An ensamble method to recover corrupted FASTQ files, drop or fix pesky lines, remove unpaired reads, and fix reads interleaving
Project description
FastqWiper
FastqWiper is a Snakemake-enabled application that wipes out bad reads from broken FASTQ files. Additionally, the available and pre-designed Snakemake workflows allows recovering corrupted fastq.gz, dropping or fixing pesky lines, removing unpaired reads, and fixing reads interleaving.
- Compatibility: Python ≥3.7, <3.11
- OS: Windows, Linux, Mac OS (Snakemake workflows through Docker for Windows)
- Contributions: bioinformatics@css-mendel.it
- Docker: https://hub.docker.com/r/mazzalab/fastqwiper
- Singularity: https://cloud.sylabs.io/library/mazzalab/fastqwiper/fastqwiper.sif
- Bug report: https://github.com/mazzalab/fastqwiper/issues
USAGE
- Case 1. You have one or a couple (R1&R2) of computer readable FASTQ files which contain pesky, unformatted, uncompliant lines: Use FastWiper to clean them;
- Case 2. You have one or a couple (R1&R2) of computer readable FASTQ files that you want to drop unpaired reads from or fix reads interleaving: Use the FastqWiper's Snakemake workflows;
- Case 3. You have one
fastq.gzfile or a couple (R1&R2) offastq.gzfiles which are corrupted (unreadable) and you want to recover healthy reads and reformat them: Use the FastqWiper's Snakemake workflows;
Installation
Case 1
This requires you to install FastqWiper and therefore does not require you to configure workflows also. You can do it for all OSs:
Use Conda
conda create -n fastqwiper python=3.10
conda activate fastqwiper
conda install -c bfxcss -c conda-forge fastqwiper
fastqwiper --help
Hint: for an healthier experience, use mamba
Use Pypi
pip install fastqwiper
fastqwiper --help
fastqwiper <options>
options:
--fastq_in TEXT The input FASTQ file to be cleaned [required]
--fastq_out TEXT The wiped FASTQ file [required]
--log_frequency INTEGER The number of reads you want to print a status message
--log_out TEXT The file name of the final quality report summary
--help Show this message and exit.
It accepts in input and outputs readable *.fastq or *.fastq.gz files.
Cases 2 & 3
There are QUICK and a SLOW methods to configure FastqWiper's workflows.
One quick way (Docker)
- Pull the Docker image from DockerHub:
docker pull mazzalab/fastqwiper
- Once downloaded the image, type:
CMD: docker run --rm -ti --name fastqwiper -v "YOUR_LOCAL_PATH_TO_DATA_FOLDER:/fastqwiper/data" mazzalab/fastqwiper paired 8 sample 50000000 33
Another quick way (Singularity)
- Pull the Singularity image from the Cloud Library:
singularity pull library://mazzalab/fastqwiper/fastqwiper.sif
- Once downloaded the image (e.g., fastqwiper.sif_2023.2.70.sif), type:
CMD singularity run --bind /scratch/tom/fastqwiper_singularity/data:/fastqwiper/data --writable-tmpfs fastqwiper.sif_2023.2.70.sif paired 8 sample 50000000 33
If you want to bind the .singularity cache folder and the logs folder, you can omit --writable-tmpfs, create the folders .singularity and logs (mkdir .singularity logs) on the host system, and use this command instead:
CMD: singularity run --bind YOUR_LOCAL_PATH_TO_DATA_FOLDER/:/fastqwiper/data --bind YOUR_LOCAL_PATH_TO_.singularity_FOLDER/:/fastqwiper/.snakemake --bind YOUR_LOCAL_PATH_TO_LOGS_FOLDER/:/fastqwiper/logs fastqwiper.sif_2023.2.70.sif paired 8 sample 50000000 33
For both Docker and Singularity:
YOUR_LOCAL_PATH_TO_DATA_FOLDERis the path of the folder where the fastq.gz files to be wiped are located;pairedtriggers the cleaning of R1 and R2. Alternatively,singlewill trigger the wipe of individual FASTQ files;8is the number of your choice of computing cores to be spawned;sampleis part of the names of the FASTQ files to be wiped. Be aware that: for paired-end files (e.g., "sample_R1.fastq.gz" and "sample_R2.fastq.gz"), your files must finish with_R1.fastq.gzand_R2.fastq.gz. Therefore, the argument to pass is everything before these texts:samplein this case. For single end/individual files (e.g., "excerpt_R1_001.fastq.gz"), your file must end with the string.fastq.gz; the preceding text, i.e., "excerpt_R1_001" in this case, will be the text to be passed to the command as an argument.50000000(optional) is the number of rows-per-chunk (used when cores>1. It must be a number multiple of 4). Increasing this number too much would reduce the parallelism advantage. Decreasing this number too much would increase the number of chunks more than the number of available cpus, making parallelism unefficient. Choose this number wisely depending on the total number of reads in your starting file.33(optional) is the ASCII offset (33=Sanger, 64=old Solexa)
The slow way (Linux & Mac OS)
To enable the use of preconfigured pipelines, you need to install Snakemake. The recommended way to install Snakemake is via Conda, because it enables Snakemake to handle software dependencies of your workflow. However, the default conda solver is slow and often hangs. Therefore, we recommend installing Mamba as a drop-in replacement via
$ conda install -c conda-forge mamba
if you have anaconda/miniconda already installed, or directly installing Mambaforge as described here.
Then, create and activate a clean environment as above:
mamba create -n fastqwiper python=3.10
mamba activate fastqwiper
Finally, install a few dependencies:
$ mamba install -c bioconda snakemake
$ mamba install colorama click
Usage
Clone the FastqWiper repository in a folder of your choice and enter it:
git clone https://github.com/mazzalab/fastqwiper.git
cd fastqwiper
It contains, in particular, a folder data containing the fastq files to be processed, a folder pipeline containing the released pipelines and a folder fastq_wiper with the source files of FastqWiper.
Input files to be processed should be copied into the data folder.
Currently, to run the FastqWiper pipelines, the following packages need to be installed manually:
required packages:
gzrt (Linux build fron source instructions, Ubuntu install instructions, Mac OS install instructions)
BBTools (install instructions)
If installed from source, gzrt scripts need to be put on PATH. bbmap must be installed in the root folder of FastqWiper, as the image below
Commands:
Copy the fastq files you want to fix in the data folder.
N.b.: In all commands above, you will pass to the workflow the name of the sample to be analyzed through the config argument: sample_name. Remember that your fastq files' names must finish with _R1.fastq.gz and _R2.fastq.gz, for paired fastq files, and with .fastq.gz, for individual fastq files, and, therefore, the text to be assigned to the variable sample_name must be everything before them. E.g., if your files are my_sample_R1.fastq.gz and my_sample_R2.fastq.gz, then --config sample_name=my_sample.
Paired-end files
-
Get a dry run of a pipeline (e.g.,
fix_wipe_pairs_reads_sequential.smk):
snakemake --config sample_name=my_sample qin=33 -s pipeline/fix_wipe_pairs_reads_sequential.smk --use-conda --cores 4 -
Generate the planned DAG:
snakemake --config sample_name=my_sample qin=33 -s pipeline/fix_wipe_pairs_reads_sequential.smk --dag | dot -Tpdf > dag.pdf
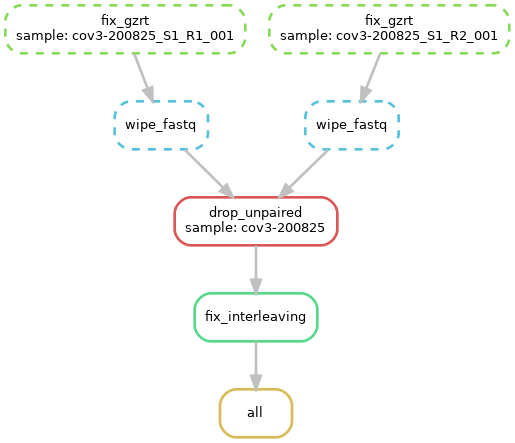
- Run the pipeline (n.b., during the first execution, Snakemake will download and install some required remote packages and may take longer). The number of computing cores can be tuned accordingly:
snakemake --config sample_name=my_sample qin=33 -s pipeline/fix_wipe_single_reads_sequential.smk --use-conda --cores 2
Fixed files will be copied in the data folder and will be suffixed with the string _fixed_wiped_paired_interleaving.
We remind that the fix_wipe_pairs_reads_sequential.smk and fix_wipe_pairs_reads_parallel.smk pipelines perform the following actions:
- execute
gzrton corrupted fastq.gz files (i.e., that cannot be unzipped because of errors) and recover readable reads; - execute
FastqWiperon recovered reads to make them compliant with the FASTQ format (source: Wipipedia) - execute
Trimmomaticon wiped reads to remove residual unpaired reads - execute
BBmap (repair.sh)on paired reads to fix the correct interleaving and sort fastq files.
Single-end files
fix_wipe_single_reads_parallel.smk and fix_wipe_single_reads_sequential.smk will not execute trimmomatic and BBmap's repair.sh.
-
Get a dry run of a pipeline (e.g.,
fix_wipe_single_reads_sequential.smk):
snakemake --config sample_name=my_sample -s pipeline/fix_wipe_single_reads_sequential.smk --use-conda --cores 2 -np -
Generate the planned DAG:
snakemake --config sample_name=my_sample -s pipeline/fix_wipe_single_reads_sequential.smk --dag | dot -Tpdf > dag.pdf
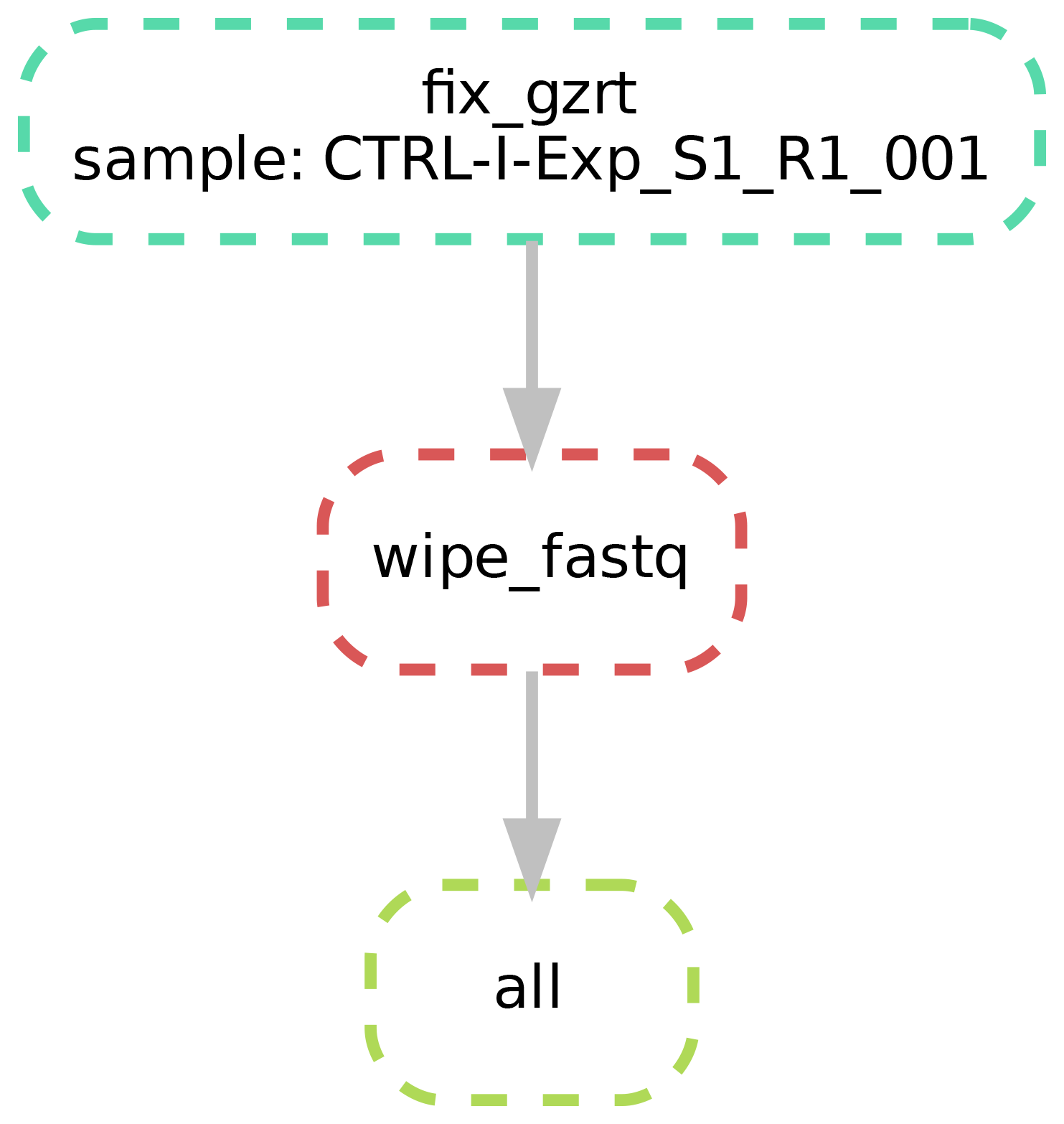
- Run the pipeline (n.b., The number of computing cores can be tuned accordingly):
snakemake --config sample_name=my_sample -s pipeline/fix_wipe_single_reads_sequential.smk --use-conda --cores 2
Author
Laboratory of Bioinformatics
Fondazione IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza
Viale Regina Margherita 261 - 00198 Roma IT
Tel: +39 06 44160526 - Fax: +39 06 44160548
E-mail: t.mazza@css-mendel.it
Web page: http://www.css-mendel.it
Web page: http://bioinformatics.css-mendel.it
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distributions
Built Distribution
File details
Details for the file fastqwiper-2024.1.86-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: fastqwiper-2024.1.86-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 15.0 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/5.1.0 CPython/3.10.14
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 6b2be93f27ba702ce36d1b6d990d29ac12b90eedac2f4c52bfc45ded748c1cdc |
|
| MD5 | ffea40a8fd9e939b92486c26bee9bfb6 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 21e70de7faeb58bbb0aba0acf81320b1500a4638de58d519a9f8903c2d9d10c4 |

























