OpenFeature integration for Django
Project description
django-openfeature


⚠️ Caution: this repository is a work-in-progress. ⚠️
Django OpenFeature is a set of utilities to use OpenFeature in your Django applications.
Features
- Django Debug Toolbar integration
- Templatetags for flag evaluation
- Automatic evaluation context from request
- Flag override mechanism for testing
Installation
pip install django-openfeature
Add django_openfeature to your INSTALLED_APPS setting.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
# ...
'django_openfeature',
# ...
]
Usage
Flag Evaluation Helpers
django-openfeature provides a set of helpers to evaluate a feature flag:
from django_openfeature import feature
feature(request, 'my_feature', False)
The feature function will infer the type of the feature flag based on the default value provided
and call the appropriate resolver method.
It will also create an evaluation context from the request. This context can be configured via the
OPENFEATURE setting (described below).
Inside templates, you can use the feature template tag to evaluate feature flags. Remember to load the
openfeature library first.
{% load openfeature %}
{% feature 'my_feature' False as my_feature_enabled %}
{% if my_feature_enabed %}
<p>Feature is enabled</p>
{% else %}
<p>Feature is disabled</p>
{% endif %}
As an alternative to evaluating feature flags to a variable you can use the iffeature template tag.
It will output the contents of the block if the boolean flag resolves to True. It supports a single
{% else %} clause that will be displayed otherwise.
{% load openfeature %}
{% iffeature 'my_feature' %}
<p>Feature is enabled</p>
{% else %}
<p>Feature is disabled</p>
{% endif %}
Configuration
OPENFEATURE = {
"CONTEXT_EVALUATOR": "myapp.utils.get_evaluation_context",
}
The CONTEXT_EVALUATOR setting should point to a function that receives a request and returns an OpenFeature EvaluationContext as defined in the openfeature-sdk package.
Alternatively, the context evaluator can point to a class that produces callable instances with the same signature. The default context evaluator is django_openfeature.context.OpenFeatureContext and looks roughly like this:
class OpenFeatureContext:
targeting_key = "id"
targeting_key_anonymous = "unknown"
user_attributes = ("username", "email")
def get_context(self, request):
user = request.user
if not user or user.is_anonymous:
return EvaluationContext(self.targeting_key_anonymous)
return self.get_user_context(user)
def get_user_context(self, user):
attributes = {}
for attr in self.user_attributes:
attributes[attr] = getattr(user, attr)
targeting_key = str(getattr(user, self.targeting_key))
return EvaluationContext(targeting_key, attributes)
def __call__(self, request):
return self.get_context(request)
Use this class as base to declaratively define your own context evaluator. For example, to change the targeting key to the user's username:
from django_openfeature.context import OpenFeatureContext
class MyOpenFeatureContext(OpenFeatureContext):
targeting_key = "username"
Then in your settings:
OPENFEATURE = {
"CONTEXT_EVALUATOR": "myapp.utils.MyOpenFeatureContext",
}
Debug Toolbar Panel
django-openfeature comes with a Feature Flags panel for the Django Debug Toolbar. You can activate it by adding openfeature.debug_toolbar.panels.FeatureFlagsPanel to your DEBUG_TOOLBAR_PANELS setting.
DEBUG_TOOLBAR_PANELS = [
# ...
'openfeature.debug_toolbar.panels.FeatureFlagsPanel',
# ...
]
The Feature Flags panel will show you the feature flag evaluations for the current request, the request evaluation context and the configured providers for those evaluations.
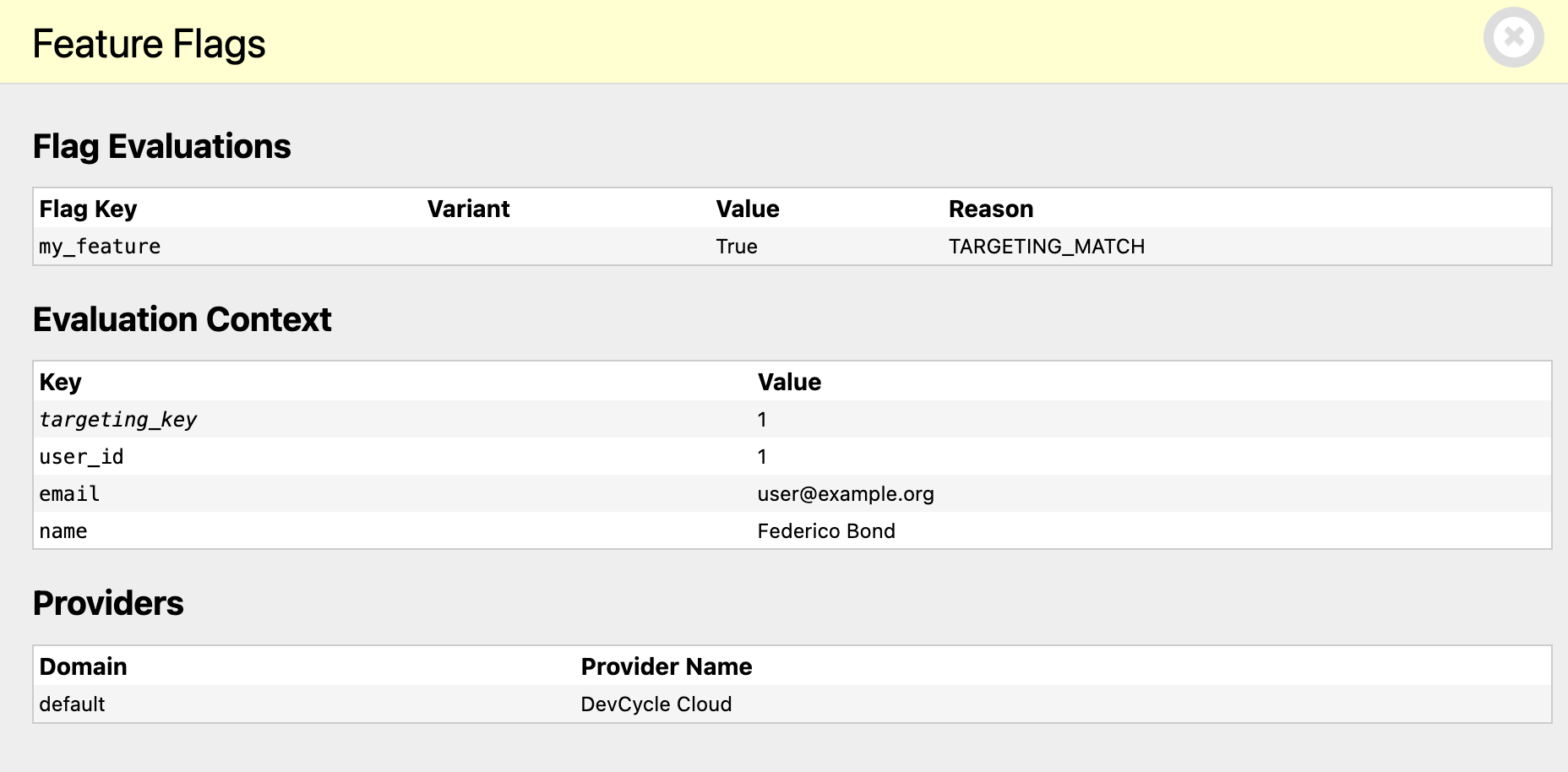
Testing Utilities
django-openfeature provides a set of utilities to help you test your feature flags. To use them, you must set the provider to an instance of django_openfeature.provider.DjangoTestProvider in your test settings.
# in your test settings
import openfeature.api
from django_openfeature.provider import DjangoTestProvider
openfeature.api.set_provider(DjangoTestProvider())
override_feature is a function decorator that allows you to override the value of a feature flag for the duration of a test.
from django_openfeature.test import override_feature
@override_feature('my_feature', True)
def test_my_feature_enabled(self):
# ...
Decorators can be stacked to override multiple feature flags.
You can also use override_feature as a context manager.
from django_openfeature.test import override_feature
def test_my_feature_enabled(self):
with override_feature('my_feature', True):
# ...
TODO
- Add support for OpenFeature domains (requires SDK release)
License
MIT License
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file django_openfeature-0.1.4.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: django_openfeature-0.1.4.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 12.4 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: Hatch/1.16.2 cpython/3.14.2 HTTPX/0.28.1
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
179c3c766f6dd3324ab5538dce525ff3ee4a47e9537d56f939c47c53bb096dab
|
|
| MD5 |
47471ea4b4648776406714718c47528c
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
ec6e664be009e5c67cb0e665031e783b73b366a0a6ed8adbe8f1206c82b79b62
|
File details
Details for the file django_openfeature-0.1.4-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: django_openfeature-0.1.4-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 11.0 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: Hatch/1.16.2 cpython/3.14.2 HTTPX/0.28.1
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
a09960e91bdb4998a3e3bb173e8022d3974e3cbc2c552badbcbc9e366db9c4be
|
|
| MD5 |
af4734f4169740a5f46002a359fcb202
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
3d10d9f42f911518b66ecbf216491f19c056e154ea9c636c4a531321e1c9b0c1
|












