AgileRL is a deep reinforcement learning library focused on improving RL development through RLOps.
Project description

Reinforcement learning streamlined.
Easier and faster reinforcement learning with RLOps. Visit our website. View documentation.
Join the Discord Server for questions, help and collaboration.
🚀 Train super-fast for free on Arena, the RLOps platform from AgileRL 🚀
AgileRL is a Deep Reinforcement Learning library focused on improving development by introducing RLOps - MLOps for reinforcement learning.
This library is initially focused on reducing the time taken for training models and hyperparameter optimization (HPO) by pioneering evolutionary HPO techniques for reinforcement learning.
Evolutionary HPO has been shown to drastically reduce overall training times by automatically converging on optimal hyperparameters, without requiring numerous training runs.
We are constantly adding more algorithms and features. AgileRL already includes state-of-the-art evolvable on-policy, off-policy, offline, multi-agent and contextual multi-armed bandit reinforcement learning algorithms with distributed training.
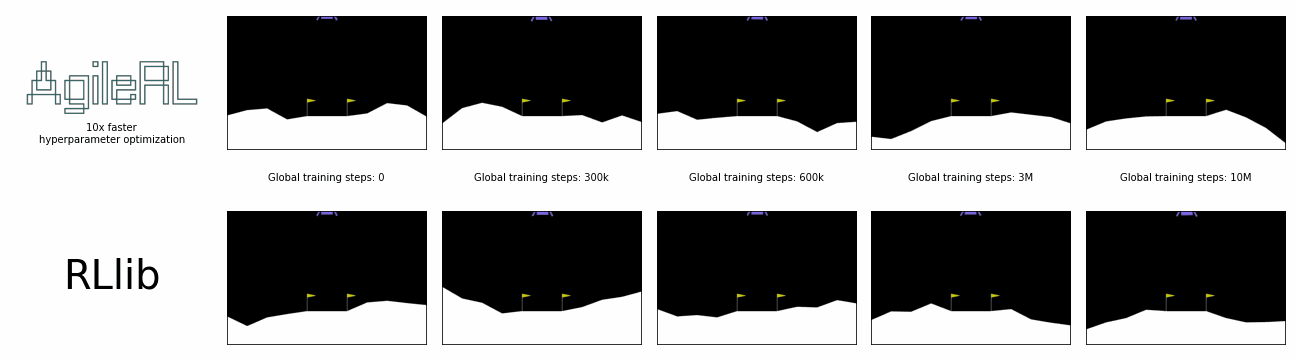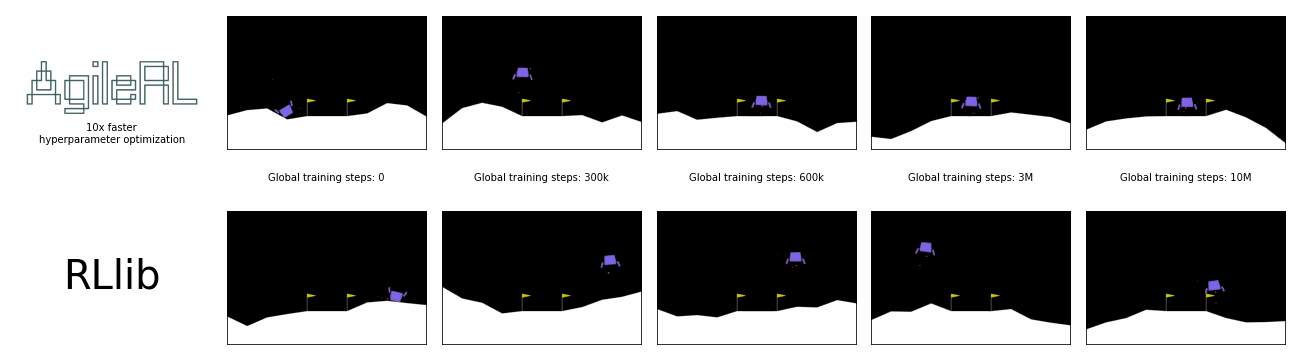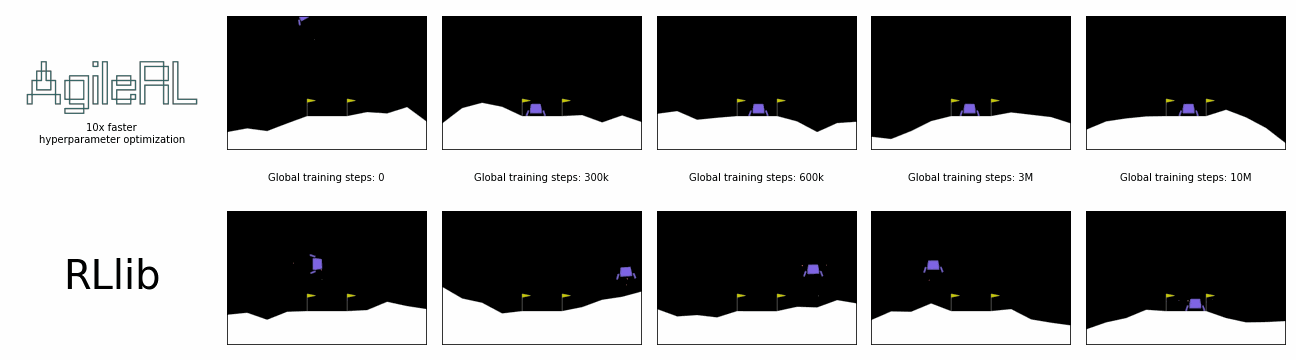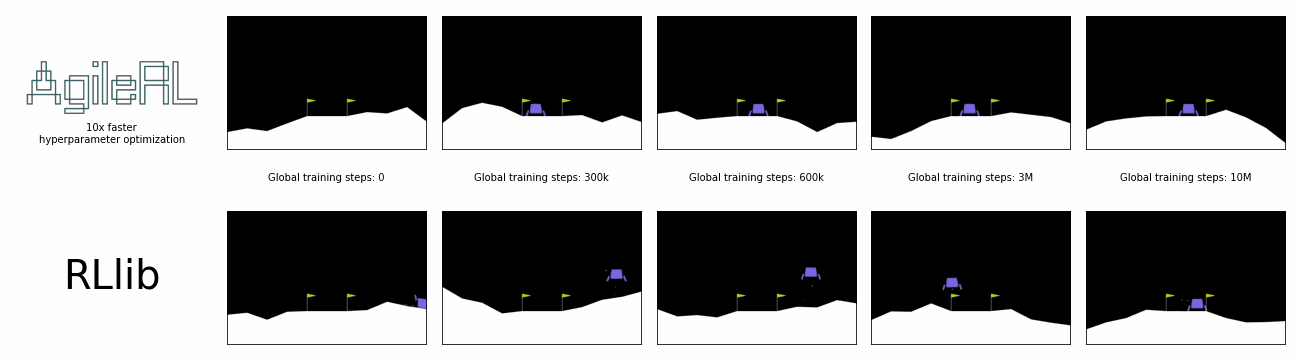
AgileRL offers 10x faster hyperparameter optimization than SOTA.
Table of Contents
Get Started
To see the full AgileRL documentation, including tutorials, visit our documentation site. To ask questions and get help, collaborate, or discuss anything related to reinforcement learning, join the AgileRL Discord Server.
Install as a package with pip:
pip install agilerl
Or install in development mode:
git clone https://github.com/AgileRL/AgileRL.git && cd AgileRL
pip install -e .
If you wish to install all additional dependencies please specify [all] or if you want to install a specific family of dependencies specify that family directly. At present, we have just one family, [llm], which contains the dependencies related to our LLM RFT algorithms (datasets, deepspeed, peft, transformers, vllm).
pip install agilerl[all]
Or in development mode:
pip install -e ".[all]"
To install the nightly version of AgileRL with the latest features, use:
pip install git+https://github.com/AgileRL/AgileRL.git@nightly
Benchmarks
Reinforcement learning algorithms and libraries are usually benchmarked once the optimal hyperparameters for training are known, but it often takes hundreds or thousands of experiments to discover these. This is unrealistic and does not reflect the true, total time taken for training. What if we could remove the need to conduct all these prior experiments?
In the charts below, a single AgileRL run, which automatically tunes hyperparameters, is benchmarked against Optuna's multiple training runs traditionally required for hyperparameter optimization, demonstrating the real time savings possible. Global steps is the sum of every step taken by any agent in the environment, including across an entire population.
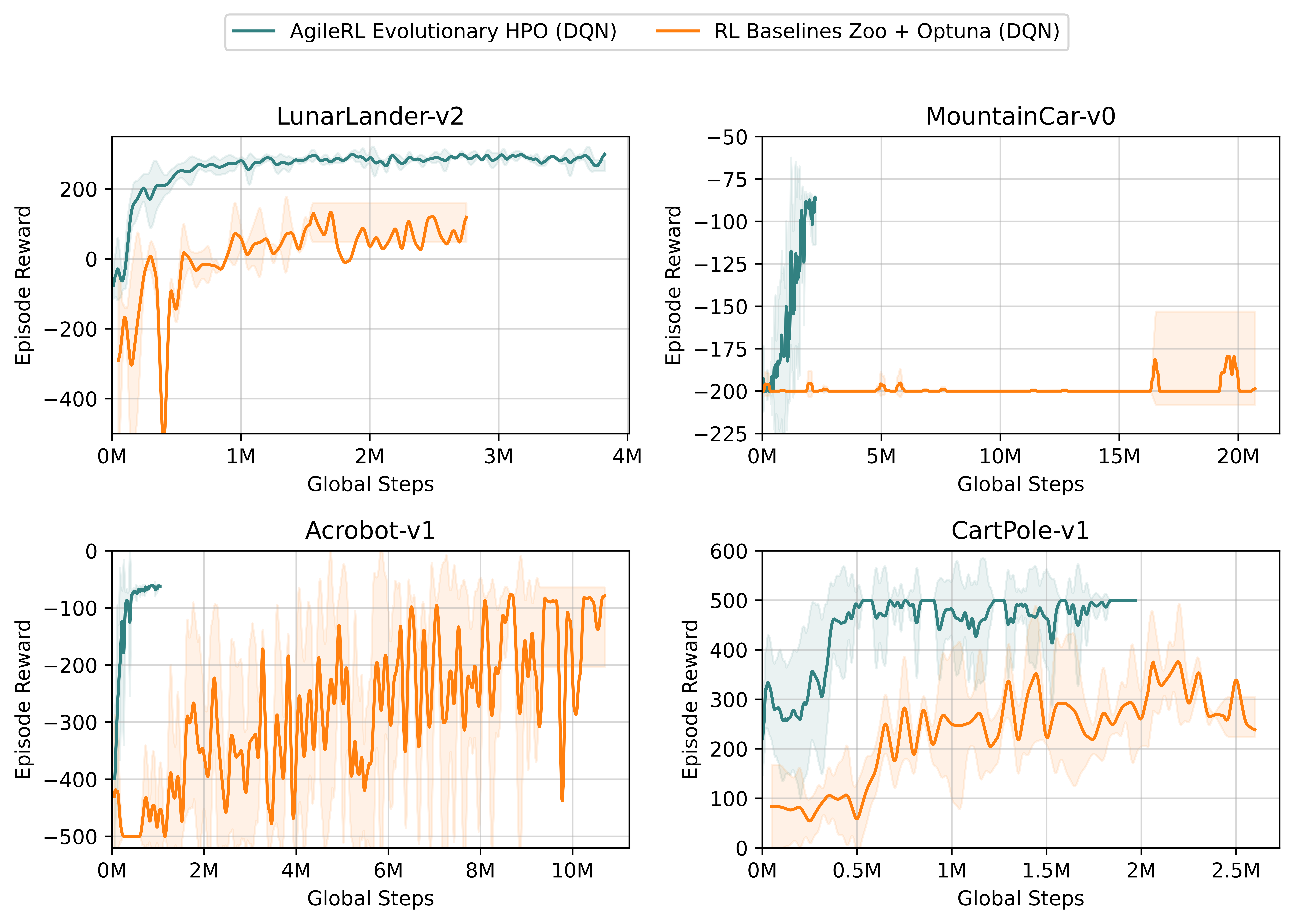
AgileRL offers an order of magnitude speed up in hyperparameter optimization vs popular reinforcement learning training frameworks combined with Optuna. Remove the need for multiple training runs and save yourself hours.
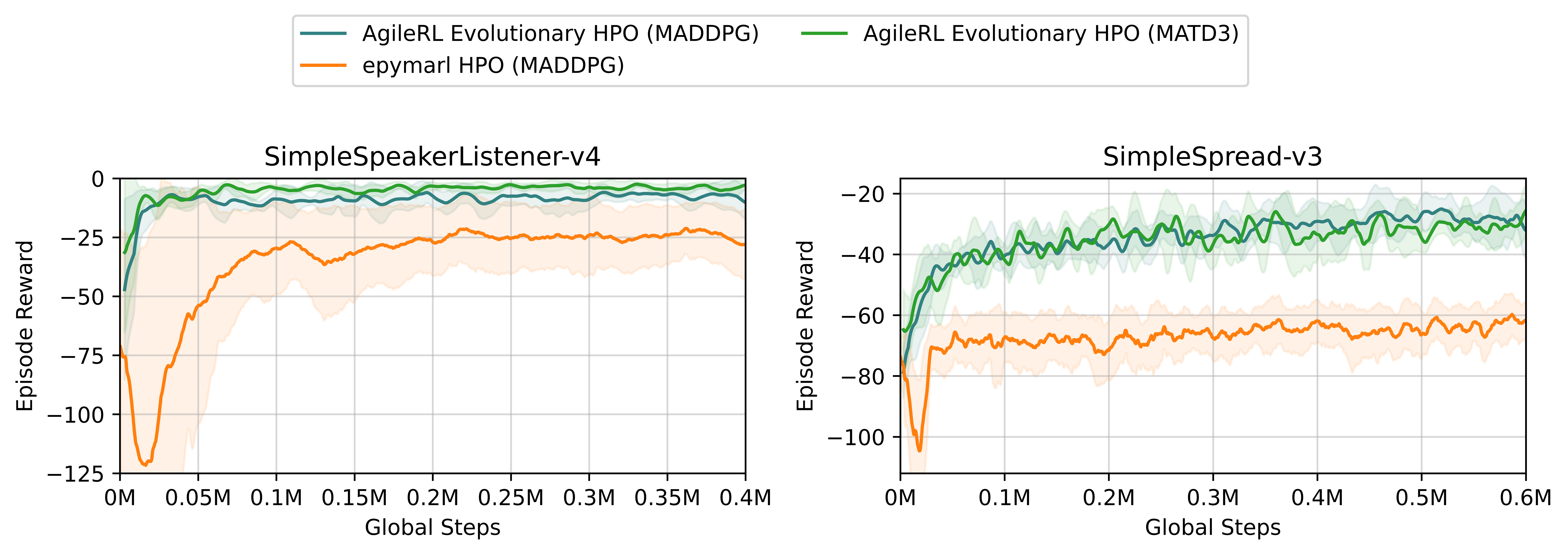
AgileRL also supports multi-agent reinforcement learning using the Petting Zoo-style (parallel API). The charts below highlight the performance of our MADDPG and MATD3 algorithms with evolutionary hyper-parameter optimisation (HPO), benchmarked against epymarl's MADDPG algorithm with grid-search HPO for the simple speaker listener and simple spread environments.
Tutorials
We are constantly updating our tutorials to showcase the latest features of AgileRL and how users can leverage our evolutionary HPO to achieve 10x faster hyperparameter optimization. Please see the available tutorials below.
| Tutorial Type | Description | Tutorials |
|---|---|---|
| Single-agent tasks | Guides for training both on and off-policy agents to beat a variety of Gymnasium environments. | PPO - Acrobot TD3 - Lunar Lander Rainbow DQN - CartPole Recurrent PPO - Masked Pendulum |
| Multi-agent tasks | Use of PettingZoo environments such as training DQN to play Connect Four with curriculum learning and self-play, and for multi-agent tasks in MPE environments. | DQN - Connect Four MADDPG - Space Invaders MATD3 - Speaker Listener |
| Hierarchical curriculum learning | Shows how to teach agents Skills and combine them to achieve an end goal. | PPO - Lunar Lander |
| Contextual multi-arm bandits | Learn to make the correct decision in environments that only have one timestep. | NeuralUCB - Iris Dataset NeuralTS - PenDigits |
| Custom Modules & Networks | Learn how to create custom evolvable modules and networks for RL algorithms. | Dueling Distributional Q Network EvolvableSimBa |
| LLM Finetuning | Learn how to finetune an LLM using AgileRL. | GRPO |
Evolvable algorithms (more coming soon!)
Single-agent algorithms
Multi-agent algorithms
| RL | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| Multi-agent | Multi-Agent Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MADDPG) Multi-Agent Twin-Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (MATD3) Independent Proximal Policy Optimization (IPPO) |
Contextual multi-armed bandit algorithms
| RL | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| Bandits | Neural Contextual Bandits with UCB-based Exploration (NeuralUCB) Neural Contextual Bandits with Thompson Sampling (NeuralTS) |
LLM Fine-tuning Algorithms
| RL | Algorithm |
|---|---|
| On-Policy | Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) |
| Off-Policy | Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) |
Train an Agent to Beat a Gym Environment
Before starting training, there are some meta-hyperparameters and settings that must be set. These are defined in INIT_HP, for general parameters, and MUTATION_PARAMS, which define the evolutionary probabilities, and NET_CONFIG, which defines the network architecture. For example:
Basic Hyperparameters
INIT_HP = {
'ENV_NAME': 'LunarLander-v3', # Gym environment name
'ALGO': 'DQN', # Algorithm
'DOUBLE': True, # Use double Q-learning
'CHANNELS_LAST': False, # Swap image channels dimension from last to first [H, W, C] -> [C, H, W]
'BATCH_SIZE': 256, # Batch size
'LR': 1e-3, # Learning rate
'MAX_STEPS': 1_000_000, # Max no. steps
'TARGET_SCORE': 200., # Early training stop at avg score of last 100 episodes
'GAMMA': 0.99, # Discount factor
'MEMORY_SIZE': 10000, # Max memory buffer size
'LEARN_STEP': 1, # Learning frequency
'TAU': 1e-3, # For soft update of target parameters
'TOURN_SIZE': 2, # Tournament size
'ELITISM': True, # Elitism in tournament selection
'POP_SIZE': 6, # Population size
'EVO_STEPS': 10_000, # Evolution frequency
'EVAL_STEPS': None, # Evaluation steps
'EVAL_LOOP': 1, # Evaluation episodes
'LEARNING_DELAY': 1000, # Steps before starting learning
'WANDB': True, # Log with Weights and Biases
}
Mutation Hyperparameters
MUTATION_PARAMS = {
# Relative probabilities
'NO_MUT': 0.4, # No mutation
'ARCH_MUT': 0.2, # Architecture mutation
'NEW_LAYER': 0.2, # New layer mutation
'PARAMS_MUT': 0.2, # Network parameters mutation
'ACT_MUT': 0, # Activation layer mutation
'RL_HP_MUT': 0.2, # Learning HP mutation
'MUT_SD': 0.1, # Mutation strength
'RAND_SEED': 1, # Random seed
}
Basic Network Configuration
NET_CONFIG = {
'latent_dim': 16
'encoder_config': {
'hidden_size': [32] # Observation encoder configuration
}
'head_config': {
'hidden_size': [32] # Network head configuration
}
}
Creating a Population of Agents
First, use utils.utils.create_population to create a list of agents - our population that will evolve and mutate to the optimal hyperparameters.
Population Creation Example
import torch
from agilerl.utils.utils import (
make_vect_envs,
create_population,
observation_space_channels_to_first
)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
num_envs = 16
env = make_vect_envs(env_name=INIT_HP['ENV_NAME'], num_envs=num_envs)
observation_space = env.single_observation_space
action_space = env.single_action_space
if INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST']:
observation_space = observation_space_channels_to_first(observation_space)
agent_pop = create_population(
algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
observation_space=observation_space, # Observation space
action_space=action_space, # Action space
net_config=NET_CONFIG, # Network configuration
INIT_HP=INIT_HP, # Initial hyperparameters
population_size=INIT_HP['POP_SIZE'], # Population size
num_envs=num_envs, # Number of vectorized environments
device=device
)
Initializing Evolutionary HPO
Next, create the tournament, mutations and experience replay buffer objects that allow agents to share memory and efficiently perform evolutionary HPO.
Mutations and Tournament Selection Example
from agilerl.components.replay_buffer import ReplayBuffer
from agilerl.hpo.tournament import TournamentSelection
from agilerl.hpo.mutation import Mutations
memory = ReplayBuffer(
max_size=INIT_HP['MEMORY_SIZE'], # Max replay buffer size
device=device,
)
tournament = TournamentSelection(
tournament_size=INIT_HP['TOURN_SIZE'], # Tournament selection size
elitism=INIT_HP['ELITISM'], # Elitism in tournament selection
population_size=INIT_HP['POP_SIZE'], # Population size
eval_loop=INIT_HP['EVAL_LOOP'], # Evaluate using last N fitness scores
)
mutations = Mutations(
no_mutation=MUTATION_PARAMS['NO_MUT'], # No mutation
architecture=MUTATION_PARAMS['ARCH_MUT'], # Architecture mutation
new_layer_prob=MUTATION_PARAMS['NEW_LAYER'], # New layer mutation
parameters=MUTATION_PARAMS['PARAMS_MUT'], # Network parameters mutation
activation=MUTATION_PARAMS['ACT_MUT'], # Activation layer mutation
rl_hp=MUTATION_PARAMS['RL_HP_MUT'], # Learning HP mutation
mutation_sd=MUTATION_PARAMS['MUT_SD'], # Mutation strength
rand_seed=MUTATION_PARAMS['RAND_SEED'], # Random seed
device=device,
)
Train A Population of Agents
The easiest training loop implementation is to use our train_off_policy() function. It requires the agent have methods get_action() and learn().
from agilerl.training.train_off_policy import train_off_policy
trained_pop, pop_fitnesses = train_off_policy(
env=env, # Gym-style environment
env_name=INIT_HP['ENV_NAME'], # Environment name
algo=INIT_HP['ALGO'], # Algorithm
pop=agent_pop, # Population of agents
memory=memory, # Replay buffer
swap_channels=INIT_HP['CHANNELS_LAST'], # Swap image channel from last to first
max_steps=INIT_HP["MAX_STEPS"], # Max number of training steps
evo_steps=INIT_HP['EVO_STEPS'], # Evolution frequency
eval_steps=INIT_HP["EVAL_STEPS"], # Number of steps in evaluation episode
eval_loop=INIT_HP["EVAL_LOOP"], # Number of evaluation episodes
learning_delay=INIT_HP['LEARNING_DELAY'], # Steps before starting learning
target=INIT_HP['TARGET_SCORE'], # Target score for early stopping
tournament=tournament, # Tournament selection object
mutation=mutations, # Mutations object
wb=INIT_HP['WANDB'], # Weights and Biases tracking
)
Citing AgileRL
If you use AgileRL in your work, please cite the repository:
@software{Ustaran-Anderegg_AgileRL,
author = {Ustaran-Anderegg, Nicholas and Pratt, Michael and Sabal-Bermudez, Jaime},
license = {Apache-2.0},
title = {{AgileRL}},
url = {https://github.com/AgileRL/AgileRL}
}
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file agilerl-2.4.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: agilerl-2.4.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 9.9 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: uv/0.9.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
fa33cc20ee9ce7f2122a1e9397ed75555e487dd375b7eda7418180bf4d43e89d
|
|
| MD5 |
f61382a00fa0dad55fab3320eac7dc79
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
85ea02044200adb05c4136f69ebae2898809de337f205b1dff6a9873cccf0186
|
File details
Details for the file agilerl-2.4.3-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: agilerl-2.4.3-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 366.7 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: uv/0.9.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9017acae2c6502726149011d3ea3a408dd5be8be9e9434b76df40f49c8088408
|
|
| MD5 |
02f452b8c040ce93314a91b6487c6084
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
89ff5cb4785feaae76f34178d3c97669900b1b2657780781e1cd03dd3206e652
|


















