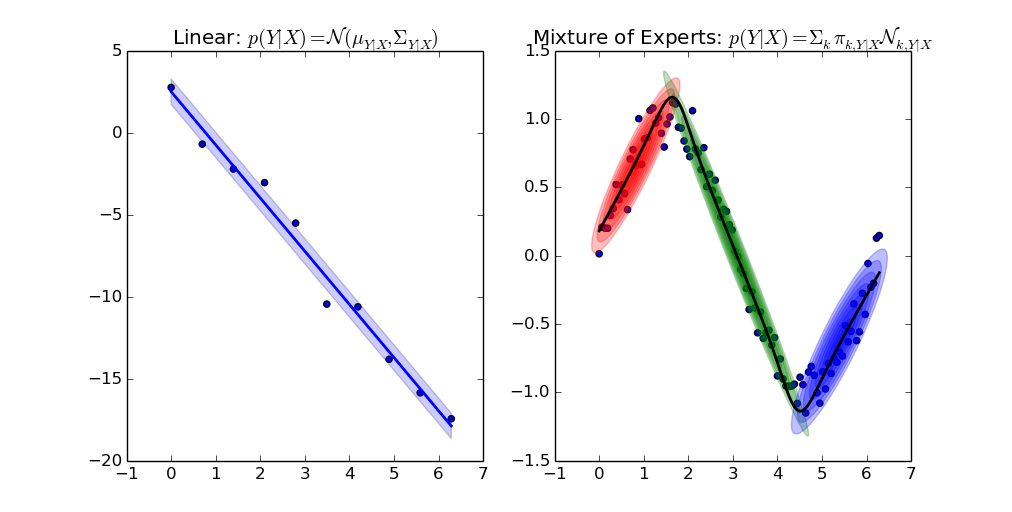
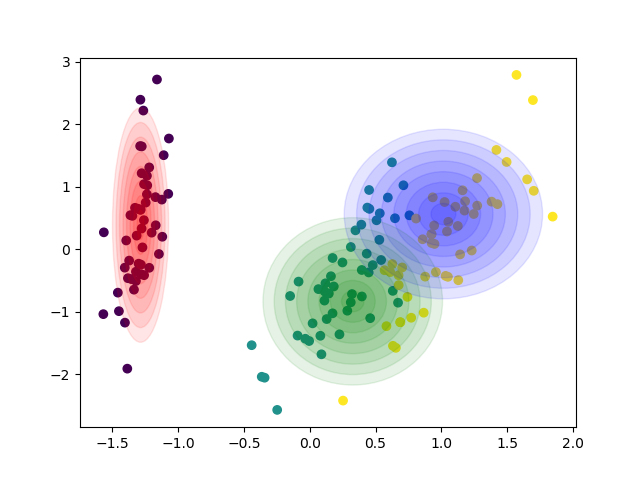
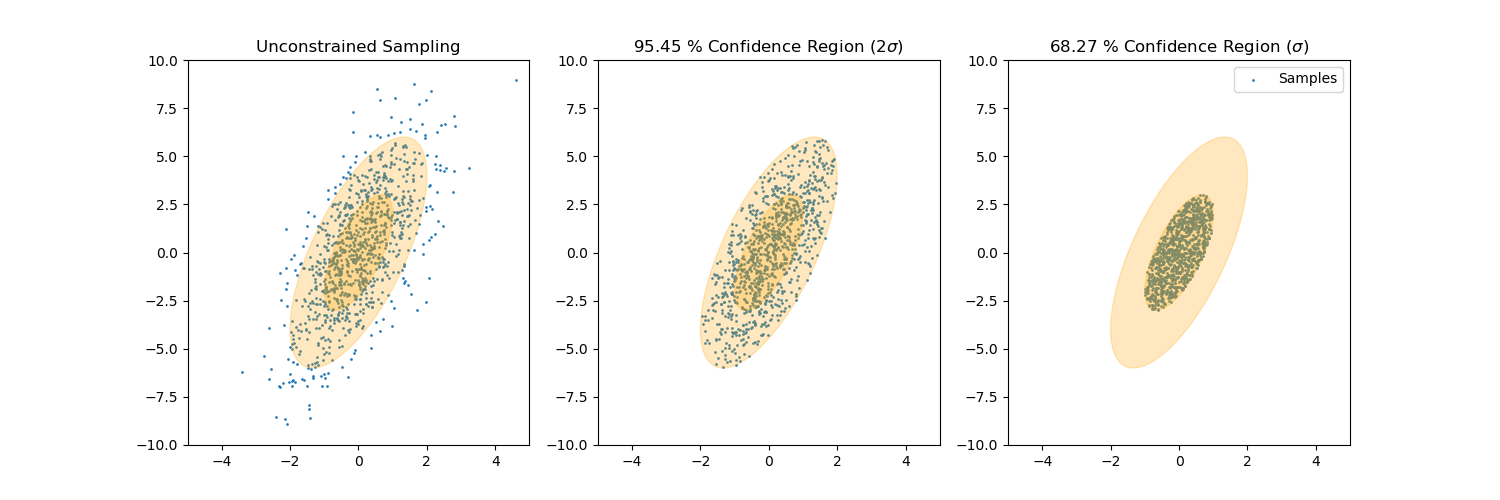
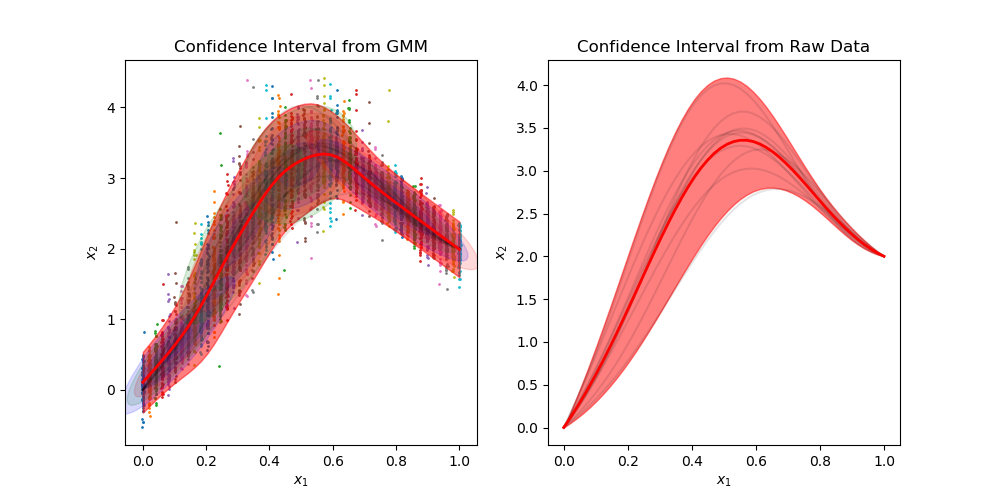
Gaussian Mixture Regression
Project description
gmr
Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) for clustering and regression in Python.
- Source code repository: https://github.com/AlexanderFabisch/gmr
- License: New BSD / BSD 3-clause
- Releases: https://github.com/AlexanderFabisch/gmr/releases
- API documentation
Documentation
Installation
Install from PyPI:
pip install gmr
If you want to be able to run all examples, pip can install all necessary examples with
pip install gmr[all]
You can also install gmr from source:
pip install -e .
Example
Estimate GMM from samples, sample from GMM, and make predictions:
import numpy as np
from gmr import GMM
# Your dataset as a NumPy array of shape (n_samples, n_features):
X = np.random.randn(100, 2)
gmm = GMM(n_components=3, random_state=0)
gmm.from_samples(X)
# Estimate GMM with expectation maximization:
X_sampled = gmm.sample(100)
# Make predictions with known values for the first feature:
x1 = np.random.randn(20, 1)
x1_index = [0]
x2_predicted_mean = gmm.predict(x1_index, x1)
For more details, see:
help(gmr)
or have a look at the API documentation
You can see the results of all the examples here.
You can find worked examples in this Google Colab notebook.
How Does It Compare to scikit-learn?
There is an implementation of Gaussian Mixture Models for clustering in scikit-learn as well. Regression could not be easily integrated in the interface of sklearn. That is the reason why I put the code in a separate repository. It is possible to initialize GMR from sklearn though:
from sklearn.mixture import GaussianMixture
from gmr import GMM
gmm_sklearn = GaussianMixture(n_components=3, covariance_type="diag")
gmm_sklearn.fit(X)
gmm = GMM(
n_components=3, priors=gmm_sklearn.weights_, means=gmm_sklearn.means_,
covariances=np.array([np.diag(c) for c in gmm_sklearn.covariances_]))
For model selection with sklearn we furthermore provide an optional regressor interface.
Gallery
Sample from confidence interval
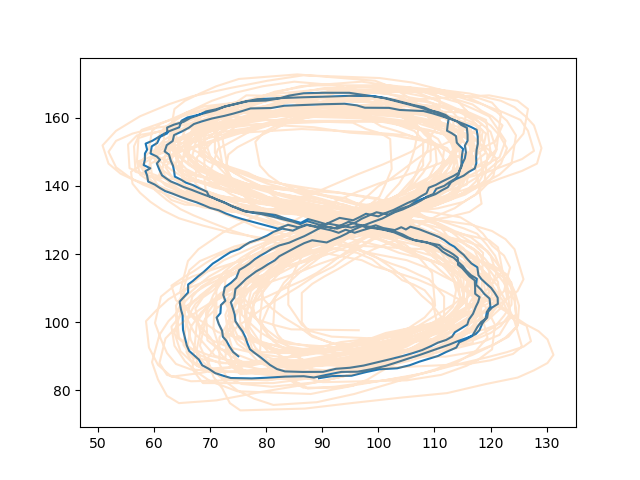
Sample time-invariant trajectories
You can find all examples here.
Saving a Model
This library does not directly offer a function to store fitted models. Since the implementation is pure Python, it is possible, however, to use standard Python tools to store Python objects. For example, you can use pickle to temporarily store a GMM:
import numpy as np
import pickle
import gmr
gmm = gmr.GMM(n_components=2)
gmm.from_samples(X=np.random.randn(1000, 3))
# Save object gmm to file 'file'
pickle.dump(gmm, open("file", "wb"))
# Load object from file 'file'
gmm2 = pickle.load(open("file", "rb"))
It might be required to store models more permanently than in a pickle file,
which might break with a change of the library or with the Python version.
In this case you can choose a storage format that you like and store the
attributes gmm.priors, gmm.means, and gmm.covariances. These can be
used in the constructor of the GMM class to recreate the object and they can
also be used in other libraries that provide a GMM implementation. The
MVN class only needs the attributes mean and covariance to define the
model.
API Documentation
API documentation is available here.
Citation
If you use the library gmr in a scientific publication, I would appreciate citation of the following paper:
Fabisch, A., (2021). gmr: Gaussian Mixture Regression. Journal of Open Source Software, 6(62), 3054, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03054
Bibtex entry:
@article{Fabisch2021,
doi = {10.21105/joss.03054},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03054},
year = {2021},
publisher = {The Open Journal},
volume = {6},
number = {62},
pages = {3054},
author = {Alexander Fabisch},
title = {gmr: Gaussian Mixture Regression},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software}
}
Contributing
How can I contribute?
If you discover bugs, have feature requests, or want to improve the documentation, you can open an issue at the issue tracker of the project.
If you want to contribute code, please open a pull request via
GitHub by forking the project, committing changes to your fork,
and then opening a
pull request
from your forked branch to the main branch of gmr.
Development Environment
I would recommend to install gmr from source in editable mode with pip and
install all dependencies:
pip install -e .[all,test,doc]
You can now run tests with
pytest
This will also generate a coverage report and output an HTML overview to
the folder htmlcov/.
Generate Documentation
The API documentation is generated with pdoc3. If you want to regenerate it, you can run
pdoc gmr --html --skip-errors
Related Publications
The first publication that presents the GMR algorithm is
[1] Z. Ghahramani, M. I. Jordan, "Supervised learning from incomplete data via an EM approach," Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 6, 1994, pp. 120-127, https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/1993/hash/f2201f5191c4e92cc5af043eebfd0946-Abstract.html
but it does not use the term Gaussian Mixture Regression, which to my knowledge occurs first in
[2] S. Calinon, F. Guenter and A. Billard, "On Learning, Representing, and Generalizing a Task in a Humanoid Robot," in IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), vol. 37, no. 2, 2007, pp. 286-298, doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2006.886952.
A recent survey on various regression models including GMR is the following:
[3] F. Stulp, O. Sigaud, "Many regression algorithms, one unified model: A review," in Neural Networks, vol. 69, 2015, pp. 60-79, doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2015.05.005.
Sylvain Calinon has a good introduction in his slides on nonlinear regression for his machine learning course.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file gmr-2.0.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: gmr-2.0.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 1.3 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.11.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
001af4f1cacc2b5fc8158f90d3b233ccd6265590224ee6484c0fddcc1a1f6624
|
|
| MD5 |
ec1536ea272c08d0865f3fa343d96c88
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
1d4a1dab54ffeae4823fa760a1a6c43bf6080ad5b5823261e450fef699a4544d
|
File details
Details for the file gmr-2.0.3-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: gmr-2.0.3-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 18.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.11.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
8fb019f2d5df0a6b281675ab5a497e721351625593943cc7748b5cb5f8b6c01a
|
|
| MD5 |
7ba446ac5b4bce0e4776b34df07c8495
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
33c66ebc9e3c5b1f5a8ddd1714f677e51b672b786c04a3481569dd3a5692551e
|