JupyterHub SLURM Spawner with specific spawn page
Project description
jupyterhub_moss: JupyterHub MOdular Slurm Spawner
jupyterhub_moss is a Python package that provides:
- A JupyterHub
Slurm Spawner that can be configured by
setting the available partitions. It is an extension of
batchspawner.SlurmSpawner. - An associated spawn page that changes according to the partitions set in the Spawner and allows the user to select Slurm resources to use.

Install
pip install jupyterhub_moss
Usage
Partition settings
To use jupyterhub_moss, you need first a working
JupyterHub instance. jupyterhub_moss
needs then to be imported in
your JupyterHub configuration file
(usually named jupyterhub_conf.py):
import batchspawner
import jupyterhub_moss
c = get_config()
# ...your config
# Init JupyterHub configuration to use this spawner
jupyterhub_moss.set_config(c)
Once jupyterhub_moss is set up, you can define the partitions available on
Slurm by setting c.MOSlurmSpawner.partitions in the same file:
# ...
# Partition descriptions
c.MOSlurmSpawner.partitions = {
"partition_1": { # Partition name # (See description of fields below for more info)
"architecture": "x86_86", # Nodes architecture
"description": "Partition 1", # Displayed description
"gpu": None, # --gres= template to use for requesting GPUs
"max_ngpus": 0, # Maximum number of GPUs per node
"max_nprocs": 28, # Maximum number of CPUs per node
"max_runtime": 12*3600, # Maximum time limit in seconds (Must be at least 1hour)
"simple": True, # True to show in Simple tab
"jupyter_environments": {
"default": { # Jupyter environment internal identifier
"path": "/env/path/bin/", # Path to Python environment bin/ used to start jupyter on the Slurm nodes
"description": "Default", # Text displayed for this environment select option
"add_to_path": True, # Toggle adding the environment to shell PATH (optional, default: True)
},
},
},
"partition_2": {
"architecture": "ppc64le",
"description": "Partition 2",
"gpu": "gpu:V100-SXM2-32GB:{}",
"max_ngpus": 2,
"max_nprocs": 128,
"max_runtime": 1*3600,
"simple": True,
"jupyter_environments": {
"default": {
"path": "/path/to/jupyter/env/for/partition_2/bin/",
"description": "Default",
"add_to_path": True,
},
},
},
"partition_3": {
"architecture": "x86_86",
"description": "Partition 3",
"gpu": None,
"max_ngpus": 0,
"max_nprocs": 28,
"max_runtime": 12*3600,
"simple": False,
"jupyter_environments": {
"default": {
"path": "/path/to/jupyter/env/for/partition_3/bin/",
"description": "Partition 3 default",
"add_to_path": True,
},
},
}
Field descriptions
architecture: The architecture of the partition. This is only cosmetic and will be used to generate subtitles in the spawn page.description: The description of the partition. This is only cosmetic and will be used to generate subtitles in the spawn page.gpu: A template string that will be used to request GPU resources through--gres. The template should therefore include a{}that will be replaced by the number of requested GPU and follow the format expected by--gres. If no GPU is available for this partition, set toNone.max_ngpus: The maximum number of GPU that can be requested for this partition. The spawn page will use this to generate appropriate bounds for the user inputs. If no GPU is available for this partition, set to0.max_nprocs: The maximum number of processors that can be requested for this partition. The spawn page will use this to generate appropriate bounds for the user inputs.max_runtime: The maximum job runtime for this partition in seconds. It should be of minimum 1 hour as the Simple tab only display buttons for runtimes greater than 1 hour.simple: Whether the partition should be available in the Simple tab. The spawn page that will be generated is organized in a two tabs: a Simple tab with minimal settings that will be enough for most users and an Advanced tab where almost all Slurm job settings can be set. Some partitions can be hidden from the Simple tab with settingsimpletoFalse.jupyter_environments: Mapping of identifer name to information about Python environment used to run Jupyter on the Slurm nodes. This information is a mapping containing:path: The path to a Python environment bin/ used to start jupyter on the Slurm nodes. jupyterhub_moss needs that a virtual (or conda) environment is used to start Jupyter. This path can be changed according to the partitions.description: Text used for display in the selection options.add_to_path: Whether or not to prepend the environmentpathto shellPATH.
Spawn page
The spawn page (available at /hub/spawn) will be generated according to the
partition settings. For example, this is the spawn page generated for the
partition settings above:

This spawn page is separated in two tabs: a Simple and an Advanced tab. On
the Simple tab, the user can choose between the partitions set though
simple: True (partition_1 and partition_2 in this case), choose to take a
minimum, a half or a maximum number of cores and choose the job duration. The
available resources are checked using sinfo and displayed on the table below.
Clicking on the Start button will request the job.
The spawn page adapts to the chosen partition. This is the page when selecting
the partition_2:
As the maximum number of cores is different, the CPUs row change accordingly.
Also, as gpu was set for partition_2, a new button row appears to enable GPU
requests.
The Advanced tab allows finer control on the requested resources.
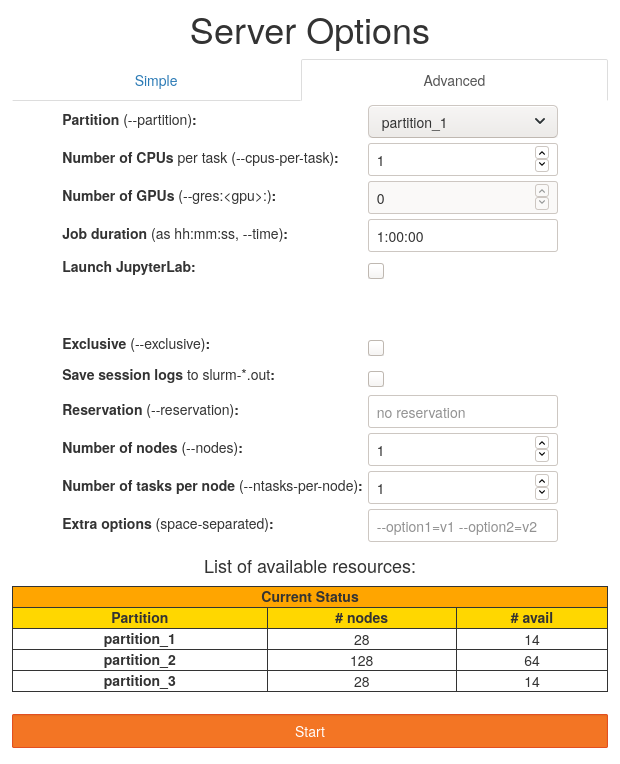
The user can select any partition (partition_3 is added in this case) and the
table of available resources reflects this. The user can also choose any number
of nodes (with the max given by max_nprocs), of GPUs (max: max_gpus) and
have more control on the job duration (max: max_runtime).
Spawn through URL
It is also possible to pass the spawning options as query arguments to the spawn
URL: https://<server:port>/hub/spawn. For example,
https://<server:port>/hub/spawn?partition=partition_1&nprocs=4 will directly
spawn a Jupyter server on partition_1 with 4 cores allocated.
The following query argument is required:
partition: The name of the SLURM partition to use.
The following optional query arguments are available:
environment_path: Path to Python environment bin/ used to start Jupyterexclusive: Set totruefor exclusive node usage (--exclusive)jupyterlab: Set totrueto start with JupyterLabmem: Total amount of memory per node (--mem)ngpus: Number of GPUs (--gres:<gpu>:)nprocs: Number of CPUs per task (--cpus-per-task)options: Extra SLURM optionsoutput: Set totrueto save logs toslurm-*.outfiles.reservation: SLURM reservation name (--reservation)runtime: Job duration as hh:mm:ss (--time)
Development
See CONTRIBUTING.md.
Credits:
We would like acknowledge the following ressources that served as base for this project and thank their authors:
- This gist for the initial spawner implementation.
- The DESY JupyterHub Slurm service for the table of available resources.
- The TUDresden JupyterHub Slurm service for the spawn page design.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for jupyterhub_moss-3.0.0-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 09767442d44af4f9dc5f740cee5c8290c902dbdd501a74285204539c963319ee |
|
| MD5 | 560af5d822d09cb17a804e877045f1d1 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | d873e756a326f8396043f43a72f66cd8d77abb43bcde5f446164c612de870653 |













