Nautobot plugin to automatically handle Circuit Maintenances Notifications
Project description
Nautobot Circuit Maintenance plugin
A plugin for Nautobot to easily handle Circuit Maintenances related to Nautobot Circuits.
nautobot-circuit-maintenance lets you handle maintenances for your Circuits based on notifications received by email by leveraging on circuit-maintenance-parser, a notifications parser library for multiple network service providers that exposes structured data following a recommendation defined in this draft NANOG BCOP.
Installation
The plugin is available as a Python package in pypi and can be installed with pip
pip install nautobot-circuit-maintenance
The plugin is compatible with Nautobot 1.0.0b4 and higher
To ensure Circuit Maintenance is automatically re-installed during future upgrades, create a file named local_requirements.txt (if not already existing) in the Nautobot root directory (alongside requirements.txt) and list the nautobot-circuit-maintenance package:
# echo nautobot-circuit-maintenance >> local_requirements.txt
Once installed, the plugin needs to be enabled in your configuration.py.
# In your configuration.py
PLUGINS = ["nautobot_circuit_maintenance"]
PLUGINS_CONFIG = {
"nautobot_circuit_maintenance": {
"raw_notification_initial_days_since": 100,
"raw_notification_size": 16384,
"notification_sources": [
{
...
}
]
}
}
Plugin config parameters:
raw_notification_initial_days_since: define how many days back the plugin will check forRawNotifications for eachNotificationSource, in order to limit the number of notifications to be processed on the first run of the plugin. In subsequent runs, the last notification date will be used as the reference to limit. If not defined, it defaults to 7 days.raw_notification_size: define how many bytes from a notification will be stored in the database to not store too big objects. If not defined, it defaults to 8192 bytes.
The notification_sources have custom definition depending on the Source type, and are defined in the Usage section.
Usage
1. Define source emails per Provider
In the Nautobot UI, under Circuits -> Providers, for each Provider that we would like to track via the Circuit Maintenance plugin, we must configure at least one email source address (or a comma-separated list of addresses) in the `Custom Fields -> Emails for Circuit Maintenance plugin field.
These are the source email addresses that the plugin will detect and will use to classify each notification for each specific provider.
Also, by default, the Provider slug is used to match the provider parser from the circuit-maintenance-parser library, but if a custom mapping is desired (i.e. CentruryLink to Lumen), you can define this custom mapping in the `Custom Fields -> Provider Parser for Circuit Maintenance plugin field.
2. Configure Notification Sources
Notification Sources are defined in two steps:
2.1 Define Notification Sources in nautobot_config.py
In nautobot_config.py, in the PLUGINS_CONFIG, under the nautobot_circuit_maintenance key, we should define the Notification Sources that will be able later in the UI, where you will be able to validate if the authentication credentials provided are working fine or not.
There are two mandatory attributes (other keys are dependent on the integration type, and will be documented below):
name: Name to identify the Source and will be available in the UI.url: URL to reach the Notification Source (i.e.imap://imap.gmail.com:993)
There is also one optional attribute:
attach_all_providers: Flag that enables auto linking of newly createdProvidersto this Notification Source.
Currently, only IMAP and HTTPS (accounts.google.com) integrations are supported as URL scheme
2.1.1 IMAP
There are 2 extra required attributes:
account: Identifier (i.e. email address) to use to authenticate.secret: Password to IMAP authentication.
Gmail example: How to setup Gmail with App Passwords
There is also one optional attribute:
source_header: Specify a particular email header to use to identify the source of a particular notification and assign it to the appropriate provider. If unset,Fromwill be used, but if your emails are not received directly from the provider but instead pass through a mailing list or alias, you might need to set this to a different value such asX-Original-Senderinstead.
PLUGINS_CONFIG = {
"nautobot_circuit_maintenance": {
"notification_sources": [
{
"name": "my custom name",
"account": os.getenv("CM_NS_1_ACCOUNT", ""),
"secret": os.getenv("CM_NS_1_SECRET", ""),
"url": os.getenv("CM_NS_1_URL", ""),
"source_header": os.getenv("CM_NS_1_SOURCE_HEADER", "From"), # optional
"attach_all_providers": True, # optional
}
]
}
}
2.1.2 Gmail API integrations
Typically the
urlsetting to configure in yourPLUGINS_CONFIGfor use with Gmail integration will be"https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth".
There are 2 extra required attributes:
account: Identifier (i.e. email address) to access via OAuth or to impersonate as service account.credentials_file: JSON file containing all the necessary data to identify the API integration (see below).
There are also the following optional attributes:
source_header: Specify a particular email header to use to identify the source of a particular notification and assign it to the appropriate provider. If unset,Fromwill be used, but if your emails are not received directly from the provider but instead pass through a mailing list or alias, you might need to set this to a different value such asX-Original-Senderinstead.limit_emails_with_not_header_from: List of emails used to restrict the emails retrieved when NOT using thesource_header"From" and we can't use theProvideroriginal emails to filter.extra_scopes: Specify a list of additional Google OAuth2 scopes to request access to in addition to Gmail API read-only access.labels: Specify a dictionary of message labels and their corresponding Gmail label IDs; used to enable the optional feature of automatically labeling messages as they are processed by this plugin for later investigation and troubleshooting. See below for how to look up the IDs for the desired labels; any labels that are not specified will be skipped. Currently supported labels are:unknown-provider- A message was inspected but the plugin could not identify which provider this message came from in order to parse it properlyparsing-failed- An error occurred while trying to parse this messageparsed- The message was parsed successfullyignored- Parsing of the message determined that there is no relevant circuit maintenance content in the messageout-of-sequence- Parsing of the message determined that it predates the latest already-processed message relevant to the same circuit maintenance event, so it is out of sequence.unknown-cids- Parsing of the message determined that it references one or more circuit IDs (CIDs) that could not be found within Nautobot's database.
If you want to use the
labelsfeature, you must include"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.modify"in theextra_scopeslist so that the plugin will be allowed to make changes to the Gmail messages to apply the labels.
PLUGINS_CONFIG = {
"nautobot_circuit_maintenance": {
"notification_sources": [
{
"name": "my custom name",
"account": os.getenv("CM_NS_1_ACCOUNT", ""),
"credentials_file": os.getenv("CM_NS_1_CREDENTIALS_FILE", ""),
"url": os.getenv("CM_NS_1_URL", ""),
"source_header": os.getenv("CM_NS_1_SOURCE_HEADER", "From"), # optional
"limit_emails_with_not_header_from": ["email@example.com"], # optional
"extra_scopes": [ # optional
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.modify",
"https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar.events",
],
"labels": { # optional
"unknown-provider": "Label_2156989743288038678",
"parsing-failed": "Label_820864599623865470",
"parsed": "Label_3930009158110411672",
"ignored": "Label_6398181635995151975",
"out-of-sequence": "Label_7702409558462584907",
"unknown-cids": "Label_870427780871495349",
},
}
]
}
}
To enable Gmail API access, there are some common steps for both Service Account and OAuth authentication:
- Create a New Project in Google Cloud Console.
- Under APIs and Services, enable Gmail API for the selected project.
2.1.2.1 Service Account
To create a Service Account integration:
- Still under APIs and Services, in Credentials, create a new Service Account and save the credentials file generated to be used when configuring Nautobot Sources.
- With Admin rights, edit the newly created Service Account and expand the Show Domain-Wide Delegation section. Enable Google Workspace Domain-wide Delegation and save the changes. Copy the Client ID shown.
- With Super Admin rights, open the Google Workspace admin console. Navigate to Security, API controls, and select the Manage Domain Wide Delegation at the bottom of the page.
- Add a new API client and paste in the Client ID copied earlier. In the OAuth scopes field add the appropriate scopes:
https://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.readonlyandhttps://mail.google.comare mandatoryhttps://www.googleapis.com/auth/gmail.modifyis additionally required if you want to use the automatic message labeling feature.
- Save the new client configuration by clicking Authorize.
2.1.2.2 OAuth
To create a OAuth 2.0 integration:
- Still under APIs and Services, in Credentials, create a new OAuth client ID selecting the Web application application type.
- Under Authorized redirect URIs add the location where your Nautobot server is listening plus
plugins/circuit-maintenance/source/google_oauth2callback/. For instance:http://localhost:8080/plugins/circuit-maintenance/source/google_oauth2callback/ - Save the credentials file generated to be used when configuring Nautobot Sources.
For OAuth integration, it's recommendable that, at least the first time, you run a manual Validate of the Notification Source to complete the OAuth authentication workflow, identifying your Google credentials.
2.1.2.3 Gmail Label IDs
While it's easy to define appropriate Gmail labels from the Gmail web UI, the UI doesn't appear to expose the underlying label IDs that need to be used with the Gmail API. The easiest way to look these up is to use the Gmail for Developers API Explorer to log in as the desired user and query for the existing labels and their IDs.
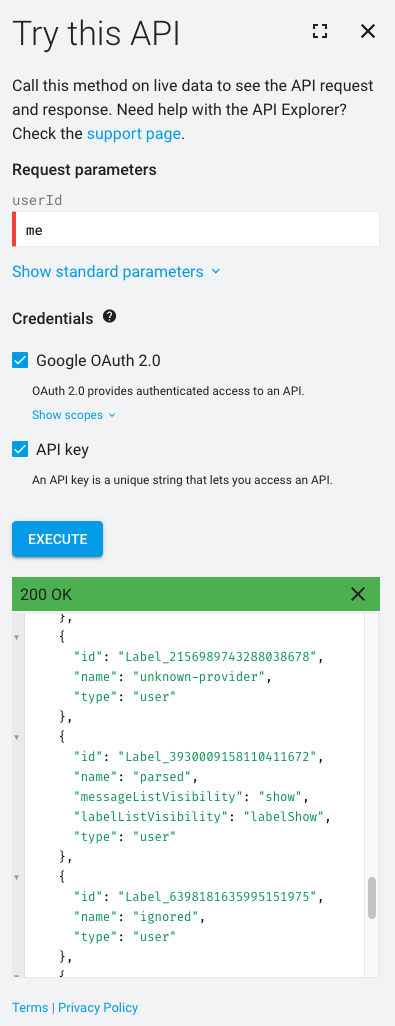
2.2 Add Providers to the Notification Sources
In the Circuit Maintenance plugin UI section, there is a Notification Sources button (yellow) where you can configure the Notification Sources to track new circuit maintenance notifications from specific providers.
Because the Notification Sources are defined by the configuration, you can only view and edit providers, but not add or delete new Notification Sources via UI or API.
Note that for emails from a given Provider to be processed, you must both define a source email address(es) for that Provider (Usage section 1, above) and add that provider to a specific Notification Source as described in this section.
3. Run Handle Notifications Job
There is an asynchronous task defined as a Nautobot Job, Handle Circuit Maintenance Notifications that will connect to the emails sources defined under the Notification Sources section (step above), and will fetch new notifications received since the last notification was fetched. Each notification will be parsed using the circuit-maintenance-parser library, and if a valid parsing is executed, a new Circuit Maintenance will be created, or if it was already created, it will updated with the new data.
So, for each email notification received, several objects will be created:
3.1 Notification
Each notification received will create a related object, containing the raw data received, and linking to the corresponding parsed notification in case the circuit-maintenance-parser was able to parse it correctly.
3.2 Parsed Notification
When a notification was successfully parsed, it will create a parsed notification object, that will contain the structured output from the parser library , following the recommendation defined in draft NANOG BCOP, and a link to the related Circuit Maintenance object created.
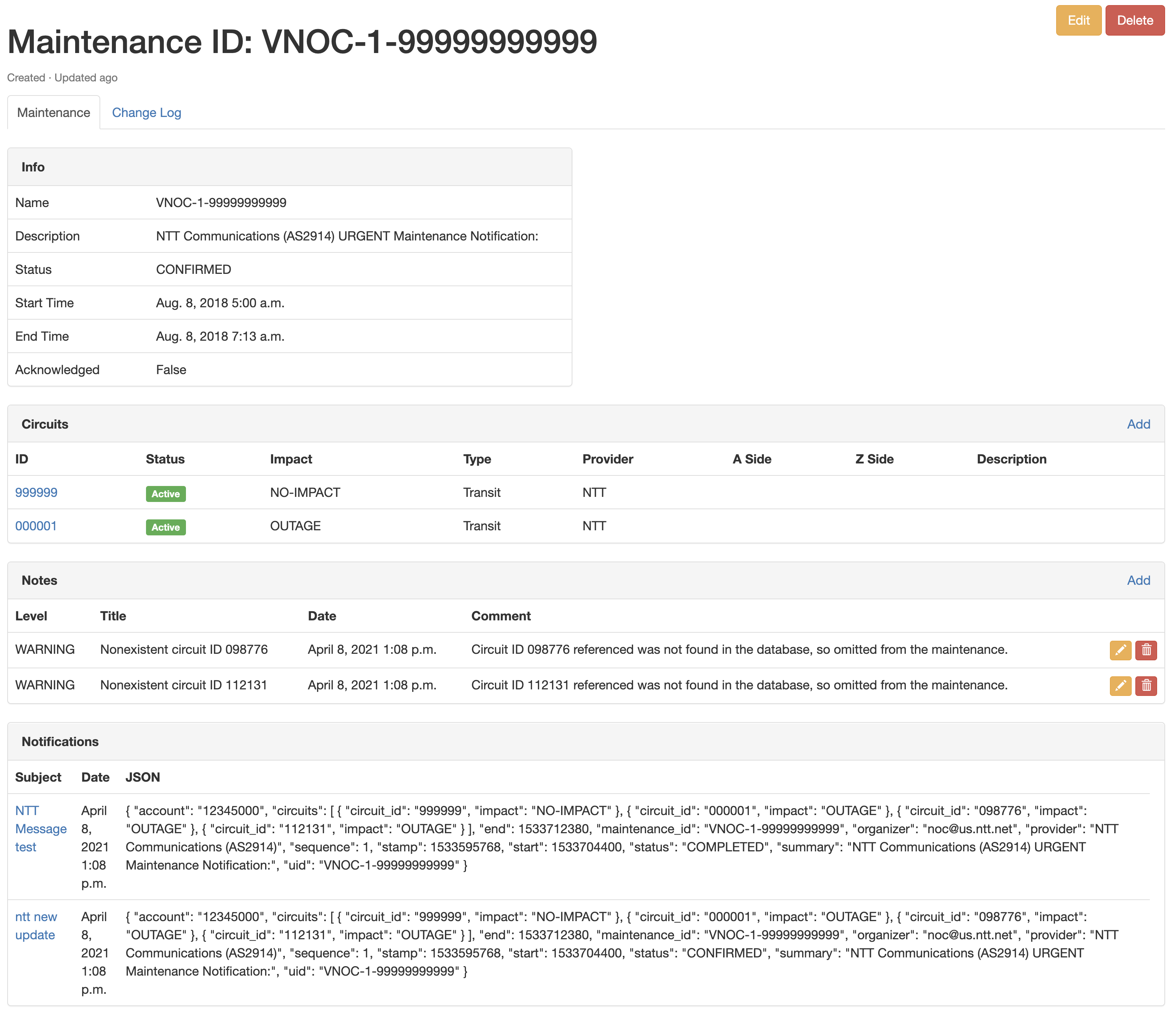
3.3 Circuit Maintenance
The Circuit Maintenance is where all the necessary information related to a Circuit maintenance is tracked, and reuses most of the data model defined in the parser library.
Attributes:
- Name: name or identifier of the maintenance.
- Description: description of the maintenance.
- Status: current state of the maintenance.
- Start time: defined start time of the maintenance work.
- End time: defined end time of the maintenance work.
- Ack: boolean to show if the maintenance has been properly handled by the operator.
- Circuits: list of circuits and its specific impact linked to this maintenance.
- Notes: list of internal notes linked to this maintenance.
- Notifications: list of all the parsed notifications that have been processed for this maintenance.
Metrics
Leveraging the nautobot-capacity-metrics plugin, the nautobot-circuit-maintenance plugin can expose application metrics at /api/plugins/capacity-metrics/app-metrics if desired.
Current exposed metric is the circuit operational status which shows the operational status for each Circuit(attached to a CircuitTermination) depending on related Circuit Maintenances (1: Operational, 2: Under active maintenance):
# HELP circuit_maintenance_status Circuit operational status
# TYPE circuit_maintenance_status gauge
circuit_maintenance_status{circuit="1111111",circuit_type="Transit",provider="ntt",site="Barcelona"} 2.0
circuit_maintenance_status{circuit="2222222",circuit_type="Peering",provider="colt",site="Girona"} 1.0
Metric generation is disabled by default, to enable them, add a enable: True in the nautobot_circuit_maintenance.metrics dict. (Of course you must also install the nautobot_capacity_metrics plugin and ensure that it is included in PLUGINS as a prerequisite to enabling this feature.)
By default, each circuit has attached some labels and values (cid, provider, type and site), but these labels can be defined in the Plugin configuration by adding an optional dictionary (under "metrics" -> "labels_attached") with the label name and the attributes within the Circuit object. (Note: in case of a value that can be multiple values, such as terminations, the first defined one will be used)
PLUGINS_CONFIG = {
"nautobot_circuit_maintenance": {
...
"metrics": {
"enable": True,
"labels_attached": {
"circuit": "circuit.cid",
"provider": "circuit.provider.name",
"circuit_type": "circuit.type.name",
"site": "site.name",
}
},
}
}
Rest API
The plugin includes 6 API endpoints to manage its related objects, complete info in the Swagger section.
- Circuit Maintenance:
/api/plugins/circuit-maintenance/maintenance - Circuit Impact:
/api/plugins/circuit-maintenance/circuitimpact - Note:
/api/plugins/circuit-maintenance/note
GraphQL API
Circuit Maintenance and Circuit Impact objects are available for GraphQL queries.
Contributing
Pull requests are welcomed and automatically built and tested against multiple version of Python and multiple version of Nautobot through TravisCI.
The project is packaged with a light development environment based on docker-compose to help with the local development of the project and to run the tests within TravisCI.
The project is following Network to Code software development guideline and is leveraging:
- Black, Pylint, Bandit and pydocstyle for Python linting and formatting.
- Django unit test to ensure the plugin is working properly.
CLI Helper Commands
The project is coming with a CLI helper based on invoke to help setup the development environment. The commands are listed below in 3 categories dev environment, utility and testing.
Each command can be executed with invoke <command>. All commands support the arguments --nautobot-ver and --python-ver if you want to manually define the version of Python and Nautobot to use. Each command also has its own help invoke <command> --help
Local dev environment
build Build all docker images.
debug Start Nautobot and its dependencies in debug mode.
destroy Destroy all containers and volumes.
restart Restart Nautobot and its dependencies.
start Start Nautobot and its dependencies in detached mode.
stop Stop Nautobot and its dependencies.
Utility
cli Launch a bash shell inside the running Nautobot container.
create-user Create a new user in django (default: admin), will prompt for password.
makemigrations Run Make Migration in Django.
nbshell Launch a nbshell session.
Testing
bandit Run bandit to validate basic static code security analysis.
black Run black to check that Python files adhere to its style standards.
flake8 This will run flake8 for the specified name and Python version.
pydocstyle Run pydocstyle to validate docstring formatting adheres to NTC defined standards.
pylint Run pylint code analysis.
tests Run all tests for this plugin.
unittest Run Django unit tests for the plugin.
Questions
For any questions or comments, please check the FAQ first and feel free to swing by the Network to Code slack channel (channel #nautobot). Sign up here
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for nautobot-circuit-maintenance-0.4.0.tar.gz
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 4ea5c24bf82edd3ef1ccddcae11683df5f3abf883441001bc94dab0ec6be4d48 |
|
| MD5 | b47c51e73ed0dbe66960ddc561f38675 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 4b3d1069659fbbbe205759291a4736729c3a35f33aa83685c50a3e7ba5bcaf82 |
Hashes for nautobot_circuit_maintenance-0.4.0-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | e6f8efd2ad9c162b2b2ac76922ee0ac5da3c59ffd5be089ffed9f4c026664bae |
|
| MD5 | 3765a372e8cf611ebe16742aa1dda213 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 2db81d119d482aeeca1ca9732c4d1444a4013f6c3fb4466360a24549b267a754 |











