RelBench: Relational Deep Learning Benchmark
Project description
Website | Position Paper | Benchmark Paper | Mailing List
News
January 12, 2026: RelBench v2 is now released!
- Introducing Autocomplete tasks: new task paradigm to predict existing columns in the database.
- 4 new databases: SALT, RateBeer, arXiv, and MIMIC-IV.
- 40 new predictive tasks, including 28 Autocomplete tasks across new and existing databases.
- CTU integration: 70+ relational datasets from the CTU repository via ReDeLEx.
- Direct SQL database connectivity via ReDeLEx.
- 4DBInfer integration: 7 relational datasets from the 4DBInfer repository in RelBench format.
- Bug fixes and performance improvements:
- Optionally include (time-censored) labels as features in the database. (#327)
- Support NDCG metric for link prediction. (#276)
- Optimize SentenceTransformer encoding with Torch for 10-20% faster processing than default NumPy encoding. (#261)
- Enable configuring RelBench cache directory via environment variable. (#336)
- ... and more (see commit history for details)
September 26, 2024: RelBench is accepted to the NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks track!
July 3rd, 2024: RelBench v1 is now released!
Overview
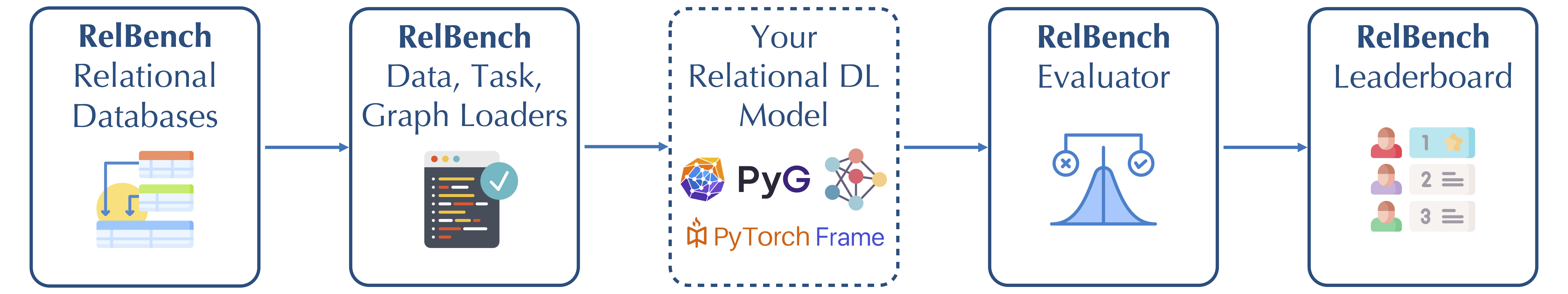
Relational Deep Learning is a new approach for end-to-end representation learning on data spread across multiple tables, such as in a relational database (see our position paper). Relational databases are the world's most widely used data management system, and are used for industrial and scientific purposes across many domains. RelBench is a benchmark designed to facilitate efficient, robust and reproducible research on end-to-end deep learning over relational databases.
RelBench v1 contains 7 realistic, large-scale, and diverse relational databases spanning domains including medical, social networks, e-commerce and sport. RelBench v2 adds 4 more, now totaling 11 databases. Each database has multiple predictive tasks (70 in total) defined, each carefully scoped to be both challenging and of domain-specific importance. It provides full support for data downloading, task specification and standardized evaluation in an ML-framework-agnostic manner.
Additionally, RelBench provides a first open-source implementation of a Graph Neural Network based approach to relational deep learning. This implementation uses PyTorch Geometric to load the data as a graph and train GNN models, and PyTorch Frame for modeling tabular data. Finally, there is an open leaderboard for tracking progress.
Key Papers
RelBench: A Benchmark for Deep Learning on Relational Databases
This paper details our approach to designing the RelBench benchmark. It also includes a key user study showing that relational deep learning can produce performant models with a fraction of the manual human effort required by typical data science pipelines. This paper is useful for a detailed understanding of RelBench and our initial benchmarking results. If you just want to quickly familiarize with the data and tasks, the website is a better place to start.
This paper outlines our proposal for how to do end-to-end deep learning on relational databases by combining graph neural networsk with deep tabular models. We reccomend reading this paper if you want to think about new methods for end-to-end deep learning on relational databases. The paper includes a section on possible directions for future research to give a snapshot of some of the research possibilities there are in this area.
Design of RelBench
RelBench has the following main components:
- 11 databases with a total of 70 tasks; both of these automatically downloadable for ease of use
- Easy data loading, and graph construction from pkey-fkey links
- Your own model, which can use any deep learning stack since RelBench is framework-agnostic. We provide a first model implementation using PyTorch Geometric and PyTorch Frame.
- Standardized evaluators - all you need to do is produce a list of predictions for test samples, and RelBench computes metrics to ensure standardized evaluation
- A leaderboard you can upload your results to, to track SOTA progress.
Installation
You can install RelBench using pip:
pip install relbench
This will allow usage of the core RelBench data and task loading functionality.
Including CTU datasets
To use datasets from the CTU repository, use:
pip install relbench[ctu]
If you use the CTU datasets in your work, please cite ReDeLEx as below:
@misc{peleska2025redelex,
title={REDELEX: A Framework for Relational Deep Learning Exploration},
author={Jakub Peleška and Gustav Šír},
year={2025},
eprint={2506.22199},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.22199},
}
Including 4DBInfer datasets
To use datasets from the 4DBInfer repository, use:
pip install relbench[dbinfer]
If you use the 4DBInfer datasets in your work, please cite 4DBInfer as below:
@article{dbinfer,
title={4DBInfer: A 4D Benchmarking Toolbox for Graph-Centric Predictive Modeling on Relational DBs},
author={Wang, Minjie and Gan, Quan and Wipf, David and Cai, Zhenkun and Li, Ning and Tang, Jianheng and Zhang, Yanlin and Zhang, Zizhao and Mao, Zunyao and Song, Yakun and Wang, Yanbo and Li, Jiahang and Zhang, Han and Yang, Guang and Qin, Xiao and Lei, Chuan and Zhang, Muhan and Zhang, Weinan and Faloutsos, Christos and Zhang, Zheng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.18209},
year={2024}
}
To additionally use relbench.modeling, which requires PyTorch, PyTorch Geometric and PyTorch Frame, install these dependencies manually or do:
pip install relbench[full]
For the scripts in the examples directory, use:
pip install relbench[example]
Then, to run a script:
git clone https://github.com/snap-stanford/relbench
cd relbench/examples
python gnn_entity.py --dataset rel-f1 --task driver-position
Package Usage
This section provides a brief overview of using the RelBench package. For a more in-depth coverage see the Tutorials section. For detailed documentations, please see the code directly.
Imports:
from relbench.base import Table, Database, Dataset, EntityTask
from relbench.datasets import get_dataset
from relbench.tasks import get_task
Get a dataset, e.g., rel-amazon:
dataset: Dataset = get_dataset("rel-amazon", download=True)
Details on downloading and caching behavior.
RelBench datasets (and tasks) are cached to disk (usually at ~/.cache/relbench, the location can be set using the RELBENCH_CACHE_DIR environment variable). If not present in cache, download=True downloads the data, verifies it against the known hash, and caches it. If present, download=True performs the verification and avoids downloading if verification succeeds. This is the recommended way.
download=False uses the cached data without verification, if present, or processes and caches the data from scratch / raw sources otherwise.
For faster download, please see this.
dataset consists of a Database object and temporal splitting times dataset.val_timestamp and dataset.test_timestamp.
To get the database:
db: Database = dataset.get_db()
Preventing temporal leakage
By default, rows with timestamp > dataset.test_timestamp are excluded to prevent accidental temporal leakage. The full database can be obtained with:
full_db: Database = dataset.get_db(upto_test_timestamp=False)
Various tasks can be defined on a dataset. For example, to get the user-churn task for rel-amazon:
task: EntityTask = get_task("rel-amazon", "user-churn", download=True)
A task provides train/val/test tables:
train_table: Table = task.get_table("train")
val_table: Table = task.get_table("val")
test_table: Table = task.get_table("test")
Preventing test leakage
By default, the target labels are hidden from the test table to prevent accidental data leakage. The full test table can be obtained with:
full_test_table: Table = task.get_table("test", mask_input_cols=False)
You can build your model on top of the database and the task tables. After training and validation, you can make prediction from your model on the test table. Suppose your prediction test_pred is a NumPy array following the order of task.test_table, you can call the following to get the evaluation metrics:
task.evaluate(test_pred)
Additionally, you can evaluate validation (or training) predictions as such:
task.evaluate(val_pred, val_table)
Tutorials
| Notebook | Try on Colab | Description |
|---|---|---|
| load_data.ipynb |  |
Load and explore RelBench data |
| train_model.ipynb |  |
Train your first GNN-based model on RelBench |
| custom_dataset.ipynb |  |
Use your own data in RelBench |
| custom_task.ipynb |  |
Define your own ML tasks in RelBench |
Contributing
Please check out CONTRIBUTING.md if you are interested in contributing datasets, tasks, bug fixes, etc. to RelBench.
Cite RelBench
If you use RelBench in your work, please cite our position and benchmark papers:
@inproceedings{rdl,
title={Position: Relational Deep Learning - Graph Representation Learning on Relational Databases},
author={Fey, Matthias and Hu, Weihua and Huang, Kexin and Lenssen, Jan Eric and Ranjan, Rishabh and Robinson, Joshua and Ying, Rex and You, Jiaxuan and Leskovec, Jure},
booktitle={Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning}
}
@misc{relbench,
title={RelBench: A Benchmark for Deep Learning on Relational Databases},
author={Joshua Robinson and Rishabh Ranjan and Weihua Hu and Kexin Huang and Jiaqi Han and Alejandro Dobles and Matthias Fey and Jan E. Lenssen and Yiwen Yuan and Zecheng Zhang and Xinwei He and Jure Leskovec},
year={2024},
eprint={2407.20060},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2407.20060},
}
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file relbench-2.0.2.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: relbench-2.0.2.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 72.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.11.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
2ce52774e45f76c15287e340562593371d2f35329d229d32abe575c47a3965ef
|
|
| MD5 |
b1c5c9108c2d497117231425cf542572
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
20adcf8a32f4a94c3b661aa8d5b87acfda76b78a0f0240a3c389db61759d28a5
|
File details
Details for the file relbench-2.0.2-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: relbench-2.0.2-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 88.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.11.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
a2e2a637250d7077535629960e0b004389b5b8c62d312ee662a101d5c2081606
|
|
| MD5 |
f3177d32203d843b0905f6ef51402c44
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
2ca99ac98774edc374e3737be964ac13a8b0a9f51761e97a5e4dc12219acdef0
|