A package to simulate compartmental epidemic models
Project description
epidemik
Compartmental Epidemic Models in Python








Table of contents
Installation
Use the package manager pip to install epidemik.
pip install epidemik
Tech Stack
Here's a brief high-level overview of the tech stack the epidemik package uses:
- The model is implemented as a directed multigraph using networkx
- Ordinary Differential Equations are numerically integrated using scipy
- Random numbers are generated by numpy
- Model structure visualizations rely on matplotlib
- Progress bars generated by tqdm
Basic Usage
epidemik provides three main modules, EpiModel, NetworkEpiModel and MetaEpiModel, usually imported directly from the epidemik package using the module name
from epidemik import EpiModel
- EpiModel -e Simple compartmental model in a homogeneously mixed population.
- NetworkEpiModel - Compartmental model on a network where nodes interact only along edges connecting them.
- MetaEpiModel - Meta population model where populations interact with one another along the edges of a network. Each sub-population has it's own internal EpiModel instance.
To instantiate a new compartmental model we just need to create a EpiModel object and add the relevant transitions:
beta = 0.2
mu = 0.1
SIR = EpiModel()
SIR.add_interaction('S', 'I', 'I', beta)
SIR.add_spontaneous('I', 'R', mu)
This fully defines the model. We can get a textual representation of the model using
print(SIR)
resulting in a simple description of hte model structure.
Epidemic Model with 3 compartments and 2 transitions:
S + I = I 0.200000
I -> R 0.100000
R0=2.00
or a graphical representation by calling draw_model():
SIR.draw_model()
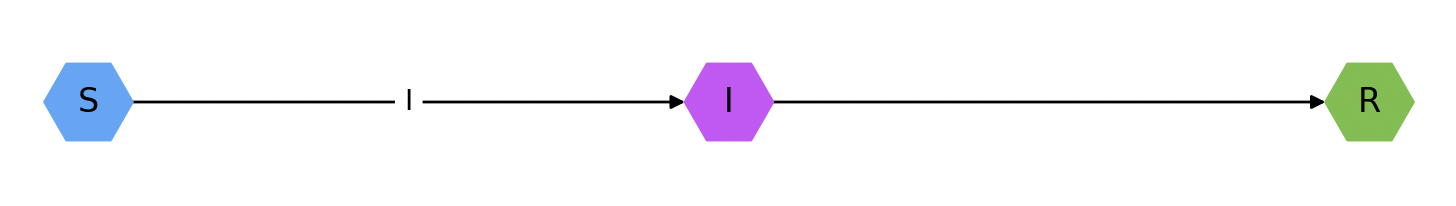
The models value of the Basic Reproductive Number (R0) can be determined using the R0() function:
SIR.R0()
There are two ways to explore the dynamics of the model, each with it's corresponding method.
To integrate numerically the Ordinary Differential Equations that describe the model dynamics, we can call the integrate() method. The first argument is the number of time steps to integrate over and the remaining arguments are the initial populations of each compartment.
N = 10_000
I0 = 10
SIR.integrate(365, S=N-I0, I=I0, R=0)
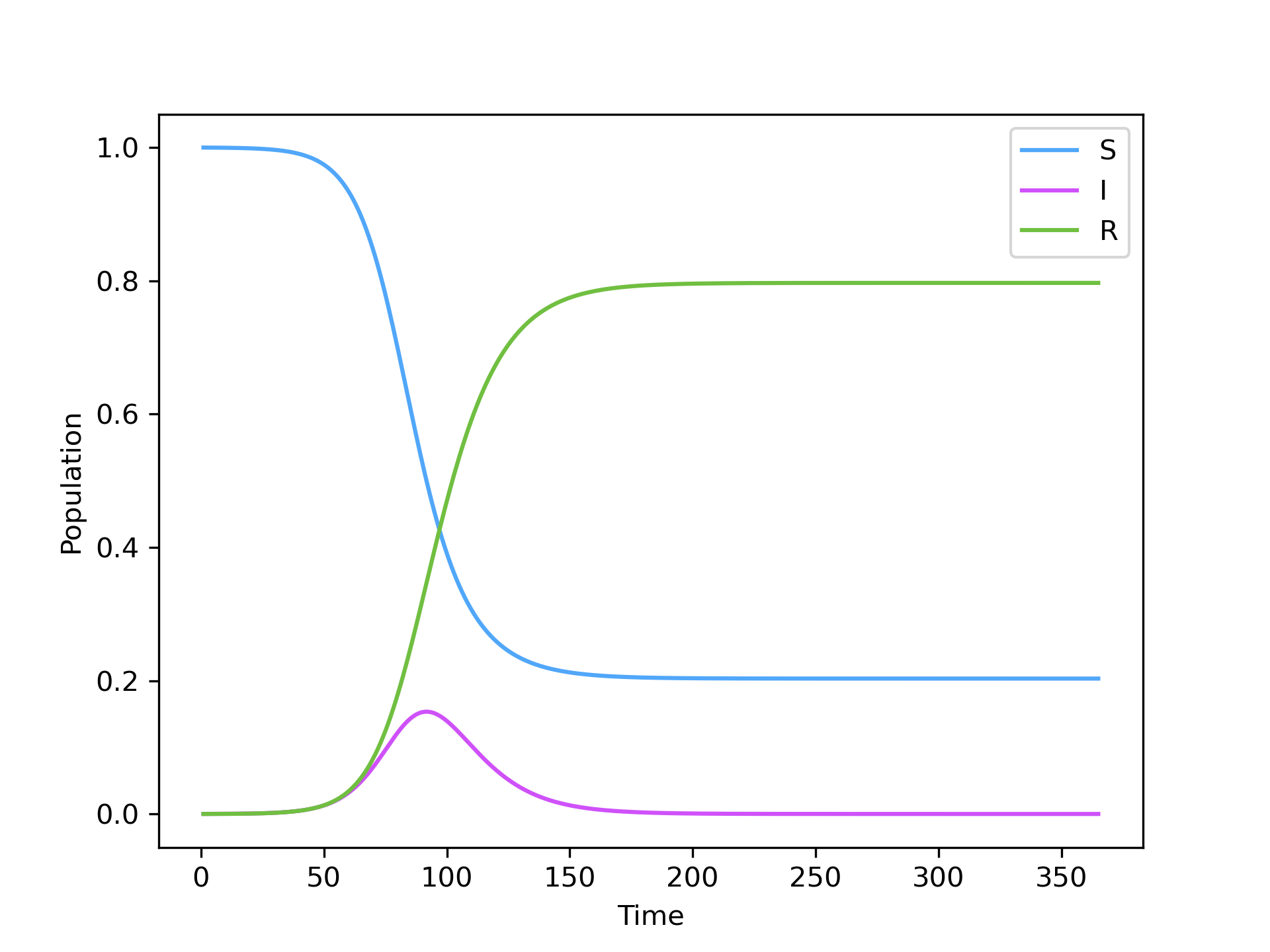
The results of the integration are stored in the values_ field. A quick visualization of the results can be obtained using:
SIR.plot()
which produces:
Documentation
The full documentation for this project is available at ReadTheDocs in html, PDF and ePub formats.
Contributing
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.
Join our project and provide assistance by:
- Checking out the list of open issues where we need help.
- If you need new features, please open a new issue or start a discussion.
Contact us for the feedback or new ideas.
Spread The Word
If you want to say thank you and/or support active development of the epidemik package:
- Add a GitHub star
to the repository to encourage contributors and helps to grow our community.
- Tweet about the project on your Twitter!
- Tag @data4sci and/or @bgoncalves
Thank you so much for your interest in growing our community!
License
epidemik is free and open-source software licensed under the MIT License [2024] - Bruno Gonçalves, Data For Science, Inc. Please have a look at the LICENSE.md for more details.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file epidemik-0.1.3.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: epidemik-0.1.3.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 18.3 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/5.1.0 CPython/3.11.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
da02ce744b264a38e81c34b0bbe7202d5c382b06ceab4d84a3e086943ddbd4e6
|
|
| MD5 |
004256f5d669b5b480a631d7cd1e19e1
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
76dafdc2cb5a52a948bb3e760c0469957be051168e7fe0179445911616e56433
|
File details
Details for the file epidemik-0.1.3.3-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: epidemik-0.1.3.3-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 18.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/5.1.0 CPython/3.11.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
5d0661e2142fe4274a0141c722125d5faef9403086489a7f0845844436d13f50
|
|
| MD5 |
cf6ff5bcd4512f9aed80ce25b9a1d2ab
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
be2196f366e663ffe6aa3fda9764599c052c11618913f8d71c84b899703d3e2f
|












