Fast text similarity with binary encoded word embeddings.
Project description
Binarized Word Mover's Distance
Scalable text similarity with encoded embedding distance.
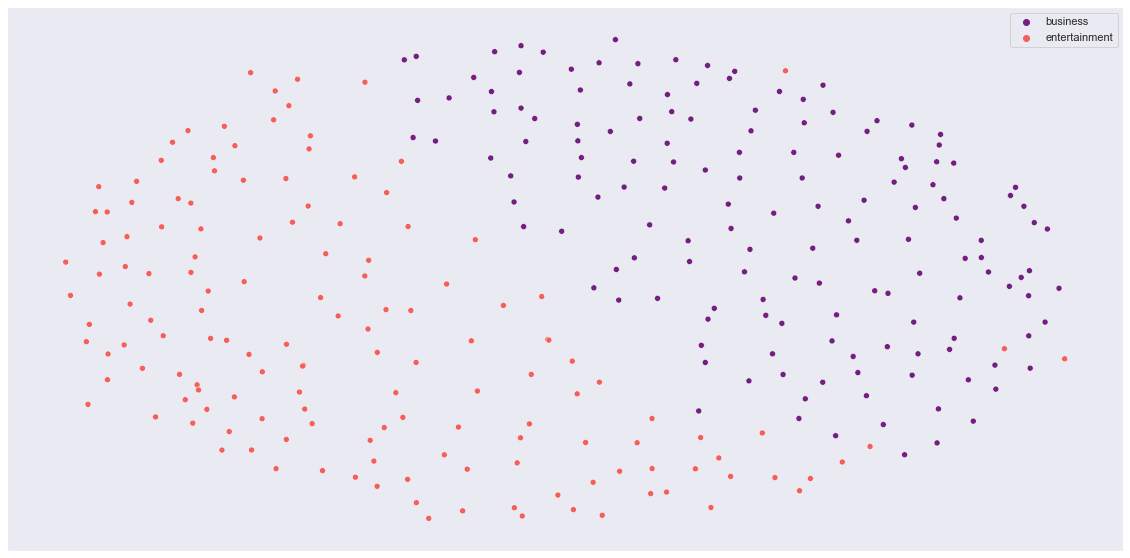
Description: MDS visualization of BBC News data. Dissimilarity matrix computed using Binarized Word Mover's Distance.
Overview
The Binarized Word Mover's Distance (BWMD) is a modification of the Word Mover's Distance, originally developed by Kusner et al. (2015). The BWMD computes a lower-bound Wasserstein word-embedding distance using binarized embeddings and an approximate-nearest-neighbor cache.
Installation
pip install bwmd
Models
To compute distances, you must provide a path to a model directory containing a compressed vector file and approximate-nearest-neighbor lookup tables. You can compute these yourself as described in the /notebooks/ directory, or use one of the models provided below.
Minimal Start
If you already possess a model directory for your language, you may quickly compute distances as in the example below.
from bwmd.distance import BWMD
# Create a corpus of documents.
corpus = [
['obama', 'speaks', 'to', 'the', 'media', 'in', 'illinois'],
['the', 'president', 'greets', 'the', 'press', 'in', 'chicago'],
['this', 'sentence', 'is', 'unrelated']
]
# Instantiate a distance object.
bwmd = BWMD(
model_path='fasttext-en-512',
dim=512,
)
# Get pairwise distances.
bwmd.pairwise(corpus)
>>> array([[0. , 0.25683594, 0.29711914],
[0.25683594, 0. , 0.27783203],
[0.29711914, 0.27783203, 0. ]])
Sample code for this minimal start and for training your own compressed vectors for any language can be found in the /notebooks/ directory.
API Details
bwmd.distance.BWMD(model_path, size_vocab, language, dim, raw_hamming=False)creates a distance object from a path containing precomputed lookup tables and compressed vectors. You must specify the total number of vocabulary items, language (for removing stopwords), and dimension of the compressed vectors. If you wish only to use the raw hamming distances and not lookup table values, specifyraw_hamming=True.bwmd.distance.BWMD().get_distance(text_a, text_b)computes the BWMD between two texts as lists of strings. This method assumes that stopwords have already been removed.bwmd.distance.BWMD().pairwise(corpus)computes a pairwise distance matrix for an array of texts as lists of strings.bwmd.distance.BWMD().preprocess_text(text)removes stopwords and out-of-vocabulary words from a single text as a list of strings.bwmd.distance.BWMD().preprocess_corpus(corpus)removes stopwords and out-of-vocabulary words from a corpus as an array of texts as lists of strings.bwmd.compressor.Compressor(original_dimensions, reduced_dimensions, compression)creates a compressor object which will accept word embeddings of dimensionoriginal_dimensionsand compress them to dimensionreduced_dimensionsaccording to the data type specified incompression.bwmd.compressor.Compressor().fit(vectors, epochs=20, batch_size=75)fits the compressor to the input vectors by training an autoencoder under the specified hyperparameters.bwmd.compressor.Compressor().transform(path, n_vectors, save=False)transforms the original vectors residing at the specified path using a trained autoencoder. Then_vectorsparameter specifies what amount of vectors, starting at the beginning of the vector file, will ultimately be transformed and returned. Ifsave=Truethe transformed vectors will be saved to the input path.bwmd.tools.load_vectors(path, size, expected_dimensions, expected_dtype, skip_first_line=True)loads and returns vectors and words from a text file containing words and vector features on each new line. The parameterskip_first_lineshould be set toTruewhen the first line of a vector file is vector metadata and not an actual vector.bwmd.tools.convert_vectors_to_dict(vectors, words)casts aligned arrays of vectors and words into a Python dictionary with words as keys.bwmd.partition.build_partitions_lookup_tables(vectors, I, real_value_path, vector_dim)uses a special partitioning algorithm similar to bisecting k-means to identify approximate-nearest-neighbors for each input vector. The free parameterIcontrols theknumber of partitions which are to be made, leading tok = 2^Ipartitions.
Obtaining Real-Valued Vectors
To compute compressed vectors such as those provided above, you must provide a txt file containing words and vector features separated by newline characters. You can obtain high-quality vectors for many languages from FastText. If using .vec files from FastText, ensure you set skip_first_line=True when loading vectors from a file. Further details on parsing real-valued vector files when training your own models can be found in the fit_model.ipynb example in the notebooks directory.
References
- Kusner, Matt & Sun, Y. & Kolkin, N.I. & Weinberger, Kilian. (2015). From word embeddings to document distances. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2015). 957-966.
- Werner, Matheus & Laber, Eduardo. (2019). Speeding up Word Mover's Distance and its variants via properties of distances between embeddings.
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file bwmd-0.2.2.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: bwmd-0.2.2.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 34.1 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.4.2 importlib_metadata/4.8.1 pkginfo/1.7.1 requests/2.25.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.61.2 CPython/3.9.5
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
c1d42b295cdd74694007492704a3a5af6386414837195244fec816e72a30b8e9
|
|
| MD5 |
c49ec4fbd88846ef52ec40965f9a8720
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
4ae333f7291c547c8ba764b3fc73e9dfd1844ae2b158da9016e4f3a61f3c827b
|
File details
Details for the file bwmd-0.2.2-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: bwmd-0.2.2-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 35.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.4.2 importlib_metadata/4.8.1 pkginfo/1.7.1 requests/2.25.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.61.2 CPython/3.9.5
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9873ff3af15eb635aea740efa315b5d7eb11ab25c18e2d35db7bf5d05ae0f733
|
|
| MD5 |
cb32038a5f238e414f0f3e081ba864c5
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
3b7873254f8a0939696a6c14f998fb3472f8a794553b00d6b37c00b8c12ad026
|