Prompt Declaration Language
Project description
PDL (Prompt Declaration Language)
PDL is a declarative language designed for developers to create reliable, composable LLM prompts and integrate them into software systems. It provides a structured way to specify prompt templates, enforce validation, and compose LLM calls with traditional rule-based systems.
Quick Start | Example | GUI | Key Features | Documentation | API Cheat Sheet
Quick Start
A PDL program is written declaratively, in YAML. The pdl command
line tool interprets this program, accumulating messages and sending
them to the models as specified by your program. PDL supports both
hosted and local models. See
here
for instructions on how to install an Ollama model locally.
To install the pdl command line tool:
pip install prompt-declaration-language
What's New
Check out AutoPDL, PDL's prompt optimizer tool Spiess et al. (2025)! AutoPDL can be used to optimize any part of a PDL program. This includes few-shots examples and textual prompts, but also prompting patterns. It outputs an optimized PDL program with optimal values.
For a tutorial on how to use AutoPDL, see AutoPDL
Example Program: A Basic LLM Call

The following program accumulates a single message write a hello world example… and sends it to the ollama/granite-3.2:8b model:
text:
- "write a hello world example, and explain how to run it"
- model: ollama/granite-3.2:8b
To run this program:
pdl <path/to/example.pdl>
For more information on the pdl CLI see
here. To try the
screenshot on the right live, click
here.
Graphical Experience
The screenshot on the right (above) shows PDL's graphical user
interface. This GUI allows for interactive debugging and live
programming. You may install this via brew install pdl on MacOS. For
other platforms, downloads are available
here. You
may also kick the tires with a web version of the GUI
here.
To generate a trace for use in the GUI:
pdl --trace <file.json> <my-example.pdl>

Key Features
- LLM Integration: Compatible with any LLM, including IBM watsonx
- Prompt Engineering:
- Template system for single/multi-shot prompting
- Composition of multiple LLM calls
- Integration with tools (code execution & APIs)
- Development Tools:
- Type checking for model I/O
- Python SDK
- Chat API support
- Live document visualization for debugging
- Control Flow: Variables, conditionals, loops, and functions
- I/O Operations: File/stdin reading, JSON parsing
- API Integration: Native REST API support (Python)
Documentation
API Cheat Sheet

Installation Details
PDL requires Python 3.11+ (Windows users should use WSL).
# Basic installation
pip install prompt-declaration-language
# Development installation with examples
pip install 'prompt-declaration-language[examples]'
Environment Setup
You can run PDL with LLM models in local using Ollama, or other cloud service. See here for instructions on how to install an Ollama model locally.
If you use watsonx:
export WX_URL="https://{region}.ml.cloud.ibm.com"
export WX_API_KEY="your-api-key"
export WATSONX_PROJECT_ID="your-project-id"
If you use Replicate:
export REPLICATE_API_TOKEN="your-token"
IDE Configuration
Install the YAML Language Support by Red Hat extension in VSCode.
VSCode setup for syntax highlighting and validation:
// .vscode/settings.json
{
"yaml.schemas": {
"https://ibm.github.io/prompt-declaration-language/dist/pdl-schema.json": "*.pdl"
},
"files.associations": {
"*.pdl": "yaml",
}
}
Code Examples
Variable Definition & Template Usage
In this example we use external content data.yaml and watsonx as an LLM provider.
description: Template with variables
defs:
user_input:
read: ../code/data.yaml
parser: yaml
text:
- model: watsonx/ibm/granite-34b-code-instruct
input: |
Process this input: ${user_input}
Format the output as JSON.
Python Code Integration
description: Code execution example
text:
- "\nFind a random number between 1 and 20\n"
- def: N
lang: python
code: |
import random
# (In PDL, set `result` to the output you wish for your code block.)
result = random.randint(1, 20)
- "\nthe result is (${ N })\n"
Chat
chat interactions:
description: chatbot
text:
- read:
def: user_input
message: "hi? [/bye to exit]\n"
contribute: [context]
- repeat:
text:
- model: ollama/granite-code:8b
- read:
def: user_input
message: "> "
contribute: [context]
until: ${ user_input == '/bye'}
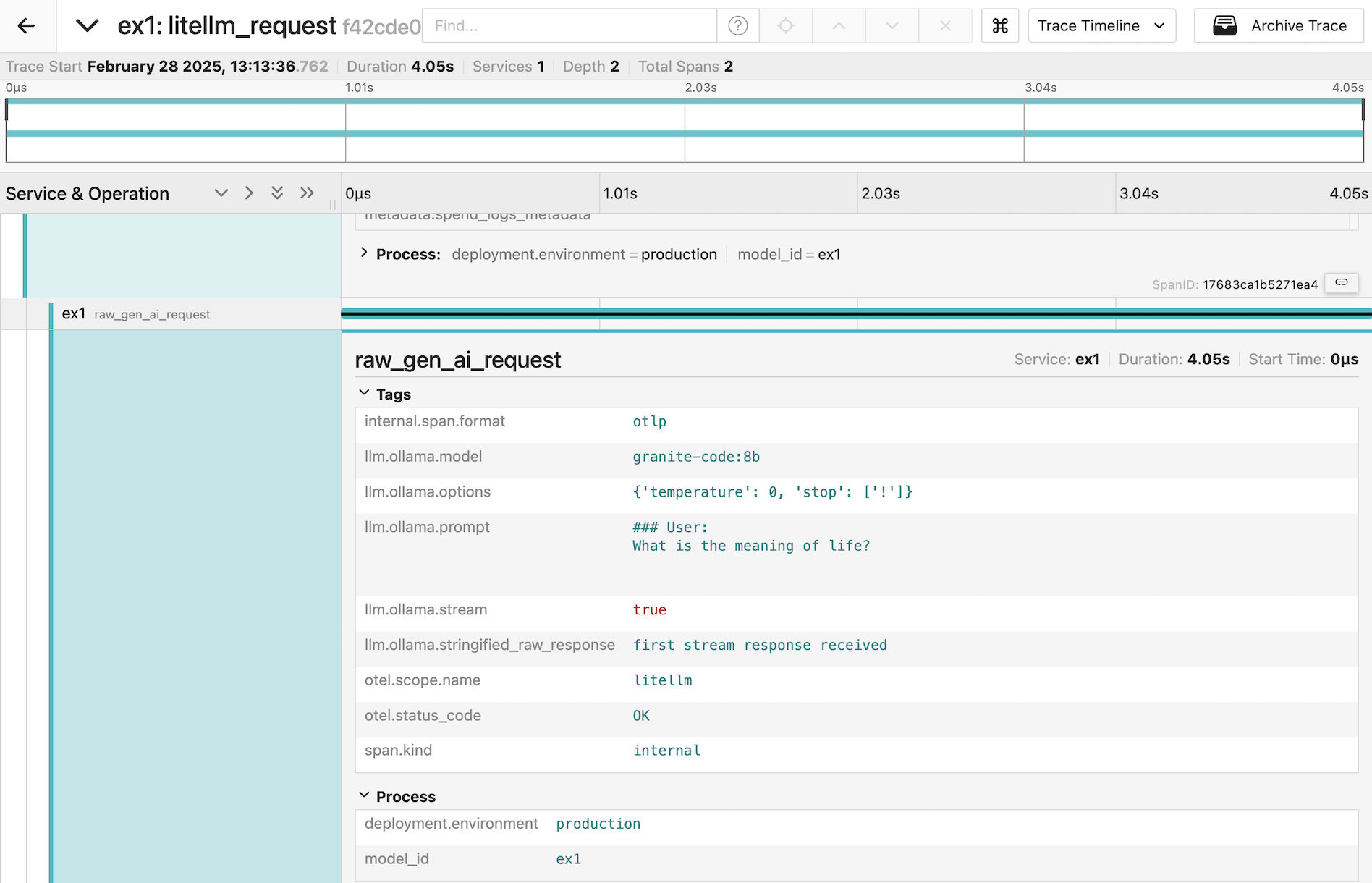
Trace Telemetry
PDL includes experimental support for gathering trace telemetry. This can be used for debugging or performance analysis, and to see the shape of prompts sent by LiteLLM to models.
For more information see here.
Contributing
See the contribution guidelines for details on:
- Code style
- Testing requirements
- PR process
- Issue reporting
References
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file prompt_declaration_language-0.9.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: prompt_declaration_language-0.9.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 4.9 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
eaa9c3570757374229450a72e13d7939624dafda09e3b38889636247ad8d3846
|
|
| MD5 |
39f5206fc44bc8e78acef0ec0f4d7afb
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
7c51de4acbe749d5337fdbc2968d058ff224340170880b94e69b64474006bb55
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for prompt_declaration_language-0.9.3.tar.gz:
Publisher:
release.yml on IBM/prompt-declaration-language
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
prompt_declaration_language-0.9.3.tar.gz -
Subject digest:
eaa9c3570757374229450a72e13d7939624dafda09e3b38889636247ad8d3846 - Sigstore transparency entry: 999489289
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
IBM/prompt-declaration-language@a160a738bf127b0a65ebf25e26ca7d757a1d3552 -
Branch / Tag:
refs/tags/v0.9.3 - Owner: https://github.com/IBM
-
Access:
public
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
release.yml@a160a738bf127b0a65ebf25e26ca7d757a1d3552 -
Trigger Event:
release
-
Statement type:
File details
Details for the file prompt_declaration_language-0.9.3-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: prompt_declaration_language-0.9.3-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 106.6 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
a549125bce9c7237bf934ca6f81fd88651fc391add8c0bbace00961c17446611
|
|
| MD5 |
0f1339001cfe9bfb6b2380a2594e9fae
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
853fc89cde58f8505d065303eddf523d3b8f4c5bc3c9eea52be39a65808e4c85
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for prompt_declaration_language-0.9.3-py3-none-any.whl:
Publisher:
release.yml on IBM/prompt-declaration-language
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
prompt_declaration_language-0.9.3-py3-none-any.whl -
Subject digest:
a549125bce9c7237bf934ca6f81fd88651fc391add8c0bbace00961c17446611 - Sigstore transparency entry: 999489348
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
IBM/prompt-declaration-language@a160a738bf127b0a65ebf25e26ca7d757a1d3552 -
Branch / Tag:
refs/tags/v0.9.3 - Owner: https://github.com/IBM
-
Access:
public
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
release.yml@a160a738bf127b0a65ebf25e26ca7d757a1d3552 -
Trigger Event:
release
-
Statement type:






















