Quantum Entanglement in Python
Project description
Quantum Entanglement in Python
Version
The releases of pyqentangle 2.x.x is incompatible with previous releases.
The releases of pyqentangle 3.x.x is incompatible with previous releases.
Since release 3.1.0, the support for Python 2 was decomissioned.
Installation
This package can be installed using pip.
>>> pip install pyqentangle
To use it, enter
>>> import pyqentangle
>>> import numpy as np
Schmidt Decomposition for Discrete Bipartite States
We first express the bipartite state in terms of a tensor. For example, if the state is |01>+|10>, then express it as
>>> tensor = np.array([[0., np.sqrt(0.5)], [np.sqrt(0.5), 0.]])
To perform the Schmidt decompostion, just enter:
>>> pyqentangle.schmidt_decomposition(tensor)
[(0.7071067811865476, array([ 0., -1.]), array([-1., -0.])),
(0.7071067811865476, array([-1., 0.]), array([-0., -1.]))]
For each tuple in the returned list, the first element is the Schmidt coefficients, the second the component for first subsystem, and the third the component for the second subsystem.
Schmidt Decomposition for Continuous Bipartite States
We can perform Schmidt decomposition on continuous systems too. For example, define the following normalized wavefunction:
>>> fcn = lambda x1, x2: np.exp(-0.5 * (x1 + x2) ** 2) * np.exp(-(x1 - x2) ** 2) * np.sqrt(np.sqrt(8.) / np.pi)
Then perform the Schmidt decomposition,
>>> modes = pyqentangle.continuous_schmidt_decomposition(biwavefcn, -10., 10., -10., 10., keep=10)
where it describes the ranges of x1 and x2 respectively, and keep=10 specifies only top 10 Schmidt modes are kept. Then we can read the Schmidt coefficients:
>>> list(map(lambda dec: dec[0], modes))
[0.9851714310094161,
0.1690286950361957,
0.02900073920775954,
0.004975740210361192,
0.0008537020544076649,
0.00014647211608480773,
2.51306421011773e-05,
4.311736522272035e-06,
7.39777032460608e-07,
1.2692567250688184e-07]
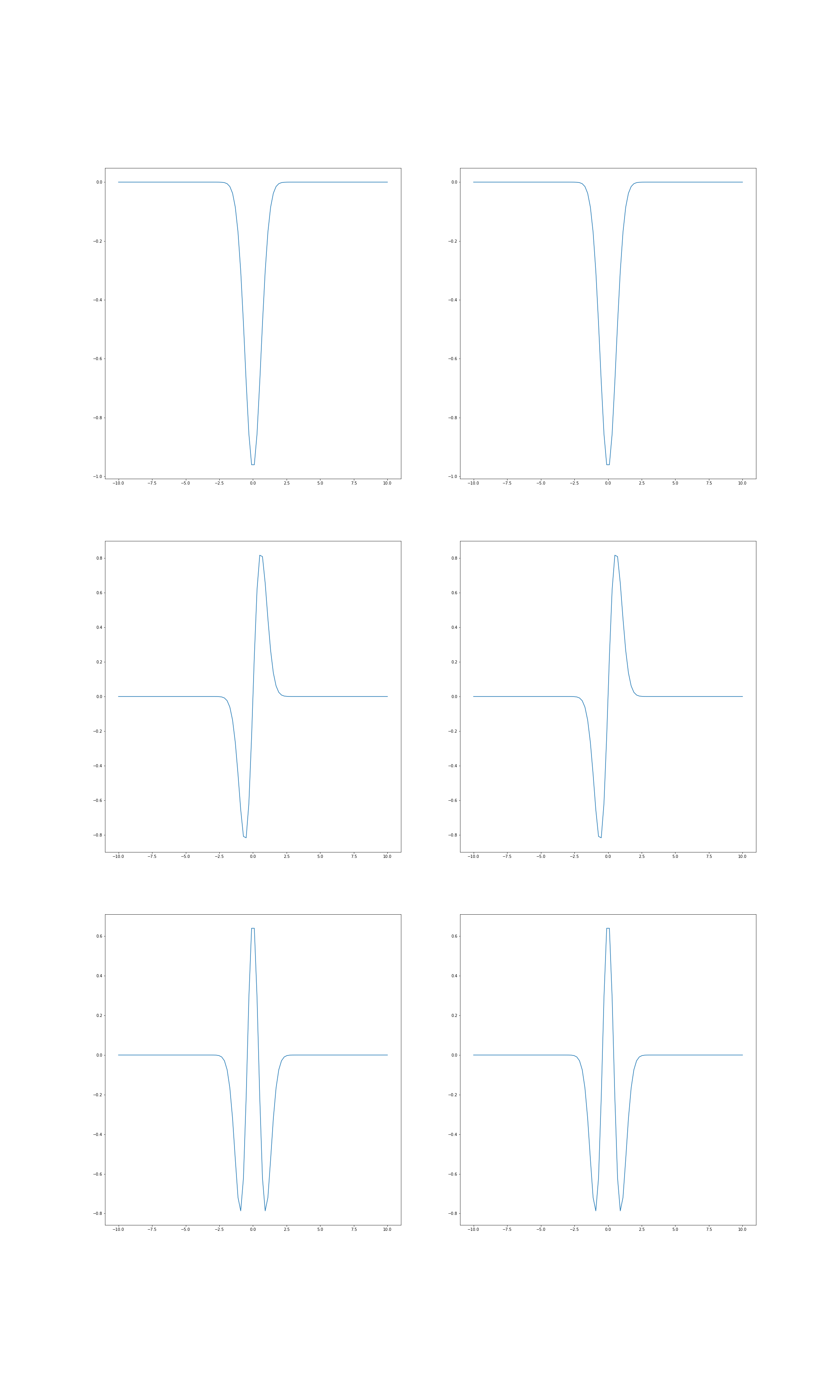
The second and the third elements in each tuple in the list decompositions are lambda functions for the modes of susbsystems A and B respectively. The Schmidt functions can be plotted:
>>> xarray = np.linspace(-10., 10., 100)
plt.subplot(3, 2, 1)
plt.plot(xarray, modes[0][1](xarray))
plt.subplot(3, 2, 2)
plt.plot(xarray, modes[0][2](xarray))
plt.subplot(3, 2, 3)
plt.plot(xarray, modes[1][1](xarray))
plt.subplot(3, 2, 4)
plt.plot(xarray, modes[1][2](xarray))
plt.subplot(3, 2, 5)
plt.plot(xarray, modes[2][1](xarray))
plt.subplot(3, 2, 6)
plt.plot(xarray, modes[2][2](xarray))
Useful Links
- Study of Entanglement in Quantum Computers: https://datawarrior.wordpress.com/2017/09/20/a-first-glimpse-of-rigettis-quantum-computing-cloud/
- Github page: https://github.com/stephenhky/pyqentangle
- PyPI page: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/pyqentangle/
- Documentation: http://pyqentangle.readthedocs.io/
- RQEntangle: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=RQEntangle (corresponding R library)
Reference
- Artur Ekert, Peter L. Knight, "Entangled quantum systems and the Schmidt decomposition", Am. J. Phys. 63, 415 (1995).
Acknowledgement
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file pyqentangle-4.0.6.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: pyqentangle-4.0.6.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 14.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
15639bed270aade27380cb12f642148c81aa46a8df9167b28351b94d594f6de5
|
|
| MD5 |
6b95191b1bb6c4d35915fedb3611b53b
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
5213aa3f7f860196b23a889d72923d852e4c506fbdaa619dc90efb2c7bf84f2a
|
File details
Details for the file pyqentangle-4.0.6-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: pyqentangle-4.0.6-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 12.4 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
53482c8facf10267d0e7b520fa09f84552e5fb549ce188d24ada78b26b8185ed
|
|
| MD5 |
9e98ca093afa0bad41c3e40edc79388f
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
e8bd2d83f858488fd67467b824f667c4f9d8b8c5328c5b40a30fdc4485c45a77
|