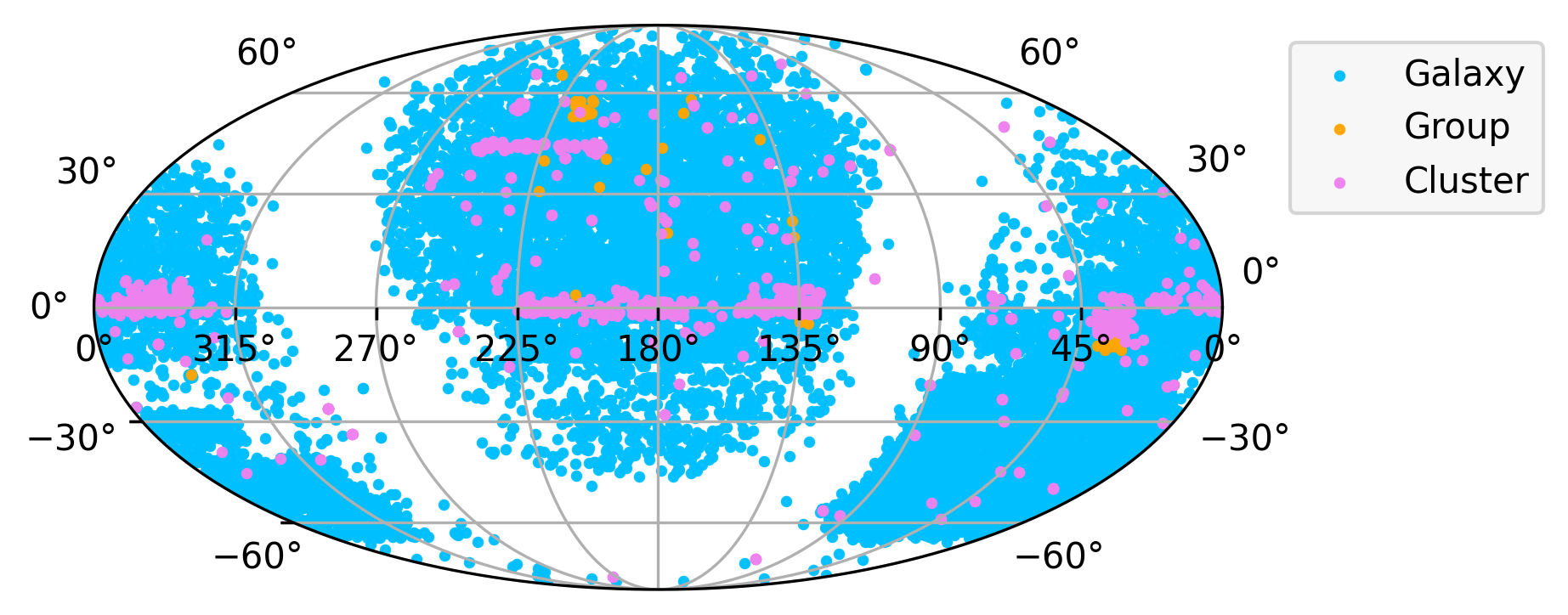
A public and community-maintained catalog of known strong gravitational lenses
Project description
$\texttt{lenscat}$
A public and community-contributed catalog of known strong gravitational lenses.
Quickstart
The catalog is available as a plain csv file under lenscat/data/catalog.csv. Alternatively, one can interact with the catalog using a web app (mobile-friendly).
We also provide a python package lenscat, available in pypi. Simply do
pip install lenscat
to install the latest version. Here we adopt the continuous deployment paradigm (similar to astroquery). Whenever there is a change in the catalog content, or a major change in the code, a new release will be available instantaneously on both GitHub and PyPI.
The code converts the catalog in the csv file into a custom Catalog object that is inherited from the Table object in astropy. To access the catalog, simply run
import lenscat; lenscat.catalog
and this will show a formatted table to the output. For example,
<Catalog length=32838>
name RA DEC zlens type grading
deg deg
str479 float64 float64 str234 str7 str9
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- --------- -------- ------------------------------ ------ ---------
J0011-0845 2.83435 -8.7643 - galaxy confident
J0013+5119 3.348077 51.3183 - galaxy confident
... ... ... ... ... ...
SDSS J153713.2+655621 | SDSS J1537+6556 | SDSSJ1537+6556 234.305 65.93913 0.251 | 0.2595 | 0.2595 group probable
HERMES J105750.9+573026 | 5438733 | DESI-164.4623+57.5071 | HERMESJ105751.1+573027 164.46256 57.50734 0.6 | 0.64259666 | 0.643 | nan group probable
Note that the code will try to assign the unit for each of the columns inferred from its name, and that it will hide the 'ref' column by default. One can show or hide the 'ref' column by calling .show_ref() and .hide_ref() on the Catalog object respectively.
Every Catalog object supports three features: basic searching with .search(), crossmatching with a skymap with .crossmatch(), and visualizing with .plot(). Note that these function will return a Catalog object, and hence they can be composed together (e.g., .crossmatch().search()).
Basic searching
This feature is implemented as .search(). One can search/filter by any combination of
- ranges of right ascension (specified as
RA_range=(RA_min, RA_max)) - ranges of declination (specified as
DEC_range=(DEC_min, DEC_max)) - ranges of lens redshift if available (specified as
zlens_range=(zlens_min, zlens_max)) - type of the lenses (specified as
lens_type) - grading of the lenses (specified as
grading)
For example, to get a list of the cluster-scale lenses which are confidently identified and with a redshift $z_{\mathrm{lens}} \geq 1$ together with the reference, run
import lenscat, numpy
lenscat.catalog.search(grading="confident", lens_type="cluster", zlens_range=(1,numpy.inf)).show_ref()
The output would be something like
<Catalog length=5>
name RA DEC zlens type grading ref
deg deg
str479 float64 float64 str234 str7 str9 str1587
---------------- ----------- ------------ ------ ------- --------- -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
021118-042729 32.827087 -4.458069 1.02 cluster confident https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.00634 https://arxiv.org/abs/1109.1821 https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.05587
023100-062139 37.7516 -6.3608 1.17 cluster confident https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.01611
220859+020655 332.2495 2.1153 1.04 cluster confident https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.01611
SPT-CLJ0356-5337 59.08672611 -53.63073944 1.0359 cluster confident Moustakas et al. (2012) - adsabs:2012hst..prop12833M
IDCSJ1426.5+3508 216.63729 35.13989 1.75 cluster confident Moustakas et al. (2012) - adsabs:2012hst..prop12833M
Crossmatching with a skymap
This feature is implemented as .crossmatch(). This function is simply a wrapper to the crossmatch() function in ligo.skymap which performs the cross-matching of a gravitational-wave (GW) skymap with a given list of coordinates. For example, to cross-match the GW skymap of GW170814 (download from here) with only galaxy-scale lenses in the lenscat catalog, simply run
import lenscat
lenscat.catalog.search(lens_type="galaxy").crossmatch("GW170814_skymap.fits.gz")
Running this will give
<CrossmatchResult length=31755>
name RA DEC zlens type grading searched probability searched area
deg deg deg2
str479 float64 float64 str234 str7 str9 float64 float64
--------------------- --------- --------- ------------ ------ -------- -------------------- ------------------
DESI-047.5128-44.2451 47.51275 -44.24506 0.278 galaxy probable 0.019409452342101355 0.383583423787917
DESI-047.1501-45.3903 47.15012 -45.39029 0.683 galaxy probable 0.03333914444622844 0.6720906143292572
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
NSCS J145222+081201 223.09342 8.20025 not measured galaxy probable 0.9999999999999997 41252.96124941707
DESI-225.5679+15.1661 225.56792 15.1661 0.551534 galaxy probable 0.9999999999999997 41252.96124941707
The cross-matching can be done to the sky localization from any type of transients as long as it is in the FITS format. For example, to cross-match the localization of GRB 240229A (download from here), simply run
import lenscat
lenscat.catalog.crossmatch("glg_healpix_all_bn240229588.fit")
In this case, the output would be
<CrossmatchResult length=32838>
name RA DEC zlens type grading searched probability searched area
deg deg deg2
str479 float64 float64 str234 str7 str9 float64 float64
--------------------- ----------- ----------- ------------ ------ --------- -------------------- ------------------
DESI-199.7131+16.3005 199.71308 16.30045 0.783 galaxy probable 0.0780098544673723 3.1473511695418765
DESI-199.0121+15.7349 199.01208 15.73486 0.336 galaxy probable 0.08790310861826113 3.5669979921474595
... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
J0113+4549 18.26925 45.81806 not measured galaxy probable 1.0 41038.10207619734
Q0957+561 0.336666667 55.89705556 0.356 galaxy confident 1.0 41038.10207619734
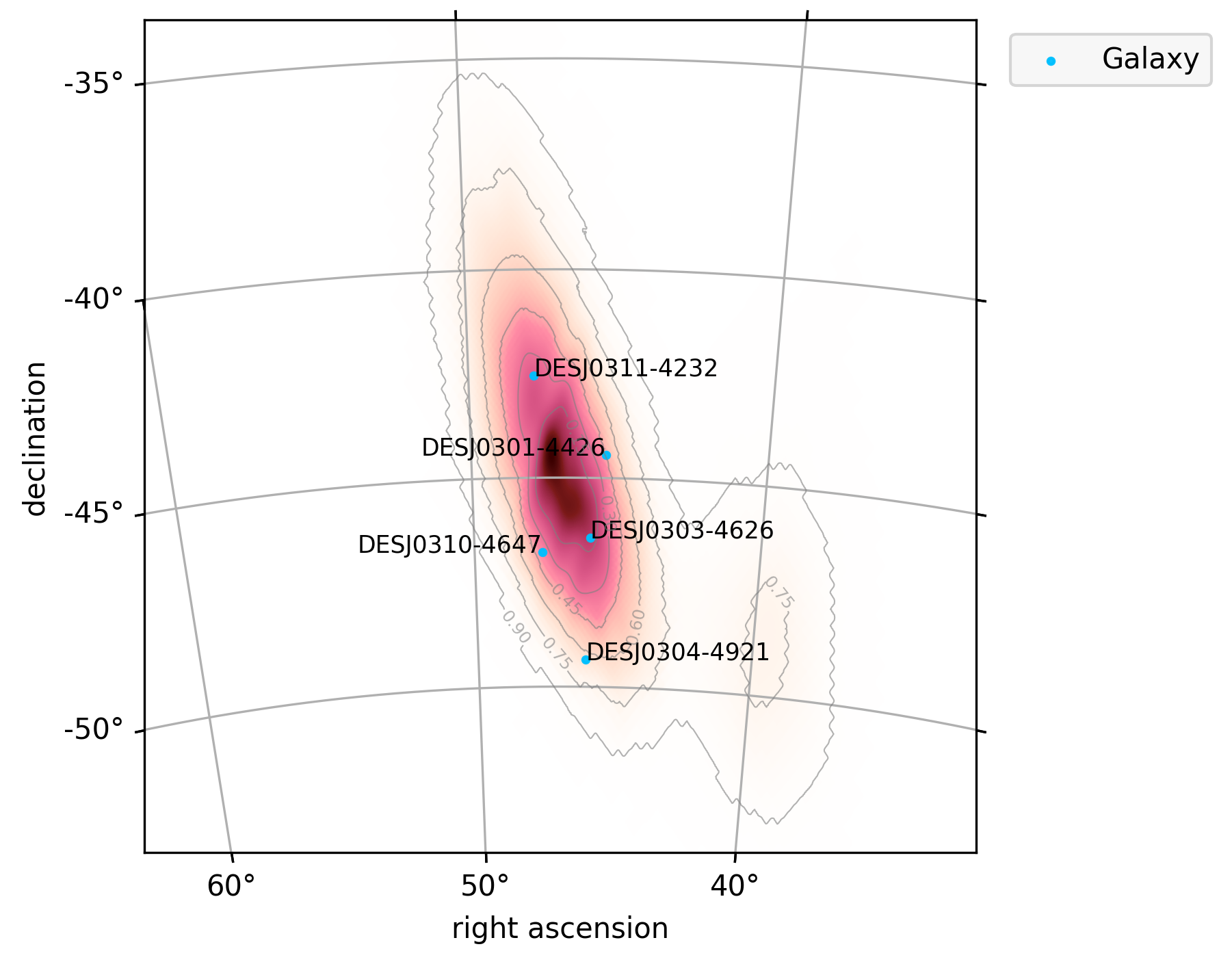
To generate a visualization of a crossmatching result, simply invoke .plot() to a crossmatching result. For example,
import lenscat
lenscat.catalog.crossmatch("GW170814_skymap.fits.gz").plot(searched_prob_threshold=0.7)
will generate a figure like this
Format
| Column name | Description |
|---|---|
name |
Names of galaxies/galaxy clusters |
RA [deg] |
Right ascension in dergees |
DEC [deg] |
Declination in degress |
zlens |
Lens redshift (if known) |
type |
Type of lens (i.e. galaxy or galaxy cluster). Eithergalaxy, group or cluster. |
grading |
Grading whether it is a confidently identified lens or a probable lens (see individual references for internal grading systems). Either confident or probable. |
ref |
Reference to the corresponding catalog or study |
References
lenscat makes use of the LaStBeRu catalog, which should be cited as “R. Alves de Oliveira, J. P. C. França, M. Makler, The Last Stand Before Rubin: a consolidated sample of strong lensing systems in wide-field surveys, in prep.".
This catalog also contains the known strong lenses from the following studies:
-
(COSMOS) LensFlow: A Convolutional Neural Network in Search of Strong Gravitational Lenses
-
Survey of Gravitationally-lensed Objects in HSC Imaging (SuGOHI) Candidate List
See also
How to cite
If you have used this code in your research that leads to a publication, please cite the following article:
@article{Vujeva:2024scq,
author = "Vujeva, L. and Lo, R. K. L. and Ezquiaga, J. M. and Chan, J. C. L.",
title = "{lenscat: a Public and Community-Contributed Catalog of Known Strong Gravitational Lenses}",
journal = {Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences},
volume = {383},
number = {2294},
pages = {20240168},
year = {2025},
doi = {10.1098/rsta.2024.0168},
eprint = "2406.04398",
archivePrefix = "arXiv",
primaryClass = "astro-ph.GA",
}
Acknowledgements
This project was supported by the research grant no. VIL37766 and no. VIL53101 from Villum Fonden, and the DNRF Chair program grant no. DNRF162 by the Danish National Research Foundation.
This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie grant agreement No 101131233.
We would also like to thank Jonah Kanner for introducing us the amazing streamlit service that hosts the web app for lenscat.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file lenscat-1.1.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: lenscat-1.1.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 649.6 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
ee3587ae88f70ff5d988d8dcaf6451553c103447f0ff9700d3eda9e9163c88d3
|
|
| MD5 |
4619e5bb622f64843042a4352e90581a
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
cb99ec78f176c9c41696d36c9e13f9c157f81d34755beb3468d7be2b4064c70b
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for lenscat-1.1.3.tar.gz:
Publisher:
create-release-tag.yml on lenscat/lenscat
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
lenscat-1.1.3.tar.gz -
Subject digest:
ee3587ae88f70ff5d988d8dcaf6451553c103447f0ff9700d3eda9e9163c88d3 - Sigstore transparency entry: 212366576
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
lenscat/lenscat@f531b8a8f3fa4bbd1ee8a58b2ddcd54e6936ea14 -
Branch / Tag:
refs/heads/main - Owner: https://github.com/lenscat
-
Access:
public
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
create-release-tag.yml@f531b8a8f3fa4bbd1ee8a58b2ddcd54e6936ea14 -
Trigger Event:
workflow_run
-
Statement type:
File details
Details for the file lenscat-1.1.3-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: lenscat-1.1.3-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 660.1 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? Yes
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
c0575ce25e53328f627f3799e943a453ac9f4e44f093097fdf78c5fcf0041ccb
|
|
| MD5 |
27ce78fcf891a7e7376f3aedfed0af04
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
feeb2d16ccab0837b5b63516ab04394b962da47e77ea95d8681ec8090bfd6c89
|
Provenance
The following attestation bundles were made for lenscat-1.1.3-py3-none-any.whl:
Publisher:
create-release-tag.yml on lenscat/lenscat
-
Statement:
-
Statement type:
https://in-toto.io/Statement/v1 -
Predicate type:
https://docs.pypi.org/attestations/publish/v1 -
Subject name:
lenscat-1.1.3-py3-none-any.whl -
Subject digest:
c0575ce25e53328f627f3799e943a453ac9f4e44f093097fdf78c5fcf0041ccb - Sigstore transparency entry: 212366578
- Sigstore integration time:
-
Permalink:
lenscat/lenscat@f531b8a8f3fa4bbd1ee8a58b2ddcd54e6936ea14 -
Branch / Tag:
refs/heads/main - Owner: https://github.com/lenscat
-
Access:
public
-
Token Issuer:
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com -
Runner Environment:
github-hosted -
Publication workflow:
create-release-tag.yml@f531b8a8f3fa4bbd1ee8a58b2ddcd54e6936ea14 -
Trigger Event:
workflow_run
-
Statement type: