CAN BUS tools.
Project description
About
CAN BUS tools in Python 3.
CAN message encoding and decoding.
Simple and extended signal multiplexing.
Diagnostic DID encoding and decoding.
candump output decoder.
Node tester.
C source code generator.
CAN bus monitor.
Python 2 support is deprecated as Python 3 has better unicode support.
Project homepage: https://github.com/eerimoq/cantools
Documentation: http://cantools.readthedocs.org/en/latest
Installation
pip install cantoolsExample usage
Scripting
The example starts by parsing a small DBC-file and printing its messages and signals.
>>> import cantools
>>> from pprint import pprint
>>> db = cantools.database.load_file('tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc')
>>> db.messages
[message('ExampleMessage', 0x1f0, False, 8, 'Example message used as template in MotoHawk models.')]
>>> example_message = db.get_message_by_name('ExampleMessage')
>>> pprint(example_message.signals)
[signal('Enable', 7, 1, 'big_endian', False, 1.0, 0, 0.0, 0.0, '-', False, None, {0: 'Disabled', 1: 'Enabled'}, None),
signal('AverageRadius', 6, 6, 'big_endian', False, 0.1, 0, 0.0, 5.0, 'm', False, None, None, ''),
signal('Temperature', 0, 12, 'big_endian', True, 0.01, 250, 229.53, 270.47, 'degK', False, None, None, None)]The example continues encoding a message and sending it on a CAN bus using the python-can package.
>>> import can
>>> can_bus = can.interface.Bus('vcan0', bustype='socketcan')
>>> data = example_message.encode({'Temperature': 250.1, 'AverageRadius': 3.2, 'Enable': 1})
>>> message = can.Message(arbitration_id=example_message.frame_id, data=data)
>>> can_bus.send(message)Alternatively, a message can be encoded using the encode_message() method on the database object.
The last part of the example receives and decodes a CAN message.
>>> message = can_bus.recv()
>>> db.decode_message(message.arbitration_id, message.data)
{'AverageRadius': 3.2, 'Enable': 'Enabled', 'Temperature': 250.09}See examples for additional examples.
Command line tool
The decode subcommand
Decode CAN frames captured with the Linux program candump.
$ candump vcan0 | cantools decode tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc
vcan0 1F0 [8] 80 4A 0F 00 00 00 00 00 ::
ExampleMessage(
Enable: 'Enabled' -,
AverageRadius: 0.0 m,
Temperature: 255.92 degK
)
vcan0 1F0 [8] 80 4A 0F 00 00 00 00 00 ::
ExampleMessage(
Enable: 'Enabled' -,
AverageRadius: 0.0 m,
Temperature: 255.92 degK
)
vcan0 1F0 [8] 80 4A 0F 00 00 00 00 00 ::
ExampleMessage(
Enable: 'Enabled' -,
AverageRadius: 0.0 m,
Temperature: 255.92 degK
)Alternatively, the decoded message can be printed on a single line:
$ candump vcan0 | cantools decode --single-line tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc
vcan0 1F0 [8] 80 4A 0F 00 00 00 00 00 :: ExampleMessage(Enable: 'Enabled' -, AverageRadius: 0.0 m, Temperature: 255.92 degK)
vcan0 1F0 [8] 80 4A 0F 00 00 00 00 00 :: ExampleMessage(Enable: 'Enabled' -, AverageRadius: 0.0 m, Temperature: 255.92 degK)
vcan0 1F0 [8] 80 4A 0F 00 00 00 00 00 :: ExampleMessage(Enable: 'Enabled' -, AverageRadius: 0.0 m, Temperature: 255.92 degK)The dump subcommand
Dump given database in a human readable format:
$ cantools dump tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc
================================= Messages =================================
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Name: ExampleMessage
Id: 0x1f0
Length: 8 bytes
Cycle time: - ms
Senders: PCM1
Layout:
Bit
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
0 |<-x|<---------------------x|<--|
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
| +-- AverageRadius
+-- Enable
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
1 |-------------------------------|
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
2 |----------x| | | | | |
B +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
y +-- Temperature
t +---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
e 3 | | | | | | | | |
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
4 | | | | | | | | |
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
5 | | | | | | | | |
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
6 | | | | | | | | |
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
7 | | | | | | | | |
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
Signal tree:
-- {root}
+-- Enable
+-- AverageRadius
+-- Temperature
Signal choices:
Enable
0 Disabled
1 Enabled
------------------------------------------------------------------------The generate C source subcommand
Generate C source code from given database.
The generated code contains:
Known limitations:
The maximum signal size is 64 bits, which in practice is never exceeded.
Below is an example of how to generate C source code from a database. The database is tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc.
$ cantools generate_c_source tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc
Successfully generated motohawk.h and motohawk.c.See motohawk.h and motohawk.c for the contents of the generated files.
In the next example we use --database-name to set a custom namespace for all generated types, defines and functions. The output file names are also changed by this option.
$ cantools generate_c_source --database-name my_database_name tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc
Successfully generated my_database_name.h and my_database_name.c.See my_database_name.h and my_database_name.c for the contents of the generated files.
In the last example we use --no-floating-point-numbers to generate code without floating point types, i.e. float and double.
$ cantools generate_c_source --no-floating-point-numbers tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc
Successfully generated motohawk.h and motohawk.c.See motohawk_no_floating_point_numbers.h and motohawk_no_floating_point_numbers.c for the contents of the generated files.
Other C code generators:
The monitor subcommand
Monitor CAN bus traffic in a text based user interface.
$ cantools monitor tests/files/dbc/motohawk.dbc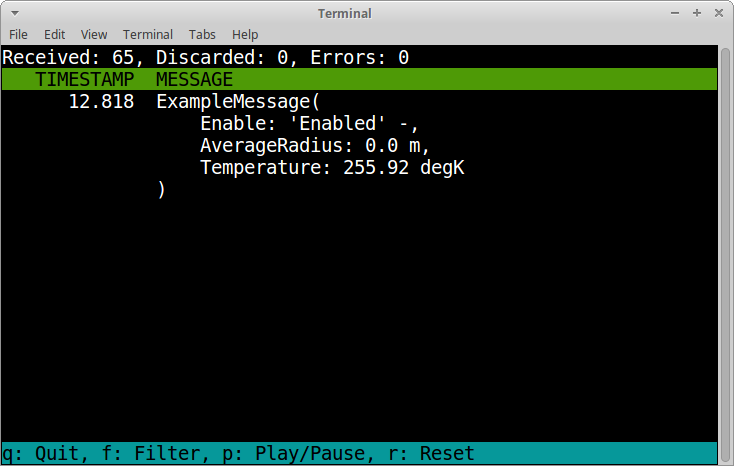
The menu at the bottom of the monitor shows the available commands.
Quit: Quit the monitor. Ctrl-C can be used as well.
Filter: Only display messages matching given regular expression. Press <Enter> to return to the menu from the filter input line.
Play/Pause: Toggle between playing and paused (or running and freezed).
Reset: Reset the monitor to its initial state.
Contributing
Fork the repository.
Install prerequisites.
pip install -r requirements.txtImplement the new feature or bug fix.
Implement test case(s) to ensure that future changes do not break legacy.
Run the tests.
make testCreate a pull request.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file cantools-32.20.2.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: cantools-32.20.2.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 245.2 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/1.13.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.21.0 setuptools/40.8.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.31.1 CPython/3.7.3
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
1da690b4bfb236f0762510faf7abf27d03022f83116694192d3239f7d69f3d6a
|
|
| MD5 |
95c4a4f8f3b9963ef6ee29f1696ae824
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
87406497d37a462592c4785122de7b68113f7e091325b7e853c4c851c6407634
|
File details
Details for the file cantools-32.20.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: cantools-32.20.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 75.7 kB
- Tags: Python 2, Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/1.13.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.21.0 setuptools/40.8.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.31.1 CPython/3.7.3
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
280cb270c656b4309d895873f06ca3e7d185496661de3a10bcb955087429f735
|
|
| MD5 |
82b115cd1803654ff004b674b3bad37f
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
9e365e4b45162c50d4fef4157331d62ee2850c89ca4f23feb6d6fdadcfe962ec
|














