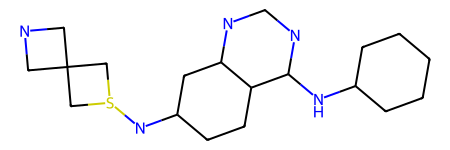
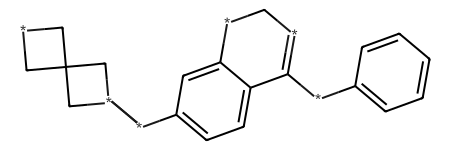
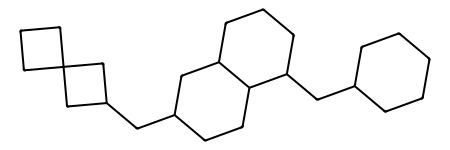
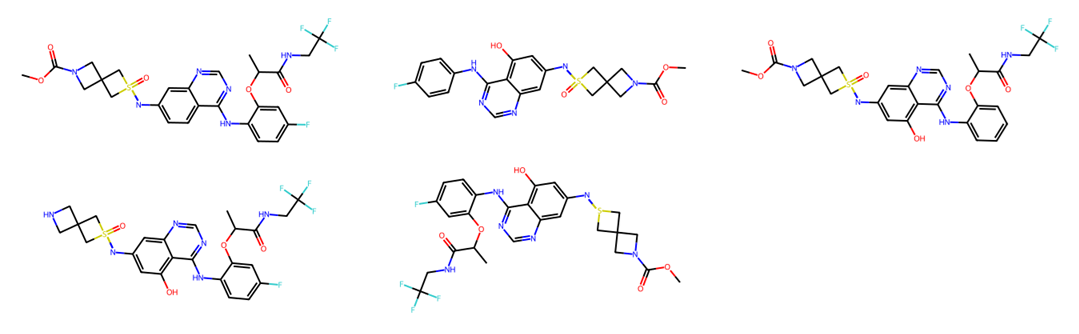
NovAna (Novelty Analysis) is a cheminformatics tool that that extends the decomposition of molecules into Bemis-Murcko frameworks (J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 15, 2887-2893) and allows the enumeration of partially decomposed scaffolds.
Project description
Introduction
Novana (Novelty Analysis) is a cheminformatics tool that allows decomposing molecules into their scaffolds and shapes. The method extends the functionalities of Bemis-Murcko scaffolds (J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 15, 2887–2893) by introducing more granularity on how atoms and bonds are treated during the decomposition. The implementation of these extra functionalities was inspired by the analysis described by Wills and Lipkus in ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 2114-2119. Novana can be used to cluster molecule data sets across multiple levels of generalisation - as an alternative to similarity methods. The tool can be used for the analysis of data sets or the creation of train/validation sets for machine learning.
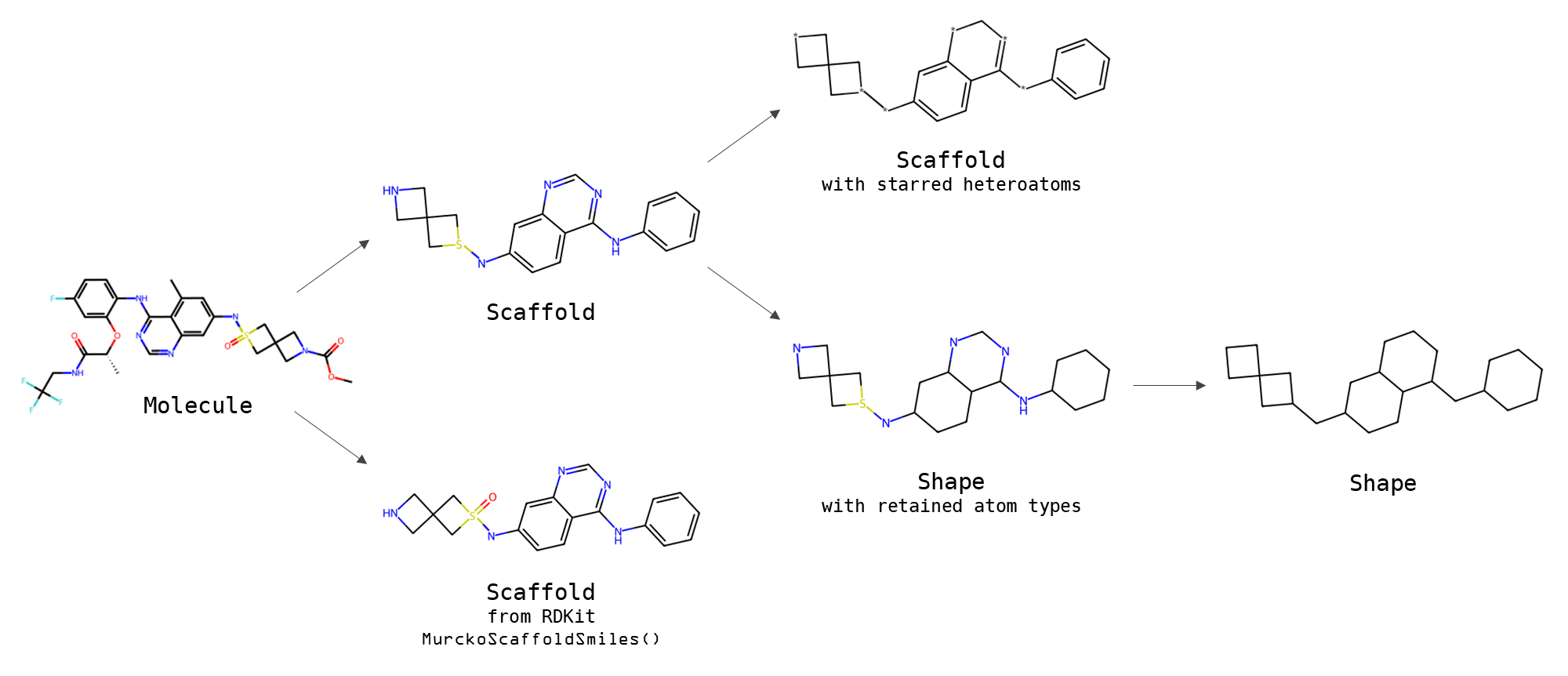
Here is an example of structural decomposition using different flavours of Novana also compared with the Bemis-Murcko decomposition in RDKit (MurckoScaffoldSmiles()):
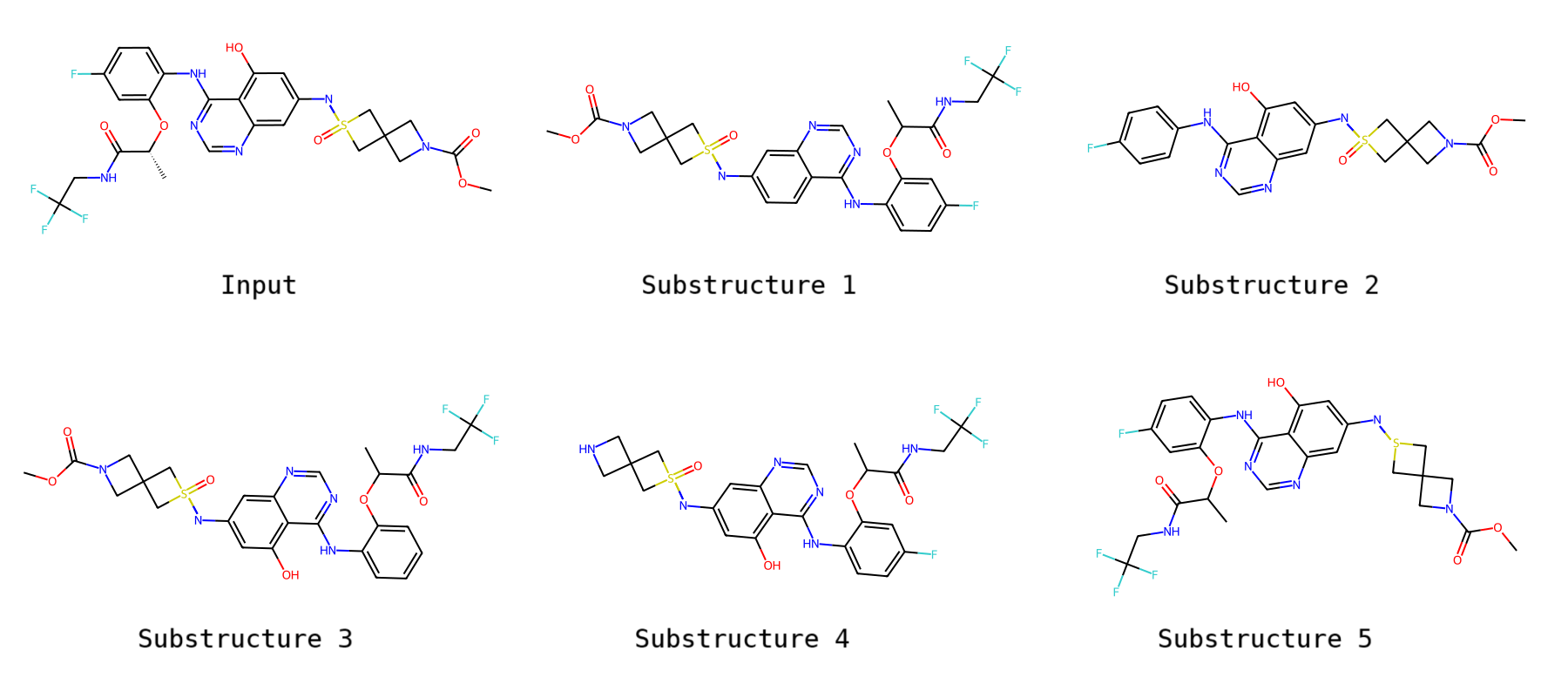
Novana was also extended to perform the partial decomposition of molecules into their scaffolds, i.e., for a given input molecule, a list of children molecules processed on isolated portions is enumerated. The partial scaffold enumeration can be used to remove sections of an input molecule yielding a set of children that can be analysed in networks or using distance methods. An example of partial scaffold enumeration is provided as follows.
Method
For a given SMILES input (molecule):
-
A scaffold is generated by removing recursively all terminal atoms until only atoms bonded with at least two different atoms are retained (e.g., cycles and chains). Non-rotatable terminal atoms (e.g., oxygens of a carbonyl/sulfonyl group) are removed. The bad valences of the retained atoms are fixed by adding or removing hydrogens according to some heuristics which can be found in
valence.py. The charges of atoms that have been modified by the algorithm are neutralised, whereas the charges of other atoms in the input remain unchanged. -
A Bemis-Murcko scaffold from RDKit is also generated to show that the RDKit implementation, in contrast to that in Novana, preserves non-rotatable terminal atoms.
-
A scaffold with starred heteroatoms can be created to generalise the atom composition of a scaffold. Heteroatoms are replaced by stars (*) and carbons and hydrogens are preserved.
-
A shape with retained atom types can be generated as a decomposition of a scaffold by preserving all atoms and converting all bonds into single bonds.
-
A shape is finally produced as a further decomposition by converting all its atoms into single bonded, non-aromatic, neutral carbons.
Novana also deals with mixtures automatically by extracting the largest fragment containing rings and using it as input to the decomposition. If no structures with rings are found in the input SMILES, Novana throws an error.
When running the enumerator of partial decompositions, the algorithm first identifies all terminal atoms and stores their positions as starting points. The algorithm then iterates through the starting points. For each starting point, a copy of the input molecule is created, and the logic performs a recursive removal as described for the scaffold only in that region.
How to install the tool
Novana can be installed from pypi (https://pypi.org/project/novana).
pip install novana
Usage
# Example of input SMILES
from rdkit import Chem
smiles = "COC(=O)N1CC2(C1)CS(=O)(=Nc1cc(C)c3c(Nc4ccc(F)cc4O[C@H](C)C(=O)NCC(F)(F)F)ncnc3c1)C2"
Chem.MolFromSmiles(smiles)
# Decompose into scaffold
from novana.api import scaffold_from_smiles
scaffold_from_smiles(smiles)
# Decompose into shape with atom types
from novana.api import shape_from_smiles
shape_from_smiles(smiles, retain_atom_types=True)
# Decompose into scaffold with starred heteroatoms
from novana.api import scaffold_from_smiles
scaffold_from_smiles(smiles, generalise_heteroatoms=True)
# Decompose into shape
from novana.api import shape_from_smiles
shape_from_smiles(smiles)
# Molecule and default scaffold and shape can also be obtained efficiently in one run
# (This function can be particularly useful for processing large sets)
from novana.api import molecule_scaffold_shape_from_smiles
mol, sfl, shp = molecule_scaffold_shape_from_smiles(smiles)
# Enumerate partially decomposed scaffolds
from novana.api import substructure_scaffolds_from_smiles
substructure_scaffolds_from_smiles(smiles)
License
Distributed under the terms of the MIT license. Novana is free and open-source software.
For developers
- The package can be installed from the wheel in the
dist/folder. When a new version needs to be released, a new wheel must be built. That can be done by changing the version of the package insidesetup.pythen callingpython setup.py bdist_wheelandpython setup.py sdistwhich will create a new build. - The code can be automatically tested using
python setup.py testwhich requirespytestto be installed - The
Makefilecan also be used for building (make build) or testing (make test) - Before committing new code, please always check that the formatting is consistent using
flake8
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file novana-0.3.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: novana-0.3.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 11.3 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.8.5
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
aadb3fe01de227cf523a6915aa45102aed1e97efc181e5d069a1595f2f974535
|
|
| MD5 |
99101a87dfd108b8f564f147504b49b1
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
60575f8b38bfefe592fc582ff6ebe6b91445ff7b6eb6bdba923eb72bb509bed4
|
File details
Details for the file novana-0.3.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: novana-0.3.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 10.9 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.8.5
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
bfc27abafb5ce218b8a0fc16b86298a662d8d727691564296150e65d87a5afec
|
|
| MD5 |
129f703a2d7d6e0341d133767abc1be0
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
98d370c93c41c67dd7bd6cdd3e5504207f6eda78879da265f192d9c29f547144
|