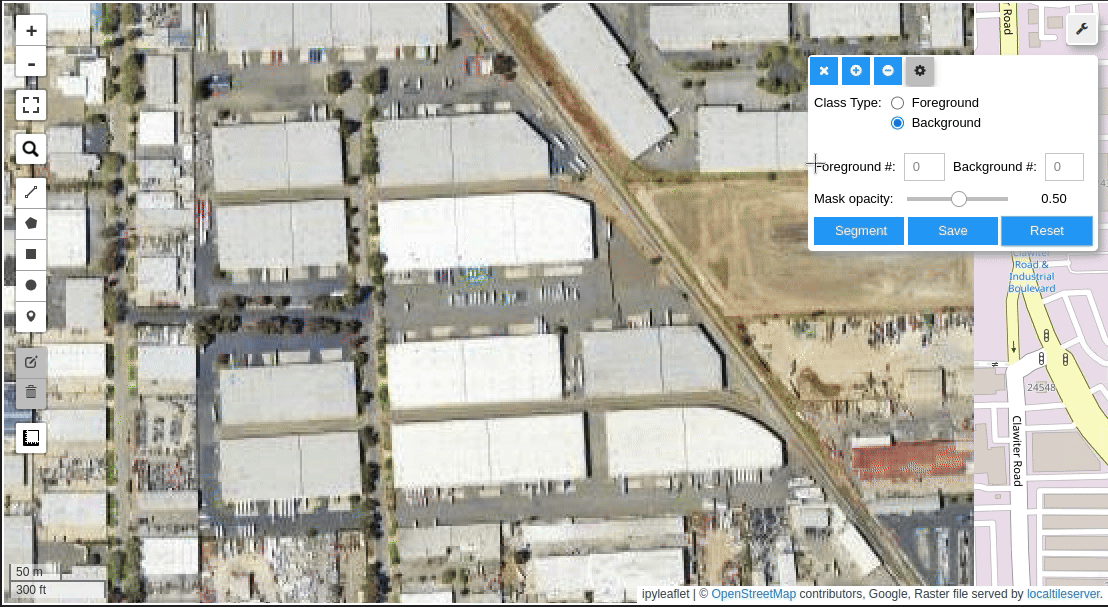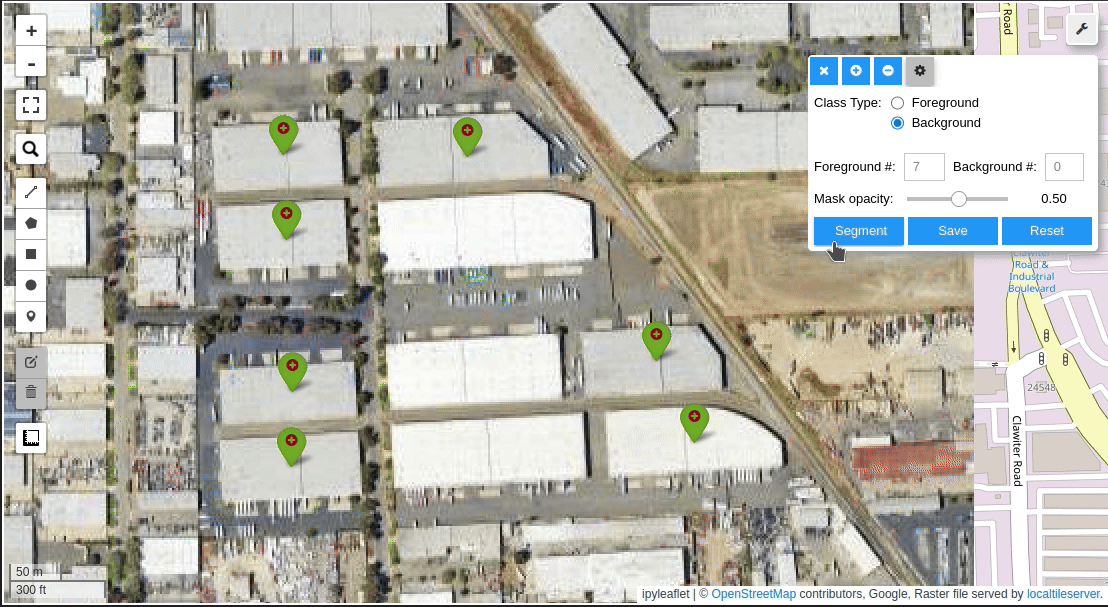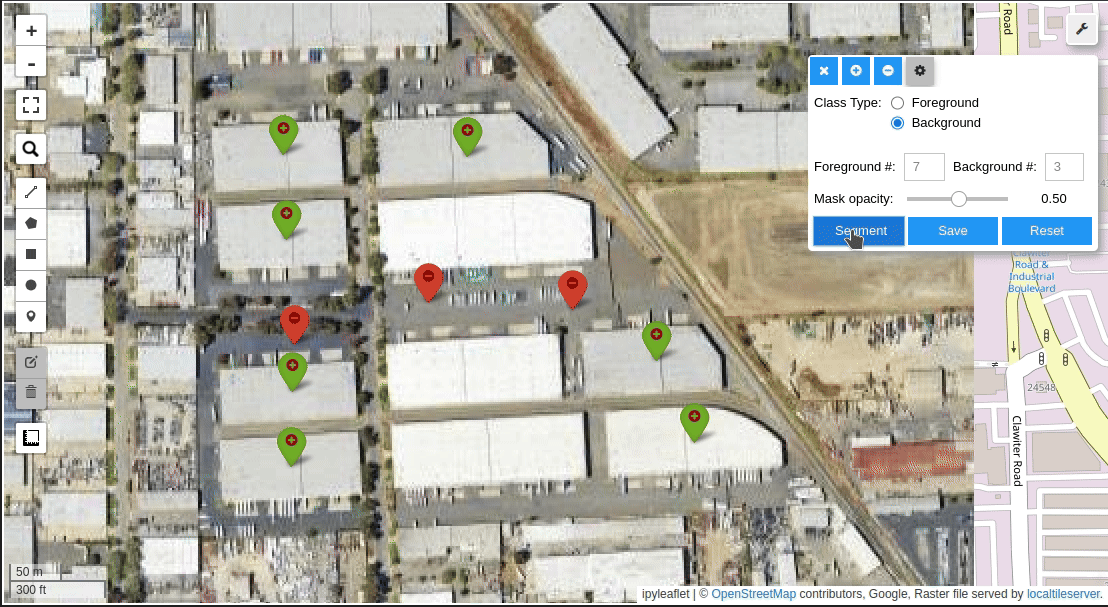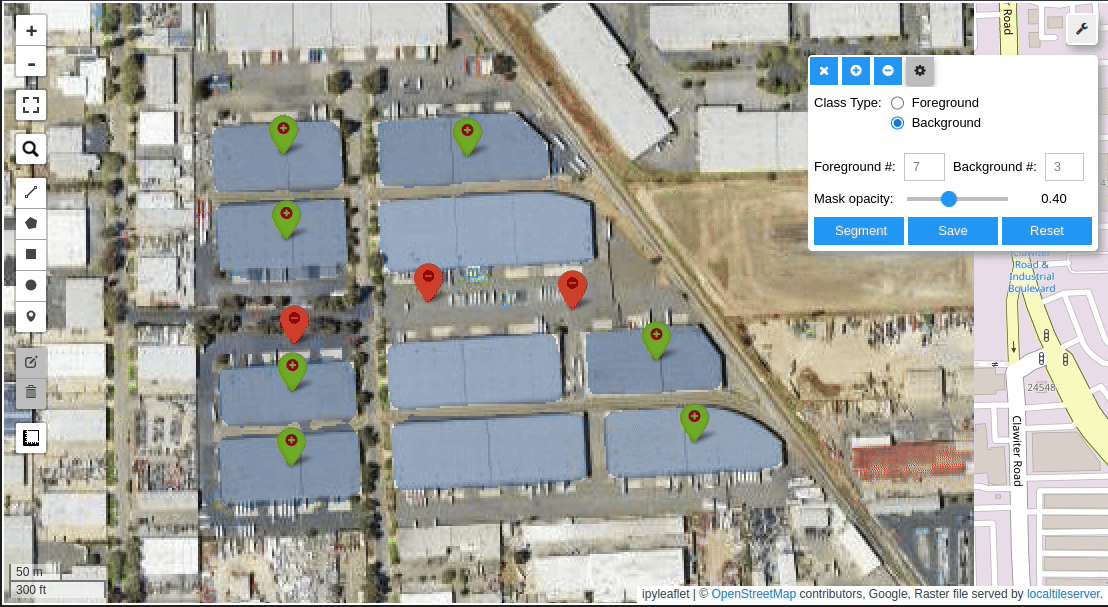
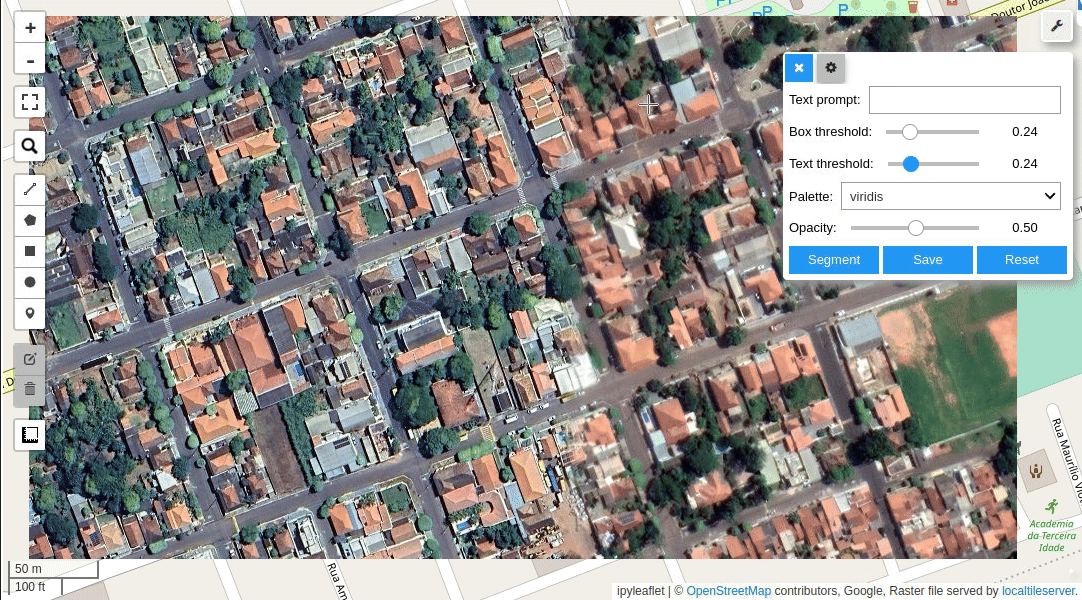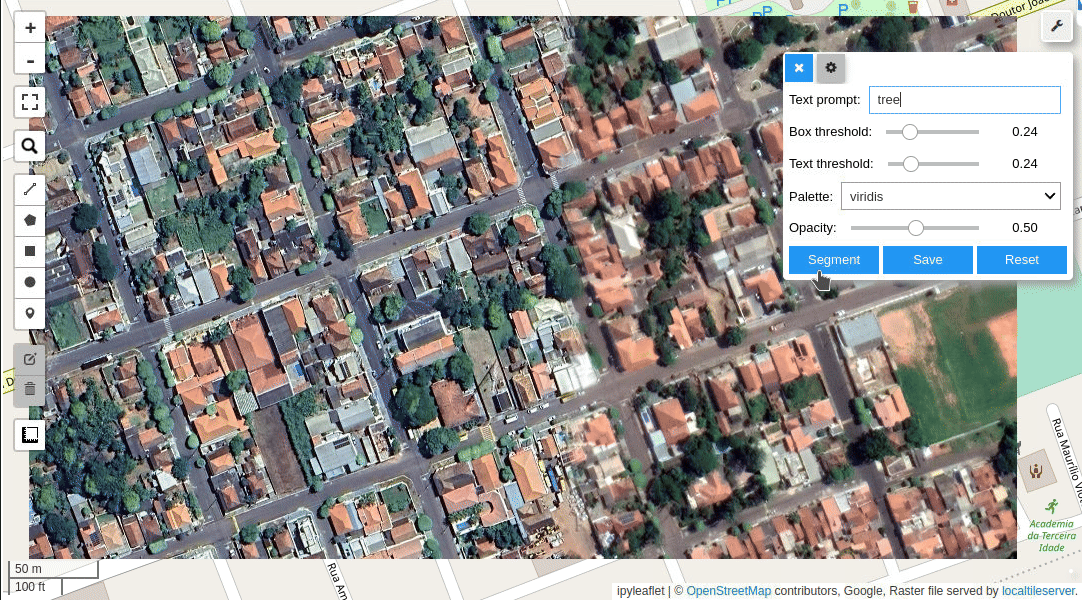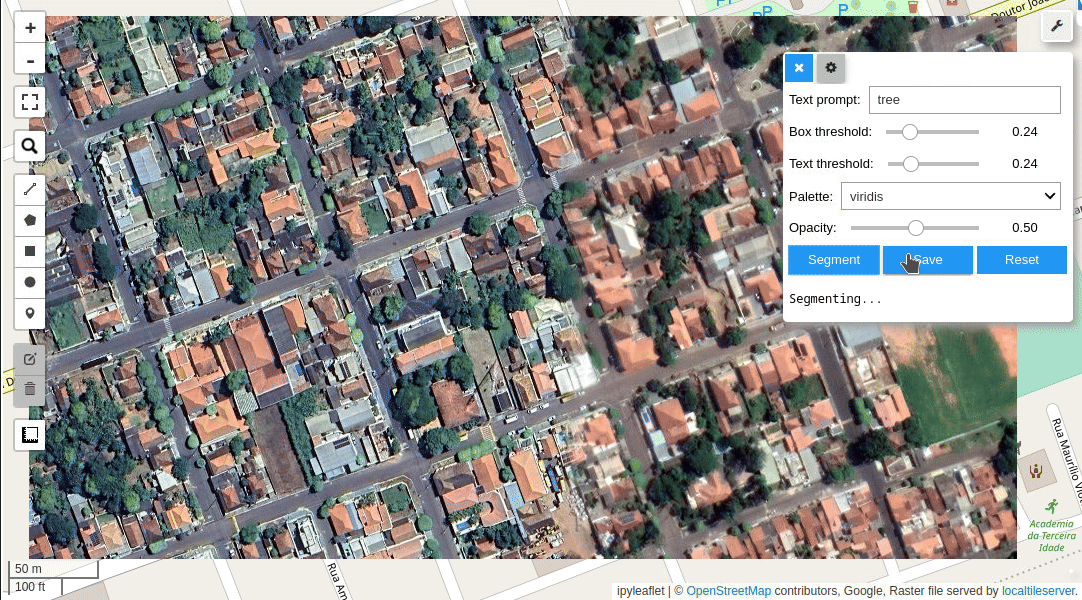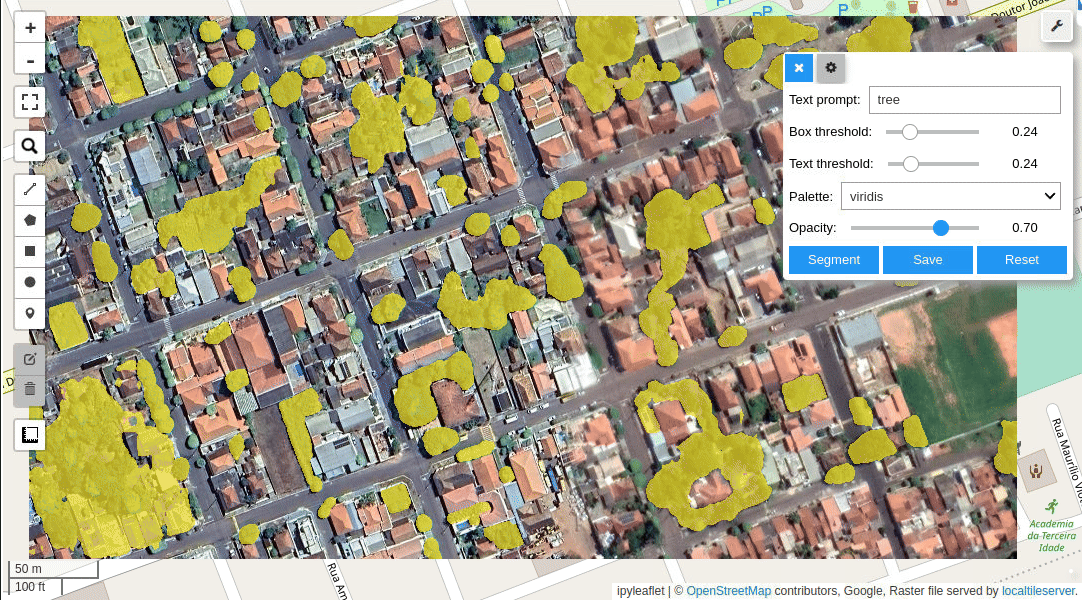
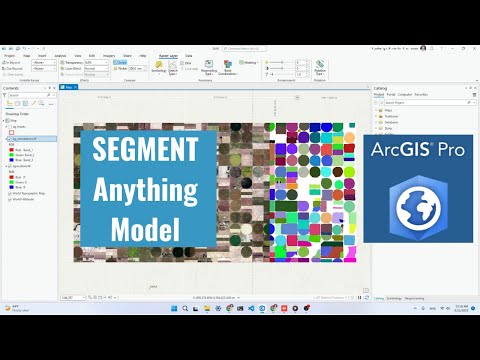
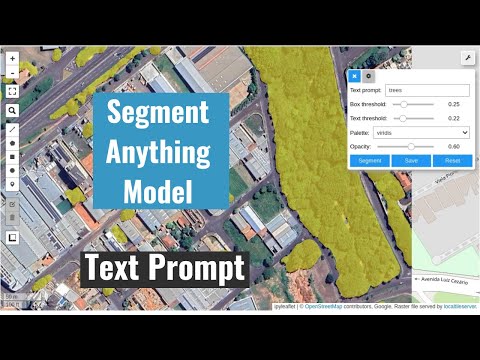
Meta AI's Segment Anything Model (SAM) for Geospatial Data.
Project description
SamGeo
A Python package for segmenting geospatial data with the Segment Anything Model (SAM)
Introduction
The SamGeo package draws its inspiration from segment-anything-eo repository authored by Aliaksandr Hancharenka. The primary objective of SamGeo is to simplify the process of leveraging SAM for geospatial data analysis by enabling users to achieve this with minimal coding effort. The source code of SamGeo was adapted from the segment-anything-eo repository, and credit for its original version goes to Aliaksandr Hancharenka.
- Free software: MIT license
- Documentation: https://samgeo.gishub.org
Citations
- Wu, Q., & Osco, L. (2023). samgeo: A Python package for segmenting geospatial data with the Segment Anything Model (SAM). Journal of Open Source Software, 8(89), 5663. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.05663
- Osco, L. P., Wu, Q., de Lemos, E. L., Gonçalves, W. N., Ramos, A. P. M., Li, J., & Junior, J. M. (2023). The Segment Anything Model (SAM) for remote sensing applications: From zero to one shot. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 124, 103540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2023.103540
Features
- Download map tiles from Tile Map Service (TMS) servers and create GeoTIFF files
- Segment GeoTIFF files using the Segment Anything Model (SAM) and HQ-SAM
- Segment remote sensing imagery with text prompts
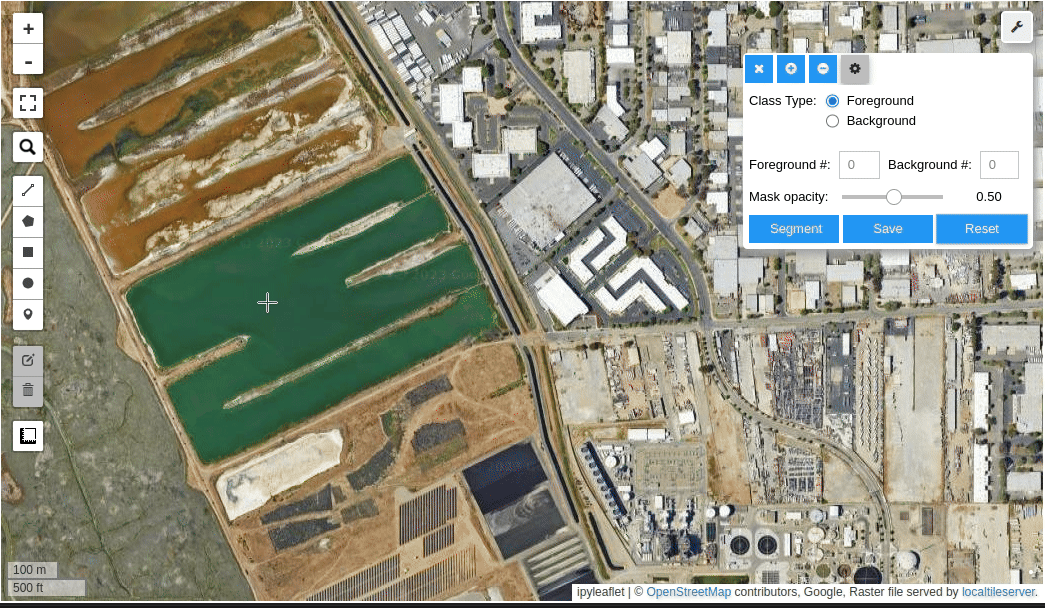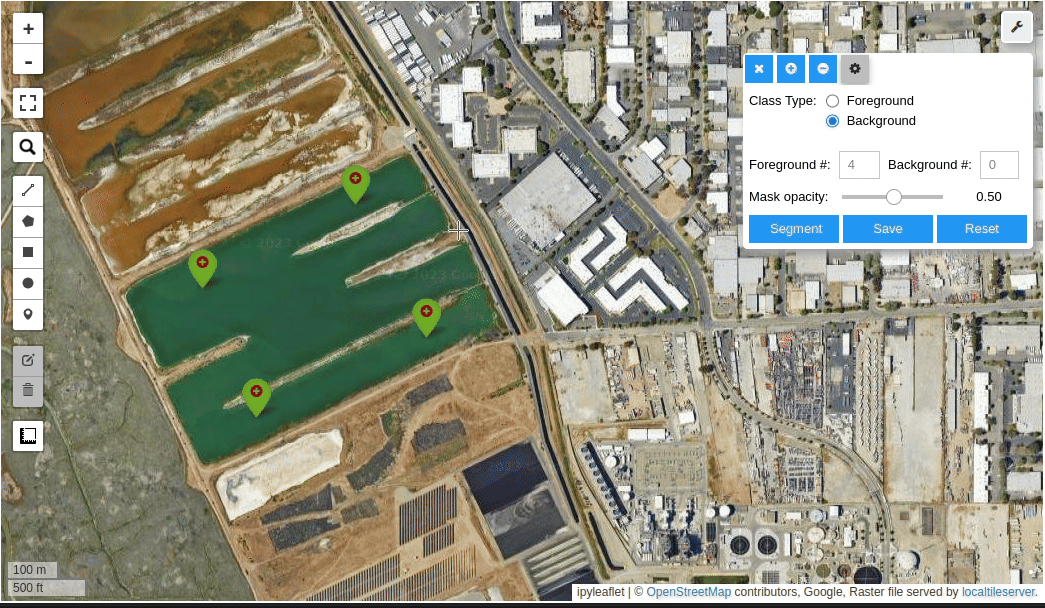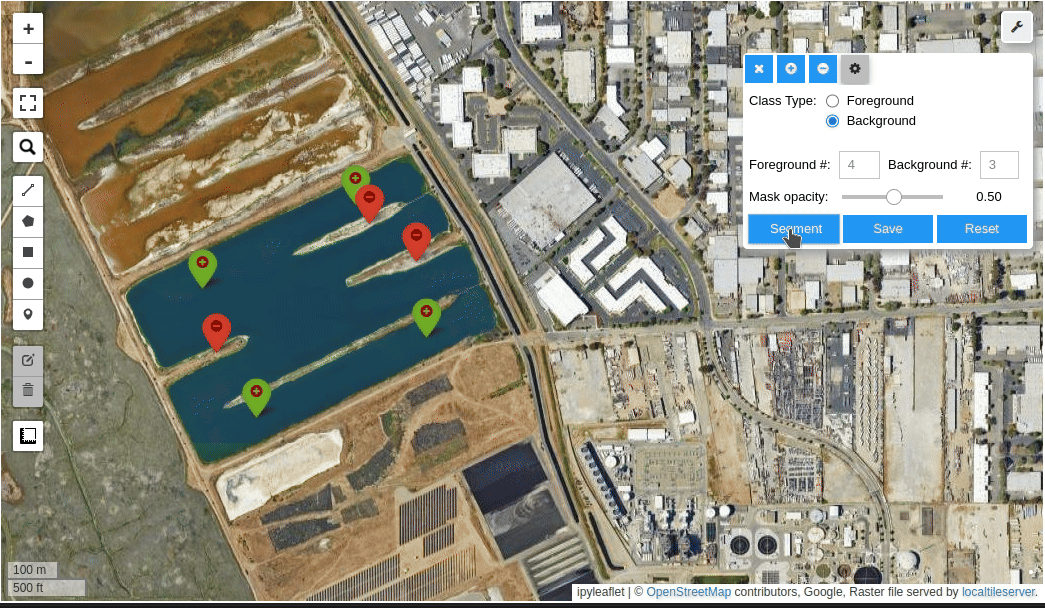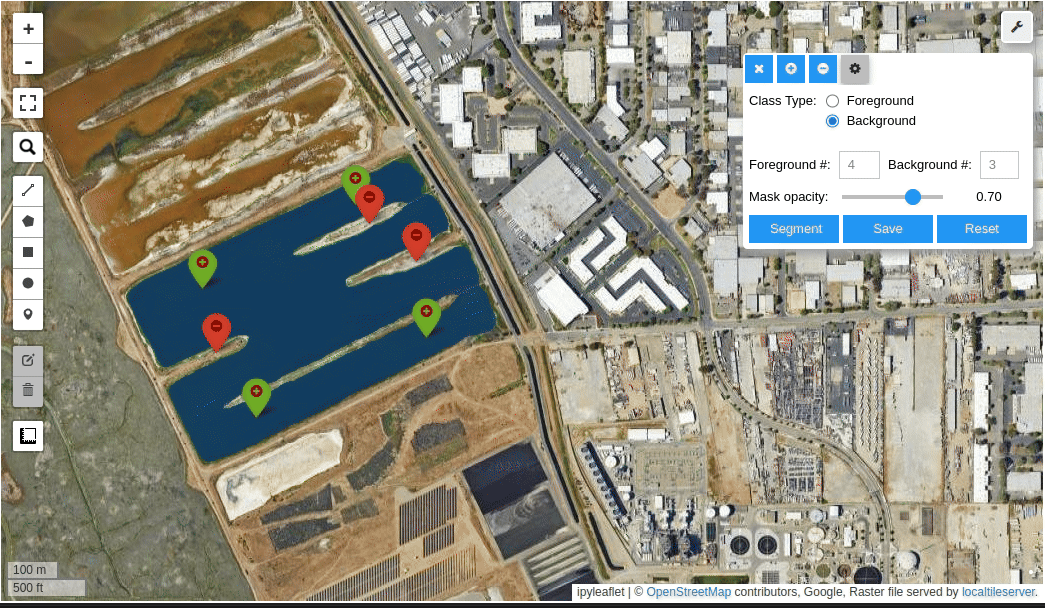
- Create foreground and background markers interactively
- Load existing markers from vector datasets
- Save segmentation results as common vector formats (GeoPackage, Shapefile, GeoJSON)
- Save input prompts as GeoJSON files
- Visualize segmentation results on interactive maps
- Segment objects from timeseries remote sensing imagery
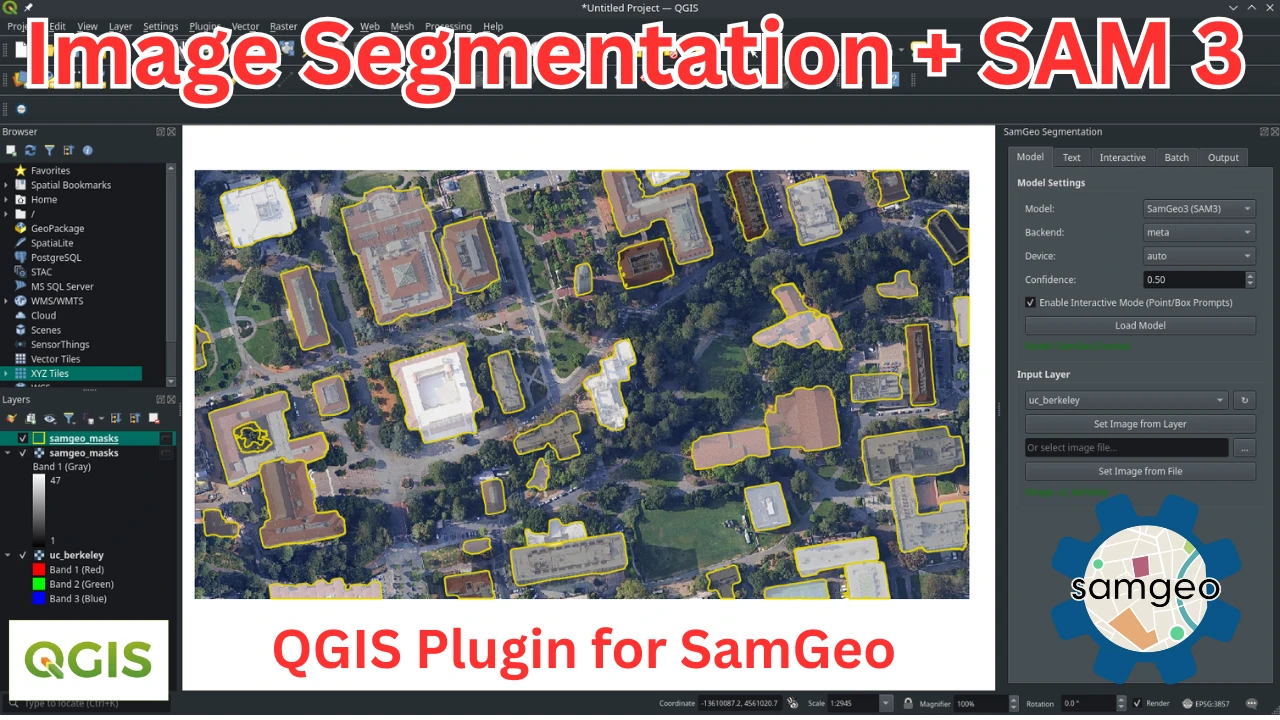
QGIS Plugin
SamGeo is also available as a QGIS plugin. Check out this short video demo and full video tutorial on how to use the plugin.
Installation
Install with pixi (Recommended)
For the most reliable installation experience, especially on Windows or when dealing with complex dependencies like PyTorch/CUDA and SAM 3, we recommend using pixi. Pixi provides faster and more reliable dependency resolution than conda/mamba and avoids common numpy version conflicts. See the full pixi installation guide for detailed instructions.
Quick start with pixi:
# Install pixi (Linux/macOS)
curl -fsSL https://pixi.sh/install.sh | sh
# Or on Windows (PowerShell)
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -c "irm -useb https://pixi.sh/install.ps1 | iex"
# Create a new pixi project
pixi init geo
cd geo
# Edit pixi.toml with your configuration (see docs for GPU/CPU examples)
# Then install
pixi install
# Start Jupyter Lab
pixi run jupyter lab
Install from PyPI
segment-geospatial is available on PyPI and can be installed in several ways so that its dependencies can be controlled more granularly. This reduces package size for CI environments, since not every time all of the models will be used.
Depending on what tools you need to use, you might want to do:
segment-geospatialorsegment-geospatial[samgeo]: Installs only the minimum required dependencies to run SAMGeosegment-geospatial[samgeo2]: Installs the dependencies to run SAMGeo 2segment-geospatial[samgeo3]: Installs the dependencies to run SAMGeo 3segment-geospatial[fast]: Installs the dependencies to run Fast SAMsegment-geospatial[hq]: Installs the dependencies to run HQ-SAMsegment-geospatial[text]: Installs Grounding DINO to use SAMGeo 1 and 2 with text promptssegment-geospatial[fer]: Installs the dependencies to run the feature edge reconstruction algorithm
Additionally, these other two optional imports are defined:
segment-geospatial[all]: Installs the dependencies to run all of the SAMGeo modelssegment-geospatial[extra]: Installs the dependencies to run all of the SAMGeo models and other utilities to run the examples like Jupyter notebook support,leafmap, etc.
Simply running the following should install the dependencies for each use case:
pip install "segment-geospatial[samgeo3]" # Or any other choice of the above
To see more in detail what packages come with each choice, please refer to pyproject.toml.
Install from conda-forge
segment-geospatial is also available on conda-forge. If you have
Anaconda or Miniconda installed on your computer, you can install segment-geospatial using the following commands. It is recommended to create a fresh conda environment for segment-geospatial. The following commands will create a new conda environment named geo and install segment-geospatial and its dependencies:
conda create -n geo python
conda activate geo
conda install -c conda-forge segment-geospatial
If your system has a GPU, but the above commands do not install the GPU version of pytorch, you can force the installation of the GPU version of pytorch using the following command:
conda install -c conda-forge segment-geospatial "pytorch=*=cuda*"
segment-geospatial has some optional dependencies that are not included in the default conda environment. To install these dependencies, run the following command:
conda install -c conda-forge groundingdino-py segment-anything-fast
Install SAM 3 on Windows
It is a bit tricky to install SAM 3 on Windows. Run the following commands on Windows to install SamGeo:
conda create -n geo python=3.12
conda activate geo
conda install pytorch torchvision pytorch-cuda=12.1 -c pytorch -c nvidia
pip install "segment-geospatial[samgeo3]"
pip install triton-windows ipykernel jupyterlab
Examples
- Segmenting remote sensing imagery
- Automatically generating object masks
- Segmenting remote sensing imagery with input prompts
- Segmenting remote sensing imagery with box prompts
- Segmenting remote sensing imagery with text prompts
- Batch segmentation with text prompts
- Using segment-geospatial with ArcGIS Pro
- Segmenting swimming pools with text prompts
- Segmenting satellite imagery from the Maxar Open Data Program
Demos
- Automatic mask generator
- Interactive segmentation with input prompts
- Input prompts from existing files
- Interactive segmentation with text prompts
Tutorials
Video tutorials are available on my YouTube Channel.
- Automatic mask generation
- Using SAM with ArcGIS Pro
- Interactive segmentation with text prompts
Using SAM with Desktop GIS
- QGIS: Check out the SamGeo QGIS Plugin.
- ArcGIS: Check out the Segment Anything Model (SAM) Toolbox for ArcGIS and the Resources for Unlocking the Power of Deep Learning Applications Using ArcGIS.
Computing Resources
The Segment Anything Model is computationally intensive, and a powerful GPU is recommended to process large datasets. It is recommended to have a GPU with at least 8 GB of GPU memory. You can utilize the free GPU resources provided by Google Colab. Alternatively, you can apply for AWS Cloud Credit for Research, which offers cloud credits to support academic research. If you are in the Greater China region, apply for the AWS Cloud Credit here.
Legal Notice
This repository and its content are provided for educational purposes only. By using the information and code provided, users acknowledge that they are using the APIs and models at their own risk and agree to comply with any applicable laws and regulations. Users who intend to download a large number of image tiles from any basemap are advised to contact the basemap provider to obtain permission before doing so. Unauthorized use of the basemap or any of its components may be a violation of copyright laws or other applicable laws and regulations.
Contributing
Please refer to the contributing guidelines for more information.
Acknowledgements
This project is based upon work partially supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) under Grant No. 80NSSC22K1742 issued through the Open Source Tools, Frameworks, and Libraries 2020 Program.
This project is also supported by Amazon Web Services (AWS). In addition, this package was made possible by the following open source projects. Credit goes to the developers of these projects.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file segment_geospatial-1.2.2.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: segment_geospatial-1.2.2.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 547.3 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.14.2
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
e347ecfb2b9a0d90c9e47171466fed205ca101031ed172497197e46bd4e34f13
|
|
| MD5 |
f8d59809b5b3c8fef3490406bc7d57df
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
f065823e496e7b9299dfdf9044b1737eb7fb93826c8de77c64b8e7a498853845
|
File details
Details for the file segment_geospatial-1.2.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: segment_geospatial-1.2.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 137.3 kB
- Tags: Python 2, Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.14.2
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
7b568c4890d6ab7e89e791dab72989fc14023f467343157ac3adec719ae0d00b
|
|
| MD5 |
358f34fa65c1aa81ce2081732a085340
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
b79641958ae0d9d1811817f1fda28a9ce74fb55439df843019f6091beff345a8
|