Documentation for `weco`, a CLI for using Weco AI's code optimizer.
Project description
Weco systematically optimizes your code, guided directly by your evaluation metrics.
Example applications include:
- GPU Kernel Optimization: Reimplement PyTorch functions using CUDA or Triton, optimizing for
latency,throughput, ormemory_bandwidth. - Model Development: Tune feature transformations, architectures or the whole training pipeline, optimizing for
validation_accuracy,AUC, orSharpe Ratio. - Prompt Engineering: Refine prompts for LLMs (e.g., for math problems), optimizing for
win_rate,relevance, orformat_adherence
Overview
The weco CLI leverages a tree search approach guided by LLMs to iteratively explore and refine your code. It automatically applies changes, runs your evaluation script, parses the results, and proposes further improvements based on the specified goal.
Install the Package
pip install weco
Getting Started
Quickstart with an example project
Configure optimization parameters yourself - If you need precise control over the optimization parameters, you can use the direct weco run command:
Example: Optimizing Simple PyTorch Operations
git clone https://github.com/WecoAI/weco-cli.git
cd weco-cli/examples/hello-world/
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run Weco with configuration
weco run --source module.py \
--eval-command "python evaluate.py --path module.py" \
--metric speedup \
--goal maximize \
--steps 10 \
--additional-instructions "Fuse operations in the forward method while ensuring the max float deviation remains small. Maintain the same format of the code."
Note: If you have an NVIDIA GPU, change the device in the --eval-command to cuda. If you are running this on Apple Silicon, set it to mps.
For more advanced examples, including Triton, CUDA kernel optimization, ML model optimization, and prompt engineering for math problems, please see the README.md files within the corresponding subdirectories under the examples/ folder.
Note: When recommend removing any backticks from your code if any are present. We currently don't support backticks but will support this in the future.
Arguments for weco run
Required:
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-s, --source |
Path to the source code file that will be optimized. | -s model.py |
-c, --eval-command |
Command to run for evaluating the code in --source. This command should print the target --metric and its value to the terminal (stdout/stderr). See note below. |
-c "python eval.py" |
-m, --metric |
The name of the metric you want to optimize (e.g., 'accuracy', 'speedup', 'loss'). This metric name does not need to match what's printed by your --eval-command exactly (e.g., its okay to use "speedup" instead of "Speedup:"). |
-m speedup |
-g, --goal |
maximize/max to maximize the --metric or minimize/min to minimize it. |
-g maximize |
Optional:
| Argument | Description | Default | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
-n, --steps |
Number of optimization steps (LLM iterations) to run. | 100 | -n 50 |
-M, --model |
Model identifier for the LLM to use (e.g., o4-mini, claude-sonnet-4-5, gpt-5). |
o4-mini |
-M o4-mini |
-i, --additional-instructions |
Natural language description of specific instructions or path to a file containing detailed instructions to guide the LLM. Supported file formats include - .txt, .md, and .rst. |
None |
-i instructions.md or -i "Optimize the model for faster inference" |
-l, --log-dir |
Path to the directory to log intermediate steps and final optimization result. | .runs/ |
-l ./logs/ |
--eval-timeout |
Timeout in seconds for each step in evaluation. | No timeout (unlimited) | --eval-timeout 3600 |
--save-logs |
Save execution output from each optimization step to disk. Creates timestamped directories with raw output files and a JSONL index for tracking execution history. | False |
--save-logs |
--apply-change |
Automatically apply the best solution to the source file without prompting. | False |
--apply-change |
--api-key |
API keys for LLM providers (BYOK). Format: provider=key. Can specify multiple providers. |
None |
--api-key openai=sk-xxx |
Command Reference
Basic Usage Patterns
| Command | Description | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
weco run [options] |
Direct optimization execution | For advanced users - When you know exactly what to optimize and how |
weco resume <run-id> |
Resume an interrupted run | Continue from the last completed step |
weco login |
Authenticate with Weco | First-time setup or switching accounts |
weco logout |
Clear authentication credentials | To switch accounts or troubleshoot authentication issues |
weco credits balance |
Check your current credit balance | Monitor usage |
weco credits topup [amount] |
Purchase additional credits | When you need more credits (default: 10) |
weco credits autotopup |
Configure automatic top-up | Set up automatic credit replenishment |
Setup Commands (Experimental)
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
weco setup claude-code |
Set up Weco skill for Claude Code |
weco setup cursor |
Set up Weco rules for Cursor |
The setup command installs Weco skills for AI coding assistants:
weco setup claude-code # For Claude Code
weco setup cursor # For Cursor
- Claude Code: Downloads the Weco skill to
~/.claude/skills/weco/and updates~/.claude/CLAUDE.md - Cursor: Downloads the Weco skill to
~/.cursor/skills/weco/and creates~/.cursor/rules/weco.mdc
Model Selection
You can specify which LLM model to use with the -M or --model flag:
weco run --model gpt-5 --source optimize.py [other options...]
Available models (31 total):
OpenAI Models:
- GPT-5 Series:
gpt-5.2,gpt-5.1,gpt-5.1-codex,gpt-5.1-codex-mini,gpt-5-codex,gpt-5-pro,gpt-5,gpt-5-mini,gpt-5-nano - O-Series Reasoning:
o3-pro,o3,o3-mini,o4-mini,o1-pro,o1,codex-mini-latest - GPT-4 Series:
gpt-4.1,gpt-4.1-mini,gpt-4.1-nano,gpt-4o,gpt-4o-mini
Anthropic Claude (via Vertex AI):
claude-opus-4-5,claude-opus-4-1,claude-opus-4,claude-sonnet-4-5,claude-sonnet-4,claude-haiku-4-5
Google Gemini:
gemini-3-pro-preview,gemini-3-flash-preview,gemini-2.5-pro,gemini-2.5-flash,gemini-2.5-flash-lite
All models are available through Weco. If no model is specified, Weco automatically selects the best model for your optimization task.
Resuming Interrupted Runs
If your optimization run is interrupted (network issues, restart, etc.), resume from the most recent node:
# Resume an interrupted run
weco resume 0002e071-1b67-411f-a514-36947f0c4b31
Arguments for weco resume:
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
run-id |
The UUID of the run to resume (shown at the start of each run) | 0002e071-1b67-411f-a514-36947f0c4b31 |
--apply-change |
Automatically apply the best solution to the source file without prompting | --apply-change |
--api-key |
(Optional) API keys for LLM providers (BYOK). Format: provider=key |
--api-key openai=sk-xxx |
Notes:
- Works only for interrupted runs (status:
error,terminated, etc.). - You’ll be prompted to confirm that your evaluation environment (source file + evaluation command) hasn’t changed.
- The source file is restored to the most recent solution before continuing.
- All progress and metrics from the original run are preserved.
- Log directory, save-logs behavior, and evaluation timeout are reused from the original run.
Performance & Expectations
Weco, powered by the AIDE algorithm, optimizes code iteratively based on your evaluation results. Achieving significant improvements, especially on complex research-level tasks, often requires substantial exploration time.
The following plot from the independent Research Engineering Benchmark (RE-Bench) report shows the performance of AIDE (the algorithm behind Weco) on challenging ML research engineering tasks over different time budgets.
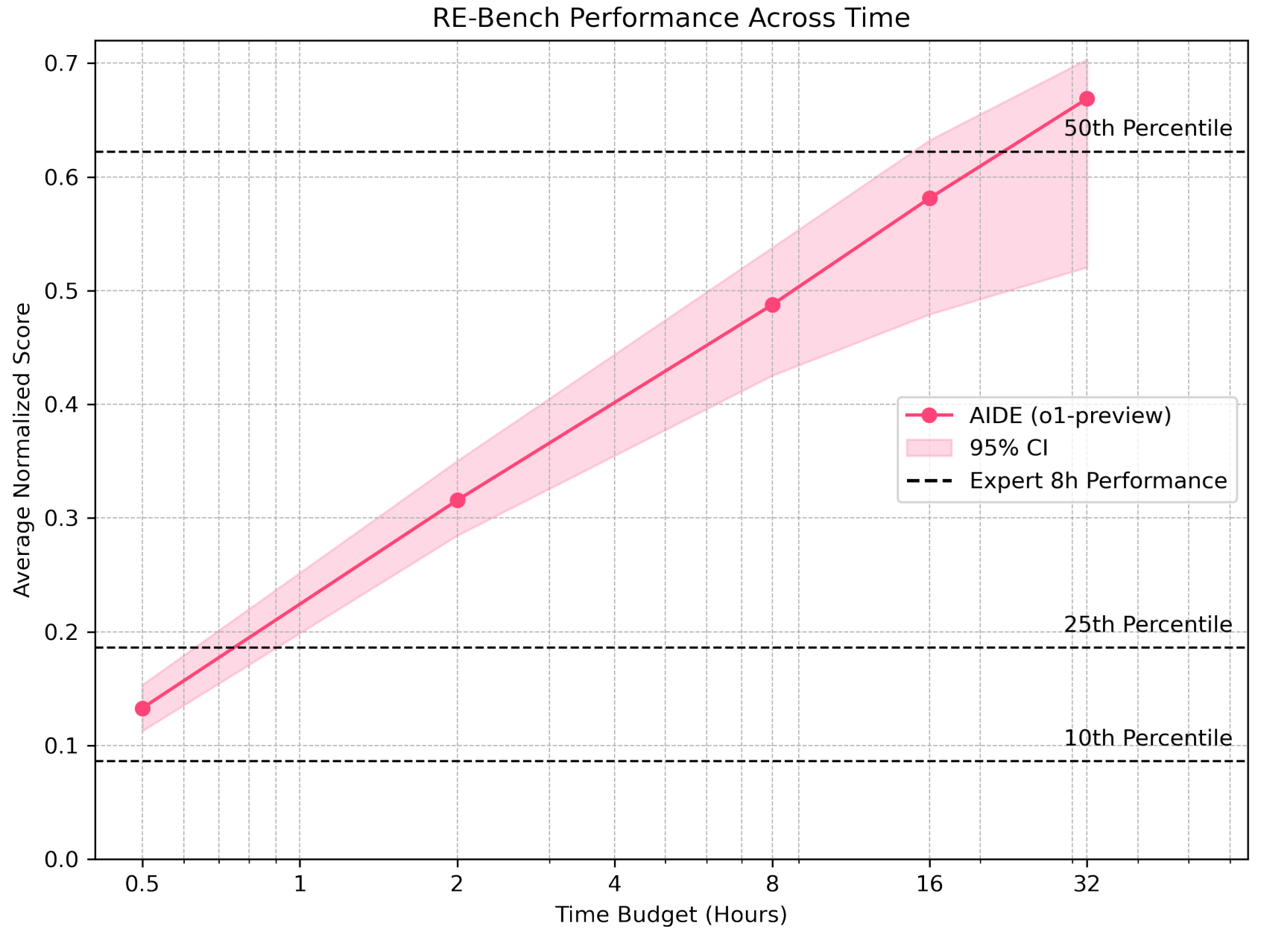
As shown, AIDE demonstrates strong performance gains over time, surpassing lower human expert percentiles within hours and continuing to improve. This highlights the potential of evaluation-driven optimization but also indicates that reaching high levels of performance comparable to human experts on difficult benchmarks can take considerable time (tens of hours in this specific benchmark, corresponding to many --steps in the Weco CLI). Factor this into your planning when setting the number of --steps for your optimization runs.
Saving Execution Logs
When using the --save-logs flag, Weco saves the execution output from each optimization step to help with debugging and analysis. The logs are organized as follows:
.runs/
└── <source-file-name>/
└── <run-uuid>/
├── exec_output.jsonl # Index file with metadata for each step
├── outputs/
│ ├── step_0.out.txt # Raw output from initial evaluation
│ ├── step_1.out.txt # Raw output from step 1
│ ├── step_2.out.txt # Raw output from step 2
│ └── ...
├── step_0.py # Code snapshot from initial evaluation
├── step_1.py # Code snapshot from step 1
├── step_2.py # Code snapshot from step 2
└── ...
Each run is organized under the source file name (e.g., spaceship-titanic for spaceship-titanic.py) and a unique UUID. The outputs/ directory and exec_output.jsonl file are only created when the --save-logs flag is used.
The exec_output.jsonl file contains one JSON object per line with:
step: The optimization step numbertimestamp: When the execution occurredoutput_file: Relative path to the full output fileoutput_length: Total length of the output
This is particularly useful for:
- Debugging why certain optimizations fail
- Analyzing patterns in evaluation results
- Keeping records of long-running optimization sessions
- Troubleshooting evaluation script issues
Important Note on Evaluation
The command specified by --eval-command is crucial. It's responsible for executing the potentially modified code from --source and assessing its performance. This command MUST print the metric you specified with --metric along with its numerical value to the terminal (standard output or standard error). Weco reads this output to understand how well each code version performs and guide the optimization process.
For example, if you set --metric speedup, your evaluation script (eval.py in the examples) should output a line like:
speedup: 1.5
or
Final speedup value = 1.5
Weco will parse this output to extract the numerical value (1.5 in this case) associated with the metric name ('speedup').
Note on Output Truncation: When evaluation output exceeds 51,000 characters, Weco truncates it to show the first 25,000 and last 25,000 characters. For best results, ensure your evaluation script prints the metric value near the end of its output.
Supported Models
A list of models we support can be found in our documentation here.
Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please see contributing.md for detailed guidelines on how to contribute to this project.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file weco-0.3.13.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: weco-0.3.13.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 22.3 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
b0a8f56d7140f0fb5f32214039298a854410642b4ba341d9d0575835759774d7
|
|
| MD5 |
85103143f8b2c820045fc6e516763d0e
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
11f6fcc562d9016736d9976d771b95d883b0885233a51b1e543adbc1c7b66031
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for weco-0.3.13.tar.gz:
Publisher:
release.yml on WecoAI/weco-cli
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
weco-0.3.13.tar.gz -
Subject digest:
b0a8f56d7140f0fb5f32214039298a854410642b4ba341d9d0575835759774d7 - Sigstore transparency entry: 937248322
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
WecoAI/weco-cli@a410a7fc5fecec9cf8d665227365baf94736379f -
Branch / Tag:
refs/heads/main - Owner: https://github.com/WecoAI
-
Access:
public
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
release.yml@a410a7fc5fecec9cf8d665227365baf94736379f -
Trigger Event:
workflow_run
-
Statement type:
File details
Details for the file weco-0.3.13-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: weco-0.3.13-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 60.1 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9423ff1b7333f16494138bd3ac54f52704ed72b68ad8bb23d085309dcd5612d8
|
|
| MD5 |
06816849e4c35feff50ab7d0a4a46c09
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
34d68e19da81ee51d876a0026e09bb45307e8bf87db1f0a56439734b2b8bdb2e
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for weco-0.3.13-py3-none-any.whl:
Publisher:
release.yml on WecoAI/weco-cli
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
weco-0.3.13-py3-none-any.whl -
Subject digest:
9423ff1b7333f16494138bd3ac54f52704ed72b68ad8bb23d085309dcd5612d8 - Sigstore transparency entry: 937248338
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
WecoAI/weco-cli@a410a7fc5fecec9cf8d665227365baf94736379f -
Branch / Tag:
refs/heads/main - Owner: https://github.com/WecoAI
-
Access:
public
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
release.yml@a410a7fc5fecec9cf8d665227365baf94736379f -
Trigger Event:
workflow_run
-
Statement type:




















