Nautobot SSoT Arista CloudVision
Project description
Nautobot to Arista CloudVision Sync
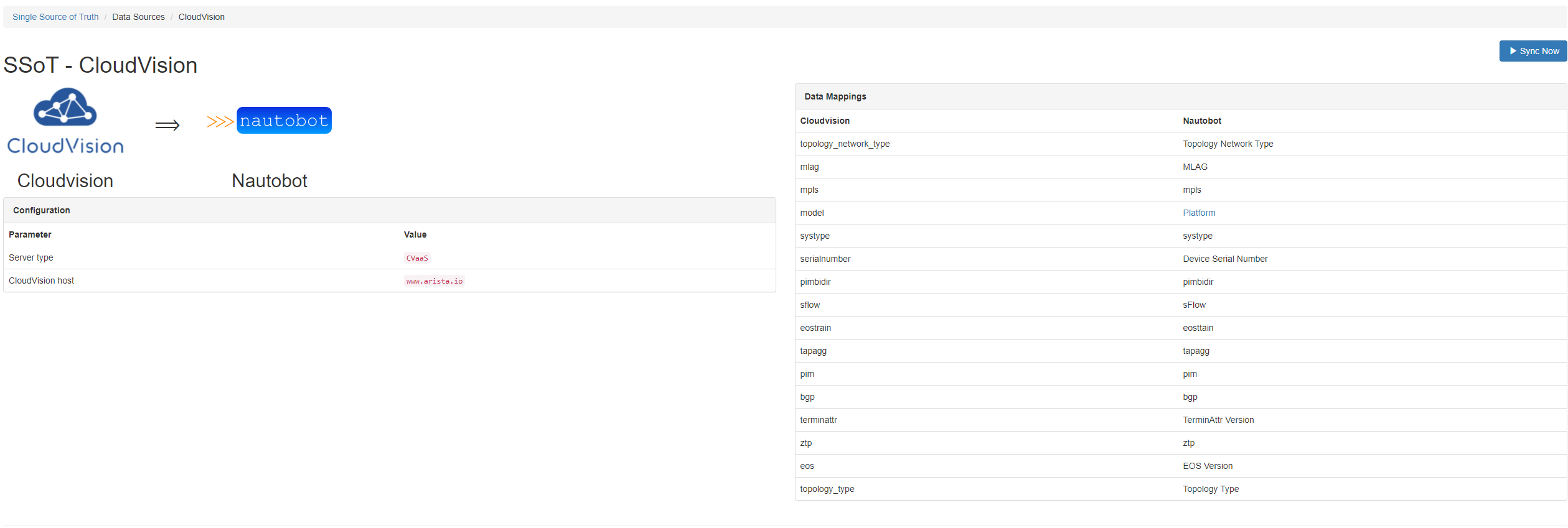
A plugin for Nautobot that allows synchronization of data directly between CloudVision and Nautobot. It synchronizes user device tags from Nautobot into CloudVision while using devices and system tags from CloudVision to ensure device synchronization and populate device metadata. Here is a table showing the data mappings when syncing from CloudVision.
| CloudVision System Tags | Nautobot Device Custom Field |
|---|---|
| topology_network_type | Topology Network Type |
| mlag | mlag |
| mpls | mpls |
| model | Device Platform* |
| systype | systype |
| serialnumber | Device Serial Number |
| pimbidir | pimbidir |
| sflow | sFlow |
| eostrain | EOS Train |
| tapagg | TAP Aggregation |
| pim | pim |
| bgp | bgp |
| terminattr | TerminAttr Version |
| ztp | ztp |
| eos | EOS Version |
| topology_type | Topology Type |
The model system tag is mapped to the device platform model in Nautobot.
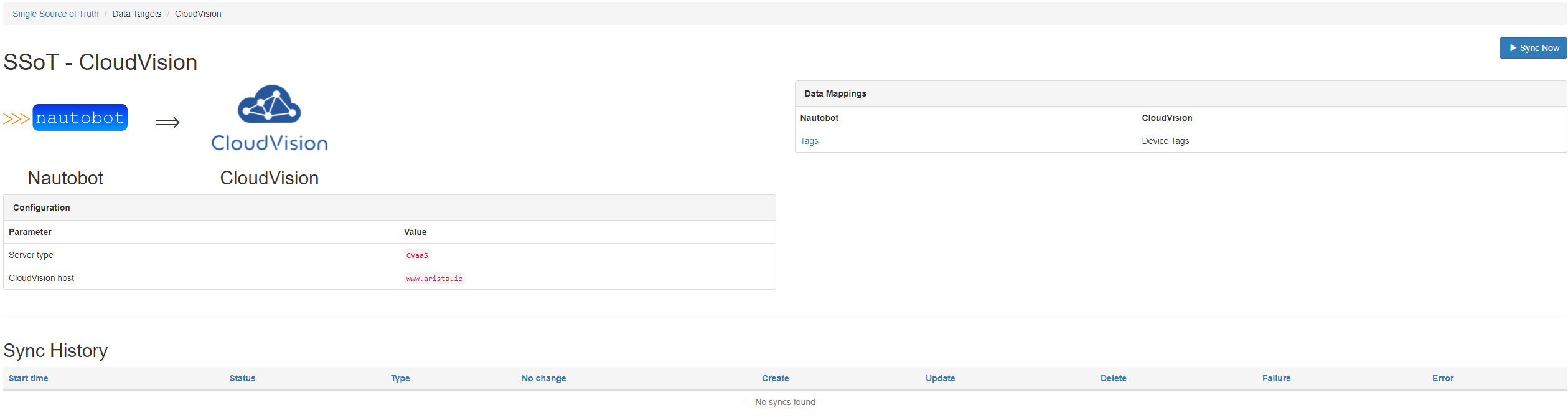
When syncing User tags from Nautobot to CloudVision the data mappings are as follows:
| Nautobot | CloudVision |
|---|---|
| Tags | Device Tags |
This plugin is an extension of the Nautobot Single Source of Truth (SSoT) and you must have that plugin installed before installing this extension.
Screenshots
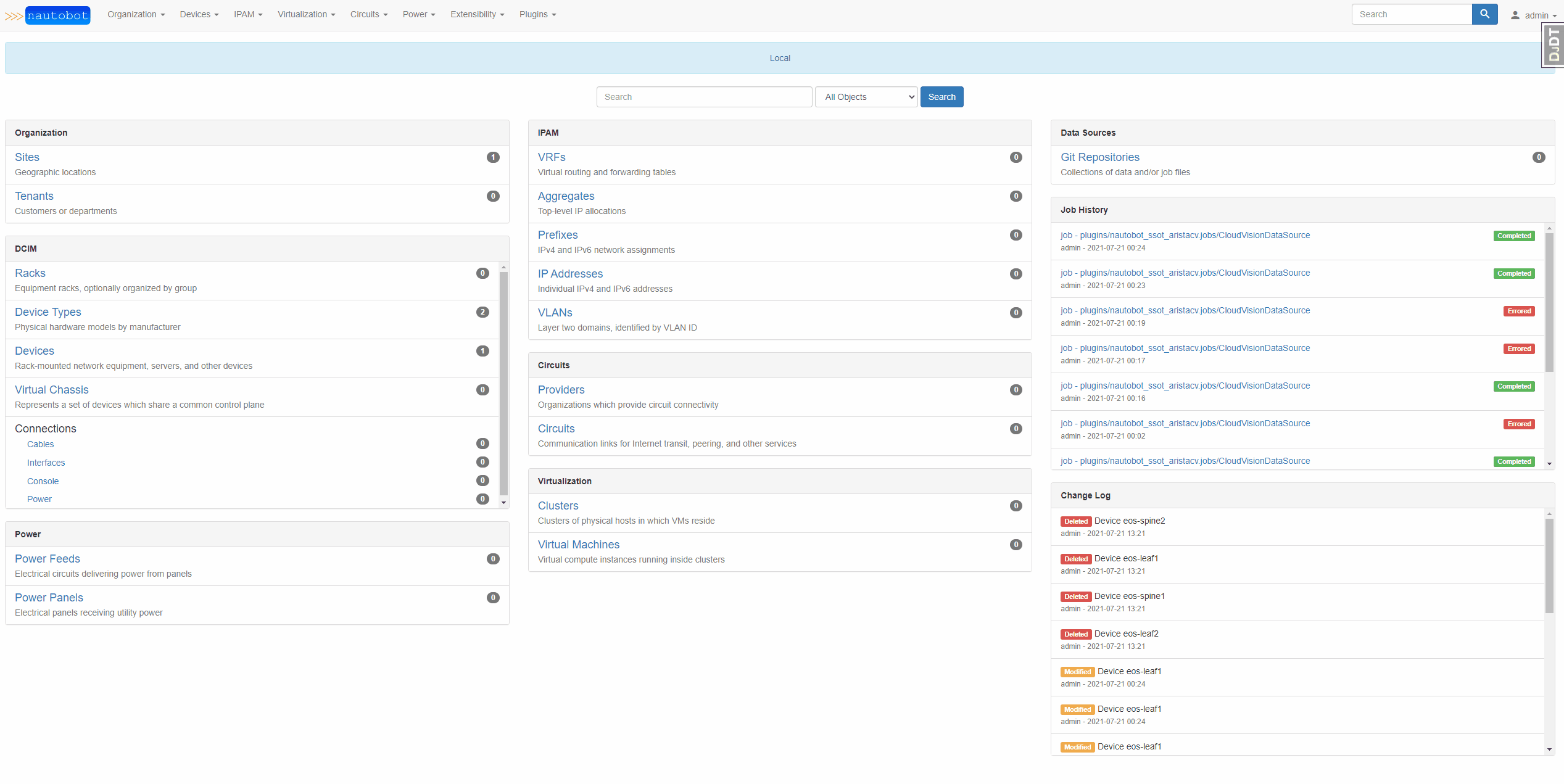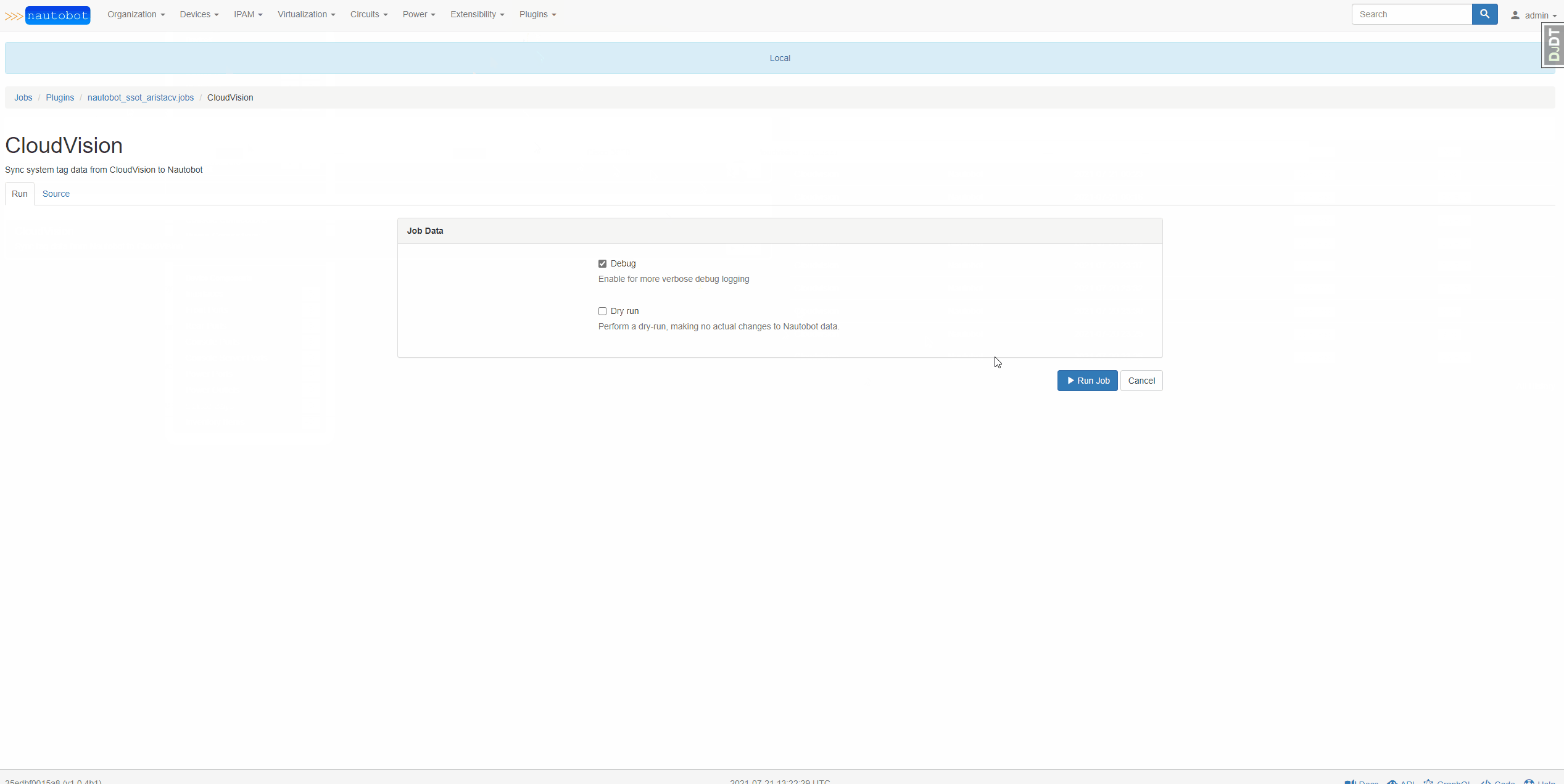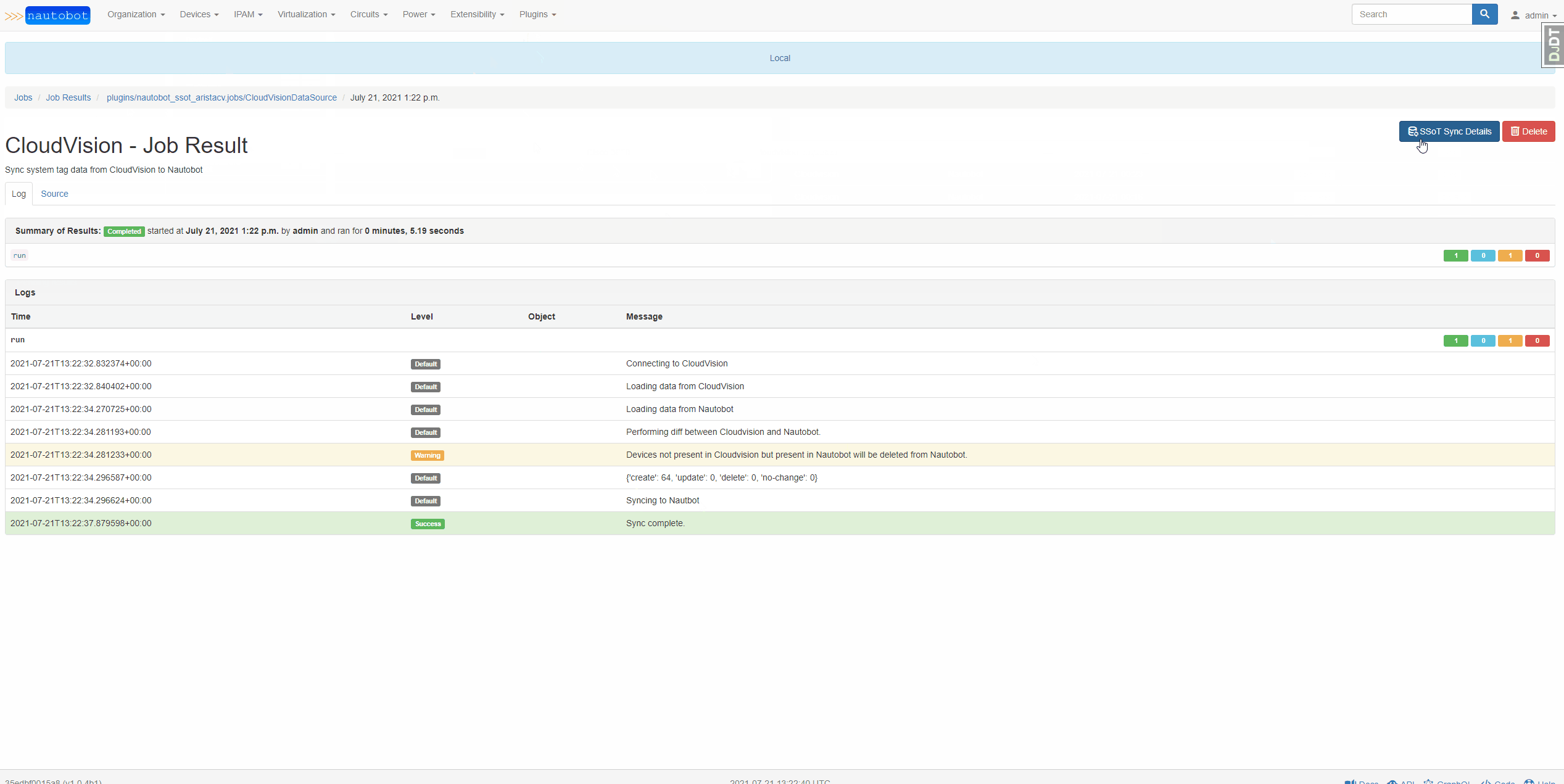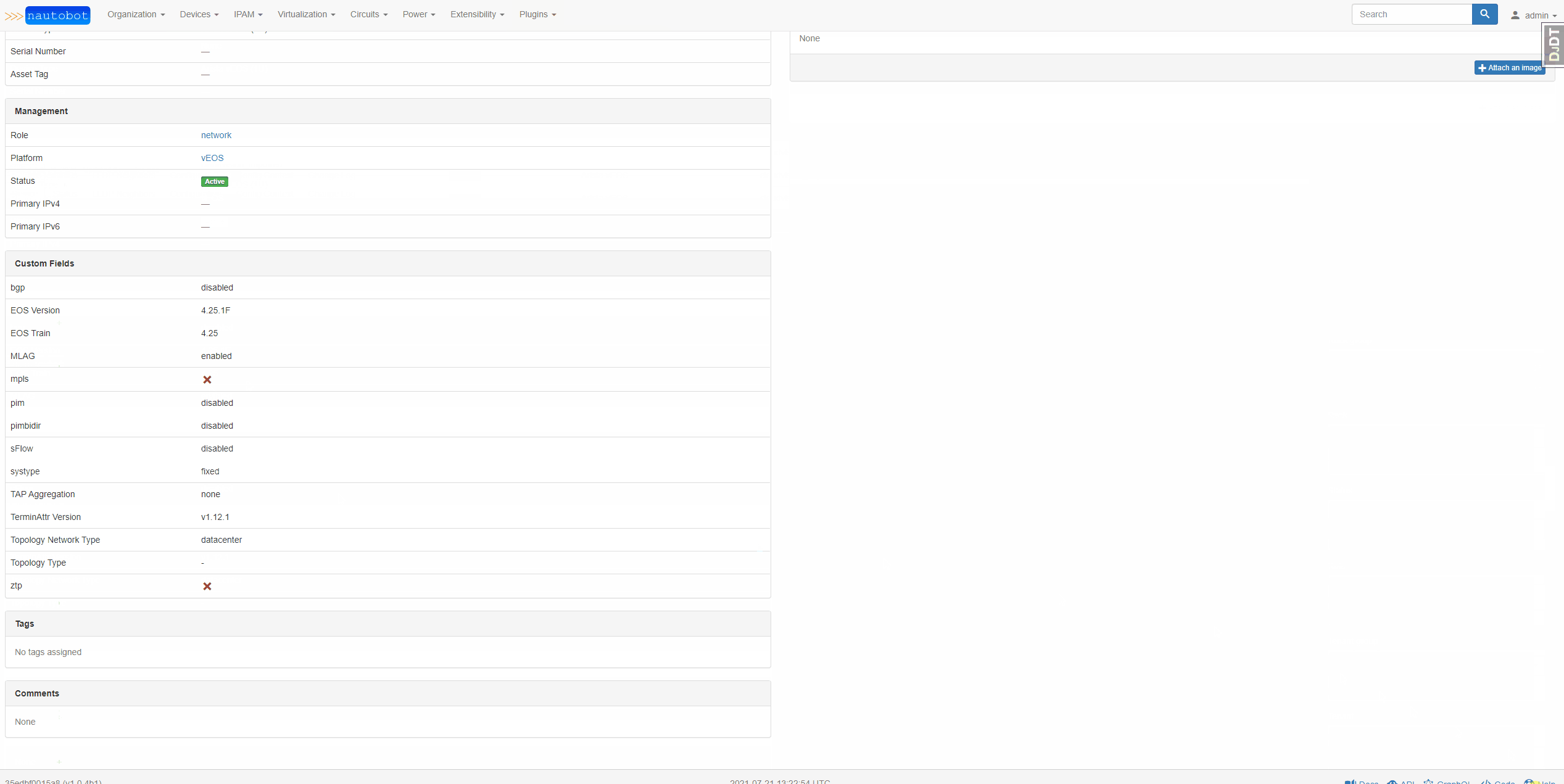
This screenshot shows the CloudVision to Nautobot home page. This contains a list of all the system tags from CloudVision and how they map to custom fields in Nautobot. This also displays current plugin configuration and sync history.
This screenshow shows the Nautobot to CloudVision home page. It also contains data mappings, plugin configuration and sync history.
Installation
The plugin is available as a Python package in pypi and can be installed with pip
pip install nautobot_ssot_aristacv
The plugin is compatible with Nautobot 1.0.0 and higher
To ensure Nautobot to Arista CloudVision Sync is automatically re-installed during future upgrades, create a file named local_requirements.txt (if not already existing) in the Nautobot root directory (alongside requirements.txt) and list the nautobot_ssot_aristacv package:
# echo nautobot_ssot_aristacv >> local_requirements.txt
Once installed, the plugin needs to be enabled in your nautobot_configuration.py and plugin settings need to be defined.
# In your configuration.py
PLUGINS = ["nautobot_ssot", "nautobot_ssot_aristacv"]
# PLUGINS_CONFIG = {
# "nautobot_ssot" : {
# ADD YOUR SETTINGS HERE
# }
# "nautobot_ssot_aristacv": {
# "cvaas_token": "",
# "cvp_host": "",
# "cvp_port": "",
# "cvp_user": "",
# "cvp_password": "",
# "insecure": "",
# "from_cloudvision_default_site": "",
# "from_cloudvision_default_device_role": "",
# "from_cloudvision_default_device_role_color": "",
# "from_cloudvision_default_device_status": "",
# "from_cloudvision_default_device_status_color": "",
# "delete_devices_on_sync": "",
# "apply_import_tag": ""
# }
# }
All plugin settings are defined in the picture above as an example. Only some will be needed as described below.
Upon installation, this plugin creates the following custom fields in Nautobot:
arista_bgparista_eosarista_eostrainarista_mlagarista_mplsarista_pimarista_pimbidirarista_sflowarista_systypearista_tapaggarista_terminattrarista_topology_network_typearista_topology_typearista_ztp
While these contain the prefix "arista" in the custom field admin portal, when looking at them on a device the prefix is removed.
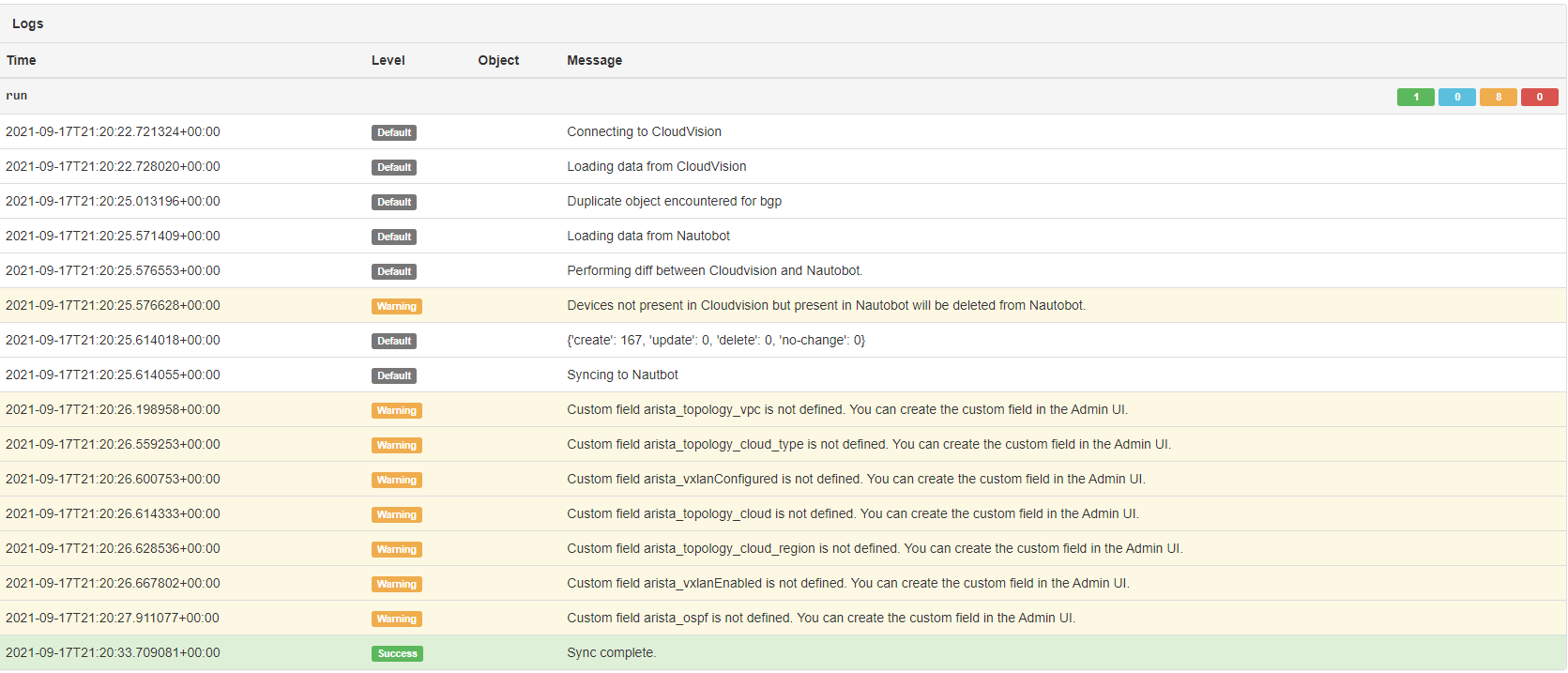
Other custom fields may need to be created by the user. When a sync is ran and a system tag for a device in CloudVision is found without a corresponding custom field, the sync log will display a message. In order to have that data synced, a custom field must be created in the Admin UI using the given name in the message.
The plugin can connect to either on-premise or a cloud instance of CloudVision. To connect to an on-premise instance, you must set the following variables in the Nautobot configuration file.
| Configuration Variable | Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| cvp_host | string | Hostname or ip address of the onprem instance of CloudVision. |
| cvp_port | string | gRPC port (defaults to 8443, but this port has changed to 443 as of CVP 2021.3.0) |
| cvp_user | string | The username used to connect to the onprem instance of CloudVision. |
| cvp_password | string | The password used by the user specified above. |
| insecure | boolean | If true, the plugin will download the certificate from CloudVision and trust it for gRPC calls. |
To connect to a cloud instance of CloudVision you must set the following variable:
| Configuration Variable | Type | Usage | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| cvaas_url | string | URL used to connect to your CvaaS instance. | www.arista.io:443 |
| cvaas_token | string | Token to be used when connecting to CloudVision as a Service. | No default set |
When syncing from CloudVision, this plugin will create new Arista devices that do not exist in Nautobot. When creating new devices in Nautobot, a site, device role, device role color, device status, and device are required. You may define which values to use by configuring the following values in your nautobot config file. If you define a default_device_role and default_device_status that already exist, the default color value for both of those will be ignored as it will pull that information from Nautobot.
| Configuration Variable | Type | Usage | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| from_cloudvision_default_site | string | Default site created when syncing new devices to Nautobot. | cloudvision_imported |
| from_cloudvision_default_device_role | string | Default role created when syncing new devices to Nautobot. | network |
| from_cloudvision_default_device_role_color | string | Default role color used for default role. | ff0000 |
| from_cloudvision_default_device_status | string | Default status used when syncing new devices to Nautobot. | cloudvision_imported |
| from_cloudvision_default_device_status_color | string | Default status color used for default status. | ff0000 |
When these variables are not defined in the plugin settings, the plugin will use the default values mentioned.
When an Arista device exists in Nautobot but not in CloudVision, this plugin can either delete or leave the device in Nautobot. That behavior can be set with the following variable in the nautobot config file.
| Configuration Variable | Type | Usage | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| delete_devices_on_sync | boolean | If true, devices in Nautobot with device type manufacturer name set to Arista that do not exist in CloudVision but do exist in Nautobot upon sync will be deleted. | False |
When this variable is not defined in the plugin settings, the plugin will default to using
False.
Lastly, an import tag with the name cloudvision_imported can be applied to devices that are imported from CloudVision.
| Configuration Variable | Type | Usage | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| apply_import_tag | boolean | Apply import tag to devices imported from CloudVision. | False |
If apply_import_tag is set to True, the tag value that is applied to devices is
cloudvision_imported.
Usage
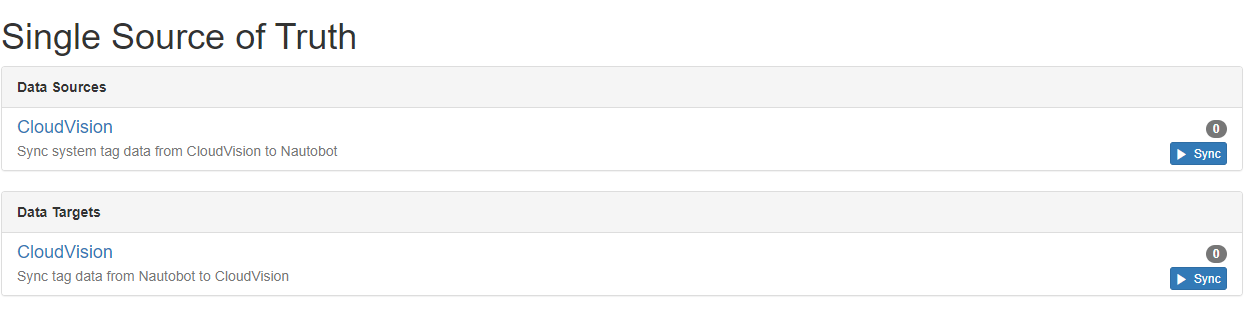
This extension can sync data both to and from Nautobot. Once the plugin has been installed succesfully two new options are available under the Nautobot Single Source of Truth (SSoT) plugin.
Syncing From CloudVision
When loading Nautobot data, this tool only loads devices with a device type that has a manufacturer of "Arista"
When syncing data from CloudVision to Nautobot, system tags as well as devices are synced. When a device exists in CloudVision that doesn't exist in Nautobot, this tool creates the device in Nautobot with the default values specified in the configuration file. When a device exists in Nautobot that does not exist in CloudVision, this tool can be configured to either delete or skip that device. You can watch the below video for an example.
When syncing data from Nautobot to CloudVision, the tag data in Nautobot is copied into User Tags in CloudVision. You can watch the video below for an example.
Contributing
Pull requests are welcomed and automatically built and tested against multiple version of Python and multiple version of Nautobot through TravisCI.
The project is packaged with a light development environment based on docker-compose to help with the local development of the project and to run the tests within TravisCI.
The project is following Network to Code software development guideline and is leveraging:
- Black, Pylint, Bandit and pydocstyle for Python linting and formatting.
- Django unit test to ensure the plugin is working properly.
Development Environment
The development environment can be used in 2 ways. First, with a local poetry environment if you wish to develop outside of Docker. Second, inside of a docker container.
Invoke tasks
The PyInvoke library is used to provide some helper commands based on the environment. There are a few configuration parameters which can be passed to PyInvoke to override the default configuration:
nautobot_ver: the version of Nautobot to use as a base for any built docker containers (default: develop-latest)project_name: the default docker compose project name (default: aristacv-sync)python_ver: the version of Python to use as a base for any built docker containers (default: 3.6)local: a boolean flag indicating if invoke tasks should be run on the host or inside the docker containers (default: False, commands will be run in docker containers)compose_dir: the full path to a directory containing the project compose filescompose_files: a list of compose files applied in order (see Multiple Compose files for more information)
Using PyInvoke these configuration options can be overridden using several methods. Perhaps the simplest is simply setting an environment variable INVOKE_ARISTACV-SYNC_VARIABLE_NAME where VARIABLE_NAME is the variable you are trying to override. The only exception is compose_files, because it is a list it must be overridden in a yaml file. There is an example invoke.yml in this directory which can be used as a starting point.
Local Poetry Development Environment
- Copy
development/creds.example.envtodevelopment/creds.env(This file will be ignored by git and docker) - Uncomment the
POSTGRES_HOST,REDIS_HOST, andNAUTOBOT_ROOTvariables indevelopment/creds.env - Create an invoke.yml with the following contents at the root of the repo:
---
aristacv_sync:
local: true
compose_files:
- "docker-compose.requirements.yml"
- Run the following commands:
poetry shell
poetry install
export $(cat development/dev.env | xargs)
export $(cat development/creds.env | xargs)
- You can now run nautobot-server commands as you would from the Nautobot documentation for example to start the development server:
nautobot-server runserver 0.0.0.0:8080 --insecure
Nautobot server can now be accessed at http://localhost:8080.
Docker Development Environment
This project is managed by Python Poetry and has a few requirements to setup your development environment:
- Install Poetry, see the Poetry Documentation for your operating system.
- Install Docker, see the Docker documentation for your operating system.
Once you have Poetry and Docker installed you can run the following commands to install all other development dependencies in an isolated python virtual environment:
poetry shell
poetry install
invoke start
Nautobot server can now be accessed at http://localhost:8080.
CLI Helper Commands
The project is coming with a CLI helper based on invoke to help setup the development environment. The commands are listed below in 3 categories dev environment, utility and testing.
Each command can be executed with invoke <command>. Environment variables INVOKE_ARISTACV-SYNC_PYTHON_VER and INVOKE_ARISTACV-SYNC_NAUTOBOT_VER may be specified to override the default versions. Each command also has its own help invoke <command> --help
Docker dev environment
build Build all docker images.
debug Start Nautobot and its dependencies in debug mode.
destroy Destroy all containers and volumes.
restart Restart Nautobot and its dependencies.
start Start Nautobot and its dependencies in detached mode.
stop Stop Nautobot and its dependencies.
Utility
cli Launch a bash shell inside the running Nautobot container.
create-user Create a new user in django (default: admin), will prompt for password.
makemigrations Run Make Migration in Django.
nbshell Launch a nbshell session.
Testing
bandit Run bandit to validate basic static code security analysis.
black Run black to check that Python files adhere to its style standards.
flake8 This will run flake8 for the specified name and Python version.
pydocstyle Run pydocstyle to validate docstring formatting adheres to NTC defined standards.
pylint Run pylint code analysis.
tests Run all tests for this plugin.
unittest Run Django unit tests for the plugin.
Questions
For any questions or comments, please check the FAQ first and feel free to swing by the Network to Code slack channel (channel #networktocode). Sign up here
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
File details
Details for the file nautobot-ssot-aristacv-1.0.6.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: nautobot-ssot-aristacv-1.0.6.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 68.1 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.0 CPython/3.9.13
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | ae1ef0efbc6c59f5690136d007e83e62cf297ef98891efa2f8c340f44839b4cc |
|
| MD5 | 63d741d44384c2d2768a0b12bfdae75d |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 8a81c711b58cc15c20bd43be3206b1d0e0377bd3e55112dbed3237c61ce491a4 |
File details
Details for the file nautobot_ssot_aristacv-1.0.6-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: nautobot_ssot_aristacv-1.0.6-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 71.7 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.0 CPython/3.9.13
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | f0d3be1e2725ecf6a5a12ff9bc6ea35a35cebc5914890e9bf914d2af2ac4d8c6 |
|
| MD5 | 38f1953cb5fda08f82131731fc3ab455 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 1d6a0c0d644ab341682344de2bc48f0c53a82c965a723322744fbe65ef673d82 |