Dynamic State Space Models in JAX.
Project description
Welcome to DYNAMAX!
Dynamax is a library for probabilistic state space models (SSMs) written in JAX. It has code for inference (state estimation) and learning (parameter estimation) in a variety of SSMs, including:
- Hidden Markov Models (HMMs)
- Linear Gaussian State Space Models (aka Linear Dynamical Systems)
- Nonlinear Gaussian State Space Models
- Generalized Gaussian State Space Models (with non-Gaussian emission models)
The library consists of a set of core, functionally pure, low-level inference algorithms, as well as a set of model classes which provide a more user-friendly, object-oriented interface. It is compatible with other libraries in the JAX ecosystem, such as optax (used for estimating parameters using stochastic gradient descent), and Blackjax (used for computing the parameter posterior using Hamiltonian Monte Carlo (HMC) or sequential Monte Carlo (SMC)).
Documentation
For tutorials and API documentation, see: https://probml.github.io/dynamax/.
For an extension of dynamax that supports structural time series models, see https://github.com/probml/sts-jax.
For an illustration of how to use dynamax inside of bayeux to perform Bayesian inference for the parameters of an SSM, see https://jax-ml.github.io/bayeux/examples/dynamax_and_bayeux/.
Installation and Testing
To install the latest releast of dynamax from PyPi:
pip install dynamax # Install dynamax and core dependencies, or
pip install dynamax[notebooks] # Install with demo notebook dependencies
To install the latest development branch:
pip install git+https://github.com/probml/dynamax.git
Finally, if you're a developer, you can install dynamax along with the test and documentation dependencies with:
git clone git@github.com:probml/dynamax.git
cd dynamax
pip install -e '.[dev]'
To run the tests:
pytest dynamax # Run all tests
pytest dynamax/hmm/inference_test.py # Run a specific test
pytest -k lgssm # Run tests with lgssm in the name
What are state space models?
A state space model or SSM is a partially observed Markov model, in which the hidden state, $z_t$, evolves over time according to a Markov process, possibly conditional on external inputs / controls / covariates, $u_t$, and generates an observation, $y_t$. This is illustrated in the graphical model below.
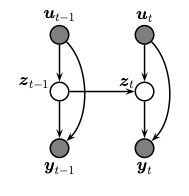
The corresponding joint distribution has the following form (in dynamax, we restrict attention to discrete time systems):
$$p(y_{1:T}, z_{1:T} \mid u_{1:T}) = p(z_1 \mid u_1) \prod_{t=2}^T p(z_t \mid z_{t-1}, u_t) \prod_{t=1}^T p(y_t \mid z_t, u_t)$$
Here $p(z_t | z_{t-1}, u_t)$ is called the transition or dynamics model, and $p(y_t | z_{t}, u_t)$ is called the observation or emission model. In both cases, the inputs $u_t$ are optional; furthermore, the observation model may have auto-regressive dependencies, in which case we write $p(y_t | z_{t}, u_t, y_{1:t-1})$.
We assume that we see the observations $y_{1:T}$, and want to infer the hidden states, either using online filtering (i.e., computing $p(z_t|y_{1:t})$ ) or offline smoothing (i.e., computing $p(z_t|y_{1:T})$ ). We may also be interested in predicting future states, $p(z_{t+h}|y_{1:t})$, or future observations, $p(y_{t+h}|y_{1:t})$, where h is the forecast horizon. (Note that by using a hidden state to represent the past observations, the model can have "infinite" memory, unlike a standard auto-regressive model.) All of these computations can be done efficiently using our library, as we discuss below. In addition, we can estimate the parameters of the transition and emission models, as we discuss below.
More information can be found in these books:
- "Machine Learning: Advanced Topics", K. Murphy, MIT Press 2023. Available at https://probml.github.io/pml-book/book2.html.
- "Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing, Second Edition", S. Särkkä and L. Svensson, Cambridge University Press, 2023. Available at http://users.aalto.fi/~ssarkka/pub/bfs_book_2023_online.pdf
Example usage
Dynamax includes classes for many kinds of SSM. You can use these models to simulate data, and you can fit the models using standard learning algorithms like expectation-maximization (EM) and stochastic gradient descent (SGD). Below we illustrate the high level (object-oriented) API for the case of an HMM with Gaussian emissions. (See this notebook for a runnable version of this code.)
import jax.numpy as jnp
import jax.random as jr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from dynamax.hidden_markov_model import GaussianHMM
key1, key2, key3 = jr.split(jr.PRNGKey(0), 3)
num_states = 3
emission_dim = 2
num_timesteps = 1000
# Make a Gaussian HMM and sample data from it
hmm = GaussianHMM(num_states, emission_dim)
true_params, _ = hmm.initialize(key1)
true_states, emissions = hmm.sample(true_params, key2, num_timesteps)
# Make a new Gaussian HMM and fit it with EM
params, props = hmm.initialize(key3, method="kmeans", emissions=emissions)
params, lls = hmm.fit_em(params, props, emissions, num_iters=20)
# Plot the marginal log probs across EM iterations
plt.plot(lls)
plt.xlabel("EM iterations")
plt.ylabel("marginal log prob.")
# Use fitted model for posterior inference
post = hmm.smoother(params, emissions)
print(post.smoothed_probs.shape) # (1000, 3)
JAX allows you to easily vectorize these operations with vmap.
For example, you can sample and fit to a batch of emissions as shown below.
from functools import partial
from jax import vmap
num_seq = 200
batch_true_states, batch_emissions = \
vmap(partial(hmm.sample, true_params, num_timesteps=num_timesteps))(
jr.split(key2, num_seq))
print(batch_true_states.shape, batch_emissions.shape) # (200,1000) and (200,1000,2)
# Make a new Gaussian HMM and fit it with EM
params, props = hmm.initialize(key3, method="kmeans", emissions=batch_emissions)
params, lls = hmm.fit_em(params, props, batch_emissions, num_iters=20)
These examples demonstrate the dynamax models, but we can also call the low-level inference code directly.
Contributing
Please see this page for details on how to contribute.
About
Core team: Peter Chang, Giles Harper-Donnelly, Aleyna Kara, Xinglong Li, Scott Linderman, Kevin Murphy.
Other contributors: Adrien Corenflos, Elizabeth DuPre, Gerardo Duran-Martin, Colin Schlager, Libby Zhang and other people listed here
MIT License. 2022
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file dynamax-1.0.1.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: dynamax-1.0.1.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 137.3 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
197d566bb1ede90652a0bc0b65f1cb9eba0a6af5f8d3b8fb9b9cf94b1978a492
|
|
| MD5 |
8320e2073e5f394dca05164970c3de9d
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
94d3875a498f7e00537b2f02637ed5e48fd4ff113cbb83a274a73f36ee682e9c
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for dynamax-1.0.1.tar.gz:
Publisher:
publish-to-pypi.yml on probml/dynamax
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
dynamax-1.0.1.tar.gz -
Subject digest:
197d566bb1ede90652a0bc0b65f1cb9eba0a6af5f8d3b8fb9b9cf94b1978a492 - Sigstore transparency entry: 209865058
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
probml/dynamax@d603b10f1bc73cc25b89c86a18d32fa4442cf2fc -
Branch / Tag:
refs/tags/1.0.1 - Owner: https://github.com/probml
-
Access:
public
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
publish-to-pypi.yml@d603b10f1bc73cc25b89c86a18d32fa4442cf2fc -
Trigger Event:
release
-
Statement type:
File details
Details for the file dynamax-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: dynamax-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 157.1 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
98748e72514d990c8a1a67392efd496320f1f1b8c174fca0dd75b9d8bc3ff0d7
|
|
| MD5 |
645a79c8bb7b0d3c8445c371e6f4f9cd
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
07c3f5a363f98e2b4db504e3852d271f7769c855dddae5e9e9c4b031eff85b23
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for dynamax-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl:
Publisher:
publish-to-pypi.yml on probml/dynamax
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
dynamax-1.0.1-py3-none-any.whl -
Subject digest:
98748e72514d990c8a1a67392efd496320f1f1b8c174fca0dd75b9d8bc3ff0d7 - Sigstore transparency entry: 209865061
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
probml/dynamax@d603b10f1bc73cc25b89c86a18d32fa4442cf2fc -
Branch / Tag:
refs/tags/1.0.1 - Owner: https://github.com/probml
-
Access:
public
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
publish-to-pypi.yml@d603b10f1bc73cc25b89c86a18d32fa4442cf2fc -
Trigger Event:
release
-
Statement type: