A full implementation of the ICAO standard atmosphere 1993
Project description






Ambiance is a full implementation of the ICAO standard atmosphere 1993 written in Python.
International Civil Aviation Organization ; Manual Of The ICAO Standard Atmosphere – 3rd Edition 1993 (Doc 7488) – extended to 80 kilometres (262 500 feet)
Basic usage
Atmospheric properties are computed from an Atmosphere object which takes the altitude (geometric height) as input. For instance, to simply retrieve sea level properties, you can write:
>>> from ambiance import Atmosphere
>>> sealevel = Atmosphere(0)
>>> sealevel.temperature
array([288.15])
>>> sealevel.pressure
array([101325.])
>>> sealevel.kinematic_viscosity
array([1.46071857e-05])List of available atmospheric properties
Collision frequency (collision_frequency)
Density (density)
Dynamic viscosity (dynamic_viscosity)
Geometric height above MSL (h)
Geopotential height (H)
Gravitational acceleration (grav_accel)
Kinematic viscosity (kinematic_viscosity)
Layer names (layer_name) [string array]
Mean free path (mean_free_path)
Mean particle speed (mean_particle_speed)
Number density (number_density)
Pressure (pressure)
Pressure scale height (pressure_scale_height)
Specific weight (specific_weight)
Speed of sound (speed_of_sound)
Temperature (temperature, temperature_in_celsius)
Thermal conductivity (thermal_conductivity)
Vector and matrix inputs
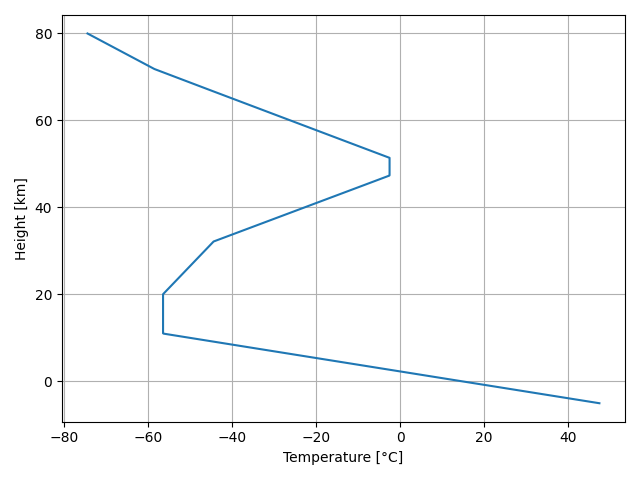
Ambiance also handles list-like input (list, tuples, Numpy arrays). The following code demonstrates how to produce a temperature plot with Matplotlib. In the example, Numpy’s linspace() function is used to produce an array with altitudes.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ambiance import Atmosphere
# Create an atmosphere object
heights = np.linspace(-5e3, 80e3, num=1000)
atmosphere = Atmosphere(heights)
# Make plot
plt.plot(atmosphere.temperature_in_celsius, heights/1000)
plt.ylabel('Height [km]')
plt.xlabel('Temperature [°C]')
plt.grid()
plt.show()The output is
Similarly, you can also pass in entire matrices. Example:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from ambiance import Atmosphere
>>> h = np.array([[0, 11, 12], [20, 21, 35], [0, 80, 50]])*1000
>>> h # Geometric heights in metres
array([[ 0, 11000, 12000],
[20000, 21000, 35000],
[ 0, 80000, 50000]])
>>> Atmosphere(h).temperature
array([[288.15 , 216.7735127 , 216.65 ],
[216.65 , 217.58085353, 236.51337209],
[288.15 , 198.63857625, 270.65 ]])
>>> Atmosphere(h).speed_of_sound
array([[340.29398803, 295.15359145, 295.06949351],
[295.06949351, 295.70270856, 308.29949587],
[340.29398803, 282.53793156, 329.798731 ]])
>>> Atmosphere([30000, 0]).layer_name
array(['stratosphere', 'troposphere'], dtype='<U42')Instantiating from given pressure or density
In some contexts it may be convenient to instantiate an Atmosphere object from a given ambient pressure or density. This can be easily achieved by using the Atmosphere.from_pressure() or Atmosphere.from_density() methods, respectively. Both methods return Atmosphere objects from which all other properties, like temperature, can be requested.
>>> Atmosphere.from_pressure([80e3, 20e3]) # 80 kPa and 20 kPa
Atmosphere(array([ 1949.58557497, 11805.91571135]))
>>> Atmosphere.from_pressure([80e3, 20e3]).pressure
array([80000., 20000.])
>>> Atmosphere.from_density(1.0) # 1.0 kg/m^3
Atmosphere(array([2064.96635895]))Complete user guide
For a comprehensive and detailed user guide, please see the complete documentation.
Installation
Pip (recommended)
Ambiance is available on PyPI and may simply be installed with
pip install ambianceConda
The package can be installed via the Conda environment with
conda install -c conda-forge ambiance


Requirements
Using Ambiance requires
Python 3.6 or higher
NumPy
SciPy
For developers: Recommended packages may be installed with the requirements.txt.
pip install -r requirements.txtLicense
License: Apache-2.0
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file ambiance-1.3.1.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: ambiance-1.3.1.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 17.0 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.8.0 colorama/0.4.4 importlib-metadata/4.6.4 keyring/23.5.0 pkginfo/1.8.2 readme-renderer/34.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 requests/2.25.1 rfc3986/1.5.0 tqdm/4.57.0 urllib3/1.26.5 CPython/3.10.6
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
ceff180945a96996da5a3aceff2f2ff4f1ae67dadd24919675223c8e01d0a416
|
|
| MD5 |
fc1905221fa0015ee9e09d3bfbc3a2df
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
de986ca0da97a869aed1375e0eaa7ecbc7d9dc1253065ebad3f33be339957ba2
|
File details
Details for the file ambiance-1.3.1-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: ambiance-1.3.1-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 15.4 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.8.0 colorama/0.4.4 importlib-metadata/4.6.4 keyring/23.5.0 pkginfo/1.8.2 readme-renderer/34.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 requests/2.25.1 rfc3986/1.5.0 tqdm/4.57.0 urllib3/1.26.5 CPython/3.10.6
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
d7ccd04390e59727ffca5c54079586fe0b40419db5445b524db563a9405f015a
|
|
| MD5 |
8e9673699cfbc8664bfbfcbb5548baa3
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
ebb7a9543c04d696a4bfe8a4959da6452f926c9766b3c27e9ef89db0a727965b
|











