Convert .py files runnable in VSCode/Python or Atom/Hydrogen to jupyter/colab .ipynb notebooks and vice versa
Project description
colab-convert
Converts ipython/Google Colab Notebooks into runable Python code and vice versa
Features
- converts files: .ipynb to .py and .py to .ipynb.
- converts ipython/colab magic % and ! to regular python code
- Supported magic commands (%)
- %pwd, %ls, %cd, %cp, %mv, %mkdir, %rm, %rmdir, %cat, %pip, %conda, %env, %setenv
- comments out unsupported ipython magic
- creates new import blocks for converted code
- logs all changes to a log file for review
- converted magic commands are appended with
#<cc-cm> - commented magic commands are prefixed with
#<cc-ac> - multi-lingual support to detect system language and let users choose
- Arabic, Dutch, English, German,
- consider helping expand translations by adding your langauge in the
/langfolder
- consider helping expand translations by adding your langauge in the
- Arabic, Dutch, English, German,
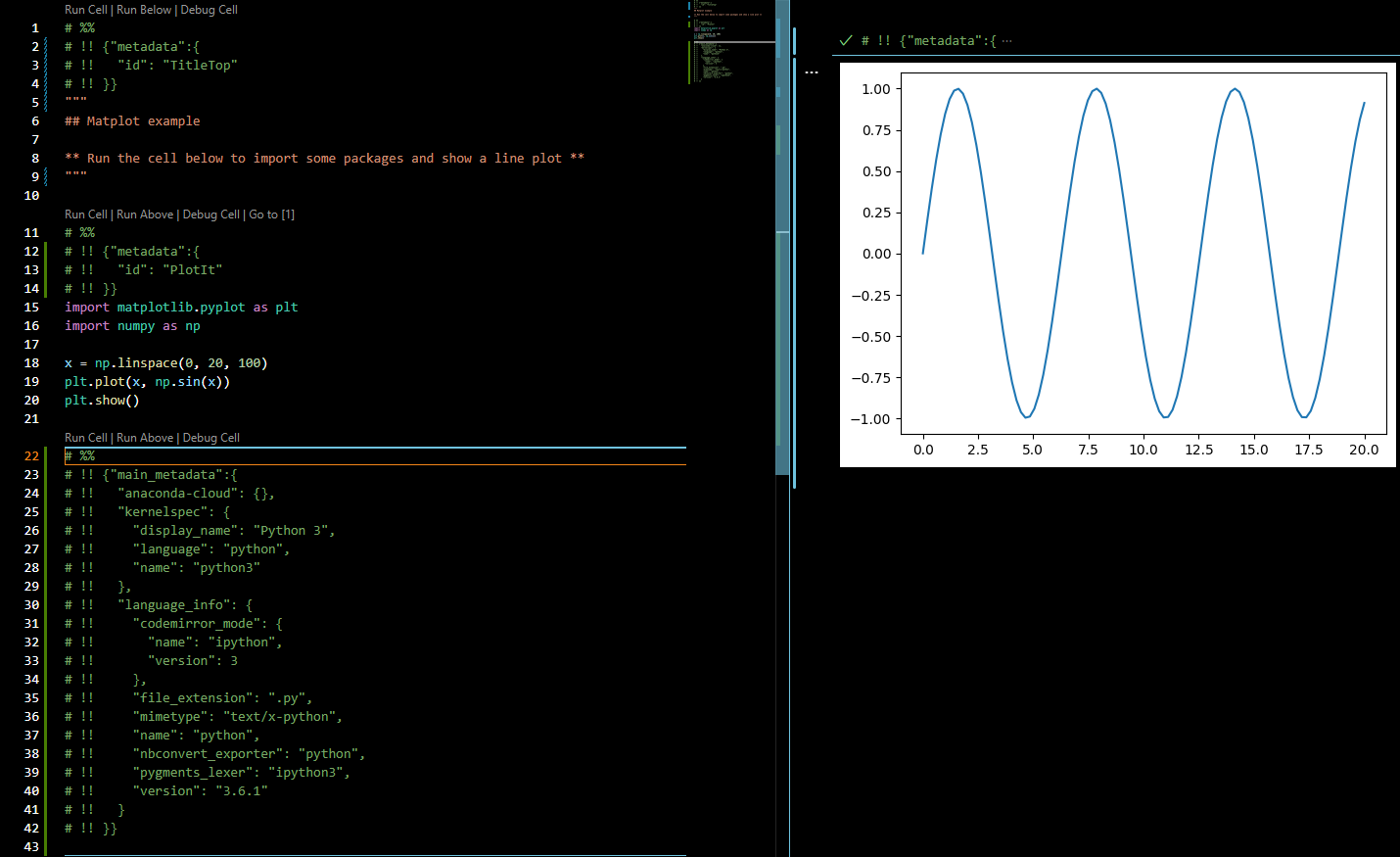
Atom/Hydrogen or VSCode/Python allows creating a python file split into cells with # %% separators having the ability to run cells via the backend of a Jupyter session and interactively show results back.
VSCode
Jupyter ipynb notebook
Install & Basic Usage
pip install colab-convert
Usage: colab-convert <input_file> <output_file> <flags>
<input_file>: input file to convert
<output_file>: output file to write to
<flags>: extra flags to pass to the converter
all flags are optional and have set defaults for best results
use flags to enable or disable certain functions on/off by default
colab-convert in.ipynb out.py -nc -rm -o
Default options and Flags
Default Flags Set (defaults are determined by input file)
ipynb input file:
[YES] convert magic , [YES] auto comment , [YES] imports , [NO] Outputs
py input file:
[NO] convert magic , [NO] auto comment , [NO] imports , [NO] Outputs
Available Flags
toggle certain items on or off
--retain-magic (-rm) : Keep magic commands in the output
.py default [ON]
.ipynb default [OFF]
--convert-magic (-cm) : Convert magic commands to python code
.py default [OFF]
.ipynb default [ON]
--auto-comment (-ac) : Convert unsupported magic commands to comments
.py default [OFF]
.ipynb default [ON]
--no-comment (-nc) : Keep unsupported magic commands
.py default [ON]
.ipynb default [OFF]
--no-imports (-ni) : Do not add imports from converted magic commands
.py default [OFF]
.ipynb default [OFF]
--outputs (-o) : Outputs to console of conversions and commented lines.
.py default [OFF]
.ipynb default [OFF]
--lang= (-l=) : Language to change output messages to
default [English]
--lang=en_US
en_US, en, english, eng, nl_NL, nl, dutch, dut, nlt, nederlands
Conversion Code used
>click me to see code<
Magic commands using bang (!)
for this particular magic we send the command to the subprocess system and print the results
# !git clone https://test.com/test/test.git
sub_p_res = subprocess.run(['git', 'clone' ,'https://test.com/test/test.git'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE).stdout.decode('utf-8')
print(sub_p_res)
Magic commands using percent (%)
%pwd - get current working directory
# %pwd
os.getcwd()
%ls - list items in directory
# %ls
os.listdir()
# %ls folderName/subFolder
os.listdir('folderName/subFolder')
%cd - change directory
# %cd test-directory
os.chdir('test-directory')
%mkdir - make a new directory
# %mkdir test/newFolder
os.makedirs('test/newFolder')
%mv - move file from one location to another
# %mv testFile.txt testFolder/
shutil.move('testFile.txt', 'testFolder/testFile.txt')
%cp - copy file from one location to another
# %cp testFolder/testFile.txt newFolder/newTestFile.txt
shutil.copy('testFolder/testFile.txt', 'newFolder/newTestFile.txt')
%cat - show the output of a file in standard format
# %cat testFolder/testFile.txt
cat_read_file = open('testFolder/testFile.txt', 'r')
cat_read_text = cat_read_file.read()
print(cat_read_text)
cat_read_file.close()
%env & %set_env - get, set or list environmental variables
this command actually has 5 ways to be used
%env
lists all environment variables/values
%env var
get value for var
[%env or %set_env] var val
set value for var
[%env or %set_env] var=val
set value for var
[%env or %set_env] var=$val
set value for var, using python expansion if possible
# %env
for k, v in os.environ.items():
print(f'{k}={v}')
# %env var
os.environ['var']
# %env var value
# %set_env var value
os.environ['var'] = 'value'
# %env var=value
# %set_env var=value
os.environ['var'] = 'value'
# %env var=$value
# %set_env var=$value
os.environ['var'] = '$value'
%pip - install a pip package or other pip functions
# %pip install colab-convert
pip_sub_p_res = subprocess.run(['pip', 'install', 'colab-convert'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE).stdout.decode('utf-8')
print(pip_sub_p_res)
%conda - install a conda package or other conda functions
# %conda install colab-convert
conda_sub_p_res = subprocess.run(['conda', 'install', 'colab-convert'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE).stdout.decode('utf-8')
print(conda_sub_p_res)
Unsupported Magic Commands
these will be commented out
# %quickref
#<cc-cm> %quickref
Example
colab-convert examples/plot.py examples/plot.ipynb
or
colab-convert examples/plot.ipynb examples/plot.py
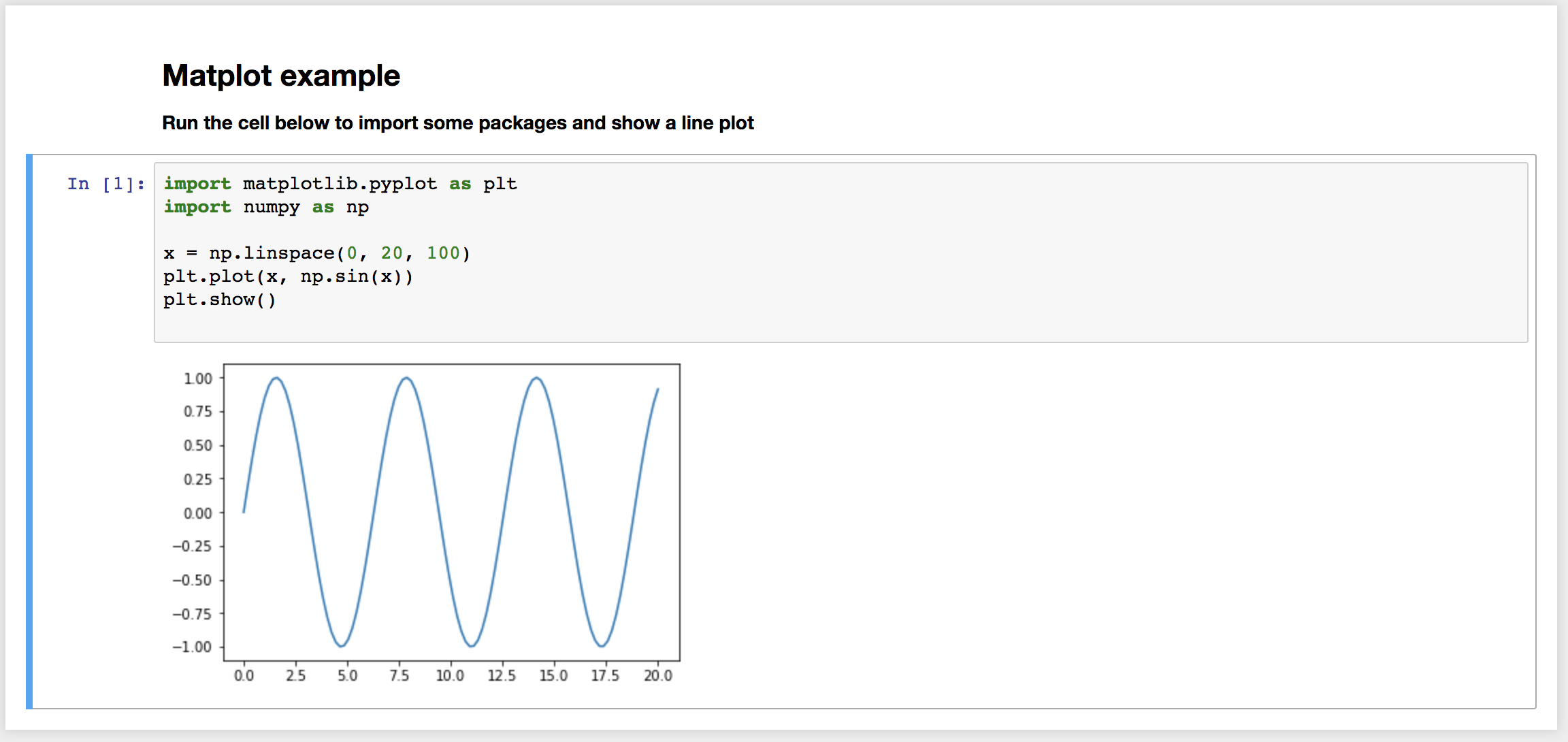
Markdown cells are converted to python multiline strings '''. Code cells are left as is.
eg. will render header section
"""
## Matplot example
** Run the cell below to import some packages and show a line plot **
"""
# %% is used by vscode as the cell marker on which 'Run Cell' action is available.
eg. will render a code cell
# %%
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Metadata is converted from notebooks into .py and vise versa using # !! to denote the meta data lines in the .py files
eg.
# %%
# !! {"metadata":{
# !! "id": "PlotIt"
# !! }}
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
eg. final code block must include atleast this
# %%
# !! {"main_metadata":{
# !! "anaconda-cloud": {},
# !! "kernelspec": {
# !! "display_name": "Python 3",
# !! "language": "python",
# !! "name": "python3"
# !! },
# !! "language_info": {
# !! "codemirror_mode": {
# !! "name": "ipython",
# !! "version": 3
# !! },
# !! "file_extension": ".py",
# !! "mimetype": "text/x-python",
# !! "name": "python",
# !! "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
# !! "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
# !! "version": "3.6.1"
# !! }
# !! }}
Troubleshooting
- If encoding problems on Windows try using
python>=3.7, settingset PYTHONUTF8=1in Windows console and usecolab-convertfor UTF-8 files only. If using Git-Bash on Windows setting:
export LANG=C.UTF-8
export PYTHONIOENCODING=utf-8
export PYTHONUTF8=1
should be enough. Also try setting default Bash settings to UTF-8: [Options] - [Text] - [Locale / Character set] - [C / UTF-8]. It might affect all Bash runs so there would be no need to setting encoding every time.
Credits
colab-convert is a fork of the ipynb-py-convert.
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
File details
Details for the file colab-convert-2.0.5.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: colab-convert-2.0.5.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 18.6 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.0 CPython/3.8.10
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
3009a84a600c51bc56baf3d391e0992d8b3b0d11dfe90bbde0665c737699816c
|
|
| MD5 |
4ece417f3e3361c287958c91edab61ad
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
19cdc67bd4a017b089a745687cd14c07e37ec13ce026397ebe8ec35165bea9bd
|