Numerical integration, quadrature for various domains
Project description
Your one-stop shop for numerical integration in Python.
More than 1500 numerical integration schemes for line segments, circles, disks, triangles, quadrilaterals, spheres, balls, tetrahedra, hexahedra, wedges, pyramids, n-spheres, n-balls, n-cubes, n-simplices, the 1D half-space with weight functions exp(-r), the 2D space with weight functions exp(-r), the 3D space with weight functions exp(-r), the nD space with weight functions exp(-r), the 1D space with weight functions exp(-r2), the 2D space with weight functions exp(-r2), the 3D space with weight functions exp(-r2), and the nD space with weight functions exp(-r2), for fast integration of real-, complex-, and vector-valued functions.
Installation
Install quadpy from PyPI with
pip install quadpy
See here on how to get a license.
Using quadpy
Quadpy provides integration schemes for many different 1D, 2D, even nD domains.
To start off easy: If you'd numerically integrate any function over any given 1D interval, do
import numpy as np
import quadpy
def f(x):
return np.sin(x) - x
val, err = quadpy.quad(f, 0.0, 6.0)
This is like scipy with the addition that quadpy handles complex-, vector-, matrix-valued integrands, and "intervals" in spaces of arbitrary dimension.
To integrate over a triangle, do
import numpy as np
import quadpy
def f(x):
return np.sin(x[0]) * np.sin(x[1])
triangle = np.array([[0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0], [0.7, 0.5]])
# get a "good" scheme of degree 10
scheme = quadpy.t2.get_good_scheme(10)
val = scheme.integrate(f, triangle)
Most domains have get_good_scheme(degree). If you would like to use a
particular scheme, you can pick one from the dictionary quadpy.t2.schemes.
All schemes have
scheme.points
scheme.weights
scheme.degree
scheme.source
scheme.test_tolerance
scheme.show()
scheme.integrate(
# ...
)
and many have
scheme.points_symbolic
scheme.weights_symbolic
You can explore schemes on the command line with, e.g.,
quadpy info s2 rabinowitz_richter_3
<quadrature scheme for S2>
name: Rabinowitz-Richter 2
source: Perfectly Symmetric Two-Dimensional Integration Formulas with Minimal Numbers of Points
Philip Rabinowitz, Nira Richter
Mathematics of Computation, vol. 23, no. 108, pp. 765-779, 1969
https://doi.org/10.1090/S0025-5718-1969-0258281-4
degree: 9
num points/weights: 21
max/min weight ratio: 7.632e+01
test tolerance: 9.417e-15
point position: outside
all weights positive: True
Also try quadpy show!
quadpy is fully vectorized, so if you like to compute the integral of a function on many
domains at once, you can provide them all in one integrate() call, e.g.,
# shape (3, 5, 2), i.e., (corners, num_triangles, xy_coords)
triangles = np.stack(
[
[[0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 1.0]],
[[1.2, 0.6], [1.3, 0.7], [1.4, 0.8]],
[[26.0, 31.0], [24.0, 27.0], [33.0, 28]],
[[0.1, 0.3], [0.4, 0.4], [0.7, 0.1]],
[[8.6, 6.0], [9.4, 5.6], [7.5, 7.4]],
],
axis=-2,
)
The same goes for functions with vectorized output, e.g.,
def f(x):
return [np.sin(x[0]), np.sin(x[1])]
More examples under test/examples_test.py.
Read more about the dimensionality of the input/output arrays in the wiki.
Advanced topics:
Schemes
Line segment (C1)

- Chebyshev-Gauss (type 1 and 2, arbitrary degree)
- Clenshaw-Curtis (arbitrary degree)
- Fejér (type 1 and 2, arbitrary degree)
- Gauss-Jacobi (arbitrary degree)
- Gauss-Legendre (arbitrary degree)
- Gauss-Lobatto (arbitrary degree)
- Gauss-Kronrod (arbitrary degree)
- Gauss-Patterson (9 nested schemes up to degree 767)
- Gauss-Radau (arbitrary degree)
- Newton-Cotes (open and closed, arbitrary degree)
See here for how to generate Gauss formulas for your own weight functions.
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.c1.gauss_patterson(5)
scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: np.exp(x), [0.0, 1.0])
1D half-space with weight function exp(-r) (E1r)

Example:
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.e1r.gauss_laguerre(5, alpha=0)
scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: x**2)
1D space with weight function exp(-r2) (E1r2)

- Gauss-Hermite (arbitrary degree)
- Genz-Keister (1996, 8 nested schemes up to degree 67)
Example:
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.e1r2.gauss_hermite(5)
scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: x**2)
Circle (U2)

- Krylov (1959, arbitrary degree)
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.u2.get_good_scheme(7)
scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: np.exp(x[0]), [0.0, 0.0], 1.0)
Triangle (T2)

Apart from the classical centroid, vertex, and seven-point schemes we have
- Hammer-Marlowe-Stroud (1956, 5 schemes up to degree 5)
- Albrecht-Collatz (1958, degree 3)
- Stroud (1971, conical product scheme of degree 7)
- Franke (1971, 2 schemes of degree 7)
- Strang-Fix/Cowper (1973, 10 schemes up to degree 7),
- Lyness-Jespersen (1975, 21 schemes up to degree 11, two of which are used in TRIEX),
- Lether (1976, degree 2n-2, arbitrary n, not symmetric),
- Hillion (1977, 10 schemes up to degree 3),
- Laursen-Gellert (1978, 17 schemes up to degree 10),
- CUBTRI (Laurie, 1982, degree 8),
- Dunavant (1985, 20 schemes up to degree 20),
- Cools-Haegemans (1987, degrees 8 and 11),
- Gatermann (1988, degree 7)
- Berntsen-Espelid (1990, 4 schemes of degree 13, the first one being DCUTRI),
- Liu-Vinokur (1998, 13 schemes up to degree 5),
- Griener-Schmid, (1999, 2 schemes of degree 6),
- Walkington (2000, 5 schemes up to degree 5),
- Wandzura-Xiao (2003, 6 schemes up to degree 30),
- Taylor-Wingate-Bos (2005, 5 schemes up to degree 14),
- Zhang-Cui-Liu (2009, 3 schemes up to degree 20),
- Xiao-Gimbutas (2010, 50 schemes up to degree 50),
- Vioreanu-Rokhlin (2014, 20 schemes up to degree 62),
- Williams-Shunn-Jameson (2014, 8 schemes up to degree 12),
- Witherden-Vincent (2015, 19 schemes up to degree 20),
- Papanicolopulos (2016, 27 schemes up to degree 25),
- all schemes for the n-simplex.
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.t2.get_good_scheme(12)
scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: np.exp(x[0]), [[0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0], [0.5, 0.7]])
Disk (S2)

- Radon (1948, degree 5)
- Peirce (1956, 3 schemes up to degree 11)
- Peirce (1957, arbitrary degree)
- Albrecht-Collatz (1958, degree 3)
- Hammer-Stroud (1958, 8 schemes up to degree 15)
- Albrecht (1960, 8 schemes up to degree 17)
- Mysovskih (1964, 3 schemes up to degree 15)
- Rabinowitz-Richter (1969, 6 schemes up to degree 15)
- Lether (1971, arbitrary degree)
- Piessens-Haegemans (1975, 1 scheme of degree 9)
- Haegemans-Piessens (1977, degree 9)
- Cools-Haegemans (1985, 4 schemes up to degree 13)
- Wissmann-Becker (1986, 3 schemes up to degree 8)
- Kim-Song (1997, 15 schemes up to degree 17)
- Cools-Kim (2000, 3 schemes up to degree 21)
- Luo-Meng (2007, 6 schemes up to degree 17)
- Takaki-Forbes-Rolland (2022, 19 schemes up to degree 77)
- all schemes from the n-ball
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.s2.get_good_scheme(6)
scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: np.exp(x[0]), [0.0, 0.0], 1.0)
Quadrilateral (C2)

- Maxwell (1890, degree 7)
- Burnside (1908, degree 5)
- Irwin (1923, 3 schemes up to degree 5)
- Tyler (1953, 3 schemes up to degree 7)
- Hammer-Stroud (1958, 3 schemes up to degree 7)
- Albrecht-Collatz (1958, 4 schemes up to degree 5)
- Miller (1960, degree 1, degree 11 for harmonic integrands)
- Meister (1966, degree 7)
- Phillips (1967, degree 7)
- Rabinowitz-Richter (1969, 6 schemes up to degree 15)
- Franke (1971, 10 schemes up to degree 9)
- Piessens-Haegemans (1975, 2 schemes of degree 9)
- Haegemans-Piessens (1977, degree 7)
- Schmid (1978, 3 schemes up to degree 6)
- Cools-Haegemans (1985, 6 schemes up to degree 17)
- Dunavant (1985, 11 schemes up to degree 19)
- Morrow-Patterson (1985, 2 schemes up to degree 20, single precision)
- Cohen-Gismalla, (1986, 2 schemes up to degree 3)
- Wissmann-Becker (1986, 6 schemes up to degree 8)
- Cools-Haegemans (1988, 2 schemes up to degree 13)
- Waldron (1994, infinitely many schemes of degree 3)
- Sommariva (2012, 55 schemes up to degree 55)
- Witherden-Vincent (2015, 11 schemes up to degree 21)
- products of line segment schemes
- all schemes from the n-cube
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.c2.get_good_scheme(7)
val = scheme.integrate(
lambda x: np.exp(x[0]),
[[[0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0]], [[0.0, 1.0], [1.0, 1.0]]],
)
The points are specified in an array of shape (2, 2, ...) such that arr[0][0]
is the lower left corner, arr[1][1] the upper right. If your c2
has its sides aligned with the coordinate axes, you can use the convenience
function
quadpy.c2.rectangle_points([x0, x1], [y0, y1])
to generate the array.
2D space with weight function exp(-r) (E2r)

- Stroud-Secrest (1963, 2 schemes up to degree 7)
- Rabinowitz-Richter (1969, 4 schemes up to degree 15)
- Stroud (1971, degree 4)
- Haegemans-Piessens (1977, 2 schemes up to degree 9)
- Cools-Haegemans (1985, 3 schemes up to degree 13)
- all schemes from the nD space with weight function exp(-r)
Example:
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.e2r.get_good_scheme(5)
scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: x[0] ** 2)
2D space with weight function exp(-r2) (E2r2)

- Stroud-Secrest (1963, 2 schemes up to degree 7)
- Rabinowitz-Richter (1969, 5 schemes up to degree 15)
- Stroud (1971, 3 schemes up to degree 7)
- Haegemans-Piessens (1977, 2 schemes of degree 9)
- Cools-Haegemans (1985, 3 schemes up to degree 13)
- Van Zandt (2019, degree 6)
- all schemes from the nD space with weight function exp(-r2)
Example:
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.e2r2.get_good_scheme(3)
scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: x[0] ** 2)
Sphere (U3)

- Albrecht-Collatz (1958, 5 schemes up to degree 7)
- McLaren (1963, 10 schemes up to degree 14)
- Lebedev (1976, 34 schemes up to degree 131)
- Bažant-Oh (1986, 3 schemes up to degree 13)
- Heo-Xu (2001, 27 schemes up to degree 39)
- Fliege-Maier (2007, 4 schemes up to degree 4, single-precision)
- all schemes from the n-sphere
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.u3.get_good_scheme(19)
# scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: np.exp(x[0]), [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 1.0)
Integration on the sphere can also be done for functions defined in spherical coordinates:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
def f(theta_phi):
theta, phi = theta_phi
return np.sin(phi) ** 2 * np.sin(theta)
scheme = quadpy.u3.get_good_scheme(19)
val = scheme.integrate_spherical(f)
Ball (S3)
- Ditkin (1948, 3 schemes up to degree 7)
- Hammer-Stroud (1958, 6 schemes up to degree 7)
- Mysovskih (1964, degree 7)
- Stroud (1971, 2 schemes up to degree 14)
- Van Zandt (2020, degree 4)
- all schemes from the n-ball
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.s3.get_good_scheme(4)
# scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: np.exp(x[0]), [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 1.0)
Tetrahedron (T3)
- Hammer-Marlowe-Stroud (1956, 3 schemes up to degree 3, also appearing in Hammer-Stroud)
- Stroud (1971, degree 7)
- Yu (1984, 5 schemes up to degree 6)
- Keast (1986, 10 schemes up to degree 8)
- Beckers-Haegemans (1990, degrees 8 and 9)
- Gatermann (1992, degree 5)
- Liu-Vinokur (1998, 14 schemes up to degree 5)
- Walkington (2000, 6 schemes up to degree 7)
- Zhang-Cui-Liu (2009, 2 schemes up to degree 14)
- Xiao-Gimbutas (2010, 15 schemes up to degree 15)
- Shunn-Ham (2012, 6 schemes up to degree 7)
- Vioreanu-Rokhlin (2014, 10 schemes up to degree 13)
- Williams-Shunn-Jameson (2014, 1 scheme with degree 9)
- Witherden-Vincent (2015, 9 schemes up to degree 10)
- Jaśkowiec-Sukumar (2020, 21 schemes up to degree 20)
- all schemes for the n-simplex.
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.t3.get_good_scheme(5)
# scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(
lambda x: np.exp(x[0]),
[[0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.5, 0.7, 0.0], [0.3, 0.9, 1.0]],
)
Hexahedron (C3)
- Sadowsky (1940, degree 5)
- Tyler (1953, 2 schemes up to degree 5)
- Hammer-Wymore (1957, degree 7)
- Albrecht-Collatz (1958, degree 3)
- Hammer-Stroud (1958, 6 schemes up to degree 7)
- Mustard-Lyness-Blatt (1963, 6 schemes up to degree 5)
- Stroud (1967, degree 5)
- Sarma-Stroud (1969, degree 7)
- Witherden-Vincent (2015, 7 schemes up to degree degree 11)
- all schemes from the n-cube
- Product schemes derived from line segment schemes
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.c3.product(quadpy.c1.newton_cotes_closed(3))
# scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(
lambda x: np.exp(x[0]),
quadpy.c3.cube_points([0.0, 1.0], [-0.3, 0.4], [1.0, 2.1]),
)
Pyramid (P3)
- Felippa (2004, 9 schemes up to degree 5)
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.p3.felippa_5()
val = scheme.integrate(
lambda x: np.exp(x[0]),
[
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.5, 0.7, 0.0],
[0.3, 0.9, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.1, 1.0],
],
)
Wedge (W3)
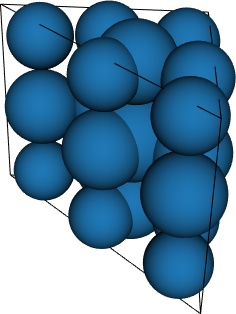
- Felippa (2004, 6 schemes up to degree 6)
- Kubatko-Yeager-Maggi (2013, 21 schemes up to degree 9)
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.w3.felippa_3()
val = scheme.integrate(
lambda x: np.exp(x[0]),
[
[[0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.5, 0.7, 0.0]],
[[0.0, 0.0, 1.0], [1.0, 0.0, 1.0], [0.5, 0.7, 1.0]],
],
)
3D space with weight function exp(-r) (E3r)
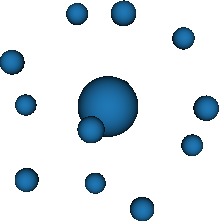
- Stroud-Secrest (1963, 5 schemes up to degree 7)
- all schemes from the nD space with weight function exp(-r)
Example:
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.e3r.get_good_scheme(5)
# scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: x[0] ** 2)
3D space with weight function exp(-r2) (E3r2)
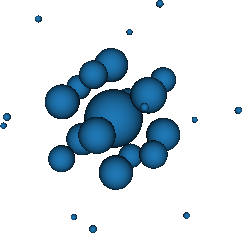
- Stroud-Secrest (1963, 7 schemes up to degree 7)
- Stroud (1971, scheme of degree 14)
- Van Zandt (2020, degree 4)
- all schemes from the nD space with weight function exp(-r2)
Example:
import quadpy
scheme = quadpy.e3r2.get_good_scheme(6)
# scheme.show()
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: x[0] ** 2)
n-Simplex (Tn)
- Lauffer (1955, 5 schemes up to degree 5)
- Hammer-Stroud (1956, 3 schemes up to degree 3)
- Stroud (1964, degree 3)
- Stroud (1966, 7 schemes of degree 3)
- Stroud (1969, degree 5)
- Silvester (1970, arbitrary degree),
- Grundmann-Möller (1978, arbitrary degree)
- Walkington (2000, 5 schemes up to degree 7)
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
dim = 4
scheme = quadpy.tn.grundmann_moeller(dim, 3)
val = scheme.integrate(
lambda x: np.exp(x[0]),
np.array(
[
[0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, 2.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 3.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 4.0, 1.0],
]
),
)
n-Sphere (Un)
- Stroud (1967, degree 7)
- Stroud (1969, 3 <= n <= 16, degree 11)
- Stroud (1971, 6 schemes up to degree 5)
- Dobrodeev (1978, n >= 2, degree 5)
- Mysovskikh (1980, 2 schemes up to degree 5)
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
dim = 4
scheme = quadpy.un.dobrodeev_1978(dim)
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: np.exp(x[0]), np.zeros(dim), 1.0)
n-Ball (Sn)
- Stroud (1957, degree 2)
- Hammer-Stroud (1958, 2 schemes up to degree 5)
- Stroud (1966, 4 schemes of degree 5)
- Stroud (1967, 4 <= n <= 7, 2 schemes of degree 5)
- Stroud (1967, n >= 3, 3 schemes of degree 7)
- Stenger (1967, 6 schemes up to degree 11)
- McNamee-Stenger (1967, 6 schemes up to degree 9)
- Dobrodeev (1970, n >= 3, degree 7)
- Dobrodeev (1978, 2 <= n <= 20, degree 5)
- Stoyanova (1997, n >= 5, degree 7)
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
dim = 4
scheme = quadpy.sn.dobrodeev_1970(dim)
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: np.exp(x[0]), np.zeros(dim), 1.0)
n-Cube (Cn)
- Ewing (1941, degree 3)
- Tyler (1953, degree 3)
- Stroud (1957, 2 schemes up to degree 3)
- Hammer-Stroud (1958, degree 5)
- Mustard-Lyness-Blatt (1963, degree 5)
- Thacher (1964, degree 2)
- Stroud (1966, 4 schemes of degree 5)
- Phillips (1967, degree 7)
- McNamee-Stenger (1967, 6 schemes up to degree 9)
- Stroud (1968, degree 5)
- Dobrodeev (1970, n >= 5, degree 7)
- Dobrodeev (1978, n >= 2, degree 5)
- Cools-Haegemans (1994, 2 schemes up to degree 5)
Example:
import numpy as np
import quadpy
dim = 4
scheme = quadpy.cn.stroud_cn_3_3(dim)
val = scheme.integrate(
lambda x: np.exp(x[0]),
quadpy.cn.ncube_points([0.0, 1.0], [0.1, 0.9], [-1.0, 1.0], [-1.0, -0.5]),
)
nD space with weight function exp(-r) (Enr)
- Stroud-Secrest (1963, 4 schemes up to degree 5)
- McNamee-Stenger (1967, 6 schemes up to degree 9)
- Stroud (1971, 2 schemes up to degree 5)
Example:
import quadpy
dim = 4
scheme = quadpy.enr.stroud_enr_5_4(dim)
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: x[0] ** 2)
nD space with weight function exp(-r2) (Enr2)
- Stroud-Secrest (1963, 4 schemes up to degree 5)
- McNamee-Stenger (1967, 6 schemes up to degree 9)
- Stroud (1967, 2 schemes of degree 5)
- Stroud (1967, 3 schemes of degree 7)
- Stenger (1971, 6 schemes up to degree 11, varying dimensionality restrictions)
- Stroud (1971, 5 schemes up to degree 5)
- Phillips (1980, degree 5)
- Cools-Haegemans (1994, 3 schemes up to degree 7)
- Lu-Darmofal (2004, degree 5)
- Xiu (2008, degree 2)
Example:
import quadpy
dim = 4
scheme = quadpy.enr2.stroud_enr2_5_2(dim)
val = scheme.integrate(lambda x: x[0] ** 2)
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distributions
Built Distributions
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file quadpy-0.17.30-cp313-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: quadpy-0.17.30-cp313-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 3.6 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.13
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
8d0d17067f8326efe9cc84b807cd34294a6f70c5defab9672d1c04a72e8d2298
|
|
| MD5 |
8987a2ada4e6f8b11de4a96393d81558
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
c3078e15fcb566c2238a629731653295227784f54cf19a3523b1438c215feafe
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for quadpy-0.17.30-cp313-none-any.whl:
Publisher:
release.yml on sigma-py/quadpy-dev
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
quadpy-0.17.30-cp313-none-any.whl -
Subject digest:
8d0d17067f8326efe9cc84b807cd34294a6f70c5defab9672d1c04a72e8d2298 - Sigstore transparency entry: 298245845
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
sigma-py/quadpy-dev@c57d39c32a96f1707c1472a10640299f4c26c5e9 -
Branch / Tag:
refs/tags/v0.17.30 - Owner: https://github.com/sigma-py
-
Access:
private
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
release.yml@c57d39c32a96f1707c1472a10640299f4c26c5e9 -
Trigger Event:
release
-
Statement type:
File details
Details for the file quadpy-0.17.30-cp312-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: quadpy-0.17.30-cp312-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 3.6 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.12
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
a983d7aeb034afc8b72fdbabb27834b8e8a618fcd4c3e7341066a34fb724f088
|
|
| MD5 |
88a36d8b48530941aad5686e98884ee4
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
3df72f594a0d22bf5e2d97e4752b3049bf1859daec43cce618870cb0327bd9c1
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for quadpy-0.17.30-cp312-none-any.whl:
Publisher:
release.yml on sigma-py/quadpy-dev
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
quadpy-0.17.30-cp312-none-any.whl -
Subject digest:
a983d7aeb034afc8b72fdbabb27834b8e8a618fcd4c3e7341066a34fb724f088 - Sigstore transparency entry: 298245863
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
sigma-py/quadpy-dev@c57d39c32a96f1707c1472a10640299f4c26c5e9 -
Branch / Tag:
refs/tags/v0.17.30 - Owner: https://github.com/sigma-py
-
Access:
private
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
release.yml@c57d39c32a96f1707c1472a10640299f4c26c5e9 -
Trigger Event:
release
-
Statement type:
File details
Details for the file quadpy-0.17.30-cp311-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: quadpy-0.17.30-cp311-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 3.8 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.11
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
e0c98fd5a9fe3960fdd45cbe966eec207f82b474eec1c0d7bcc770e3f9e846b1
|
|
| MD5 |
eb15ea7ab50bb8043b5d8c81d0bd3708
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
3e43634c08bae91fcf2e46570353056830ed13cecc2bab679747982dbdd774a3
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for quadpy-0.17.30-cp311-none-any.whl:
Publisher:
release.yml on sigma-py/quadpy-dev
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
quadpy-0.17.30-cp311-none-any.whl -
Subject digest:
e0c98fd5a9fe3960fdd45cbe966eec207f82b474eec1c0d7bcc770e3f9e846b1 - Sigstore transparency entry: 298245895
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
sigma-py/quadpy-dev@c57d39c32a96f1707c1472a10640299f4c26c5e9 -
Branch / Tag:
refs/tags/v0.17.30 - Owner: https://github.com/sigma-py
-
Access:
private
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
release.yml@c57d39c32a96f1707c1472a10640299f4c26c5e9 -
Trigger Event:
release
-
Statement type:
File details
Details for the file quadpy-0.17.30-cp310-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: quadpy-0.17.30-cp310-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 3.2 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.10
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
224282e6ca753c8f9799e642768260bd530aedffff7a28ff0bdb60e344177f91
|
|
| MD5 |
3a9f4be812afad16f7f8333eb0ff8b7e
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
c4d4f0ecbc36c070aeee52959d76387ec07c6c0d6fbab67996bf339e15f7fb57
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for quadpy-0.17.30-cp310-none-any.whl:
Publisher:
release.yml on sigma-py/quadpy-dev
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
quadpy-0.17.30-cp310-none-any.whl -
Subject digest:
224282e6ca753c8f9799e642768260bd530aedffff7a28ff0bdb60e344177f91 - Sigstore transparency entry: 298245880
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
sigma-py/quadpy-dev@c57d39c32a96f1707c1472a10640299f4c26c5e9 -
Branch / Tag:
refs/tags/v0.17.30 - Owner: https://github.com/sigma-py
-
Access:
private
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
release.yml@c57d39c32a96f1707c1472a10640299f4c26c5e9 -
Trigger Event:
release
-
Statement type:

















