No project description provided
Project description
rbnf-rts
Runtime support for generated parsers of RBNF.hs
P.S:
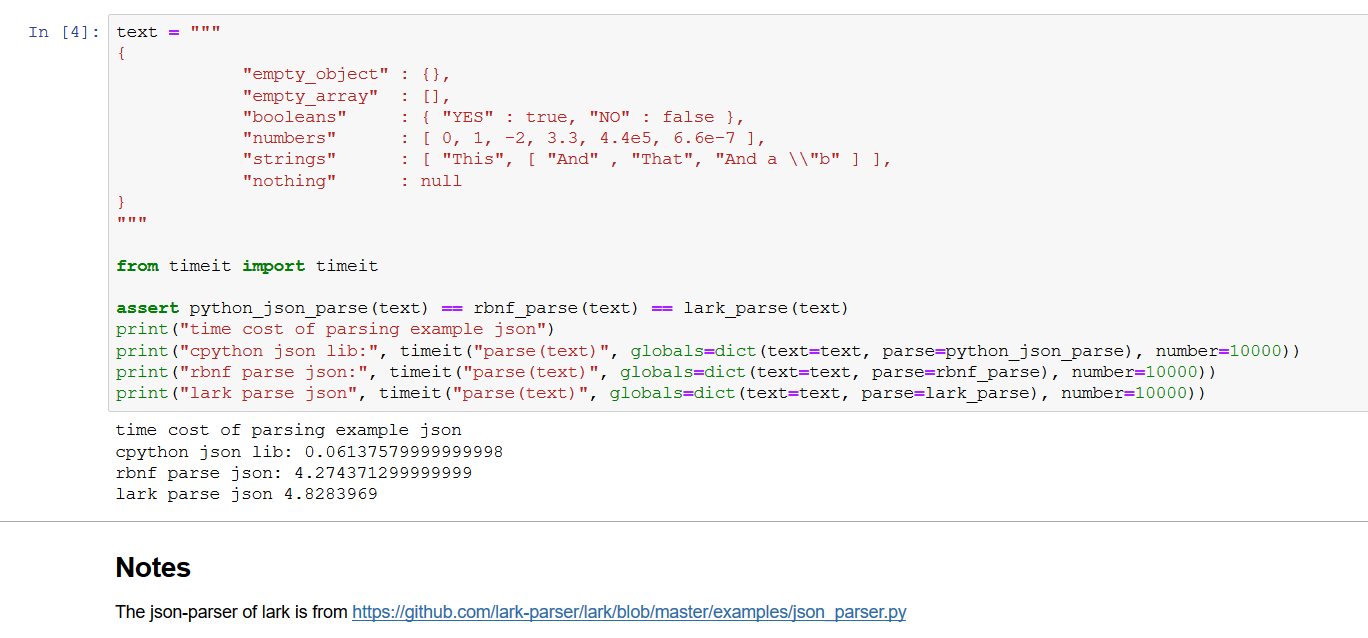
rbnf-rts is the new fastest Python parser generator by 2020, according to a benchmark given by benchmark-json.
Features
- Syntax-driven
- Left recursion with LL parsing(yes, left recur in LL, it's right)
- Grammar inline optimizations
- Smarter lookahead via ID3 algorithm
- Statically generated(no need to create the parser again and again when starting your application)
- Good error reports(including the position and nested rule names of parsing error)
- RBNF.hs is language independent
- [WIP]: context sensitive parsing as an extension to CFG
More Examples
Check the test directory:
- test
- multiply : parser/lexer implementation for multiplications
- arith : parser/lexer implementation for arithmetics
- relax : parser/lexer implementation for a full-featured programming language
- llvmir: parser/lexer implementation for LLVM IR, nearly full-featured
- rbnfjson: a json parser implemented by RBNF.hs and rbnf-rts
In each sub-directory of test, you can run tests via directly invoking the test.sh., like cd test/llvmir && bash test.sh
Native Dependencies
-
The Haskell Stack Toolchain
-
The executable
rbnf-pgenin PATH.If
~/.local/binis already in PATH:git clone https://github.com/thautwarm/RBNF.hs cd RBNF.hs stack install .
Example: Multiplications
- write a
multiply.exrbnffile
# 'mul' is a python global which should be marked as 'required' in .rlex
Mul : lhs=Mul "*" rhs=Atom { mul(lhs, rhs) }
| a=Atom {a}
;
# 'unwrap' should be marked as 'required', just as 'mul'
Atom : "(" !a=Mul ")" {a} ;
| <number> { unwrap($0) };
START ::= <BOF> Mul <EOF> { $1 };
or write a multiply.rbnf file:
# 'mul' is a python global which should be marked as 'required' in .rlex
Mul : !lhs=Mul "*" !rhs=Atom -> mul(lhs, rhs);
Mul : !a=Atom -> a;
Atom : "(" !a=Mul ")" -> a;
# 'unwrap' should be marked as 'required', just as 'mul'
Atom : !a=<number> -> unwrap(a);
START ::= <BOF> !a=Mul <EOF> -> a;
- write a
multiply.rlexfile:
%require mul
%require unwrap
%ignore space
number [+-]?\d+
space \s+
- codegen
sh> rbnf-pygen multiply.rbnf multiply.rlex multiply.py --k 1 --traceback
- run statically-generated parsers and lexers and enjoy its efficiency
from rbnf_rts.rts import Tokens, State
from multiply import run_lexer, mk_parser
import operator
def unwrap(x: Token):
return int(x.value)
scope = dict(mul=operator.mul, unwrap=unwrap)
parse = mk_parser(**scope)
tokens = list(run_lexer("<current file>", "-1 * 2 * (3 * 4)"))
got = parse(State(), Tokens(tokens))
print(got)
Got (True, -24), where True indicates the parsing succeeded.
If False, a list of errors will be given in the second element of
the return tuple.
- Menhir-like syntax sugars including
listandseparated_list.
A json parser more than 20% efficient than that of lark-parser(lol), written as a .exrbnf file.
START: <BOF> value <EOF> { $1 };
value: <ESCAPED_STRING> { DQString(*$0) }
| <SIGNED_INT> { int(*$0) }
| <SIGNED_FLOAT> { float(*$0) }
| "true" { True }
| "null" { None }
| "false" { False }
# array
| '[' ']' {[]}
| '[' separated_list(',', value) ']' { $1 }
# object
| '{' '}' { dict() }
| '{' separated_list(',', pair) '}' { dict($1) }
;
pair : <ESCAPED_STRING> ":" value { (DQString(*$0), $2) };
Check rbnfjson for more information.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distributions
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file rbnf_rts-1.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: rbnf_rts-1.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 99.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.1.1 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.22.0 setuptools/41.4.0 requests-toolbelt/0.8.0 tqdm/4.36.1 CPython/3.7.4
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
85955ddf7c76ab97a36e8f31fcdcc2168b18e3bc7457dcf1691f510dd4a0b4f8
|
|
| MD5 |
8962e3a66b25640a8bb2ce279d5af907
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
23dd1be8d22b206b86d59bfe1c341403eab73dd566986b59bdeb39afbd02d381
|