Lock context manager implemented via redis SETNX/BLPOP.
Project description
Lock context manager implemented via redis SETNX/BLPOP.
Free software: BSD license
Interface targeted to be exactly like threading.Lock.
Usage
Because we don’t want to require users to share the lock instance across processes you will have to give them names. Eg:
conn = StrictRedis()
with redis_lock.Lock(conn, "name-of-the-lock"):
print("Got the lock. Doing some work ...")
time.sleep(5)
Eg:
lock = redis_lock.Lock(conn, "name-of-the-lock")
if lock.acquire(blocking=False):
print("Got the lock.")
else:
print("Someone else has the lock.")
Avoid dogpile effect in django
The dogpile is also known as the thundering herd effect or cache stampede. Here’s a pattern to avoid the problem without serving stale data. The work will be performed a single time and every client will wait for the fresh data.
To use this you will need django-redis, however, python-redis-lock provides you a cache backend that has a cache method for your convenience. Just install python-redis-lock like this:
pip install "python-redis-lock[django]"
Now put something like this in your settings:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'redis_lock.django_cache.RedisCache',
'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:6379',
'OPTIONS': {
'DB': 1
}
}
}
This backend just adds a convenient .lock(name, expire=None) function to django-redis’s cache backend.
You would write your functions like this:
from django.core.cache import cache
def function():
val = cache.get(key)
if val:
return val
else:
with cache.lock(key):
val = cache.get(key)
if val:
return val
else:
# DO EXPENSIVE WORK
val = ...
cache.set(key, value)
return val
Troubleshooting
In some cases, the lock remains in redis forever (like a server blackout / redis or application crash / an unhandled exception). In such cases, the lock is not removed by restarting the application. One solution is to use the reset_all() function when the application starts:
# On application start/restart import redis_lock redis_lock.reset_all()
Alternativelly, you can reset individual locks via the reset method.
Use these carefully, if you understand what you do.
Features
based on the standard SETNX recipe
optional expiry
no spinloops at acquire
Implementation
redis_lock will use 2 keys for each lock named <name>:
lock:<name> - a string value for the actual lock
lock-signal:<name> - a list value for signaling the waiters when the lock is released
This is how it works:
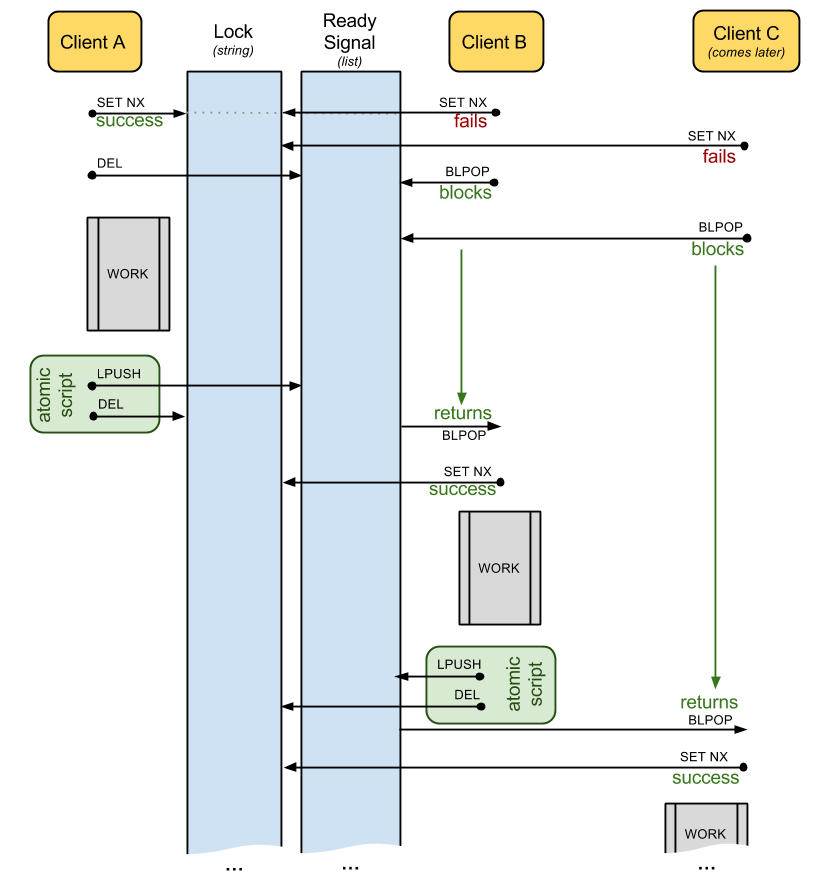
Documentation
Development
To run the all tests run:
tox
Requirements
- OS:
Any
- Runtime:
Python 2.6, 2.7, 3.2, 3.3 or PyPy
- Services:
Redis 2.6.12 or later.
Similar projects
bbangert/retools - acquire does spinloop
distributing-locking-python-and-redis - acquire does polling
cezarsa/redis_lock - acquire does not block
andymccurdy/redis-py - acquire does spinloop
mpessas/python-redis-lock - blocks fine but no expiration
Changelog
1.0.0
Fix Django integration. (reported by Jardel Weyrich)
Reorganize tests to use py.test.
Add test for Django integration.
Add reset_all functionality. (contributed by Yokotoka)
Add Lock.reset functionality.
Expose the Lock.token attribute.
0.1.2 (2013-11-05)
?
0.1.1 (2013-10-26)
?
0.1.0 (2013-10-26)
?
0.0.1 (2013-10-25)
First release on PyPI.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file python-redis-lock-1.0.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: python-redis-lock-1.0.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 85.2 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
3e5eacd0e36b132c2360342a4529128027229205b90dd6d8b051e0237a1218c2
|
|
| MD5 |
4196f1f2e064fb91fcbdd2dd29b36133
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
135461a7e5eea8389dd0fb28667bfa7d437baec214853b583101983bd0d0654f
|
File details
Details for the file python_redis_lock-1.0.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: python_redis_lock-1.0.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 8.9 kB
- Tags: Python 2, Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
db29d3bde7a493c4e8ed1791f5b8ff0de7f0d5b52aec351d83f7345c35b96c9b
|
|
| MD5 |
3fa87305d0c277ee92fb5f0dd3d56702
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
0959fd1e2f6842b369b78d6e4af25207be24b9fb80696cce6a8b6627f8fd8459
|






















