A bisiumlation data-aware algorithm for Communicating Finite State Machines with edge assertions (knowledge as a-CFSM)
Project description
Communicating Finite State Machines Bisimulation with edge assertions
An algorithm to decide if two Communicating Finite State Machines (CFSM) with edge assertions, known as Asserted Communicating Finite State Machines (a-CFSM) are bisimilars. You can read about this CFSM extension in "Design-by-Contract for Flexible Multiparty Session Protocols" Section 4.3 (by Lorenzo Gheri, Ivan Lanese, Neil Sayers, Emilio Tuosto, and Nobuko Yoshida).
What does this package do?
This library provides both, a model for creating a-CFSMs and an algorithm for evaluating bisimulation. The main idea behind the algorithm is based on the fact that two automata do not have to coincide in the names of their participants, messages or variables used. Therefore, the algorithm constructs a matching of names as it builds the bisimulation relationship between the evaluated automata (if this is not possible, the automata are not bisimilar). For example, the following two automata would be bisimilar:
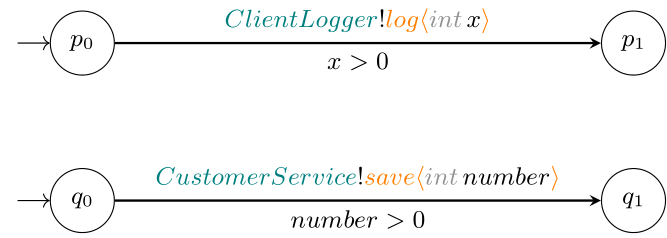
Installation
At first, you will need to install z3 and z3-solver as dependencies. You can use pip:
pip install z3-solver cfsm-bisimulation
Usage
The simplest use is to create the two CFSM models that you want to evaluate. We will use the z3 models as a way to construct the constraints.
from cfsm_bisimulation import CommunicatingFiniteStateMachine
from z3 import Int
cfsm_service = CommunicatingFiniteStateMachine(['Client', 'Logger'])
cfsm_service.add_states('p0', 'p1')
cfsm_service.set_as_initial('p0')
cfsm_service.add_transition_between(
'p0',
'p1',
'ClientLogger!log(int x)',
Int('x') > 0
)
cfsm_provider = CommunicatingFiniteStateMachine(['Customer', 'Service'])
cfsm_provider.add_states('q0', 'q1')
cfsm_provider.set_as_initial('q0')
cfsm_provider.add_transition_between(
'q0',
'q1',
'CustomerService!save(int number)',
Int('number') > 0
)
To evaluate these automata, you can simply:
relation, matches = cfsm_service.calculate_bisimulation_with(cfsm_provider)
The result of the relation is a set of pairs (state, knowledge) which is in fact not the minimal possible relationship. If you want to obtain the minimum possible relationship between the automata, execute using the option:
relation, matches = cfsm_service.calculate_bisimulation_with(cfsm_provider, minimize=True)
The result of matches is a dictionary with matches for participants, messages and variables. Each value, in turn, is a dictionary with the matches themselves.
relation = {
(('p0'), ('q0')),
(('p1', Int('x') > 0), (Int('number') > 0)),
}
matches = {
'participants': {'Client': 'Customer', 'Logger': 'Service'},
'messages': {'log(int x)': 'save(int number)'},
'variables': {'number': 'x'}
}
Contributing
Bug reports and pull requests are welcome on GitHub at https://github.com/diegosenarruzza/bisimulation. If you are interested in updating or maintaining this package and need more information, please write to me at diegosenarruzza@gmail.com so I can explain in detail the idea behind the code.
License
The package is available as open source under the terms of the Mit License.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file cfsm_bisimulation-2.1.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: cfsm_bisimulation-2.1.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 19.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.10.12
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
235a1266805f0985f6d0883ad18c4348c6310c7536de2ce5e2f1d5605e589712
|
|
| MD5 |
d57d6191550f99172c14980ca9ff8f8d
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
36a7f86456a21149624d111b7dd21434cdb7b190dfff303ca43235116cdd7542
|
File details
Details for the file cfsm_bisimulation-2.1.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: cfsm_bisimulation-2.1.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 30.2 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.10.12
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9aa1197491fde8762f7c88459d6a6c274d72a5162a652602e2fdabcb28aa94d8
|
|
| MD5 |
e6e193acfa1828b8514dbed0e7da7004
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
e6fca53ec49093e7823aea4aa5e7684df6058a70dcb89cec0344d41bad4985b8
|











