DEPRECATED: Use 'agent-squad' instead. Multi-agent orchestrator framework.
Project description
Multi-Agent Orchestrator
|
⚠️ IMPORTANT: This package has been renamed to agent-squad. Please use pip install agent-squad instead.See: https://pypi.org/project/agent-squad |
Flexible and powerful framework for managing multiple AI agents and handling complex conversations.






🔖 Features
- 🧠 Intelligent intent classification — Dynamically route queries to the most suitable agent based on context and content.
- 🌊 Flexible agent responses — Support for both streaming and non-streaming responses from different agents.
- 📚 Context management — Maintain and utilize conversation context across multiple agents for coherent interactions.
- 🔧 Extensible architecture — Easily integrate new agents or customize existing ones to fit your specific needs.
- 🌐 Universal deployment — Run anywhere - from AWS Lambda to your local environment or any cloud platform.
- 📦 Pre-built agents and classifiers — A variety of ready-to-use agents and multiple classifier implementations available.
- 🔤 TypeScript support — Native TypeScript implementation available.
What's the Multi-Agent Orchestrator ❓
The Multi-Agent Orchestrator is a flexible framework for managing multiple AI agents and handling complex conversations. It intelligently routes queries and maintains context across interactions.
The system offers pre-built components for quick deployment, while also allowing easy integration of custom agents and conversation messages storage solutions.
This adaptability makes it suitable for a wide range of applications, from simple chatbots to sophisticated AI systems, accommodating diverse requirements and scaling efficiently.
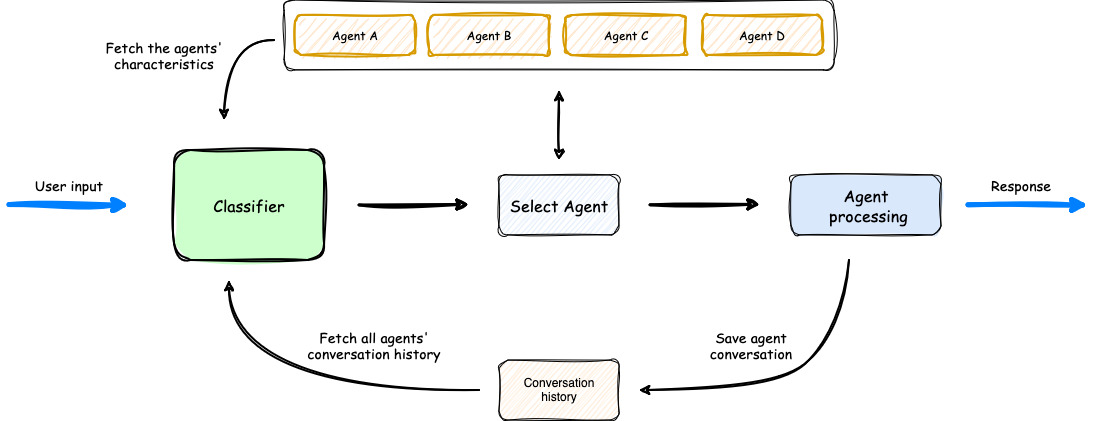
🏗️ High-level architecture flow diagram
- The process begins with user input, which is analyzed by a Classifier.
- The Classifier leverages both Agents' Characteristics and Agents' Conversation history to select the most appropriate agent for the task.
- Once an agent is selected, it processes the user input.
- The orchestrator then saves the conversation, updating the Agents' Conversation history, before delivering the response back to the user.
💬 Demo App
To quickly get a feel for the Multi-Agent Orchestrator, we've provided a Demo App with a few basic agents. This interactive demo showcases the orchestrator's capabilities in a user-friendly interface. To learn more about setting up and running the demo app, please refer to our Demo App section.
In the screen recording below, we demonstrate an extended version of the demo app that uses 6 specialized agents:
- Travel Agent: Powered by an Amazon Lex Bot
- Weather Agent: Utilizes a Bedrock LLM Agent with a tool to query the open-meteo API
- Restaurant Agent: Implemented as an Amazon Bedrock Agent
- Math Agent: Utilizes a Bedrock LLM Agent with two tools for executing mathematical operations
- Tech Agent: A Bedrock LLM Agent designed to answer questions on technical topics
- Health Agent: A Bedrock LLM Agent focused on addressing health-related queries
Watch as the system seamlessly switches context between diverse topics, from booking flights to checking weather, solving math problems, and providing health information. Notice how the appropriate agent is selected for each query, maintaining coherence even with brief follow-up inputs.
The demo highlights the system's ability to handle complex, multi-turn conversations while preserving context and leveraging specialized agents across various domains.
Click on the image below to see a screen recording of the demo app on the GitHub repository of the project:
🚀 Getting Started
Check out our documentation for comprehensive guides on setting up and using the Multi-Agent Orchestrator!
Core Installation
# Optional: Set up a virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows use `venv\Scripts\activate`
pip install multi-agent-orchestrator[aws]
Default Usage
Here's an equivalent Python example demonstrating the use of the Multi-Agent Orchestrator with a Bedrock LLM Agent and a Lex Bot Agent:
import sys
import asyncio
from multi_agent_orchestrator.orchestrator import MultiAgentOrchestrator
from multi_agent_orchestrator.agents import BedrockLLMAgent, LexBotAgent, BedrockLLMAgentOptions, LexBotAgentOptions, AgentStreamResponse
orchestrator = MultiAgentOrchestrator()
tech_agent = BedrockLLMAgent(BedrockLLMAgentOptions(
name="Tech Agent",
streaming=True,
description="Specializes in technology areas including software development, hardware, AI, \
cybersecurity, blockchain, cloud computing, emerging tech innovations, and pricing/costs \
related to technology products and services.",
model_id="anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0",
))
orchestrator.add_agent(tech_agent)
health_agent = BedrockLLMAgent(BedrockLLMAgentOptions(
name="Health Agent",
streaming=True,
description="Specializes in health and well being",
))
orchestrator.add_agent(health_agent)
async def main():
# Example usage
response = await orchestrator.route_request(
"What is AWS Lambda?",
'user123',
'session456',
{},
True
)
# Handle the response (streaming or non-streaming)
if response.streaming:
print("\n** RESPONSE STREAMING ** \n")
# Send metadata immediately
print(f"> Agent ID: {response.metadata.agent_id}")
print(f"> Agent Name: {response.metadata.agent_name}")
print(f"> User Input: {response.metadata.user_input}")
print(f"> User ID: {response.metadata.user_id}")
print(f"> Session ID: {response.metadata.session_id}")
print(f"> Additional Parameters: {response.metadata.additional_params}")
print("\n> Response: ")
# Stream the content
async for chunk in response.output:
async for chunk in response.output:
if isinstance(chunk, AgentStreamResponse):
print(chunk.text, end='', flush=True)
else:
print(f"Received unexpected chunk type: {type(chunk)}", file=sys.stderr)
else:
# Handle non-streaming response (AgentProcessingResult)
print("\n** RESPONSE ** \n")
print(f"> Agent ID: {response.metadata.agent_id}")
print(f"> Agent Name: {response.metadata.agent_name}")
print(f"> User Input: {response.metadata.user_input}")
print(f"> User ID: {response.metadata.user_id}")
print(f"> Session ID: {response.metadata.session_id}")
print(f"> Additional Parameters: {response.metadata.additional_params}")
print(f"\n> Response: {response.output.content}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
The following example demonstrates how to use the Multi-Agent Orchestrator with two different types of agents: a Bedrock LLM Agent with Converse API support and a Lex Bot Agent. This showcases the flexibility of the system in integrating various AI services.
This example showcases:
- The use of a Bedrock LLM Agent with Converse API support, allowing for multi-turn conversations.
- Integration of a Lex Bot Agent for specialized tasks (in this case, travel-related queries).
- The orchestrator's ability to route requests to the most appropriate agent based on the input.
- Handling of both streaming and non-streaming responses from different types of agents.
Working with Anthropic or OpenAI
If you want to use Anthropic or OpenAI for classifier and/or agents, make sure to install the multi-agent-orchestrator with the relevant extra feature.
pip install "multi-agent-orchestrator[anthropic]"
pip install "multi-agent-orchestrator[openai]"
Full package installation
For a complete installation (including Anthropic and OpenAi):
pip install multi-agent-orchestrator[all]
Building Locally
This guide explains how to build and install the multi-agent-orchestrator package from source code.
Prerequisites
- Python 3.11
- pip package manager
- Git (to clone the repository)
Building the Package
-
Navigate to the Python package directory:
cd python
-
Install the build dependencies:
python -m pip install build
-
Build the package:
python -m build
This process will create distribution files in the python/dist directory, including a wheel (.whl) file.
Installation
-
Locate the current version number in
setup.cfg. -
Install the built package using pip:
pip install ./dist/multi_agent_orchestrator-<VERSION>-py3-none-any.whl
Replace
<VERSION>with the version number fromsetup.cfg.
Example
If the version in setup.cfg is 1.2.3, the installation command would be:
pip install ./dist/multi_agent_orchestrator-1.2.3-py3-none-any.whl
Troubleshooting
- If you encounter permission errors during installation, you may need to use
sudoor activate a virtual environment. - Make sure you're in the correct directory when running the build and install commands.
- Clean the
distdirectory before rebuilding if you encounter issues:rm -rf python/dist/*
🤝 Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please see our Contributing Guide for more details.
📄 LICENSE
This project is licensed under the Apache 2.0 licence - see the LICENSE file for details.
📄 Font License
This project uses the JetBrainsMono NF font, licensed under the SIL Open Font License 1.1. For full license details, see FONT-LICENSE.md.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file multi_agent_orchestrator-0.1.15.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: multi_agent_orchestrator-0.1.15.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 56.2 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.10
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
b68ddc9916e6bbe7c30f7f594e12d20b9bc8ea97904208bfe620d514e36812a4
|
|
| MD5 |
3d3757b6041425c5f89d1a9c4a36b703
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
044531c2b4203b96f864ed4612b378693361030a2205e2a4724bb7d785790b2c
|
File details
Details for the file multi_agent_orchestrator-0.1.15-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: multi_agent_orchestrator-0.1.15-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 73.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.10
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
3d5745a784470e0ee4a5d7dfe9028f2cd9eecfcd2336285667b73c997f816d91
|
|
| MD5 |
249e49baed32039d38cb7286b567e502
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
f3d58c40726cf7de044873c77e8f7a23f9c328090f73eee1048e55ef8b51f949
|