A package for causal inference and statistical modeling in brain time series
Project description
effconnpy
Overview

Effconnpy is a Python library for advanced causal inference and connectivity analysis in time series data, offering both bivariate and multivariate approaches.
The toolbox assumes that neuroimging data (e.g. from Nifti files) have been already pre-processed e.g. with fMRI-prep, and parcellated, therefore the time series have been saved in text files as .tsv
and can easily be loaded into a dataframe.
Bivariate Causality Analysis

Two core classes provide bivariate causal inference methods:
1. CausalityAnalyzer
Basic methods include:
- Bivariate Granger Causality (traditional linear, and non-linear implemented by reservoir computing networks)
- Bivariate Transfer Entropy
- Bivariate Convergent Cross Mapping
2. ExtendedCausalityAnalyzer
Extended methods include:
- Dynamic Bayesian Network
- Structural Equation Modeling
- DoWhy Causal Discovery
- Dynamic Causal Modeling
Multivariate Causality Analysis
Three specialized multivariate approaches:
1. Multivariate Granger Causality
- Based on methodology by Barnett & Seth, Journal of Neuroscience Methods 2014
- VAR model-based causality inference
- Log-likelihood ratio testing
2. Multivariate Convergent Cross-Mapping (CCM)
- Inspired by Nithya & Tangirala, ICC 2019
- Nonlinear causality detection
- Network-based causal relationship visualization
3. Multivariate Transfer Entropy
- Methodology from Duan et al. 2022
- Information-theoretic causality measure
- Supports conditional transfer entropy
N.B. The multivariate implementations are not considered state-of-the-art and are not fully tested, please report any error or bug.
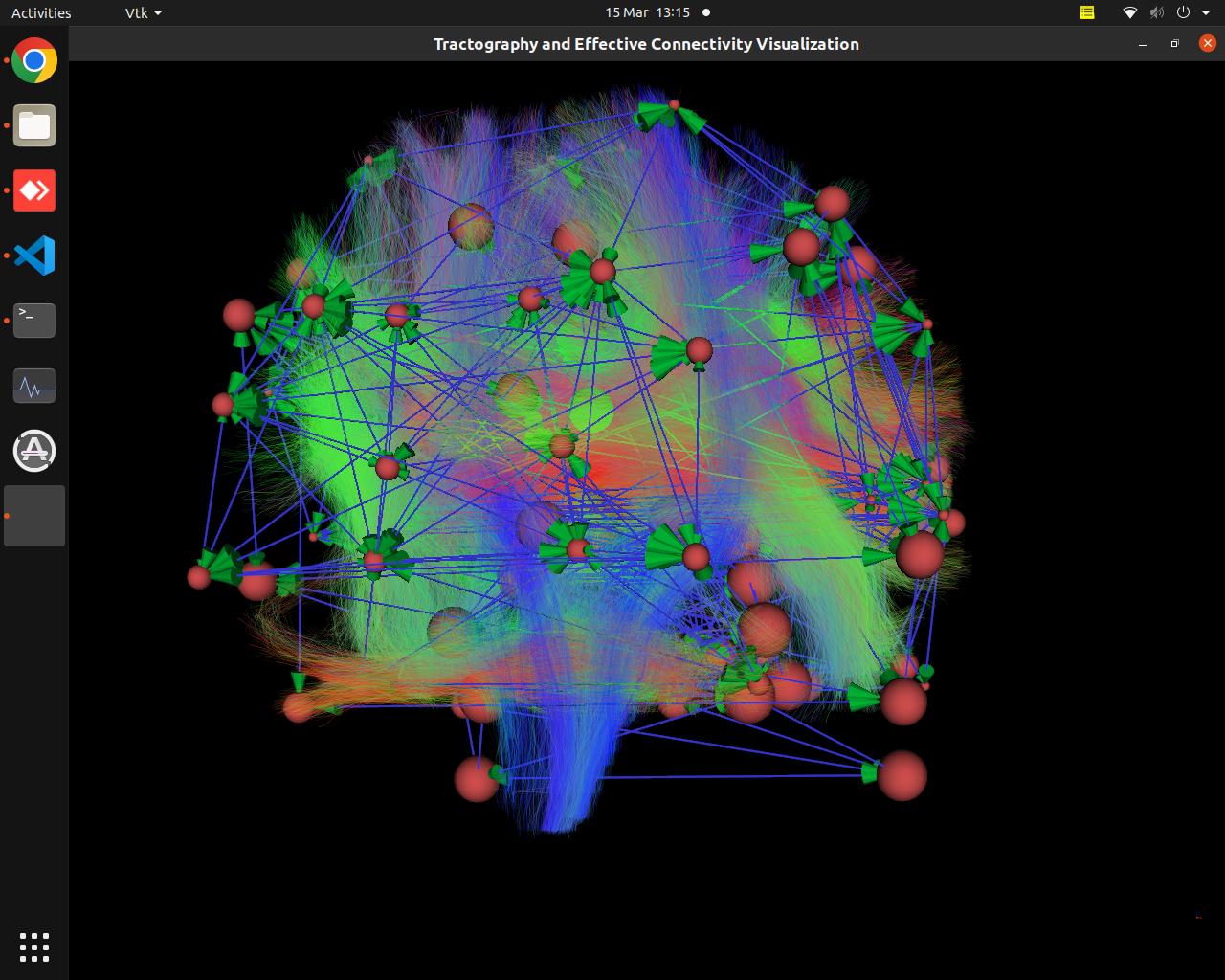
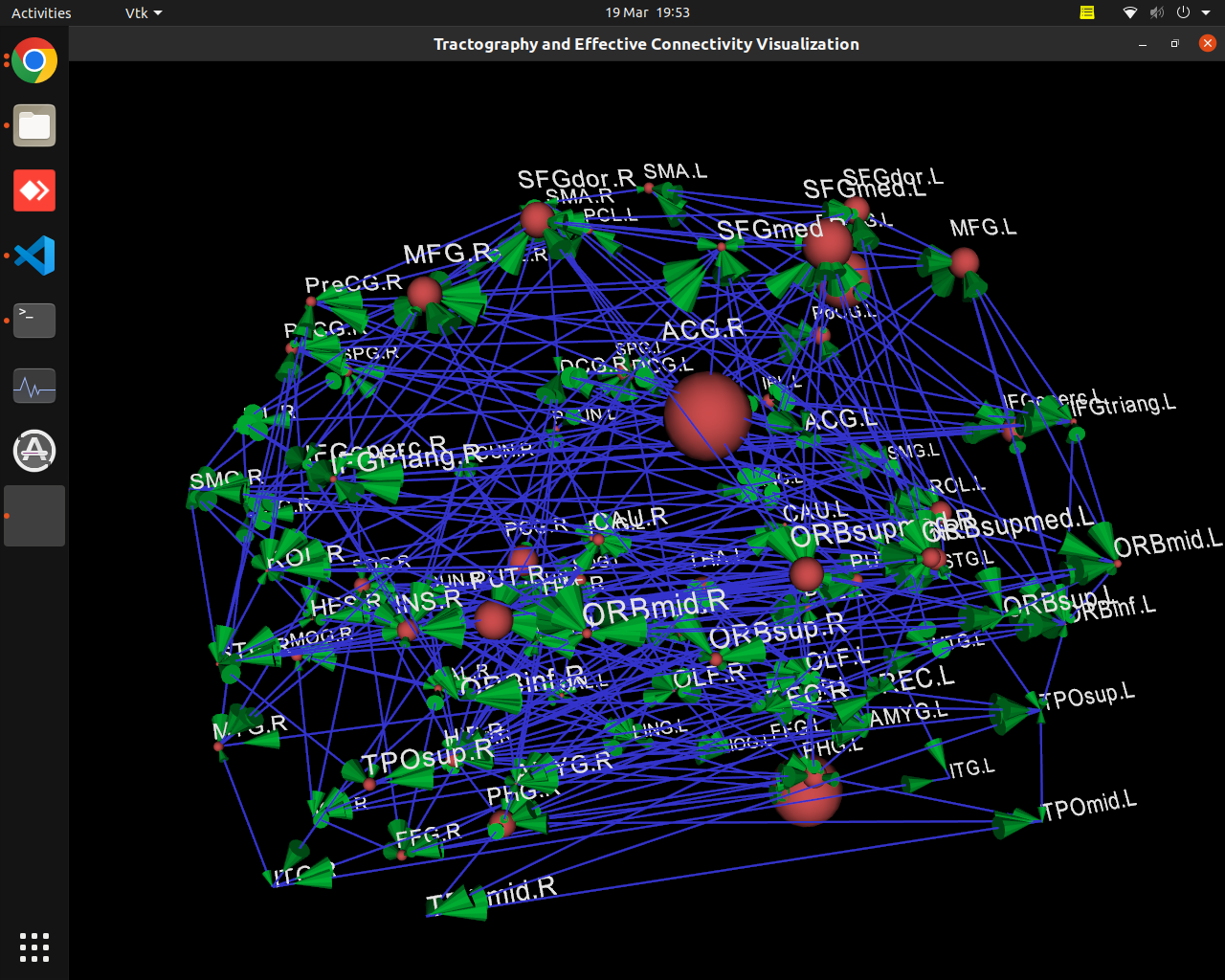
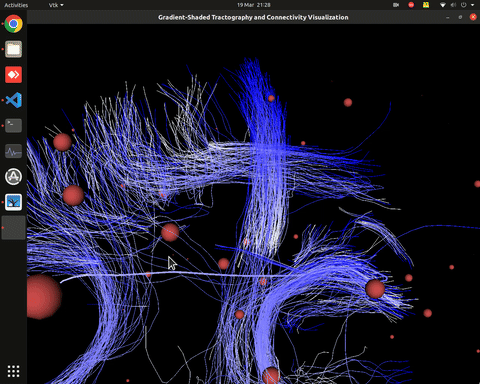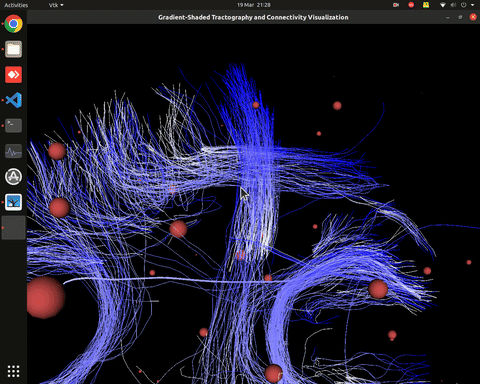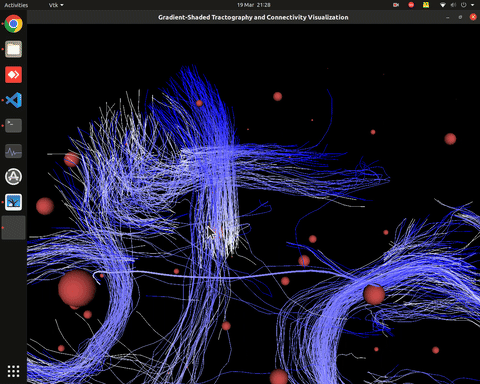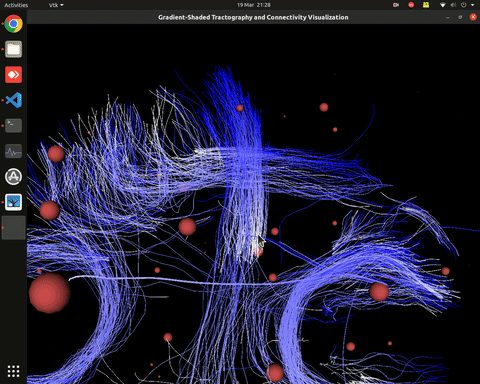
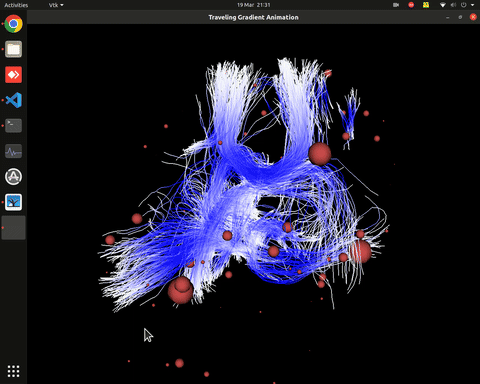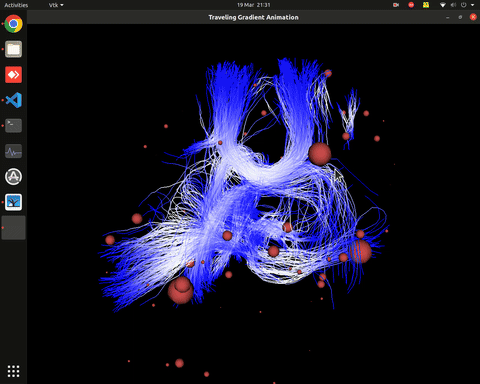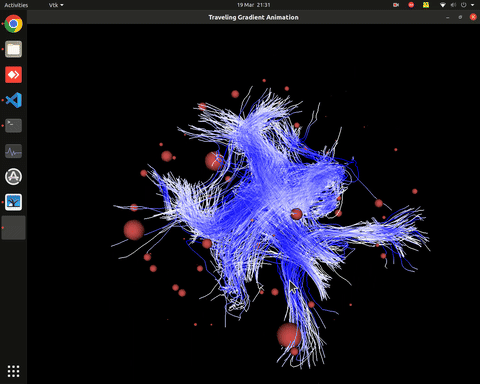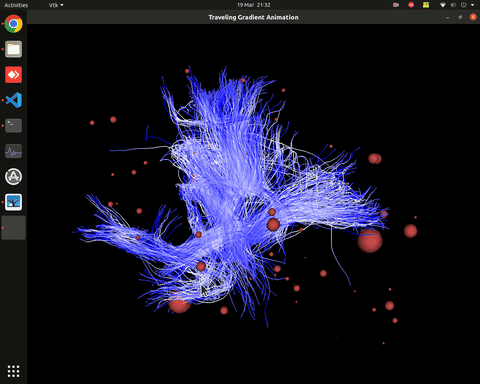
Visualization of effective connectivity
-
Plotting of directed graphs, also overlapping with tractography and node labels
-
Directionality of the connections as color gradients
-
Visualization of time series over structural connections (currently not working properly[https://github.com/alecrimi/effconnpy/issues/8])
Installation
pip install effconnpy
Quick Example
from effconnpy import CausalityAnalyzer , create_connectivity_matrix
import numpy as np
# Generate sample time series
data = np.random.rand(100, 3)
analyzer = CausalityAnalyzer(data)
results = analyzer.causality_test(method='granger')
print(results)
binary_matrix = create_connectivity_matrix(results, method = 'granger')
print(binary_matrix)
Multivariate GC Example using causal logistic maps
from effconnpy.multivariateGC import MultivariateGrangerCausality
from effconnpy import create_connectivity_matrix
import numpy as np
# Generate sample time series
#The first 2 time series are related by a logistic causal mapping,
#while the third is random and has no causal relationship with the others
# Parameters
T = 100 # Number of time steps
x = np.zeros(T)
y = np.zeros(T)
# Initial conditions
x[0] = 0.5
y[0] = 0.5
# Iterate the system
for t in range(T - 1):
x[t + 1] = x[t] * (3.8 - 3.8 * x[t])
y[t + 1] = y[t] * (3.1 - 3.1 * y[t] - 0.8 * x[t])
z = np.random.rand(100)
data = np.vstack((x, y,z)).T
analyzer = MultivariateGrangerCausality(data)
results = analyzer.multivariate_granger_causality()
print(results)
Indeed, there is also a causal time series generator script to generate ground-truth time series which can be complemented by random or other time series:
from effconnpy import timeseriesgenerator
# Create an instance of the generator
generator = TimeSeriesGenerator()
# Generate some example data
n_points = 1000
# Lorenz system
t, x, y, z = generator.lorenz_system(n_points)
# Coupled logistic map
logistic_x, logistic_y = generator.coupled_logistic_map(n_points)
# Kuramoto oscillators
kura1, kura2 = generator.kuramoto_oscillators(n_points)
# AR process
ar_x, ar_y = generator.ar_process(n_points)
# Nonlinear coupled system
nl_x, nl_y = generator.nonlinear_coupled_system(n_points)
Visualization of effective connectivity example
from effconnpy import vis_effconn
node_file = "Node_AAL90.node"
edge_file = "my_effconn.csv"
vis_effconn(node_file, edge_file, show_tractography=True)
This will show the overlay of a tractography from the HCP dataset over a connectome according to an atlas with given nodes coordinates, and the effective connectivity computed and saved in a csv file. If a structural connectivity matrix (non-effective) is passed, the function will show arrows on both directions for all edges.
Citation
If you use the tool please refer to those papers
"Structurally constrained Granger causality" A. Crimi et al. Neuroimage 2021
Contributing
Contributions welcome! Please read our contributing guidelines before submitting pull requests. Currently disabled, just open issues and I will follow up
License
MIT License
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file effconnpy-0.1.25.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: effconnpy-0.1.25.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 27.7 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.4
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9203c2873512bb5a5d96f61eed5d332d2c1861ff8bb35965e66a1bfae7b7f034
|
|
| MD5 |
def4e255c166b9a8b835783c44823925
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
362f6e24d529ebb04fcac7028b9eca435d41f31dc76ea5fd9293db68598990a5
|
File details
Details for the file effconnpy-0.1.25-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: effconnpy-0.1.25-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 33.4 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.4
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
2fd01ebbceafc47a7736e503b574b5421911fb79b2d54a817b587c65261530d5
|
|
| MD5 |
57f7812781c7dc8e6551698f6ed33b61
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
0c778bf0947d05f2f88753da3a898f06b53921817234309c79bdabc2bb63bbc0
|















