist. A set is for example a part-of-speech tagset, and the invidual part-of-speech tags would be the classes. FoLiA itself never prescribes sets, only annotation types, it is up to the user to decide what set to use and anybody can freely create sets! This offers a great deal of flexibility, as you can use FLAT and FoLiA with whatever tagset you desire (provided you make a set definition for it).
Sets are defined in Set Definition files, these tie the classes to nice human presentable labels (they may also impose taxonomies, put constraints on class combinations, and link to data category registries). FLAT relies on these set definitions a great deal, as it uses them to present the labels for the classes.
For more information about FoLiA, see https://proycon.github.io/folia , the format itself is extensively documented.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Hashes for FoLiA-Linguistic-Annotation-Tool-0.5.tar.gz
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | cad83121074b0b71ba1a3263ef0961e4537f09710aa14623cb8a4260d41ce008 |
|
| MD5 | d157e8d05b72f6ea54ff11e3fd38daf5 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 219bf6aa634e46178ad65ccdbf1efc8b82725a9a66054e00e25a9ed2d376a712 |











