scikit-activeml is a Python library for active learning on top of SciPy and scikit-learn.
Project description

A Comprehensive and User-friendly Active Learning Library
Machine learning models often require substantial amounts of training data to perform effectively. While unlabeled data can be gathered with relative ease, labeling is typically difficult, time-consuming, or expensive. Active learning addresses this challenge by querying labels for the most informative samples, achieving high performance with fewer labeled examples. With this goal in mind, scikit-activeml has been developed as a Python library for active learning on top of scikit-learn. As a result, it natively supports deep active learning via skorch. Illustrations for pool-based and stream-based active learning with code snippets are given below:
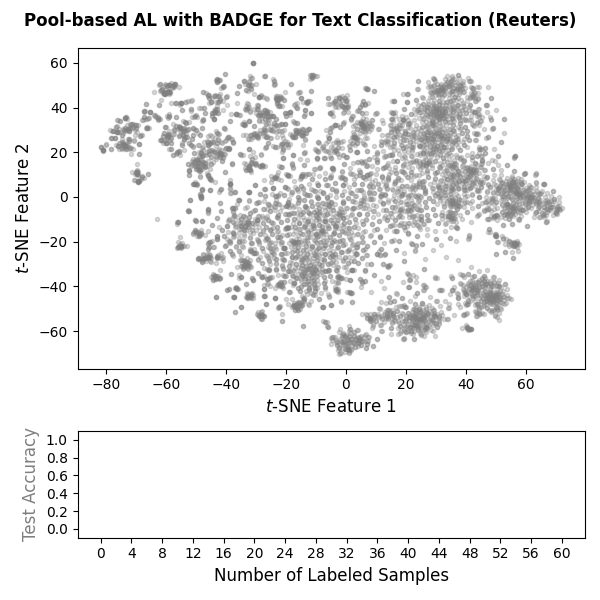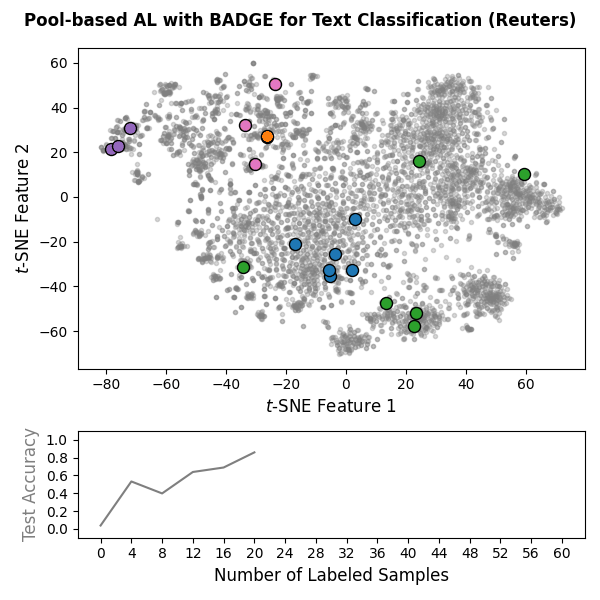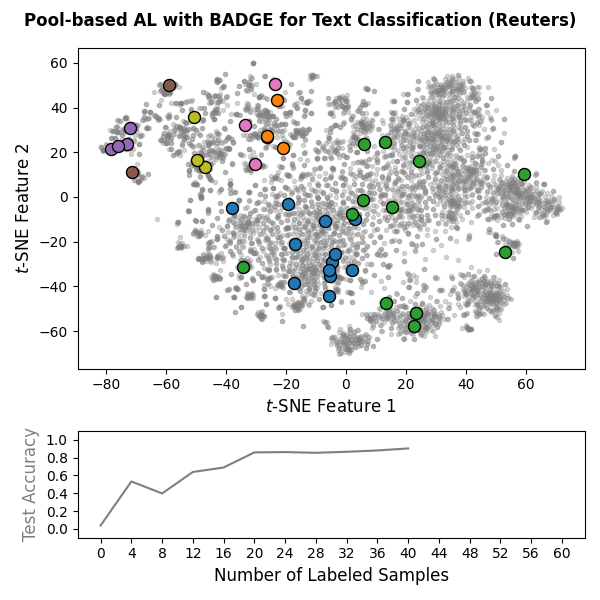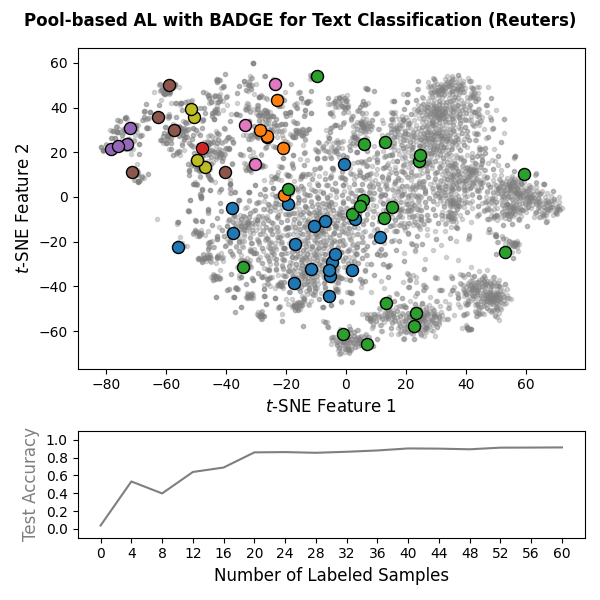
|
|
🏊 Pool-based Active Learning: Code Snippet
The following snippet implements an active learning cycle with 15
iterations using a PyTorch-based classifier (wrapped via
SkorchClassifier) and the BADGE query strategy on
sentence-transformer embeddings of the Reuters-21578 dataset obtained
from the pretrained SentenceTransformer model all-MiniLM-L6-v2.
Unlabeled data is represented by the value missing_label in the
label vector y_train. Note that the packages torch,
sentence_transformers, and datasets are not included in the
default skactiveml installation and must be installed separately. You
can do this via:
pip install -U torch torchvision
pip install -U scikit-activeml[opt] datasets sentence-transformersNote that you might need to adjust this command for GPU support with
torch.
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import CosineAnnealingLR
from datasets import load_dataset
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
from skorch.callbacks import LRScheduler
from skactiveml.classifier import SkorchClassifier
from skactiveml.pool import Badge
# Define the device depending on its availability.
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# Load data from Huggingface and encode it via `sentence_transformers`.
ds_train = load_dataset("yangwang825/reuters-21578", split="train")
ds_test = load_dataset("yangwang825/reuters-21578", split="test")
mdl = SentenceTransformer("all-MiniLM-L6-v2", device=device)
X_pool = mdl.encode(ds_train["text"])
y_pool = np.asarray(ds_train["label"], dtype=np.int64)
X_test = mdl.encode(ds_test["text"])
y_test = np.asarray(ds_test["label"], dtype=np.int64)
n_features, classes = X_pool.shape[1], np.unique(y_pool)
missing_label = -1
# Build your `torch` module for classification, which outputs:
# - classification logits,
# - learned sample embeddings.
class ClassificationModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_features, n_classes, n_hidden_units):
super().__init__()
self.linear_1 = nn.Linear(n_features, n_hidden_units)
self.linear_2 = nn.Linear(n_hidden_units, n_classes)
self.activation = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
x_embed = self.linear_1(x)
logits = self.linear_2(self.activation(x_embed))
return logits, x_embed
# Wrap your torch module via a `skactiveml` wrapper, which requires the
# definition of training parameters.
clf = SkorchClassifier(
module=ClassificationModule,
criterion=nn.CrossEntropyLoss,
forward_outputs={"proba": (0, nn.Softmax(dim=-1)), "emb": (1, None)},
neural_net_param_dict={
# Module-related parameters.
"module__n_features": n_features,
"module__n_hidden_units": 128,
"module__n_classes": len(classes),
# Optimizer-related parameters.
"max_epochs": 100,
"batch_size": 16,
"lr": 0.01,
"optimizer": torch.optim.RAdam,
"callbacks": [
("lr_scheduler", LRScheduler(policy=CosineAnnealingLR, T_max=100))
],
# General parameters.
"verbose": 0,
"device": device,
"train_split": False,
"iterator_train__shuffle": True,
},
classes=classes,
missing_label=missing_label,
).initialize()
# Start the active learning cycle with zero initial labels.
y_train = np.full_like(y_pool, missing_label)
# Create a deep active learning query strategy.
qs = Badge(
missing_label=missing_label,
clf_embedding_flag_name={"extra_outputs": "emb"},
)
# Define the active learning parameters.
n_cycles = 15
batch_size = 4
# Execute active learning cycles.
for c in range(n_cycles):
query_idx = qs.query(
X=X_pool,
y=y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
clf=clf,
fit_clf=False,
)
y_train[query_idx] = y_pool[query_idx]
clf.fit(X_pool, y_train)
print(f"Final accuracy: {clf.score(X_test, y_test)}")🌊 Stream-based Active Learning: Code Snippet
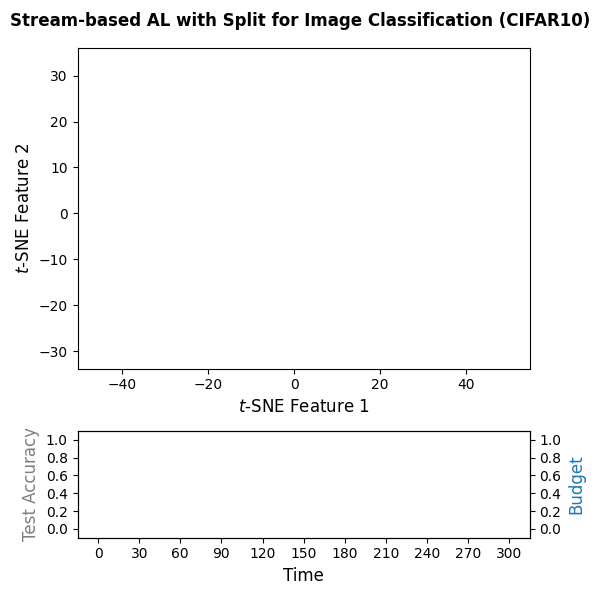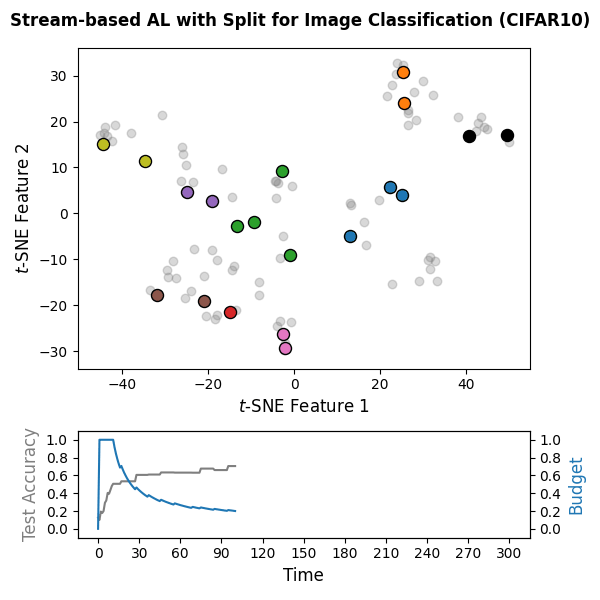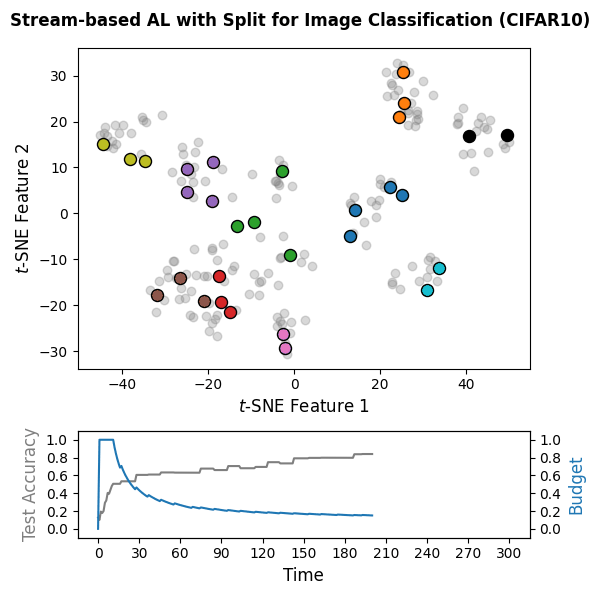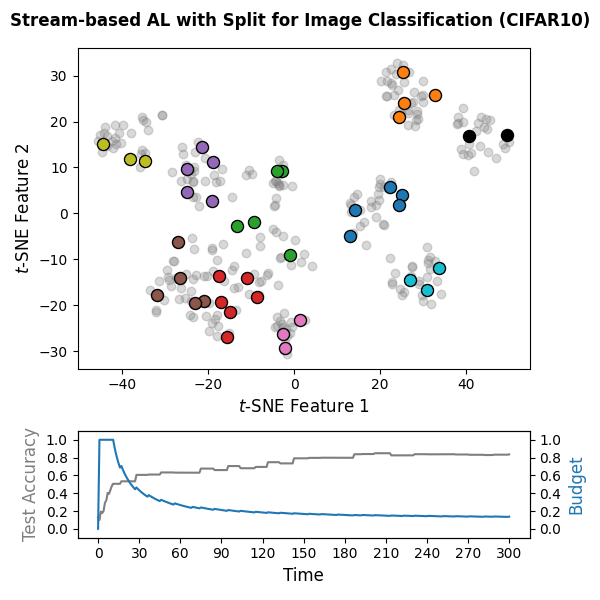
The following snippet implements a stream-based active learning cycle over
300 time steps on CIFAR-10 embeddings computed with the pretrained DINOv2
vision transformer. A PyTorch-based classifier
(wrapped via SkorchClassifier) is trained online, and the
Split query strategy is used with a labeling budget of 10% of the
stream. Unlabeled data is represented by the value missing_label in
the label vector y_train. Note that the packages torch,
transformers, and datasets are not included in the
default skactiveml installation and must be installed separately.
pip install -U torch torchvision
pip install -U scikit-activeml[opt] datasets transformersNote that you might need to adjust this command for GPU support with
torch.
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import CosineAnnealingLR
from datasets import load_dataset
from skorch.callbacks import LRScheduler
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, Dinov2Model
from skactiveml.classifier import SkorchClassifier
from skactiveml.stream import Split
# Define the device depending on its availability.
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# Load data.
ds = load_dataset("cifar10")
processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained(
"facebook/dinov2-small", use_fast=True
)
model = Dinov2Model.from_pretrained("facebook/dinov2-small").to(device).eval()
def embed(batch):
inputs = processor(images=batch["img"], return_tensors="pt").to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
out = model(**inputs).last_hidden_state[:, 0]
batch["emb"] = out.cpu().numpy()
return batch
ds = ds.map(embed, batched=True, batch_size=128)
X_stream = np.stack(ds["train"]["emb"], dtype=np.float32)[:300]
y_stream = np.array(ds["train"]["label"], dtype=np.int64)[:300]
X_test = np.stack(ds["test"]["emb"], dtype=np.float32)
y_test = np.array(ds["test"]["label"], dtype=np.int64)
n_features, classes = X_stream.shape[1], np.unique(y_stream)
missing_label = -1
# Build `torch` module for classification, outputting classification logits.
class ClassificationModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_features, n_classes, n_hidden_units):
super().__init__()
self.linear_1 = nn.Linear(n_features, n_hidden_units)
self.linear_2 = nn.Linear(n_hidden_units, n_classes)
self.activation = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
x_embed = self.linear_1(x)
logits = self.linear_2(self.activation(x_embed))
return logits
# Wrap your torch module via a `skactiveml` wrapper, which requires the
# definition of training parameters.
clf = SkorchClassifier(
module=ClassificationModule,
criterion=nn.CrossEntropyLoss,
neural_net_param_dict={
# Module-related parameters.
"module__n_features": n_features,
"module__n_hidden_units": 128,
"module__n_classes": len(classes),
# Optimizer-related parameters.
"max_epochs": 100,
"batch_size": 16,
"lr": 0.01,
"optimizer": torch.optim.RAdam,
"callbacks": [
("lr_scheduler", LRScheduler(policy=CosineAnnealingLR, T_max=100))
],
# General parameters.
"verbose": 0,
"device": device,
"train_split": False,
"iterator_train__shuffle": True,
},
classes=classes,
missing_label=missing_label,
).initialize()
# Initialize training data as empty lists.
y_train = np.full_like(y_stream, missing_label)
# Execute active learning cycle.
qs = Split(random_state=0, budget=0.1)
n_cycles = len(X_stream)
query_idx = []
for t in range(n_cycles):
query_idx = qs.query(
candidates=X_stream[[t]], y=y_stream[t], clf=clf, fit_clf=False
)
qs.update(candidates=X_stream[[t]], queried_indices=query_idx)
if len(query_idx) > 0:
y_train[t] = y_stream[t]
clf.fit(X_stream, y_train)
print(f"Final accuracy: {clf.score(X_test, y_test)}")💾 User Installation
In most cases, we recommend installing scikit-activeml together with the optional dependencies for better support of deep active learning:
pip install -U scikit-activeml[opt]The opt installs additional packages such as skorch to enable more sophisticated deep learning support. Version constraints are chosen to be reasonably flexible so that scikit-activeml can integrate well into an existing environment. The optional deep learning functionality (via skorch) assumes that torch (PyTorch) is already installed in your environment. Since the correct PyTorch build depends on your hardware and CUDA setup, we do not install PyTorch automatically.
Please install PyTorch separately by following the installation instructions of from skorch.
Minimal Installation
The minimum way to install scikit-activeml is using:
pip install -U scikit-activemlThis installs only the minimum requirements to avoid potential package downgrades within your existing environment.
Tested Fallback Installation
If you prefer a configuration where dependency versions have been tested explicitly for this release, you can install scikit-activeml with the maximum tested core and optional requirements:
pip install -U scikit-activeml[max,opt_max]This setup uses the versions listed in requirements_max.txt and requirements_opt_max.txt and corresponds to the configuration used in our continuous integration tests. You can also install only the maximum tested core dependencies via:
pip install -U scikit-activeml[max]🗂️ Query Strategy Overview
For better orientation, we provide an overview (including paper references and visual examples) of the over 60 query strategies implemented by skactiveml. The following mind map illustrates different attributes of a query strategy.

📚 In-depth Tutorials
The table below summarizes a subset of our many in-depth tutorials. Each entry lists the active learning scenario, prediction task, data modality, and models used in the tutorial.
Tutorial |
Scenario |
Task |
Data |
Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Pool |
Classification |
Image |
|
|
Pool |
Regression |
Tabular |
|
|
Stream |
Classification |
Text |
|
📝 Citing
If you use skactiveml in your research or projects, please cite the following work and consider starring the repository to help others discover it:
@article{skactiveml2025,
title={{scikit-activeml: A Comprehensive and User-friendly Active Learning Library}},
author={Herde, Marek and Pham, Minh Tuan and Kottke, Daniel and Benz, Alexander and L{\"u}hrs, Lukas and Mergard, Pascal and Sandrock, Christoph and Cheng, Jiaying and Roghman, Atal and M{\"u}jde, Mehmet and Rauch, Lukas and Sick, Bernahrd},
journal={Preprints},
doi={10.20944/preprints202507.0252.v1},
year={2025},
url={https://github.com/scikit-activeml/scikit-activeml}
}Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file scikit_activeml-1.0.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: scikit_activeml-1.0.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 192.3 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.25
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
bd1845c5ebfa8107b75767d08a8395d9d67e52a27561e9524e931f0b38877103
|
|
| MD5 |
6037b96ea161a00a179b659438c9c391
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
e6884b636831cf06d3e162df407d9a10ab817d6f9becf787859ae6072e7b6cf0
|
File details
Details for the file scikit_activeml-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: scikit_activeml-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 255.4 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.25
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
34e8d3a594cd98ed6210d0c91d651829f01119822e0337cd42302a33480ed292
|
|
| MD5 |
427023177af90208077299d36b04cdc1
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
4a49bb935b2e68cf31e2b2face9d0841ac97447b6d0387d0c2d2255c7a2867da
|



















