Alternative method for data clustering using Node2Vec algorithm.
Project description
XNode2Vec - An Alternative Data Clustering Procedure
Description
This repository proposes an alternative method for data classification and clustering, based on the Node2Vec algorithm that is applied to a properly transformed N-dimensional dataset. The original Node2Vec algorithm was replaced with an extremely faster version, called FastNode2Vec. The application of the algorithm is provided by a function that works with networkx objects, that are quite user-friendly. At the moment there are few easy data transformations, but they will be expanded in more complex and effective ones.
Installation
In order to install the Xnode2vec package simply use pip:
- pip install Xnode2vec
If there are some problems with the installation, please read the "Note" below.
How to Use
The idea behind is straightforward:
- Take a dataset, or generate one.
- Apply the proper transformation to the dataset.
- Build a networkx object that embeds the dataset with its crucial properties.
- Perform a node classification analysis with Node2Vec algorithm.
import numpy as np
import Xnode2vec as xn2v
x1 = np.random.normal(16, 1, 20)
y1 = np.random.normal(9, 1, 20)
x2 = np.random.normal(17, 2, 20)
y2 = np.random.normal(13, 1, 20)
family1 = np.column_stack((x1, y1)) # REQUIRED ARRAY FORMAT
family2 = np.column_stack((x2, y2)) # REQUIRED ARRAY FORMAT
dataset = np.concatenate((family1,family2),axis=0) # Generic dataset
transf_dataset = xn2v.best_line_projection(dataset) # Points transformation
df = xn2v.complete_edgelist(transf_dataset) # Pandas edge list generation
edgelist = xn2v.generate_edgelist(df)
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_weighted_edges_from(a) # Feed the graph with the edge list
nodes, similarity = similar_nodes(G, dim=128, walk_length=20, context=5, p=0.1, q=0.9, workers=4)
Objects Syntax
Here we report the list of structures required to use the Xnode2vec package:
- Dataset:
dataset = np.array([[1,2,3,..], ..., [1,2,3,..]]); the rows corresponds to each point, while the coulumns to the coordinates. - Edge List:
edgelist = [(node_a,node_b,weight), ... , (node_c,node_d,weight)]; this is a list of tuples, structured as [starting_node, arriving_node, weight] - DataFrame:
pandas.DataFrame(np.array([[1, 2, 3.7], [1, 3, 0.33], [2, 7, 12]]), columns=['node1', 'node2', 'weight'])
Note
9/17/2021: I had some issues when installing the fastnode2vec package; in particular, the example given by Louis Abraham gives an error. I noticed that after the installation, the declaration of the file "node2vec.py" wasn't the same as the latest version available on its GitHub (at the moment). My brutal solution was simply to just copy the whole content into the node2vec.py file. This solves the problem.
Examples
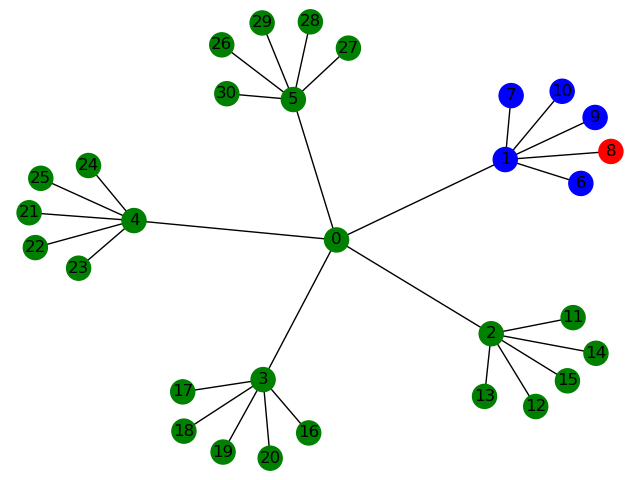
Most Similar Nodes, Balanced Tree
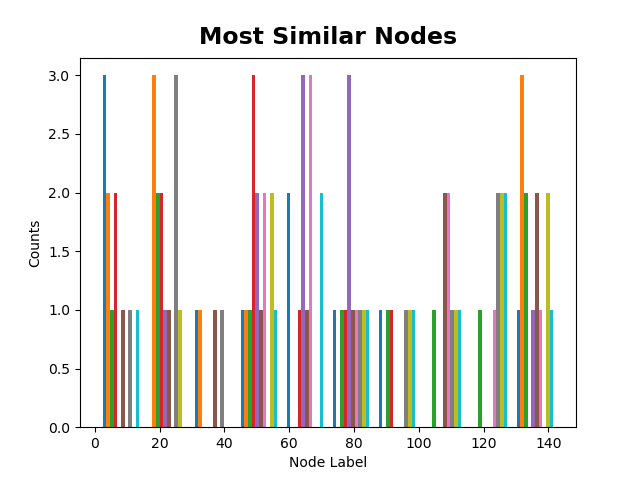
Most Similar Nodes Distribution, E-R
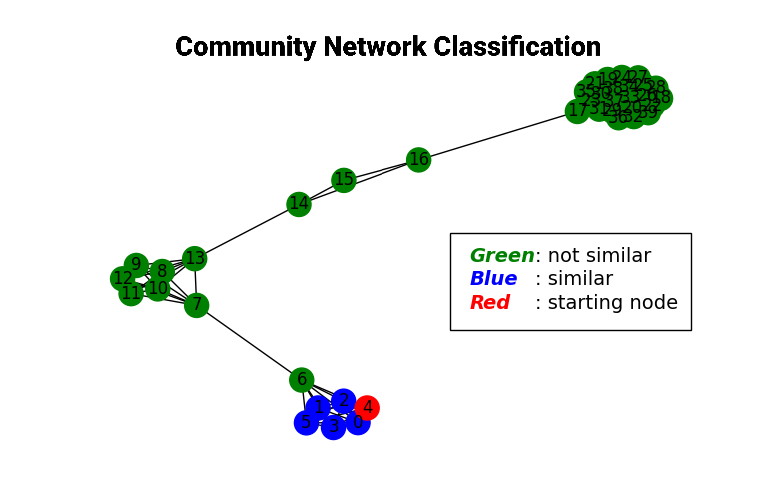
Community Network
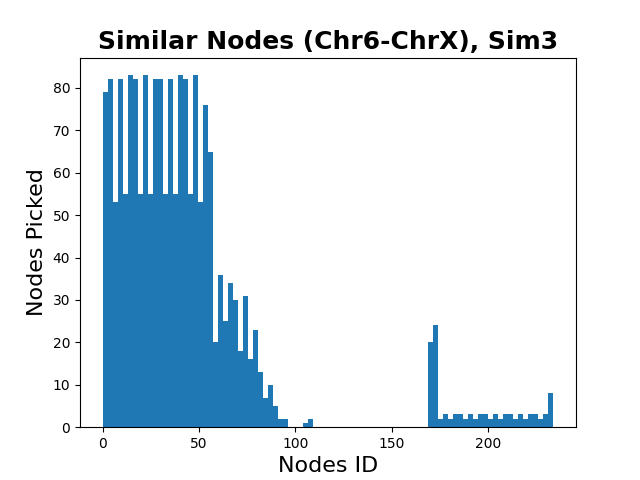
Hi-C Translocation Detection
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
File details
Details for the file Xnode2vec-0.0.6.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: Xnode2vec-0.0.6.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 21.5 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.1.1 pkginfo/1.4.2 requests/2.22.0 setuptools/45.2.0 requests-toolbelt/0.8.0 tqdm/4.30.0 CPython/3.8.10
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
d37b9308779880af207648a020d7cdd8fd8fea5234e0ce46deb63bc64811e388
|
|
| MD5 |
ce033a8ecae66acec357266522b0127b
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
1a172a3c43f14b9637b099bf86e4dcabcb2142efab8eb485f1874f4bd828a65c
|