Efficient Python library for Evolutionary Game Theory (EGT)
Project description
EGTTools – Evolutionary Game Theory Toolbox
EGTTools is a modular toolbox for simulating and analyzing evolutionary dynamics in strategic environments. It combines analytical methods (replicator dynamics, fixation probabilities) and numerical simulations (Monte Carlo with parallel C++ backends) under a unified interface.
📑 Table of Contents
Testing & Continuous Integration
- Features
- Installation
- Platform Notes
- Advanced Configuration
- Build from Source
- Usage Examples
- Documentation
- Testing & CI
- Citation
- License
- Acknowledgements
- Caveats
🚀 Features
- ✅ Replicator dynamics for 2-strategy and N-player games
- ✅ Stochastic dynamics using the pairwise comparison rule
- ✅ Numerical simulation of evolutionary processes in finite populations
- ✅ Monte Carlo estimation of fixation probabilities and strategy distributions
- ✅ OpenMP parallelization for large-scale simulations (Linux/macOS)
- ✅ Modular game and strategy framework, extensible in both Python and C++
- ✅ Visual tools for plotting gradients, stationary distributions, and simplex diagrams
- ✅ Support for Boost, Eigen, and BLAS integration (configurable)
- ✅ Cross-platform wheels (Linux, macOS, Windows; x86_64 and ARM64)
📦 Installation
EGTTools is distributed via PyPI and includes prebuilt wheels for major platforms:
| Platform | Architectures | Python Versions | OpenMP Supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linux (x86_64) | x86_64 | 3.10 – 3.12 | ✅ Yes |
| macOS (x86/arm) | x86_64, arm64 (M1/M2) | 3.10 – 3.12 | ✅ Yes |
| Windows | x86_64, arm64 | 3.10 – 3.12 | ❌ Not available |
▶️ Install with pip
pip install egttools
For a more reliable installation on macOS with conda-based environments:
conda install numpy scipy matplotlib networkx seaborn pip install egttools --no-deps
🖥️ Platform Notes
🐧 Linux
- OpenMP is fully supported and enabled by default.
- Wheels are built with optimized BLAS/LAPACK and Boost.
- Recommended for high-performance simulation runs.
🍎 macOS (Intel or Apple Silicon)
- Supported on both
x86_64andarm64. - OpenMP is enabled by default and linked via
libomp. - If using
conda, preferminiforgeormambaforgefor ABI compatibility. - To skip dependency resolution and control packages manually:
pip install egttools --no-deps
conda install numpy scipy matplotlib networkx seaborn
🪟 Windows (x86_64 and ARM64)
- Windows wheels are available for both Intel and ARM architectures.
- OpenMP is currently not available on Windows.
- Simulations will fall back to single-threaded mode.
- BLAS/LAPACK can be enabled via conda or system libraries if building from source.
⚙️ Advanced Configuration (BLAS, OpenMP, vcpkg)
The C++ backend of EGTTools supports several build-time options that can be toggled when building from source:
| Feature | CMake Option | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenMP | -DEGTTOOLS_USE_OPENMP=ON |
ON (Linux/macOS) | Enables parallel computation for simulations |
| BLAS/LAPACK | -DEGTTOOLS_USE_BLAS=ON |
OFF | Enables matrix acceleration (e.g., OpenBLAS) |
| Use vcpkg | -DEGTTOOLS_USE_VCPKG=ON |
ON | Automatically fetches Boost and Eigen |
| Disable vcpkg | -DEGTTOOLS_USE_VCPKG=OFF |
Allows using system-provided libraries manually |
🧰 When to disable vcpkg
You may want to disable vcpkg in CI environments or when using a distribution that provides all necessary dependencies
system-wide. To do this:
cmake -DEGTTOOLS_USE_VCPKG=OFF .
In this case, you are responsible for ensuring that compatible versions of Boost and Eigen are available in your system paths.
🔧 Build from Source (with vcpkg)
To build EGTTools from source with all dependencies managed via vcpkg, run:
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/Socrats/EGTTools.git
cd EGTTools
pip install .
To configure optional features manually, such as OpenMP or BLAS support:
cmake -DEGTTOOLS_USE_OPENMP=ON -DEGTTOOLS_USE_BLAS=ON -DEGTTOOLS_USE_VCPKG=OFF .
make
If using conda, make sure to activate your environment first and ensure that Python, NumPy, and compiler toolchains
are compatible.
🧪 Usage Examples
Calculate Gradient of Selection
from egttools.analytical import PairwiseComparison
from egttools.games import Matrix2PlayerGameHolder
A = [[-0.5, 2], [0, 0]]
game = Matrix2PlayerGameHolder(2, A)
evolver = PairwiseComparison(100, game)
gradient = evolver.calculate_gradient_of_selection(beta=1.0, state=[10, 90])
Estimate fixation probability numerically
from egttools.numerical import PairwiseComparisonNumerical
from egttools.games import Matrix2PlayerGameHolder
A = [[-0.5, 2], [0, 0]]
game = Matrix2PlayerGameHolder(2, A)
numerical_evolver = PairwiseComparisonNumerical(game, population_size=100, cache=1_000_000)
fp = numerical_evolver.estimate_fixation_probability(
index_invading_strategy=1,
index_resident_strategy=0,
nb_runs=500,
nb_generations=5000,
beta=1.0
)
More Examples of usage
The Analytical example is a jupyter notebook which analyses analytically the evolutionary dynamics in a (2-person, 2-actions, one-shot) Hawk-Dove game.
The Numerical example is a jupyter notebook which analyses through numerical simulations the evolutionary dynamics in a (2-person, 2-actions, one-shot) Hawk-Dove game.
The Invasion example is a jupyter notebook calculates the fixation probabilities and stationary distribution of a Normal Form Game with 5 strategies and then plots an invasion diagram.
The Plot 2 Simplex is a jupyter notebook that shows how to use EGTtools to plot the evolutionary dynamics in a 2 Simplex (a triangle), both for infinite and finite populations.
You can also check all these notebooks and a bit more on this tutorial repository
For example, assuming the following payoff matrix:
You can plot the gradient of selection in a finite population of (Z=100) individuals and assuming and intensity of
selection 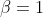
import numpy as np
from egttools.analytical import PairwiseComparison
from egttools.games import Matrix2PlayerGameHolder
beta = 1;
Z = 100;
nb_strategies = 2;
A = np.array([[-0.5, 2.], [0., 0.]])
pop_states = np.arange(0, Z + 1, 1)
game = Matrix2PlayerGameHolder(nb_strategies, payoff_matrix=A)
# Instantiate evolver and calculate gradient
evolver = PairwiseComparison(population_size=Z, game=game)
gradients = np.array([evolver.calculate_gradient_of_selection(beta, np.array([x, Z - x])) for x in range(Z + 1)])
Afterward, you can plot the results with:
from egttools.plotting import plot_gradients
plot_gradients(gradients, figsize=(4, 4), fig_title="Hawk-Dove game stochastic dynamics",
marker_facecolor='white',
xlabel="frequency of hawks (k/Z)", marker="o", marker_size=20, marker_plot_freq=2)
And you can plot the stationary distribution for a mutation
rate 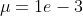
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from egttools.utils import calculate_stationary_distribution
transitions = evolver.calculate_transition_matrix(beta, mu=1e-3)
stationary_with_mu = calculate_stationary_distribution(transitions.transpose())
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 4))
fig.patch.set_facecolor('white')
lines = ax.plot(np.arange(0, Z + 1) / Z, stationary_with_mu)
plt.setp(lines, linewidth=2.0)
ax.set_ylabel('stationary distribution', size=16)
ax.set_xlabel('$k/Z$', size=16)
ax.set_xlim(0, 1)
plt.show()
We can get the same results through numerical simulations. The error will depend on how many independent simulations you perform and for how long you let the simulation run. While a future implementation will offer an adaptive method to vary these parameters depending on the variations between the estimated distributions, for the moment it is important that you let the simulation run for enough generations after it has achieved a steady state. Here is a comparison between analytical and numerical results:
from egttools.numerical import PairwiseComparisonNumerical
from egttools.games import NormalFormGame
# Instantiate the game
game = NormalFormGame(1, A)
numerical_evolver = PairwiseComparisonNumerical(Z, game, 1000000)
# We do this for different betas
betas = np.logspace(-4, 1, 50)
stationary_points = []
# numerical simulations
for i in range(len(betas)):
stationary_points.append(numerical_evolver.stationary_distribution(30, int(1e6), int(1e3),
betas[i], 1e-3))
stationary_points = np.asarray(stationary_points)
# Now we estimate the probability of Cooperation for each possible state
state_frequencies = np.arange(0, Z + 1) / Z
coop_level = np.dot(state_frequencies, stationary_points.T)
Lastly, we plot the results:
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
mse = mean_squared_error(1 - coop_level_analytical, coop_level)
# Finally, we plot and compare visually (and check how much error we get)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 5))
# ax.scatter(betas, coop_level, label="simulation")
ax.scatter(betas, coop_level_analytical, marker='x', label="analytical")
ax.scatter(betas, coop_level, marker='o', label="simulation")
ax.text(0.01, 0.535, 'MSE = {0:.3e}'.format(mse), style='italic',
bbox={'facecolor': 'red', 'alpha': 0.5, 'pad': 10})
ax.legend()
ax.set_xlabel(r'$\beta$', fontsize=15)
ax.set_ylabel('Cooperation level', fontsize=15)
ax.set_xscale('log')
plt.show()
Finally, you may also visualize the result of independent simulations:
init_states = np.random.randint(0, Z + 1, size=10, dtype=np.uint64)
output = []
for i in range(10):
output.append(evolver.run(int(1e6), 1, 1e-3,
[init_states[i], Z - init_states[i]]))
# Plot each year's time series in its own facet
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 4))
for run in output:
ax.plot(run[:, 0] / Z, color='gray', linewidth=.1, alpha=0.6)
ax.set_ylabel('k/Z')
ax.set_xlabel('generation')
ax.set_xscale('log')
Plotting the dynamics in a 2 Simplex
EGTtools can also be used to visualize the evolutionary dynamics in a 2 Simplex. In the example bellow, we use the
egttools.plotting.plot_replicator_dynamics_in_simplex which calculates the gradients on a simplex given an initial
payoff matrix and returns a egttools.plotting.Simplex2D object which can be used to plot the 2 Simplex.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from egttools.plotting import plot_replicator_dynamics_in_simplex
payoffs = np.array([[1, 0, 0],
[0, 2, 0],
[0, 0, 3]])
type_labels = ['A', 'B', 'C']
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8))
simplex, gradient_function, roots, roots_xy, stability = plot_replicator_dynamics_in_simplex(payoffs, ax=ax)
plot = (simplex.add_axis(ax=ax)
.draw_triangle()
.draw_gradients(zorder=0)
.add_colorbar()
.add_vertex_labels(type_labels)
.draw_stationary_points(roots_xy, stability)
.draw_trajectory_from_roots(gradient_function,
roots,
stability,
trajectory_length=15,
linewidth=1,
step=0.01,
color='k', draw_arrow=True,
arrowdirection='right',
arrowsize=30, zorder=4, arrowstyle='fancy')
.draw_scatter_shadow(gradient_function, 300, color='gray', marker='.', s=0.1, zorder=0)
)
ax.axis('off')
ax.set_aspect('equal')
plt.xlim((-.05, 1.05))
plt.ylim((-.02, simplex.top_corner + 0.05))
plt.show()
The same can be done for finite populations, with the added possibility to plot the stationary distribution inside the triangle (see simplex plotting and simplified simplex plotting for a more in-depth example).
📚 Documentation
- 📘 API Reference (ReadTheDocs): https://egttools.readthedocs.io
- 🌍 Live Tutorial & Examples: https://efernandez.eu/EGTTools/
You can find a full description of available games, strategies, and simulation methods, along with Jupyter notebooks and real-world use cases.
🧪 Testing & Continuous Integration
EGTTools uses GitHub Actions for full CI/CD automation:
- 🧱
wheels.ymlbuilds wheels for all platforms (Linux, macOS, Windows; x86_64 and arm64) - 📘
docs.ymlbuilds documentation and deploys it to GitHub Pages and ReadTheDocs - ✅ Unit tests run with
pytestand are included in each CI matrix build - 🧪 Python stub files are auto-generated from
pybind11bindings for better typing support
To run tests locally:
pytest tests
You can also build and validate docs locally with:
cd docs
make html
📖 Citation
If you use EGTtools in your publications, please cite it in the following way with bibtex:
@article{Fernandez2023,
author = {Fernández Domingos, Elias and Santos, Francisco C. and Lenaerts, Tom},
title = {EGTtools: Evolutionary game dynamics in Python},
journal = {iScience},
volume = {26},
number = {4},
pages = {106419},
year = {2023},
issn = {2589-0042},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2023.106419}
}
Or in text format:
Fernández Domingos, E., Santos, F. C. & Lenaerts, T. EGTtools: Evolutionary game dynamics in Python. iScience 26, 106419 (2023).
And to cite the current version of EGTtools you can use:
@misc{Fernandez2020,
author = {Fernández Domingos, Elias},
title = {EGTTools: Toolbox for Evolutionary Game Theory (0.1.12)},
year = {2022},
month = {Dec},
journal = {Zenodo},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.7458631}
}
Moreover, you may find our article at here.
📄 License
EGTTools is released under the GPLv3 or later.
🙏 Acknowledgements
Developed and maintained by Elias Fernández.
- Great parts of this project have been possible thanks to the help of Yannick Jadoul author of Parselmouth and Eugenio Bargiacchi author of AIToolBox. They are both great programmers and scientists, so it is always a good idea to check out their work.
- EGTtools makes use of the amazing pybind11. library to provide a Python interface for optimized monte-carlo simulations written in C++.
⚠️ Caveats
- On Windows, OpenMP is currently not supported. All simulations will run single-threaded.
- On macOS, OpenMP is supported but performance may depend on the installed
libomp. If usingconda, make surellvm-openmpis available. - Wheels are only built for Python 3.10 – 3.12.
- Numerical simulations require large RAM allocations when using large population sizes or caching; ensure you configure the
cachesize accordingly. - Advanced users building from source should ensure Boost, Eigen, and BLAS/LAPACK libraries are compatible with their compiler toolchain.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distributions
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 3.4 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
55abc057b1f0897351205f25940b19b9998bc982ef3a921f4fbf84012dbcdb9f
|
|
| MD5 |
1b98122dc2c1f110c08087a0929ce7ca
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
e2703fdb2ddc369eccfdd90156da85060d968b0b28d6f83b7ff1dc459615aa55
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-win_arm64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-win_arm64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.6 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.12, Windows ARM64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
77a37839ab9447e31cb9714686cee16f1c10845fae6fb2e12dd3612688a77fba
|
|
| MD5 |
e6c8286486594d94f0453f018b876ad8
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
a59347c858c868778fd103fd9163e6e9b5a8d0c48dbb8a24d04a0d1421dcbef6
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-win_amd64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-win_amd64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.9 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.12, Windows x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
feae3675855f4eb19e266027f4b0ca8381a3f2dd2301949911a83f0af02a891b
|
|
| MD5 |
1d6419e83b84216cf9d5a26eaab8a950
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
2d734f3856c991f2c76431193d6b1e6c17daeec9380af44cb09199e0c89539d8
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-manylinux2014_x86_64.manylinux_2_17_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-manylinux2014_x86_64.manylinux_2_17_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 15.8 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.12, manylinux: glibc 2.17+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
f6533ebac5575c8387e7ea7ee17ce7fa135c4ce16d5e699878dbbdfe39b9d824
|
|
| MD5 |
8832481fdf081556fd4052fa31c2475f
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
8d3638d101cd85cab73b89db8e42de0755d7d54099e8fd7d7a2d28e0e8871c76
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-macosx_14_0_arm64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-macosx_14_0_arm64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.12, macOS 14.0+ ARM64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
38d4eb75308f6f809b2cdb5c917bfbcd5c4da7002f7507f1da6e8fab9375547c
|
|
| MD5 |
ebadfea9e44087beb6e8ee85e5a1ffc8
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
4add0068a0c9be16bc1dd0e1d753bb05b632aa4f8123eff8d3abe1f97be84570
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-macosx_13_0_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp312-cp312-macosx_13_0_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.2 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.12, macOS 13.0+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
8c64568c95937adb77b75164efb7eb215409c534073f900ba586cac405b62fbc
|
|
| MD5 |
9524c26f0712dbffa2ba26232ee7f893
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
18747b17ef476b08c561592d484578a2be498924517b4ea6c68a5180c210aba3
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-win_arm64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-win_arm64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.6 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.11, Windows ARM64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
50a29f4c2f75461f85c665ee3a2aafba5cd14b352b50122b85f6ea0cdb3b728d
|
|
| MD5 |
a90a270f253edc88633f7eb3b8213b65
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
2baf11705eaeb758ce3a385ef7d8bad87ef59c6afba8b31c09866fb2040ffe66
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-win_amd64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-win_amd64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.9 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.11, Windows x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
7d8e9385da6b6b311816378d4195e839723f75df7e37804be2ddf0dfe6472256
|
|
| MD5 |
369f0f1dba11c38e83954e245db25c23
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
124d351f932887783448b334f48a9b1e51d02d833c6a04fce4edf8d427be9979
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-manylinux2014_x86_64.manylinux_2_17_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-manylinux2014_x86_64.manylinux_2_17_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 15.8 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.11, manylinux: glibc 2.17+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
e1f0ae13c0dbdff739018302e5c72bf6b8864fe1cd32be95dd7d1660e5004abd
|
|
| MD5 |
f71d4d747dacea82e42369a041edfb05
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
c6b26203872745dfc2519218a0f019e7c941ebd973553f7de27e1bb2b0c435e1
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-macosx_14_0_arm64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-macosx_14_0_arm64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.11, macOS 14.0+ ARM64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
fd7fc6f893a31c92e3c3a9e0a40e647e1707a281bf891c5990f4832536fe0e6b
|
|
| MD5 |
3ec5fedc8529a85b028094c62fb9b61b
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
a7ddbb6cd70603870c7edfe65d22cf00e36fe367ea9981414c73cd04c12028d9
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-macosx_13_0_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp311-cp311-macosx_13_0_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.2 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.11, macOS 13.0+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
f8b39a20a9a248272882104ab616a2e36656f054f8a759e2e3f48f01d67c6c08
|
|
| MD5 |
46ade5aecb172ee6eba7733f7a95a577
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
1789ce8dd84548b1cbd93a5b62465c4c175503a6a0c4b43c0ecbe4a4334ecefc
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-win_arm64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-win_arm64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.6 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.10, Windows ARM64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
c11155a8ba9c8576248216281b7c1ba57b3690b25b9a8782aa633edaf33a687f
|
|
| MD5 |
f182d8629863f7cf5f478470ff440bb3
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
67e622c3b6b67eaca4f3e65389174a93a3581302e7b3ab8a64b05c20d7f363cb
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-win_amd64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-win_amd64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.9 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.10, Windows x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
a37ee60784f04c991ba49bb421c2b2cc98fe456c369f8e806a3bbc6c77fb979e
|
|
| MD5 |
4f00e72b161907c0352e4faffa3bd739
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
9b164c8eb3bf0e197747bbcd36b2e70914f0f383ad56840862659d56838fd3d2
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-manylinux2014_x86_64.manylinux_2_17_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-manylinux2014_x86_64.manylinux_2_17_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 15.8 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.10, manylinux: glibc 2.17+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
7c8affc22dc3ef332121eb538b1b6a18eba2b6f3e1408be3508b2c44e56707a9
|
|
| MD5 |
357d70825cd262fe81fc27f03e3e5b41
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
1cf6bb5131b50e35cf3235f79bf58e90f713c6513bb0a6cb4fc0196d83088b64
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-macosx_14_0_arm64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-macosx_14_0_arm64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.0 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.10, macOS 14.0+ ARM64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
4cea474bdc709ed73d35d5f4aab15f5c0e5aed98739e3d713effbb9f7fceb972
|
|
| MD5 |
6755b9494b34a170a70155e090a51f00
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
cfc462fb9a35c3d70ced24c362b9e1752ff6983c029f76f5939db830d6e7ef38
|
File details
Details for the file egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-macosx_13_0_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: egttools-0.1.14.2-cp310-cp310-macosx_13_0_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 5.2 MB
- Tags: CPython 3.10, macOS 13.0+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
cbd9bf8d5ecc546588e8ca87dd94be366557df2a340cd050aaf86989e0703b84
|
|
| MD5 |
048fa62f3f40cbe07e46682d1063c346
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
72deba85f7e1d057b1a725b4e27289d4cb41a607245fe5a3591af49c67334dba
|