Uses SSH agent to encrypt/decrypt arbitrary data
Project description
sagecipher
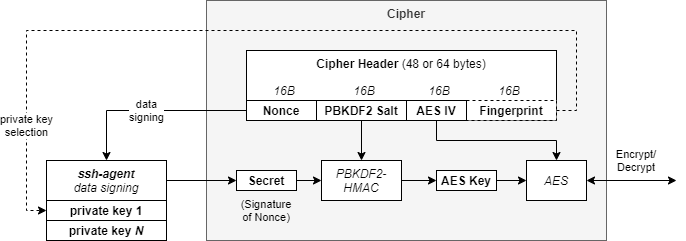
sagecipher (ssh agent cipher) provides an AES cipher, whose key is obtained by signing nonce data via SSH agent. This is illustrated below.
This can be used in turn by the keyring library, and by ansible-vault to encrypt/decrypt files or secrets via the users' local or forwarded ssh-agent session.
Contents
Installation
pip install sagecipher
Usage
Before using, ssh-agent must be running with at least one ssh-key available for producing cipher key material:
$ source <(ssh-agent)
Agent pid 3710
$ ssh-add
Enter passphrase for /home/somebody/.ssh/id_rsa:
Identity added: /home/somebody/.ssh/id_rsa (/home/somebody/.ssh/id_rsa)
Using the keyring backend
Here we will set the following environment variables:
| Environment Variable | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
PYTHON_KEYRING_BACKEND |
sagecipher.keyring.Keyring |
Tells keyring explicitly to use the sagecipher backend |
KEYRING_PROPERTY_SSH_KEY_FINGERPRINT |
<hex fingerprint of ssh key> | Pre-selects the SSH key for the sagecipher backend to use |
If no other keyring backends are available, sagecipher will be selected as the default backend with a priority of 1. The PYTHON_KEYRING_BACKEND environment variable can be set to explicitly set the backend. See the keyring docs for more help using the keyring library.
$ sagecipher list-keys # paramiko does not yet expose key comments, unfortunately..
[ssh-rsa] e8:19:fe:c5:0a:b4:57:5d:96:27:b3:e3:ec:ba:24:3c
[ssh-rsa] 38:c5:94:45:ca:01:65:d1:d0:c5:ee:5e:cd:b3:94:39
$ export PYTHON_KEYRING_BACKEND=sagecipher.keyring.Keyring
$ keyring set svc user1
Password for 'user' in 'svc':
Please select from the following keys...
[1] ssh-rsa e8:19:fe:c5:0a:b4:57:5d:96:27:b3:e3:ec:ba:24:3c
[2] ssh-rsa 38:c5:94:45:ca:01:65:d1:d0:c5:ee:5e:cd:b3:94:39
Selection (1..2): 1
$ keyring get svc user1
password1
$ export KEYRING_PROPERTY_SSH_KEY_FINGERPRINT=e8:19:fe:c5:0a:b4:57:5d:96:27:b3:e3:ec:ba:24:3c
$ keyring get svc user2
password2
$ python
Python 3.6.8 (default, Jan 14 2019, 11:02:34)
[GCC 8.0.1 20180414 (experimental) [trunk revision 259383]] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import keyring
>>> keyring.get_password('svc', 'user1')
'password1'
>>> keyring.get_password('svc', 'user2')
'password2'
Using with ansible-vault
In this example we create a secret key in the keyring for use with ansible-vault.
This process will work with any keyring backend, but it's assumed we are up and
running with the sagecipher keyring backend per the previous section.
For more information, see: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/user_guide/vault.html
-
Set up environment variables
Environment Variable Value Description PYTHON_KEYRING_BACKENDsagecipher.keyring.KeyringTells keyringto use thesagecipherbackendKEYRING_PROPERTY_SSH_KEY_FINGERPRINT<hex fingerprint of ssh key> Pre-selects the SSH key for the sagecipherbackend to useANSIBLE_VAULT_PASSWORD_FILE<path to password script> ansible-vaultwill use this script to find the vault encryption keyReplace the key fingerprint below with your own.
export PYTHON_KEYRING_BACKEND=sagecipher.keyring.Keyring export KEYRING_PROPERTY_SSH_KEY_FINGERPRINT=e8:19:fe:c5:0a:b4:57:5d:96:27:b3:e3:ec:ba:24:3c export ANSIBLE_VAULT_PASSWORD_FILE=~/vault-pass.sh
-
Generate a random key for ansible-vault and store in the keyring
keyring set ansible-vault key < <(dd if=/dev/urandom bs=32 count=1 | base64)
-
Create the vault password script to retrieve the vault key
$ cat <<EOF > ~/vault-pass.sh #!/bin/sh keyring get ansible-vault key EOF $ chmod +x vault-pass.sh
-
Test it out with
ansible-vault$ ansible-vault encrypt_string "secret_password" --name "secret_attribute" > secrets.yml $ ansible localhost -m debug -a var="secret_attribute" -e "@secrets.yml" [WARNING]: No inventory was parsed, only implicit localhost is available localhost | SUCCESS => { "secret_attribute": "secret_password" }
Using sagecipher directly in Python
>>> from sagecipher import Cipher
>>>
>>> # Encrypts using the first SSH key available from SSH agent...
>>> enc_text = Cipher.encrypt_string("hello, world")
>>> text = Cipher.decrypt_string(enc_text)
>>> text
"hello, world"
Using the sagecipher CLI tool
Check sagecipher --help for usage. By default, the 'decrypt' operation will create a FIFO file, and then start a loop to decrypt out to the FIFO whenever it is opened.
The FIFO is created with mode 600 by default, and if the permissions are altered or the parent shell is terminated then the sagecipher background session will end.
$ sagecipher encrypt - encfile
Please select from the following keys...
[1] ssh-rsa e8:19:fe:c5:0a:b4:57:5d:96:27:b3:e3:ec:ba:24:3c
[2] ssh-rsa 38:c5:94:45:ca:01:65:d1:d0:c5:ee:5e:cd:b3:94:39
Selection (1..2): 1
Reading from STDIN...
secret sauce
(CTRL-D)
$ sagecipher decrypt encfile
secret sauce
$ mkfifo decfile
$ sagecipher decrypt encfile decfile &
[1] 16753
$ cat decfile # decfile is just a FIFO
secret sauce
$
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
File details
Details for the file sagecipher-0.7.5.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: sagecipher-0.7.5.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 12.2 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.2.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.24.0 setuptools/44.0.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.47.0 CPython/3.8.2
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
b7330f2b2f5b3d0207f94c25973d24282a1fe9ca04f39dfb1dd09939c47abad4
|
|
| MD5 |
6f794155c872b96e6e4e7fa46412bf6b
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
79bb5cf41087b5eb5b8482023b5d0b885c54311900c96e434d78749c69941deb
|