spatial-kfold: A Python Package for Spatial Resampling Toward More Reliable Cross-Validation in Spatial Studies.
Project description
spatial-kfold
spatial-kfold: A Python Package for Spatial Resampling Toward More Reliable Cross-Validation in Spatial Studies.
spatial-kfold is a python library for performing spatial resampling to ensure more robust cross-validation in spatial studies. It offers spatial clustering and block resampling technique with user-friendly parameters to customize the resampling. It enables users to conduct a "Leave Region Out" cross-validation, which can be useful for evaluating the model's generalization to new locations as well as improving the reliability of feature selection and hyperparameter tuning in spatial studies.
spatial-kfold can be integrated easily with scikit-learn's LeaveOneGroupOut cross-validation technique. This integration enables you to further leverage the resampled spatial data for performing feature selection and hyperparameter tuning.
Main Features
spatial-kfold allow conducting "Leave Region Out" using two spatial resampling techniques:
-
- Spatial clustering with KMeans or BisectingKMeans
-
- Spatial blocks (rect / hex)
- Random blocks
- Continuous blocks
- tb-lr : top-bottom, left-right
- bt-rl : bottom-top, right-left
Installation
spatial-kfold can be installed from PyPI
pip install spatial-kfold
Example
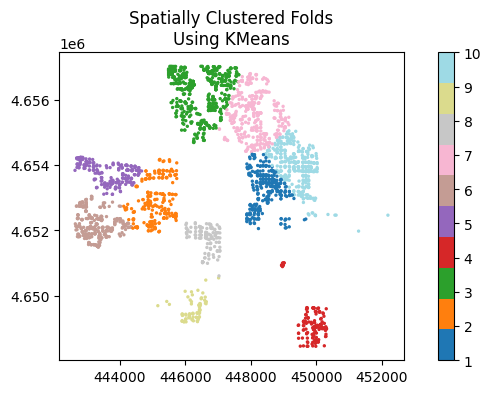
1. Spatial clustering with KMeans 
import geopandas as gpd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
import matplotlib.colors as colors
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap, LinearSegmentedColormap
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator import inset_axes
from spatialkfold.blocks import spatial_blocks
from spatialkfold.datasets import load_ames
from spatialkfold.clusters import spatial_kfold_clusters
# Load ames data
ames = load_ames()
ames_prj = ames.copy().to_crs(ames.estimate_utm_crs())
ames_prj['id'] = range(len(ames_prj))
# 1. Spatial cluster resampling
ames_clusters = spatial_kfold_clusters(
gdf=ames_prj,
name='id',
nfolds=10,
algorithm='kmeans', # "bisectingkmeans"
n_init="auto",
random_state=569
)
# Get the 'tab20' colormap
cols_tab = cm.get_cmap('tab20', 10)
# Generate a list of colors from the colormap
cols = [cols_tab(i) for i in range(10)]
# create a color ramp
color_ramp = ListedColormap(cols)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,1 , figsize=(9, 4))
ames_clusters.plot(column='folds', ax=ax, cmap= color_ramp, markersize = 2, legend=True)
ax.set_title('Spatially Clustered Folds\nUsing KMeans')
plt.show()
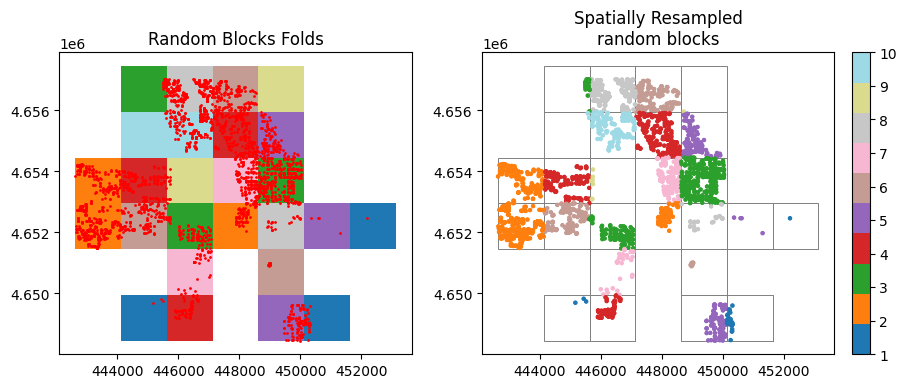
2. Spatial blocks 
# 2.1 spatial resampled random blocks
# create 10 random blocks
ames_rnd_blocks = spatial_blocks(
gdf=ames_prj,
width=1500,
height=1500,
method="random", # "continuous"
orientation="tb-lr", # "bt-rl"
grid_type="rect", # "hex"
random_state=135
)
# resample the ames data with the prepared blocks
ames_res_rnd_blk = gpd.overlay(ames_prj, ames_rnd_blocks)
# plot the resampled blocks
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1,2 , figsize=(10, 6))
# plot 1
ames_rnd_blocks.plot(column='folds',cmap=color_ramp, ax=ax[0] ,lw=0.7, legend=False)
ames_prj.plot(ax=ax[0], markersize = 1, color = 'r')
ax[0].set_title('Random Blocks Folds')
# plot 2
ames_rnd_blocks.plot(facecolor="none",edgecolor='grey', ax=ax[1] ,lw=0.7, legend=False)
ames_res_rnd_blk.plot(column='folds', cmap=color_ramp, legend=False, ax=ax[1], markersize=3)
ax[1].set_title('Spatially Resampled\nrandom blocks')
im1 = ax[1].scatter(ames_res_rnd_blk.geometry.x , ames_res_rnd_blk.geometry.y, c=ames_res_rnd_blk['folds'], cmap=color_ramp, s=5)
axins1 = inset_axes(
ax[1],
width="5%", # width: 5% of parent_bbox width
height="50%", # height: 50%
loc="lower left",
bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 0, 1, 2),
bbox_transform=ax[1].transAxes,
borderpad=0
)
fig.colorbar(im1, cax=axins1, ticks= range(1,11))
plt.show()
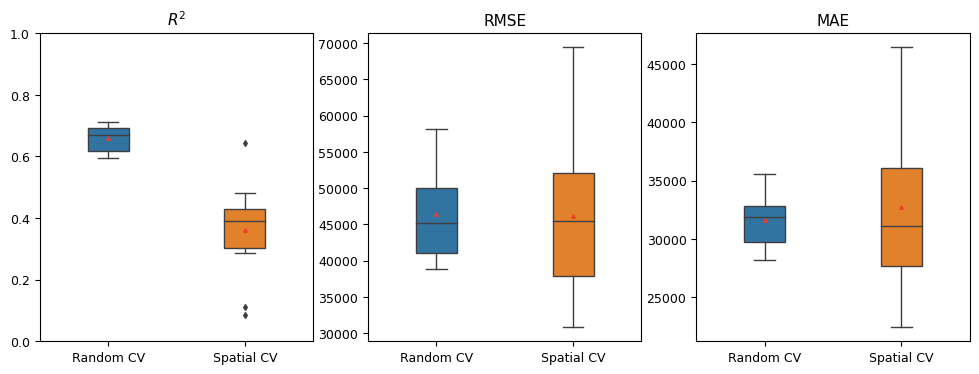
3. Compare Random and Spatial cross validation 
4 .Feature Selection with spatial-kfold
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import LeaveOneGroupOut
clf = RandomForestRegressor()
group_cvs = LeaveOneGroupOut()
spatial_folds = ames_clusters.folds.values.ravel()
rfecv = RFECV(estimator=clf, step=1, cv=group_cvs)
rfecv.fit(X, y, groups=spatial_folds)
5. Hyperparameter tuning with spatial-kfold
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import LeaveOneGroupOut, GridSearchCV
clf = RandomForestRegressor()
param_grid = {
'n_estimators': [50, 100, 150],
'max_depth': [None, 10, 20],
'min_samples_split': [2, 5],
}
group_cvs = LeaveOneGroupOut()
spatial_folds = ames_clusters.folds.values.ravel()
grid_search = GridSearchCV(estimator=clf, param_grid=param_grid, cv=group_cvs)
grid_search.fit(X, y, groups=spatial_folds)
Credits
This package was inspired by the following R packages:
Dependencies
This project relies on the following dependencies:
Citation
If you use My Package in your research or work, please cite it using the following entries:
- MLA Style:
Ghariani, Walid. "spatial-kfold: A Python Package for Spatial Resampling Toward More Reliable Cross-Validation in Spatial Studies." 2023. GitHub, https://github.com/WalidGharianiEAGLE/spatial-kfold
- BibTex Style:
@Misc{spatial-kfold,
author = {Walid Ghariani},
title = {spatial-kfold: A Python Package for Spatial Resampling Toward More Reliable Cross-Validation in Spatial Studies},
howpublished = {GitHub},
year = {2023},
url = {https://github.com/WalidGharianiEAGLE/spatial-kfold}
}
Resources
A list of tutorials and resources mainly in R explaining the importance of spatial resampling and spatial cross validation
- Hanna Meyer: "Machine-learning based modelling of spatial and spatio-temporal data"
- Jannes Münchow: "The importance of spatial cross-validation in predictive modeling"
- Julia Silge: Spatial resampling for more reliable model evaluation with geographic data
Bibliography
Meyer, H., Reudenbach, C., Wöllauer, S., Nauss, T. (2019): Importance of spatial predictor variable selection in machine learning applications - Moving from data reproduction to spatial prediction. Ecological Modelling. 411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2019.108815
Schratz, Patrick, et al. "Hyperparameter tuning and performance assessment of statistical and machine-learning algorithms using spatial data." Ecological Modelling 406 (2019): 109-120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2019.06.002
Schratz, Patrick, et al. "mlr3spatiotempcv: Spatiotemporal resampling methods for machine learning in R." arXiv preprint arXiv:2110.12674 (2021). https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.12674
Valavi, Roozbeh, et al. "blockCV: An r package for generating spatially or environmentally separated folds for k-fold cross-validation of species distribution models." Biorxiv (2018): 357798. https://doi.org/10.1101/357798
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file spatial_kfold-0.0.4.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: spatial_kfold-0.0.4.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 261.3 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.8.15
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
2cc8af90095c2f445ecb7fe044557c2d362ee4932a7bae6ac72bab2e081e2667
|
|
| MD5 |
7776214cf5fcaf125bcb8f5bdb562bcf
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
063061ca2605f44c7ab288b56fc46770c79b0981fc0b98e703b66fffcc005298
|
File details
Details for the file spatial_kfold-0.0.4-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: spatial_kfold-0.0.4-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 288.3 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.8.15
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9c1893efdf40c16e22d7808e828159685904c3fd332964c83c131b37fabebb81
|
|
| MD5 |
543df078b2cdc167a1096d386e5eebdd
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
97efcf3fe860c05f6b4f9da77bc8938525db87545c7e2a994363219db81f060d
|














