A Python library for Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART) algorithms.
Project description
AdaptiveResonanceLib
Welcome to AdaptiveResonanceLib, a comprehensive and modular Python library for Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART) algorithms. Based on scikit-learn, our library offers a wide range of ART models designed for both researchers and practitioners in the field of machine learning and neural networks. Whether you're working on classification, clustering, or pattern recognition, AdaptiveResonanceLib provides the tools you need to implement ART algorithms efficiently and effectively.
Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART)
Adaptive Resonance Theory (ART) is both
- A neuroscientific theory of how the brain balances plasticity (learning new information) with stability (retaining what it already knows), and
- A family of machine‑learning algorithms that operationalise this idea for clustering, classification, continual‑learning, and other tasks.
First proposed by Stephen Grossberg and Gail Carpenter in the mid‑1970s , ART models treat learning as an interactive search between bottom‑up evidence and top‑down expectations:
-
Activation. A new input pattern activates stored memories (categories) in proportion to their similarity to the input.
-
Candidate selection. The most active memory (call it J) is tentatively chosen to represent the input.
-
Vigilance check (resonance test). The match between the input and memory J is compared to a user‑chosen threshold (ρ) (the vigilance parameter).
- If the match ≥ (ρ) → Resonance. The memory and input are deemed compatible; J is updated to incorporate the new information.
- If the match < (ρ) → Mismatch‑reset. Memory J is temporarily inhibited, and the next best candidate is tested.
- If no memory passes the test → a new category is created directly from the input.
-
Output. In clustering mode, the index of the resonant (or newly created) memory is returned as the cluster label.
A step-by-step flow chart depicting the generalized ART algorithm can be found here.
Vigilance
ρ sets an explicit upper bound on how dissimilar two inputs can be while still ending up in the same category:
| Vigilance (ρ) | Practical effect |
|---|---|
| ( ρ = 0 ) | All inputs merge into a single, broad category |
| Moderate (( 0 < ρ < 1 )) | Finer granularity as (ρ) increases |
| ( ρ = 1 ) | Every distinct input forms its own category (memorisation) |
This single knob lets practitioners trade off specificity against generality without retraining from scratch.
Notable Variants
| Variant | Input type | Task | Trait |
|---|---|---|---|
| ART 1 | Binary | Unsupervised clustering | Original model |
| Fuzzy ART | Real‑valued ([0,1]) | Unsupervised clustering | Uses fuzzy AND operator for analog inputs, resulting in rectagular categories |
| ARTMAP | Paired inputs ((X, y)) | Supervised classification | Two ART modules linked by an associative map field |
| Gaussian ART | Real‑valued | Clustering | Replace rectangular category fields with Gaussian ones for smoother decision boundaries |
| FALCON | Paired inputs ((State, Action, Reward)) | Reinforcement Learning | Uses three ART modules to create a dynamic SARSA grid for solving reinforcement learning tasks |
All variants share the same resonance‑test backbone, so you can grasp one and quickly extend to the others.
Strengths and Things to Watch
- Online / incremental learning – adapts one sample at a time without replay.
- Explicit category prototypes – easy to inspect and interpret.
- Built‑in catastrophic‑forgetting control via (ρ).
- Parameter sensitivity – vigilance (and, in many variants, the learning rate (\beta)) must be tuned to your data.
- Order dependence – the sequence of inputs can affect category formation; shuffling your training data is recommended for unbiased results.
Available Models
AdaptiveResonanceLib includes implementations for the following ART models:
-
Elementary Clustering
-
Metric Informed
-
Topological
-
Classification
-
Regression
-
Hierarchical
-
Data Fusion
-
Reinforcement Learning
-
Biclustering
-
C++ Accelerated
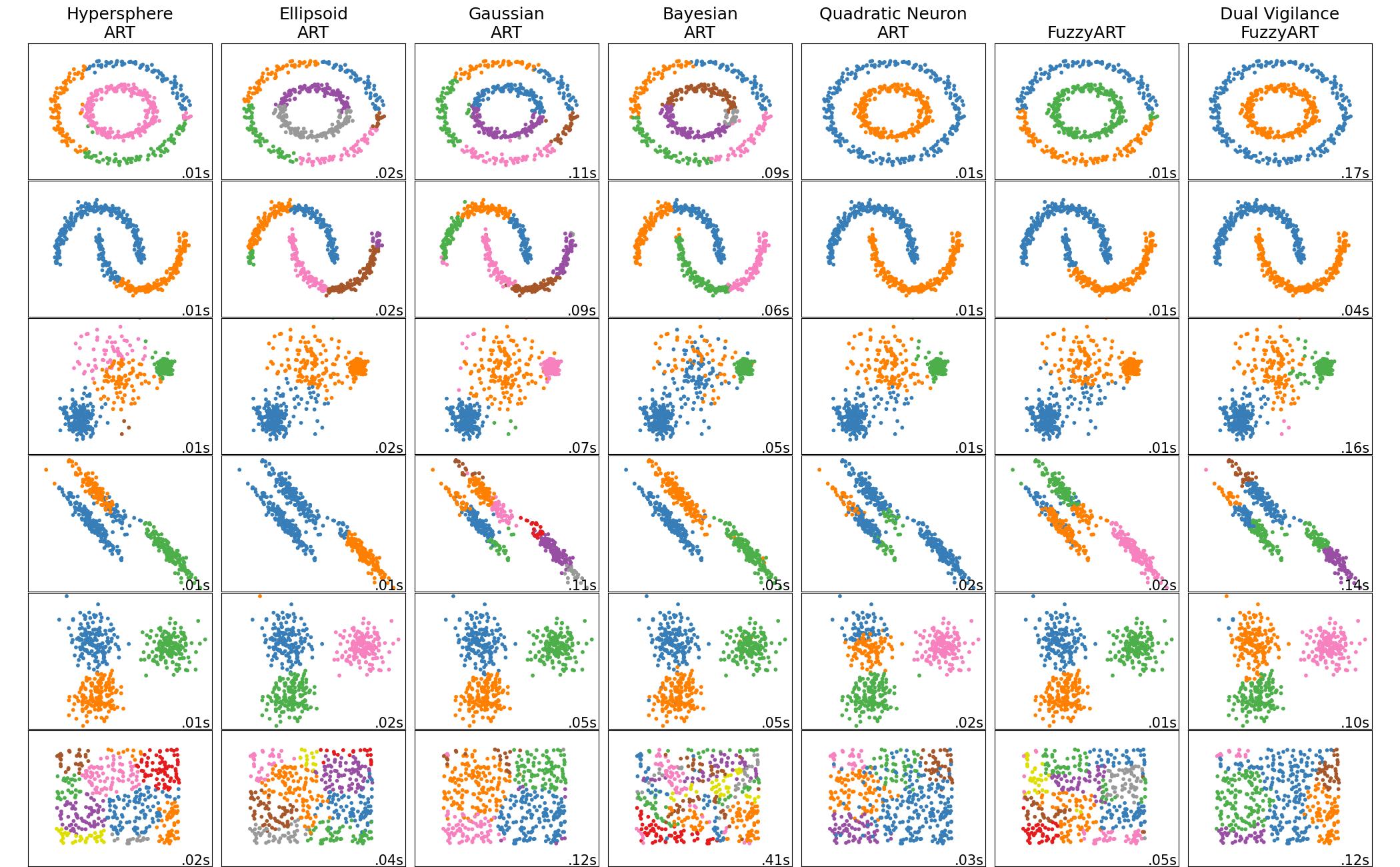
Comparison of Elementary Models
Installation
To install AdaptiveResonanceLib, simply use pip:
pip install artlib
Or to install directly from the most recent source:
pip install git+https://github.com/NiklasMelton/AdaptiveResonanceLib.git@develop
Ensure you have Python 3.9 or newer installed.
Quick Start
Here are some quick examples to get you started with AdaptiveResonanceLib:
Clustering Data with the Fuzzy ART model
from artlib import FuzzyART
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
# Load the MNIST dataset
n_dim = 28*28
(X_train, _), (X_test, _) = mnist.load_data()
X_train = X_train.reshape((-1, n_dim)) # flatten images
X_test = X_test.reshape((-1, n_dim))
# Initialize the Fuzzy ART model
model = FuzzyART(rho=0.7, alpha = 0.0, beta=1.0)
# (Optional) Tell the model the data limits for normalization
lower_bounds = np.array([0.]*n_dim)
upper_bounds = np.array([255.]*n_dim)
model.set_data_bounds(lower_bounds, upper_bounds)
# Prepare Data
train_X_prep = model.prepare_data(X_train)
test_X_prep = model.prepare_data(X_test)
# Fit the model
model.fit(train_X_prep)
# Predict data labels
predictions = model.predict(test_X_prep)
Fitting a Classification Model with SimpleARTMAP
from artlib import GaussianART, SimpleARTMAP
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
# Load the MNIST dataset
n_dim = 28*28
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
X_train = X_train.reshape((-1, n_dim)) # flatten images
X_test = X_test.reshape((-1, n_dim))
# Initialize the Gaussian ART model
sigma_init = np.array([0.5]*X_train.shape[1]) # variance estimate for each feature
module_a = GaussianART(rho=0.0, sigma_init=sigma_init)
# (Optional) Tell the model the data limits for normalization
lower_bounds = np.array([0.]*n_dim)
upper_bounds = np.array([255.]*n_dim)
module_a.set_data_bounds(lower_bounds, upper_bounds)
# Initialize the SimpleARTMAP model
model = SimpleARTMAP(module_a=module_a)
# Prepare Data
train_X_prep = model.prepare_data(X_train)
test_X_prep = model.prepare_data(X_test)
# Fit the model
model.fit(train_X_prep, y_train)
# Predict data labels
predictions = model.predict(test_X_prep)
Fitting a Regression Model with FusionART
from artlib import FuzzyART, HypersphereART, FusionART
import numpy as np
# Your dataset
X_train = np.array([...]) # shape (n_samples, n_features_X)
y_train = np.array([...]) # shape (n_samples, n_features_y)
test_X = np.array([...])
# Initialize the Fuzzy ART model
module_x = FuzzyART(rho=0.0, alpha = 0.0, beta=1.0)
# Initialize the Hypersphere ART model
r_hat = 0.5*np.sqrt(X_train.shape[1]) # no restriction on hyperpshere size
module_y = HypersphereART(rho=0.0, alpha = 0.0, beta=1.0, r_hat=r_hat)
# Initialize the FusionARTMAP model
gamma_values = [0.5, 0.5] # eqaul weight to both channels
channel_dims = [
2*X_train.shape[1], # fuzzy ART complement codes data so channel dim is 2*n_features
y_train.shape[1]
]
model = FusionART(
modules=[module_x, module_y],
gamma_values=gamma_values,
channel_dims=channel_dims
)
# Prepare Data
train_Xy = model.join_channel_data(channel_data=[X_train, y_train])
train_Xy_prep = model.prepare_data(train_Xy)
test_Xy = model.join_channel_data(channel_data=[X_train], skip_channels=[1])
test_Xy_prep = model.prepare_data(test_Xy)
# Fit the model
model.fit(train_Xy_prep)
# Predict y-channel values and clip X values outside previously observed ranges
pred_y = model.predict_regression(test_Xy_prep, target_channels=[1], clip=True)
Data Normalization
AdaptiveResonanceLib models require feature data to be normalized between 0.0 and 1.0 inclusively. This requires identifying the boundaries of the data space.
If the first batch of your training data is representative of the entire data space, you dont need to do anything and artlib will identify the data bounds automatically. However, this will often not be sufficient and the following work-arounds will be needed:
Users can manually set the bounds using the following code snippet or similar:
# Set the boundaries of your data for normalization
lower_bounds = np.array([0.]*n_features)
upper_bounds = np.array([1.]*n_features)
model.set_data_bounds(lower_bounds, upper_bounds)
Or users can present all batches of data to the model for automatic boundary identification:
# Find the boundaries of your data for normalization
all_data = [train_X, test_X]
_, _ = model.find_data_bounds(all_data)
If only the boundaries of your testing data are unknown, you can call
model.predict() with clip=True to clip testing data to the bounds seen during
training. Only use this if you understand what you are doing.
C++ Optimizations
Most ARTlib classes rely on NumPy / SciPy for linear-algebra routines, but several go further:
| Level | Accelerated components | Implementations |
|---|---|---|
| Python (Numba JIT) | Activation & vigilance kernels | ART1, Fuzzy ART, Binary Fuzzy ART |
| Native C++ (Pybind11) | Entire fit / predict pipelines | Fuzzy ARTMAP, Hypersphere ARTMAP, Gaussian ARTMAP, Binary Fuzzy ARTMAP |
How the C++ variants work
- End-to-end native execution – Training and inference run entirely in C++, eliminating Python-level overhead.
- State hand-off – After fitting, the C++ routine exports cluster weights and metadata back to the corresponding pure-Python class. You can therefore:
• inspect attributes (
weights_,categories_, …) • serialize withpickle• plug them into any downstream ARTlib or scikit-learn pipeline exactly as you would with the Python-only models. - Trade-off – The C++ versions sacrifice some modularity (you cannot swap out internal ART components) in exchange for significantly shorter run-times.
C++ Acceleration Quick reference
| Class | Acceleration method | Primary purpose |
|---|---|---|
| ART1 | Numba JIT kernels | Clustering |
| Fuzzy ART | Numba JIT kernels | Clustering |
| Binary Fuzzy ART | Numba JIT kernels | Clustering |
| Fuzzy ARTMAP | Full C++ implementation | Classification |
| Hypersphere ARTMAP | Full C++ implementation | Classification |
| Gaussian ARTMAP | Full C++ implementation | Classification |
| Binary Fuzzy ARTMAP | Full C++ implementation | Classification |
Example Usage
from artlib import FuzzyARTMAP
import numpy as np
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist
# Load the MNIST dataset
n_dim = 28*28
(X_train, y_train), (X_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
X_train = X_train.reshape((-1, n_dim)) # flatten images
X_test = X_test.reshape((-1, n_dim))
# Initialize the Fuzzy ART model
model = FuzzyARTMAP(rho=0.7, alpha = 0.0, beta=1.0)
# (Optional) Tell the model the data limits for normalization
lower_bounds = np.array([0.]*n_dim)
upper_bounds = np.array([255.]*n_dim)
model.set_data_bounds(lower_bounds, upper_bounds)
# Prepare Data
train_X_prep = model.prepare_data(X_train)
test_X_prep = model.prepare_data(X_test)
# Fit the model
model.fit(train_X_prep, y_train)
# Predict data labels
predictions = model.predict(test_X_prep)
Timing Comparison
The below figures demonstrate the acceleration seen by the C++ ARTMAP variants in comparison to their baseline Python versions for a 1000 sample subset of the MNIST dataset.
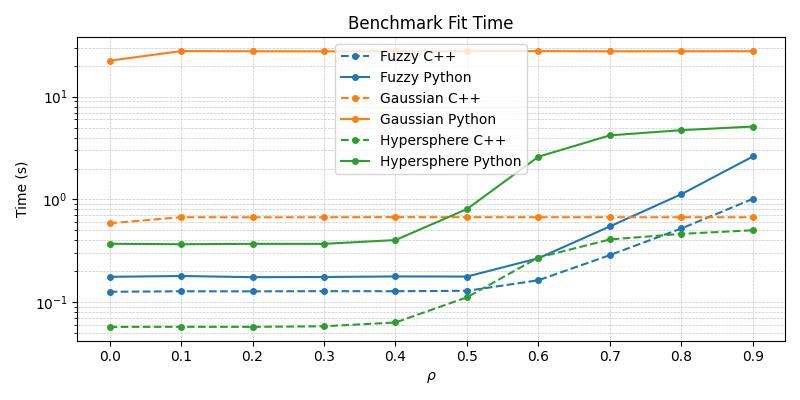
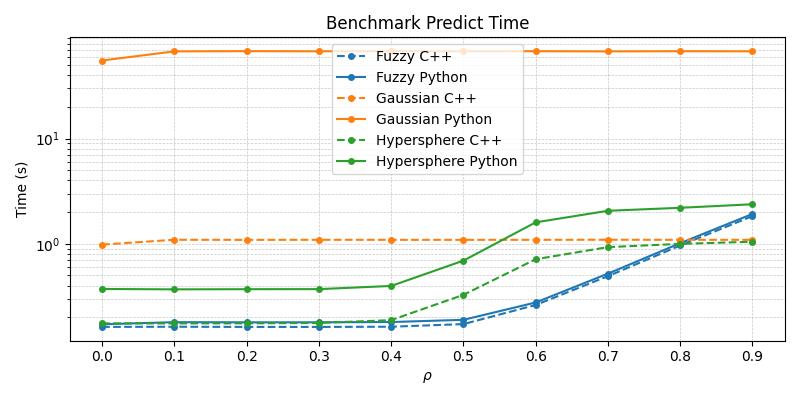
From the above plots, it becomes apparent that the C++ variants are superior in their runtime performance and should be the default choice of practitioners wishing to work with these specific compound models.
While the current selection remains limited, future releases will expand the native C++ implementation as user demand for them increases.
Documentation
For more detailed documentation, including the full list of parameters for each model, visit our Read the Docs page.
Examples
For examples of how to use each model in AdaptiveResonanceLib, check out the /examples directory in our repository.
Contributing
We welcome contributions to AdaptiveResonanceLib! If you have suggestions for improvements, or if you'd like to add more ART models, please see our CONTRIBUTING.md file for guidelines on how to contribute.
You can also join our Discord server and participate directly in the discussion.
License
AdaptiveResonanceLib is open source and available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.
Contact
For questions and support, please open an issue in the GitHub issue tracker or message us on our Discord server. We'll do our best to assist you.
Happy Modeling with AdaptiveResonanceLib!
Citing this Repository
If you use this project in your research, please cite it as:
Melton, N. (2025). AdaptiveResonanceLib (Version 0.1.7)
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distributions
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 104.9 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
0b094ec6ff56b98aac6c175d84992282b2b86329b35a0e65632533d916bb22c8
|
|
| MD5 |
31123faa0b2e3337154bee63a32c5718
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
aa58a8f65003ed45e7234456b64c604aac1fbb8f50817abddb106d6f845aba6e
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp314-cp314t-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp314-cp314t-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 7.3 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.14t, musllinux: musl 1.2+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
368f9b5b759abad9be352aa9c617506738bae5e176c5aeb9fe5078fd8ddd1b79
|
|
| MD5 |
9df36eac704dbef152b460c0200b41f1
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
71d81d0fe5049d5367d51b632172eaa167d3210a20cf21a35d6c00c83fa2a24c
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp314-cp314t-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp314-cp314t-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.3 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.14t, manylinux: glibc 2.27+ x86-64, manylinux: glibc 2.28+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
b7e457db433097f1f77f079c20108aa7aa7f4c934330f25847d1ea7af9cc8d29
|
|
| MD5 |
af2ae1781012eded047b70c69050f2cb
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
2bd5a8bb69b8c307efe4ec72621210b1aa96186aec9475088fcfea553c26190a
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp314-cp314-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp314-cp314-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 7.1 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.14, musllinux: musl 1.2+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
6ea5faf21483042da850711262517d24bb2eb5b2a1c6d17f9740441e2bf6fbbe
|
|
| MD5 |
54b5b1aeddfb3ae564595f5b72bea2aa
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
dd26e16308142cfa3cd1c00451bda8eefbd51f02313af0149a74216b43bf397f
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp314-cp314-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp314-cp314-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.2 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.14, manylinux: glibc 2.27+ x86-64, manylinux: glibc 2.28+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
4514f9a4dd0c639773c6c373dd739af5a3a3e5776259f63e39d94908bdd387df
|
|
| MD5 |
276e80a1b9de607263b1ee80c84a0305
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
298a8e794fe2a2751d0590648c07d949895db2529363eaebaf51d9cb0065e9bb
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp313-cp313-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp313-cp313-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 7.1 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.13, musllinux: musl 1.2+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
99a5580469c176a6d326ba0b2b41c4304149ac99dcfbae0042e795d4eb12b3e0
|
|
| MD5 |
55ca3d91f59e9481a7d202e35a10afaa
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
9821b2bd8ad5d50fb0058fd8e0393bb09c9b01efb5d664d317fc340d526e977e
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp313-cp313-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp313-cp313-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.2 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.13, manylinux: glibc 2.27+ x86-64, manylinux: glibc 2.28+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
c308c02024571f892d35a8f93e30228c16fe5d24ef2b0274a59d5032f9828b6a
|
|
| MD5 |
878591d4b48579451656264caf1b4df9
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
f129befd29e76cbbcd6e724b89457be9b9f49ce1dfca1f0fd8f716f4f44f800c
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp312-cp312-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp312-cp312-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 7.1 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.12, musllinux: musl 1.2+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
27c96e326beb8a4a29766af7c0b1dced554a521f161c02ba2883c87ab1f12095
|
|
| MD5 |
7f0ff97743283f04cd163895e894d496
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
fd7f266f3b95c552e2f032dd2c484349dcf9dcb854d84e1e14137d1bdedcc4ed
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp312-cp312-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp312-cp312-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.2 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.12, manylinux: glibc 2.27+ x86-64, manylinux: glibc 2.28+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
857a834ea4e65eee2d3fb7f97ca807c6ba92317478c30a816020ff72dee55e1b
|
|
| MD5 |
03192245b804963ffc3a2dfeda30a74c
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
3ada66976bae1c17ae7b699472dfcbe2a65567e40f6c8cfcef8a91ee861ff9b9
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp311-cp311-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp311-cp311-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 7.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.11, musllinux: musl 1.2+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
3fa4223232fe1d0a003d3078bc0be9d3b37569fed7978ac79519f00b7a513b4f
|
|
| MD5 |
9ec826a6c2a25f65add92782e5a47038
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
834ac30256a2e9c502cc5dc7c447e315cd6464e726d801c0be39f6205350813f
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp311-cp311-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp311-cp311-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.11, manylinux: glibc 2.27+ x86-64, manylinux: glibc 2.28+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
e2c2ea0f5b7db08c0c47709d9369ba9e800a067c61827c78b18dc80f278e51f8
|
|
| MD5 |
96de75a02cb4a017c92a620f284ac8de
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
64447d9f506840c54163255f37aa3d59582cda414f0024236f50599013ccac4d
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp310-cp310-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp310-cp310-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 7.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.10, musllinux: musl 1.2+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
539452bdd59ecf715ca5bee034977576e7aeafa83478392973d9527fd29e0642
|
|
| MD5 |
0775866774507b9a922aa43d8b0df40e
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
d02d9b803b08c6b6a525ede4ddac339209b0f5aac8b47f953183098c4f110e78
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.10, manylinux: glibc 2.27+ x86-64, manylinux: glibc 2.28+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
3da78d8d353e5fd02860d0794acb3f95d7f60ad606b7036be19a81b36ae4c3eb
|
|
| MD5 |
baa6b784468a747e485e2892b1550f7a
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
71219b6de3fb416e4f200af26ba96dc61d24b69a345f12bf1e95a9723bf26499
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp39-cp39-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp39-cp39-musllinux_1_2_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 7.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.9, musllinux: musl 1.2+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
3cc5f6de0eaa17ecf829d7e37eb1ab4f5b39d90f1637345d2f5bf9396fd54a4f
|
|
| MD5 |
75c20f557e120aa481cacda13b546b4f
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
ce19d102ac12d8586148d69de0809b8e672fe34499ef17f5b091e684e9dfea64
|
File details
Details for the file artlib-0.1.7-cp39-cp39-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: artlib-0.1.7-cp39-cp39-manylinux_2_27_x86_64.manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.9, manylinux: glibc 2.27+ x86-64, manylinux: glibc 2.28+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.9.23
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
b733be1116c3bc5cf808599c45ca69f4be0fbc1d8797be5141f2de649763dcfd
|
|
| MD5 |
a883da1b6834755bbd78d11686bfc1e6
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
a25270b7b0dfb5c8dbc0888a998e12fc5c965701cfdb3e4df861d11f89f5ab62
|