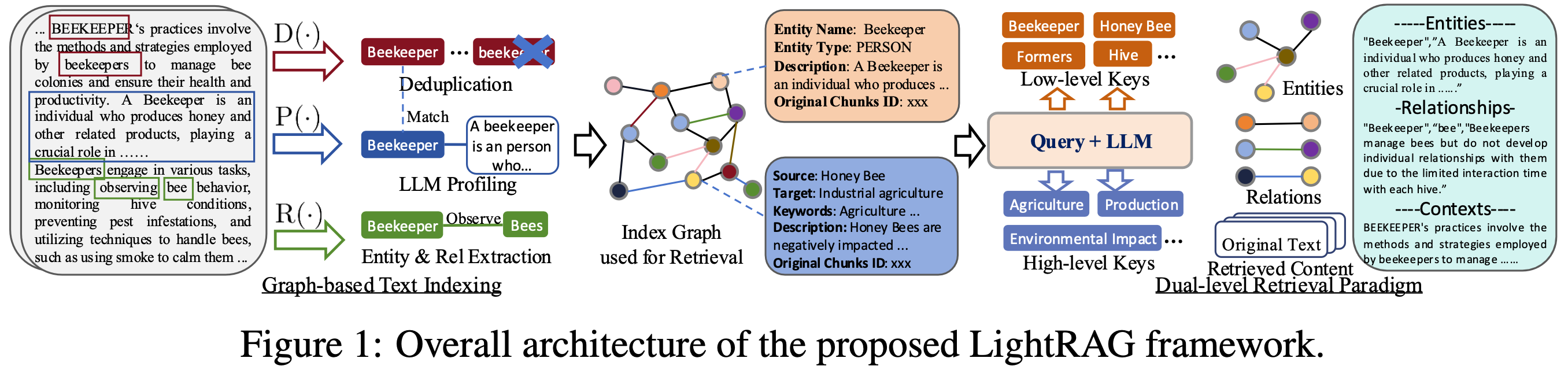
LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Project description
LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation
🎉 News
- [2024.10.15]🎯🎯📢📢LightRAG now supports Hugging Face models!
Install
- Install from source
cd LightRAG
pip install -e .
- Install from PyPI
pip install lightrag-hku
Quick Start
- Set OpenAI API key in environment if using OpenAI models:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="sk-...". - Download the demo text "A Christmas Carol by Charles Dickens":
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gusye1234/nano-graphrag/main/tests/mock_data.txt > ./book.txt
Use the below Python snippet to initialize LightRAG and perform queries:
from lightrag import LightRAG, QueryParam
from lightrag.llm import gpt_4o_mini_complete, gpt_4o_complete
WORKING_DIR = "./dickens"
if not os.path.exists(WORKING_DIR):
os.mkdir(WORKING_DIR)
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=gpt_4o_mini_complete # Use gpt_4o_mini_complete LLM model
# llm_model_func=gpt_4o_complete # Optionally, use a stronger model
)
with open("./book.txt") as f:
rag.insert(f.read())
# Perform naive search
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="naive")))
# Perform local search
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="local")))
# Perform global search
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="global")))
# Perform hybrid search
print(rag.query("What are the top themes in this story?", param=QueryParam(mode="hybrid")))
Using Hugging Face Models
If you want to use Hugging Face models, you only need to set LightRAG as follows:
from lightrag.llm import hf_model_complete, hf_embedding
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
# Initialize LightRAG with Hugging Face model
rag = LightRAG(
working_dir=WORKING_DIR,
llm_model_func=hf_model_complete, # Use Hugging Face complete model for text generation
llm_model_name='meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct', # Model name from Hugging Face
# Use Hugging Face embedding function
embedding_func=EmbeddingFunc(
embedding_dim=384,
max_token_size=5000,
func=lambda texts: hf_embedding(
texts,
tokenizer=AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2"),
embed_model=AutoModel.from_pretrained("sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
)
),
)
Batch Insert
# Batch Insert: Insert multiple texts at once
rag.insert(["TEXT1", "TEXT2",...])
Incremental Insert
# Incremental Insert: Insert new documents into an existing LightRAG instance
rag = LightRAG(working_dir="./dickens")
with open("./newText.txt") as f:
rag.insert(f.read())
Evaluation
Dataset
The dataset used in LightRAG can be download from TommyChien/UltraDomain.
Generate Query
LightRAG uses the following prompt to generate high-level queries, with the corresponding code located in example/generate_query.py.
Given the following description of a dataset:
{description}
Please identify 5 potential users who would engage with this dataset. For each user, list 5 tasks they would perform with this dataset. Then, for each (user, task) combination, generate 5 questions that require a high-level understanding of the entire dataset.
Output the results in the following structure:
- User 1: [user description]
- Task 1: [task description]
- Question 1:
- Question 2:
- Question 3:
- Question 4:
- Question 5:
- Task 2: [task description]
...
- Task 5: [task description]
- User 2: [user description]
...
- User 5: [user description]
...
Batch Eval
To evaluate the performance of two RAG systems on high-level queries, LightRAG uses the following prompt, with the specific code available in example/batch_eval.py.
---Role---
You are an expert tasked with evaluating two answers to the same question based on three criteria: **Comprehensiveness**, **Diversity**, and **Empowerment**.
---Goal---
You will evaluate two answers to the same question based on three criteria: **Comprehensiveness**, **Diversity**, and **Empowerment**.
- **Comprehensiveness**: How much detail does the answer provide to cover all aspects and details of the question?
- **Diversity**: How varied and rich is the answer in providing different perspectives and insights on the question?
- **Empowerment**: How well does the answer help the reader understand and make informed judgments about the topic?
For each criterion, choose the better answer (either Answer 1 or Answer 2) and explain why. Then, select an overall winner based on these three categories.
Here is the question:
{query}
Here are the two answers:
**Answer 1:**
{answer1}
**Answer 2:**
{answer2}
Evaluate both answers using the three criteria listed above and provide detailed explanations for each criterion.
Output your evaluation in the following JSON format:
{{
"Comprehensiveness": {{
"Winner": "[Answer 1 or Answer 2]",
"Explanation": "[Provide explanation here]"
}},
"Empowerment": {{
"Winner": "[Answer 1 or Answer 2]",
"Explanation": "[Provide explanation here]"
}},
"Overall Winner": {{
"Winner": "[Answer 1 or Answer 2]",
"Explanation": "[Summarize why this answer is the overall winner based on the three criteria]"
}}
}}
Overall Performance Table
| Agriculture | CS | Legal | Mix | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaiveRAG | LightRAG | NaiveRAG | LightRAG | NaiveRAG | LightRAG | NaiveRAG | LightRAG | |
| Comprehensiveness | 32.69% | 67.31% | 35.44% | 64.56% | 19.05% | 80.95% | 36.36% | 63.64% |
| Diversity | 24.09% | 75.91% | 35.24% | 64.76% | 10.98% | 89.02% | 30.76% | 69.24% |
| Empowerment | 31.35% | 68.65% | 35.48% | 64.52% | 17.59% | 82.41% | 40.95% | 59.05% |
| Overall | 33.30% | 66.70% | 34.76% | 65.24% | 17.46% | 82.54% | 37.59% | 62.40% |
| RQ-RAG | LightRAG | RQ-RAG | LightRAG | RQ-RAG | LightRAG | RQ-RAG | LightRAG | |
| Comprehensiveness | 32.05% | 67.95% | 39.30% | 60.70% | 18.57% | 81.43% | 38.89% | 61.11% |
| Diversity | 29.44% | 70.56% | 38.71% | 61.29% | 15.14% | 84.86% | 28.50% | 71.50% |
| Empowerment | 32.51% | 67.49% | 37.52% | 62.48% | 17.80% | 82.20% | 43.96% | 56.04% |
| Overall | 33.29% | 66.71% | 39.03% | 60.97% | 17.80% | 82.20% | 39.61% | 60.39% |
| HyDE | LightRAG | HyDE | LightRAG | HyDE | LightRAG | HyDE | LightRAG | |
| Comprehensiveness | 24.39% | 75.61% | 36.49% | 63.51% | 27.68% | 72.32% | 42.17% | 57.83% |
| Diversity | 24.96% | 75.34% | 37.41% | 62.59% | 18.79% | 81.21% | 30.88% | 69.12% |
| Empowerment | 24.89% | 75.11% | 34.99% | 65.01% | 26.99% | 73.01% | 45.61% | 54.39% |
| Overall | 23.17% | 76.83% | 35.67% | 64.33% | 27.68% | 72.32% | 42.72% | 57.28% |
| GraphRAG | LightRAG | GraphRAG | LightRAG | GraphRAG | LightRAG | GraphRAG | LightRAG | |
| Comprehensiveness | 45.56% | 54.44% | 45.98% | 54.02% | 47.13% | 52.87% | 51.86% | 48.14% |
| Diversity | 19.65% | 80.35% | 39.64% | 60.36% | 25.55% | 74.45% | 35.87% | 64.13% |
| Empowerment | 36.69% | 63.31% | 45.09% | 54.91% | 42.81% | 57.19% | 52.94% | 47.06% |
| Overall | 43.62% | 56.38% | 45.98% | 54.02% | 45.70% | 54.30% | 51.86% | 48.14% |
Reproduce
All the code can be found in the ./reproduce directory.
Step-0 Extract Unique Contexts
First, we need to extract unique contexts in the datasets.
def extract_unique_contexts(input_directory, output_directory):
os.makedirs(output_directory, exist_ok=True)
jsonl_files = glob.glob(os.path.join(input_directory, '*.jsonl'))
print(f"Found {len(jsonl_files)} JSONL files.")
for file_path in jsonl_files:
filename = os.path.basename(file_path)
name, ext = os.path.splitext(filename)
output_filename = f"{name}_unique_contexts.json"
output_path = os.path.join(output_directory, output_filename)
unique_contexts_dict = {}
print(f"Processing file: {filename}")
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as infile:
for line_number, line in enumerate(infile, start=1):
line = line.strip()
if not line:
continue
try:
json_obj = json.loads(line)
context = json_obj.get('context')
if context and context not in unique_contexts_dict:
unique_contexts_dict[context] = None
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"JSON decoding error in file {filename} at line {line_number}: {e}")
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"File not found: {filename}")
continue
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred while processing file {filename}: {e}")
continue
unique_contexts_list = list(unique_contexts_dict.keys())
print(f"There are {len(unique_contexts_list)} unique `context` entries in the file {filename}.")
try:
with open(output_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as outfile:
json.dump(unique_contexts_list, outfile, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
print(f"Unique `context` entries have been saved to: {output_filename}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred while saving to the file {output_filename}: {e}")
print("All files have been processed.")
Step-1 Insert Contexts
For the extracted contexts, we insert them into the LightRAG system.
def insert_text(rag, file_path):
with open(file_path, mode='r') as f:
unique_contexts = json.load(f)
retries = 0
max_retries = 3
while retries < max_retries:
try:
rag.insert(unique_contexts)
break
except Exception as e:
retries += 1
print(f"Insertion failed, retrying ({retries}/{max_retries}), error: {e}")
time.sleep(10)
if retries == max_retries:
print("Insertion failed after exceeding the maximum number of retries")
Step-2 Generate Queries
We extract tokens from both the first half and the second half of each context in the dataset, then combine them as the dataset description to generate queries.
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained('gpt2')
def get_summary(context, tot_tokens=2000):
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(context)
half_tokens = tot_tokens // 2
start_tokens = tokens[1000:1000 + half_tokens]
end_tokens = tokens[-(1000 + half_tokens):1000]
summary_tokens = start_tokens + end_tokens
summary = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_string(summary_tokens)
return summary
Step-3 Query
For the queries generated in Step-2, we will extract them and query LightRAG.
def extract_queries(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
data = f.read()
data = data.replace('**', '')
queries = re.findall(r'- Question \d+: (.+)', data)
return queries
Code Structure
.
├── examples
│ ├── batch_eval.py
│ ├── generate_query.py
│ ├── lightrag_openai_demo.py
│ └── lightrag_hf_demo.py
├── lightrag
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── base.py
│ ├── lightrag.py
│ ├── llm.py
│ ├── operate.py
│ ├── prompt.py
│ ├── storage.py
│ └── utils.py
├── reproduce
│ ├── Step_0.py
│ ├── Step_1.py
│ ├── Step_2.py
│ └── Step_3.py
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
└── setup.py
Citation
@article{guo2024lightrag,
title={LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation},
author={Zirui Guo and Lianghao Xia and Yanhua Yu and Tu Ao and Chao Huang},
year={2024},
eprint={2410.05779},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.IR}
}
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
File details
Details for the file lightrag_hku-0.0.5.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: lightrag_hku-0.0.5.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 31.9 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/5.1.1 CPython/3.10.14
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | c9cdb499c012b31357cc690e8bdf2b907d32c6010a5a7f07acf692d332a829a8 |
|
| MD5 | ddf7fd89df4f9284bf4252781afa9dce |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 17d8a804a548f3d0fb7780e1a71be8ee2e110628910ed301c0d663b70f313081 |
File details
Details for the file lightrag_hku-0.0.5-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: lightrag_hku-0.0.5-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 29.3 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/5.1.1 CPython/3.10.14
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | b40dc641cf5cffa13119b9d1c5ecddcdff6548e7e88faf02eec93baf3d30180b |
|
| MD5 | 456391fe70574f05ccb990aa85d32a6d |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 1562a773f0a17832ea97372e8a25a494f939d0ac7ba9503b5015b73e674234a5 |