Fourier modal method with Jax
This project has been archived.
The maintainers of this project have marked this project as archived. No new releases are expected.
Project description
FMMAX: Fourier Modal Method with Jax
FMMAX is an implementation of the Fourier modal method (FMM) using jax.
Fourier modal method
The FMM--also known as rigorous coupled wave analysis (RCWA)--is a semianalytical method that solves Maxwell's equations in periodic stratified media, where in-plane directions are treated with a truncated Fourier basis and the normal direction is handled by a scattering matrix approach [1, 2]. This allows certain classes of structures to be modeled with relatively low computational cost.
The use of JAX enables GPU acceleration and automatic differentiation of FMM simulations. Additionally, FMMAX supports Brillouin zone integration, advanced vector FMM formulations which improve convergence, and anisotropic and magnetic materials.
Brillouin zone integration
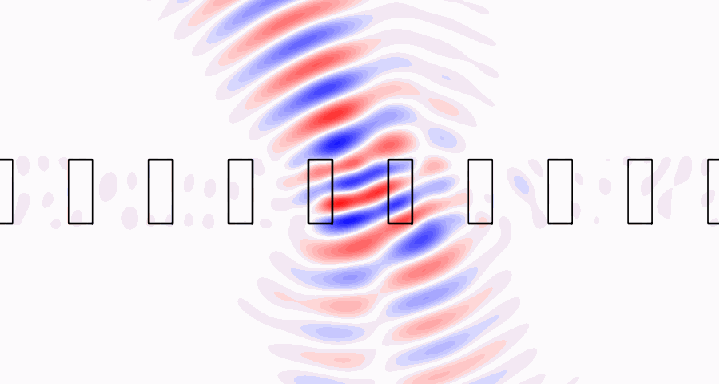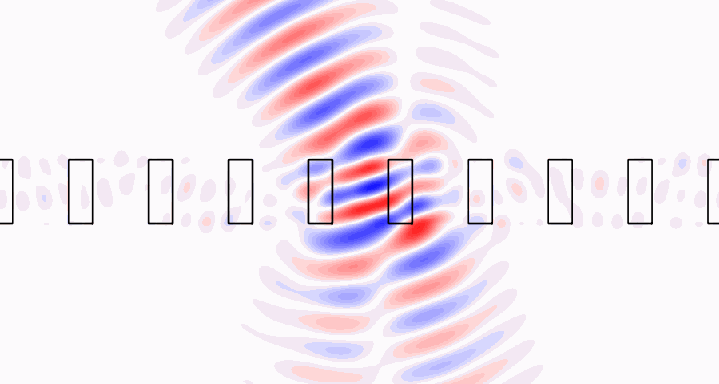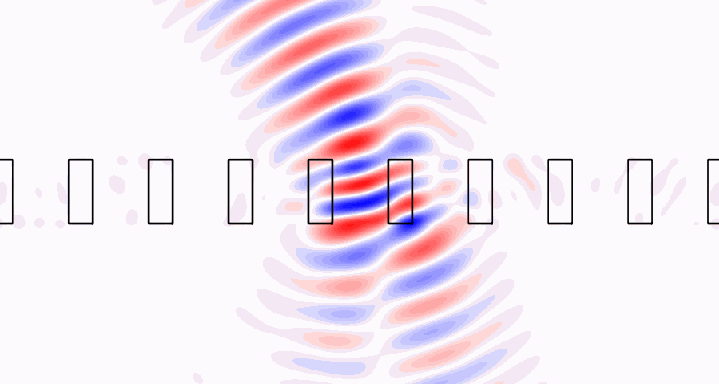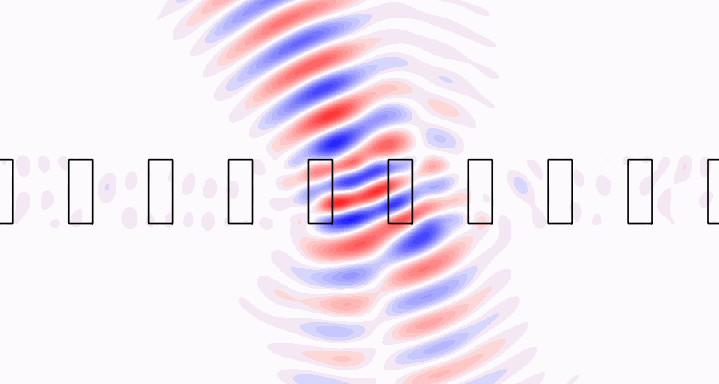
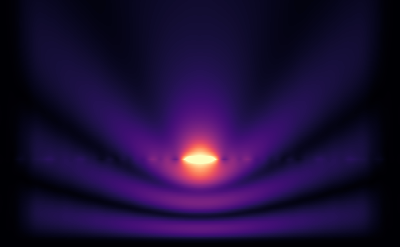
Brillouin zone integration [3] allows modeling of localized sources in periodic structures. Check out the crystal example to see how we model a Gaussian beam incident upon a photonic crystal slab, or an isolated dipole embedded within the slab. The Gaussian beam fields are shown below.
Vector FMM formulations
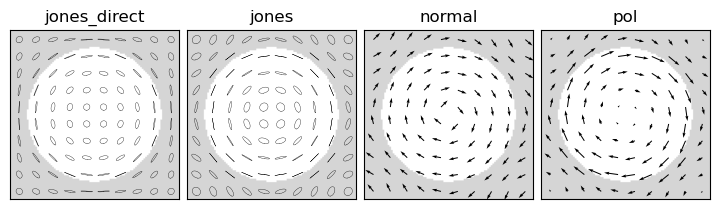
Vector FMM formulations introduce local coordinate systems at each point in the unit cell, which are normal and tangent to all interfaces. This allows normal and tangent field components to be treated differently and improves convergence. FMMAX implements several vector formulations of the FMM, with automatic vector field generation based on functional minimization similar to [4]. FMMAX includes the Pol, Normal, and Jones methods from [4], and introduce a new Jones direct method can yield superior convergence. These are supported also with anisotropic and magnetic materials. The vector_fields example computes vector fields by these methods for an example structure.
Anisotropic, magnetic materials
FMMAX's support of anisotropic, magnetic materials allows modeling of uniaxial perfectly matched layers. This is demonstrated in the metal_dipole example, which simulates in vaccuum located above a metal substrate. The resulting electric fields are shown below.
FMM Conventions
- The speed of light, vacuum permittivity, and vacuum permeability are all 1.
- Fields evolve in time as $\exp(-i \omega t)$.
- If $\mathbf{u}$ and $\mathbf{v}$ are the primitive lattice vectors, the unit cell is defined by the parallelogram with vertices at $\mathbf{0}$, $\mathbf{u}$, $\mathbf{u} + \mathbf{v}$, and $\mathbf{v}$.
- For quantities defined on a grid (such as the permittivity distribution of a patterned layer) the value at grid index (0, 0) corresponds to the value at physical location $(\mathbf{du} + \mathbf{dv}) / 2$.
- The scattering matrix block $\mathbf{S}_{11}$ relates incident and transmitted forward-going fields, and other blocks have corresponding definitions. This differs from the convention e.g. in photonic integrated circuits.
Batching
Batched calculations are supported, and should be used where possible to avoid looping. The batch axes are the leading axes, except for the wave amplitudes and electromagnetic fields, where a trailing batch axis is assumed. This allows e.g. computing the transmission through a structure for multiple polarizations via a matrix-matrix operation (i.e. transmitted_amplitudes = S11 @ incident_amplitudes), rather than a batched matrix-vector operation.
Installation
FMMAX can be installed via pip:
pip install fmmax
For developers requiring a local installation, you will need to first clone this repository and then perform a local install from within the root directory using:
pip install -e ".[dev]"
The [dev] modifier specifies optional dependencies for developers which are listed in pyproject.toml. (For this to work, it may be necessary to first update your pip installation using e.g. python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip.)
License and Credit
FMMAX is available under the MIT License. It was originally developed and open-sourced at Meta; this project was forked from the (also MIT-licensed) original repo after the primary author left Meta and contains significant improvements to the original version. The FMMAX pypi project is based on this repo. If you use FMMAX, please cite the paper,
@article{schubert2023fourier,
title={Fourier modal method for inverse design of metasurface-enhanced micro-LEDs},
author={Schubert, Martin F and Hammond, Alec M},
journal={Optics Express},
volume={31},
number={26},
pages={42945--42960},
year={2023},
publisher={Optica Publishing Group}
}
References
- V. Liu and S. Fan, S4: A free electromagnetic solver for layered structures structures, Comput. Phys. Commun. 183, 2233-2244 (2012).
- D. M. Whittaker and I. S. Culshaw, Scattering-matrix treatment of patterned multilayer photonic structures, Phys. Rev. B 60, 2610 (1999).
- W. Jin, W. Li, M. Orenstein, and S. Fan Inverse design of lightweight broadband reflector for relativistic lightsail propulsion, ACS Photonics 7, 9, 2350-2355 (2020).
- E. Lopez-Fraguas, F. Binkowski, S. Burger, B. Garcia-Camara, R. Vergaz, C. Becker and P. Manley Tripling the light extraction efficiency of a deep ultraviolet LED using a nanostructured p-contact, Scientific Reports 12, 11480 (2022).
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file fmmax-1.7.1.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: fmmax-1.7.1.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 58.3 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
8d5eb11bd8a62be00110f5dbc4af97a886d6ee298e65674454184c55e78b4705
|
|
| MD5 |
7a70181fd97d4abc74e3cad08688d553
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
f5361e0a415a136f3c2a102c07033a1a058847b13e03307cb26f447ce506a234
|
File details
Details for the file fmmax-1.7.1-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: fmmax-1.7.1-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 65.2 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
537ccd7ceeb517107fe0404a2dc7d2d27562690505a5b698c9e3b118e90fda3a
|
|
| MD5 |
922cc3f494689d3a88f58a622010c4a0
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
86581b7d6077edbd13fd5447279c5fc41b1920bd602a52a3c5cd0f4e0a8a058b
|