Starlake Python Distribution For Dagster
Project description
starlake-dagster
starlake-dagster is the Starlake Python Distribution for Dagster.
It is recommended to use it in combinaison with starlake dag generation, but can be used directly as is in your DAGs.
Prerequisites
Before installing starlake-dagster, ensure the following minimum versions are installed on your system:
- starlake: 1.0.0 or higher
- python: 3.8 or higher
Installation
pip install starlake-orchestration[dagster] --upgrade
StarlakeDagsterJob
ai.starlake.dagster.StarlakeDagsterJob is an abstract factory class that extends the generic factory interface ai.starlake.job.IStarlakeJob and is responsible for generating the Dagster node that will run the import, load and transform starlake commands.
sl_import
It generates the Dagster node that will run the starlake import command.
def sl_import(
self,
task_id: str,
domain: str,
**kwargs) -> op:
#...
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| task_id | str | the optional task id ({domain}_import by default) |
| domain | str | the required domain to import |
sl_load
It generates the Dagster node that will run the starlake load command.
def sl_load(
self,
task_id: str,
domain: str,
table: str,
spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig=None,
**kwargs) -> op:
#...
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| task_id | str | the optional task id ({domain}_{table}_load by default) |
| domain | str | the required domain of the table to load |
| table | str | the required table to load |
| spark_config | StarlakeSparkConfig | the optional ai.starlake.job.StarlakeSparkConfig |
sl_transform
It generates the Dagster node that will run the starlake transform command.
def sl_transform(
self,
task_id: str,
transform_name: str,
transform_options: str=None,
spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig=None, **kwargs) -> op:
#...
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| task_id | str | the optional task id ({transform_name} by default) |
| transform_name | str | the transform to run |
| transform_options | str | the optional transform options |
| spark_config | StarlakeSparkConfig | the optional ai.starlake.job.StarlakeSparkConfig |
sl_job
Ultimately, all these methods will call the sl_job method that needs to be implemented in all concrete factory classes.
def sl_job(
self,
task_id: str,
arguments: list,
spark_config: StarlakeSparkConfig=None,
**kwargs) -> op:
#...
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| task_id | str | the required task id |
| arguments | list | The required arguments of the starlake command to run |
| spark_config | StarlakeSparkConfig | the optional ai.starlake.job.StarlakeSparkConfig |
Init
To initialize this class, you may specify the optional pre load strategy and options to use.
def __init__(self, pre_load_strategy: Union[StarlakePreLoadStrategy, str, None], options: dict=None, **kwargs) -> None:
"""Overrides IStarlakeJob.__init__()
Args:
pre_load_strategy (Union[StarlakePreLoadStrategy, str, None]): The pre-load strategy to use.
options (dict): The options to use.
"""
super().__init__(pre_load_strategy, options, **kwargs)
#...
StarlakePreLoadStrategy
ai.starlake.job.StarlakePreLoadStrategy is an enum that defines the different pre load strategies that can be used to conditionaly load a domain.
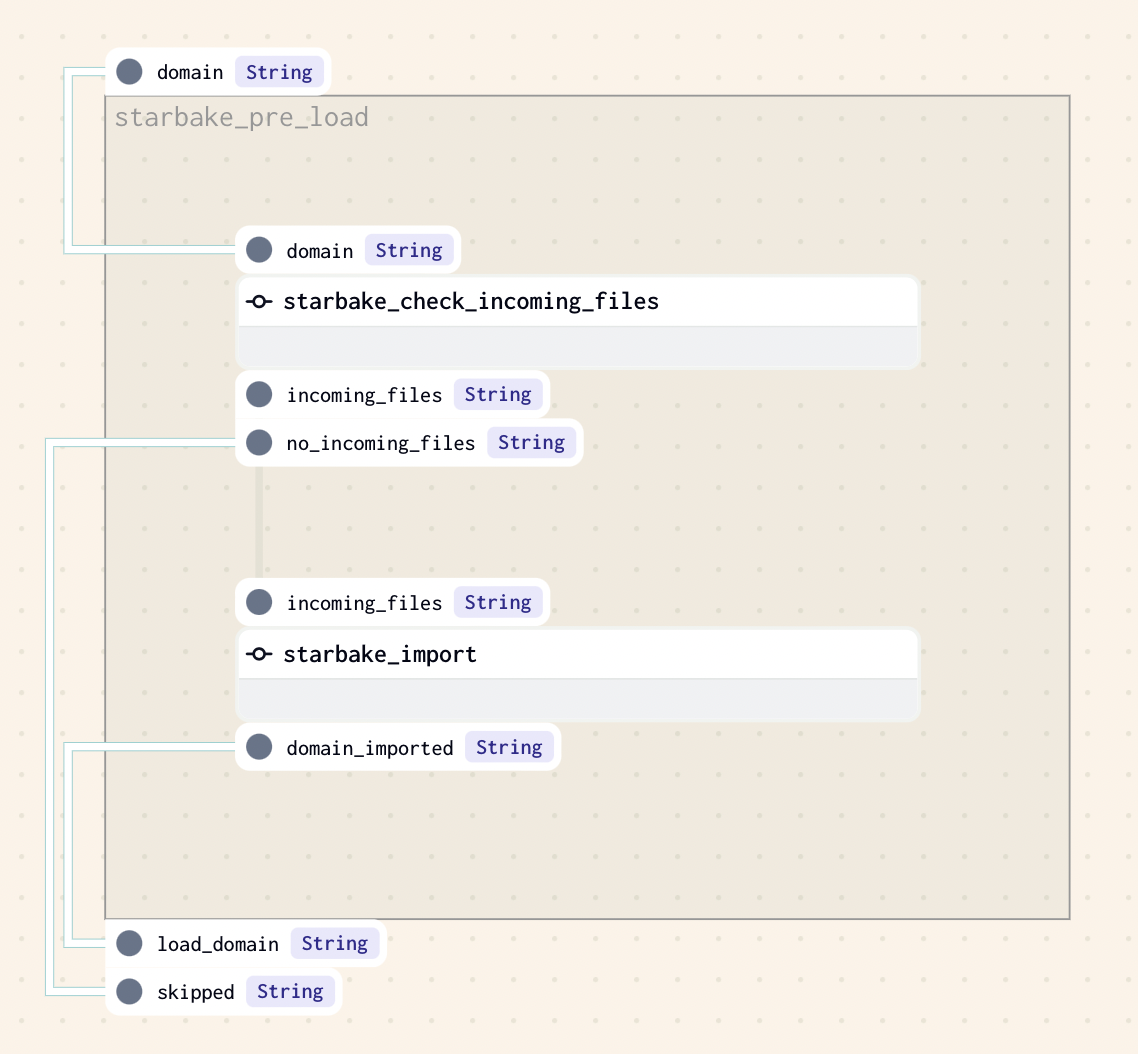
The pre-load strategy is implemented by sl_pre_load method that will generate the Dagster node corresponding to the choosen strategy.
def sl_pre_load(
self,
domain: str,
pre_load_strategy: Union[StarlakePreLoadStrategy, str, None]=None,
**kwargs) -> op:
#...
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| domain | str | the domain to load |
| pre_load_strategy | str | the optional pre load strategy (self.pre_load_strategy by default) |
NONE
The load of the domain will not be conditionned and no pre-load op will be executed.
IMPORTED
This strategy implies that at least one file is present in the landing area (SL_ROOT/importing/{domain} by default, if option incoming_path has not been specified). If there is one or more files to load, the method sl_import will be called to import the domain before loading it, otherwise the loading of the domain will be skipped.
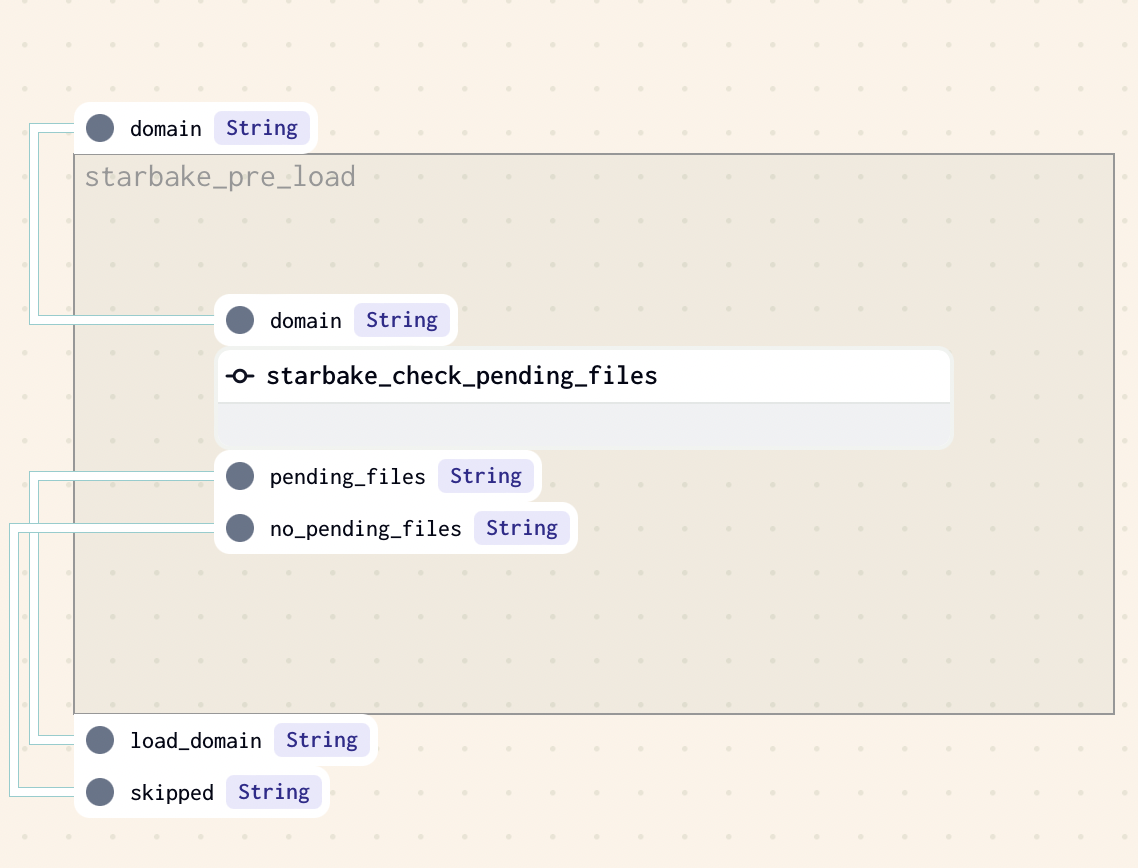
PENDING
This strategy implies that at least one file is present in the pending datasets area of the domain (SL_ROOT/datasets/pending/{domain} by default if option pending_path has not been specified), otherwise the loading of the domain will be skipped.
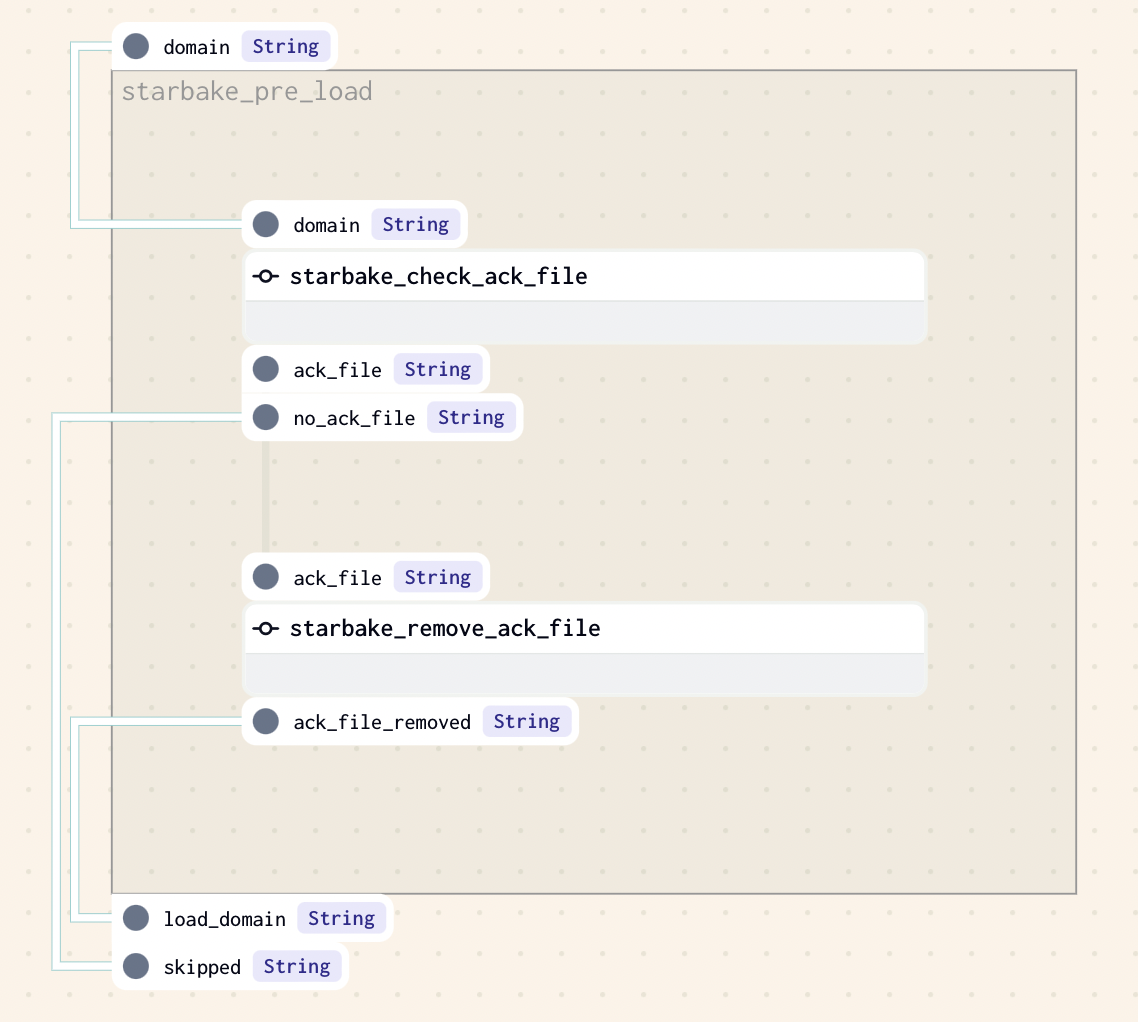
ACK
This strategy implies that an ack file is present at the specified path (option global_ack_file_path), otherwise the loading of the domain will be skipped.
Options
The following options can be specified in all concrete factory classes:
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| sl_env_var | str | optional starlake environment variables passed as an encoded json string |
| pre_load_strategy | str | one of none (default), imported, pending or ack |
| incoming_path | str | path to the landing area for the domain to load ({SL_ROOT}/incoming by default) |
| pending_path | str | path to the pending datastets for the domain to load ({SL_DATASETS}/pending by default) |
| global_ack_file_path | str | path to the ack file ({SL_DATASETS}/pending/{domain}/{{{{ds}}}}.ack by default) |
| ack_wait_timeout | int | timeout in seconds to wait for the ack file(1 hour by default) |
On premise
StarlakeDagsterShellJob
This class is a concrete implementation of StarlakeDagsterJob that generates nodes using dagster-shell library. Usefull for on premise execution.
An additional SL_STARLAKE_PATH option is required to specify the path to the starlake executable.
StarlakeDagsterShellJob Load Example
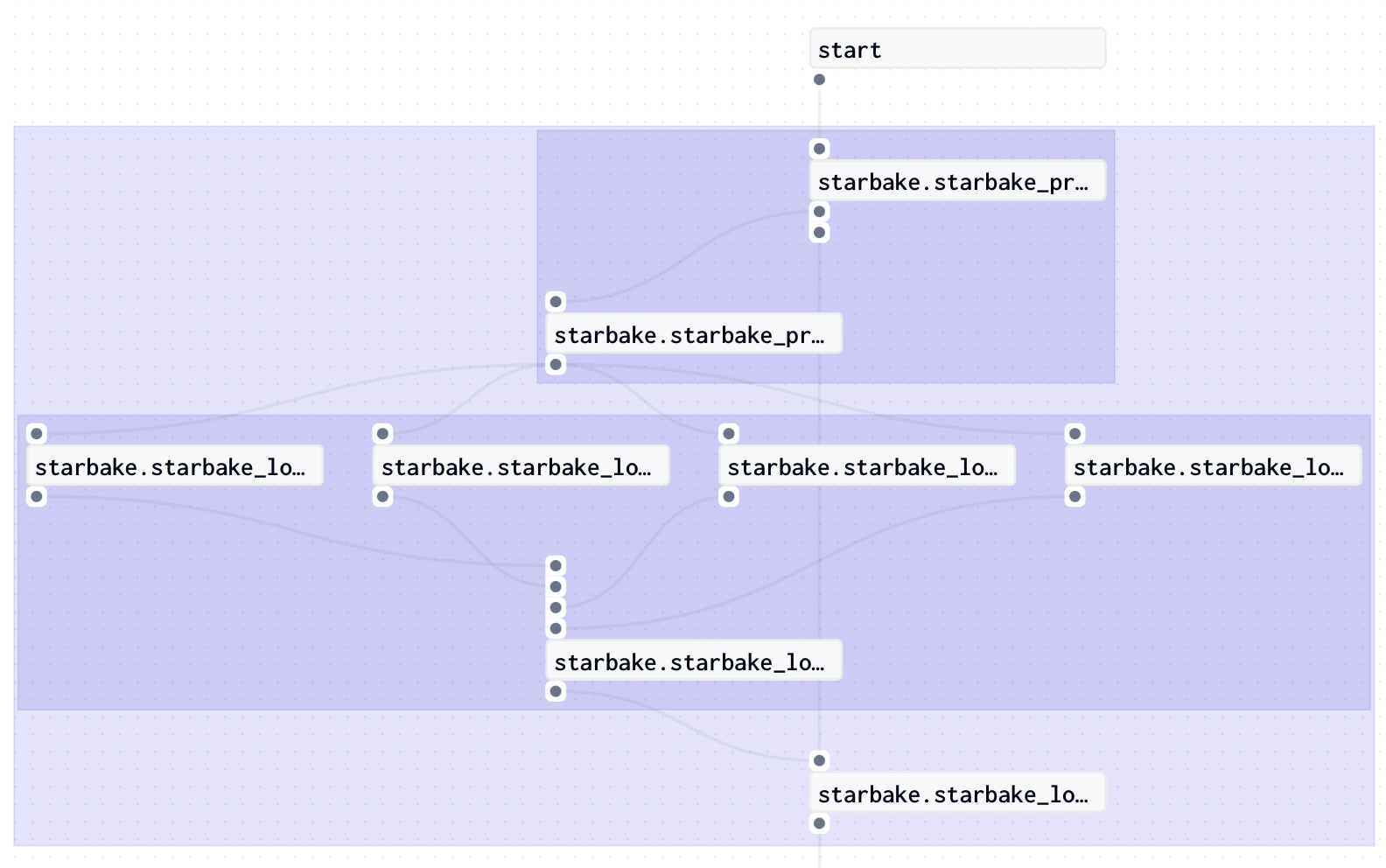
The following example shows how to use StarlakeDagsterShellJob to generate dynamically Jobs that load domains using starlake and record corresponding Dagster assets.
description="""example to load domain(s) using dagster starlake shell job"""
options = {
# General options
'sl_env_var':'{"SL_ROOT": "/starlake/samples/starbake"}',
'pre_load_strategy':'ack',
# Bash options
'SL_STARLAKE_PATH':'/starlake/starlake.sh',
}
from ai.starlake.dagster.shell import StarlakeDagsterShellJob
sl_job = StarlakeDagsterShellJob(options=options)
import os
from dagster import ScheduleDefinition, GraphDefinition, Definitions, DependencyDefinition, JobDefinition, In, InputMapping, Out, Output, OutputMapping, graph, op
from dagster._core.definitions.input import InputDefinition
schedules= [
{
'schedule': 'None',
'cron': '0 0 * * *',
'domains': [
{
'name':'starbake',
'final_name':'starbake',
'tables': [
{
'name': 'Customers',
'final_name': 'Customers'
},
{
'name': 'Ingredients',
'final_name': 'Ingredients'
},
{
'name': 'Orders',
'final_name': 'Orders'
},
{
'name': 'Products',
'final_name': 'Products'
}
]
}
]
}
]
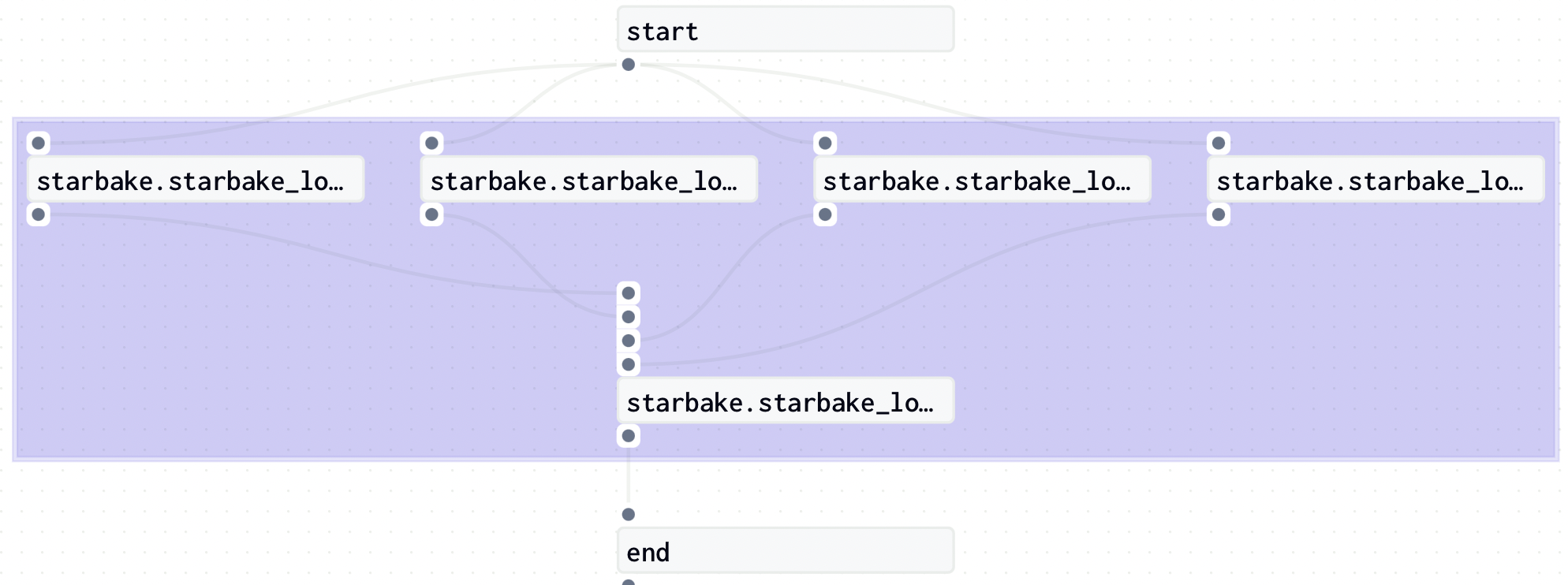
start = sl_job.dummy_op(task_id="start")
def load_domain(domain: dict) -> GraphDefinition:
tables = [table["name"] for table in domain["tables"]]
ins = {"domain": In(str)}
op_tables = [sl_job.sl_load(task_id=None, domain=domain["name"], table=table, ins=ins) for table in tables]
ld_end = sl_job.dummy_op(task_id=f"{domain['name']}_load_ended", ins={f"{op_table._name}": In(str) for op_table in op_tables}, out="domain_loaded")
ld_end_dependencies = dict()
for op_table in op_tables:
ld_end_dependencies[f"{op_table._name}"] = DependencyDefinition(op_table._name, 'result')
ld_dependencies = {
ld_end._name: ld_end_dependencies
}
ld_input_mappings=[
InputMapping(
graph_input_name="domain",
mapped_node_name=f"{op_table._name}",
mapped_node_input_name="domain",
)
for op_table in op_tables
]
ld_output_mappings=[
OutputMapping(
graph_output_name="domain_loaded",
mapped_node_name=f"{ld_end._name}",
mapped_node_output_name="domain_loaded",
)
]
ld = GraphDefinition(
name=f"{domain['name']}_load",
node_defs=op_tables + [ld_end],
dependencies=ld_dependencies,
input_mappings=ld_input_mappings,
output_mappings=ld_output_mappings,
)
pld = sl_job.sl_pre_load(domain=domain["name"])
@op(
name=f"{domain['name']}_load_result",
ins={"inputs": In()},
out={"result": Out(str)},
)
def load_domain_result(context, inputs):
context.log.info(f"inputs: {inputs}")
yield Output(str(inputs), "result")
@graph(
name=f"{domain['name']}",
input_defs=[InputDefinition(name="domain", dagster_type=str)],
)
def domain_graph(domain):
if pld:
load_domain, skip = pld(domain)
return load_domain_result([ld(load_domain), skip])
else:
return ld(domain)
return domain_graph
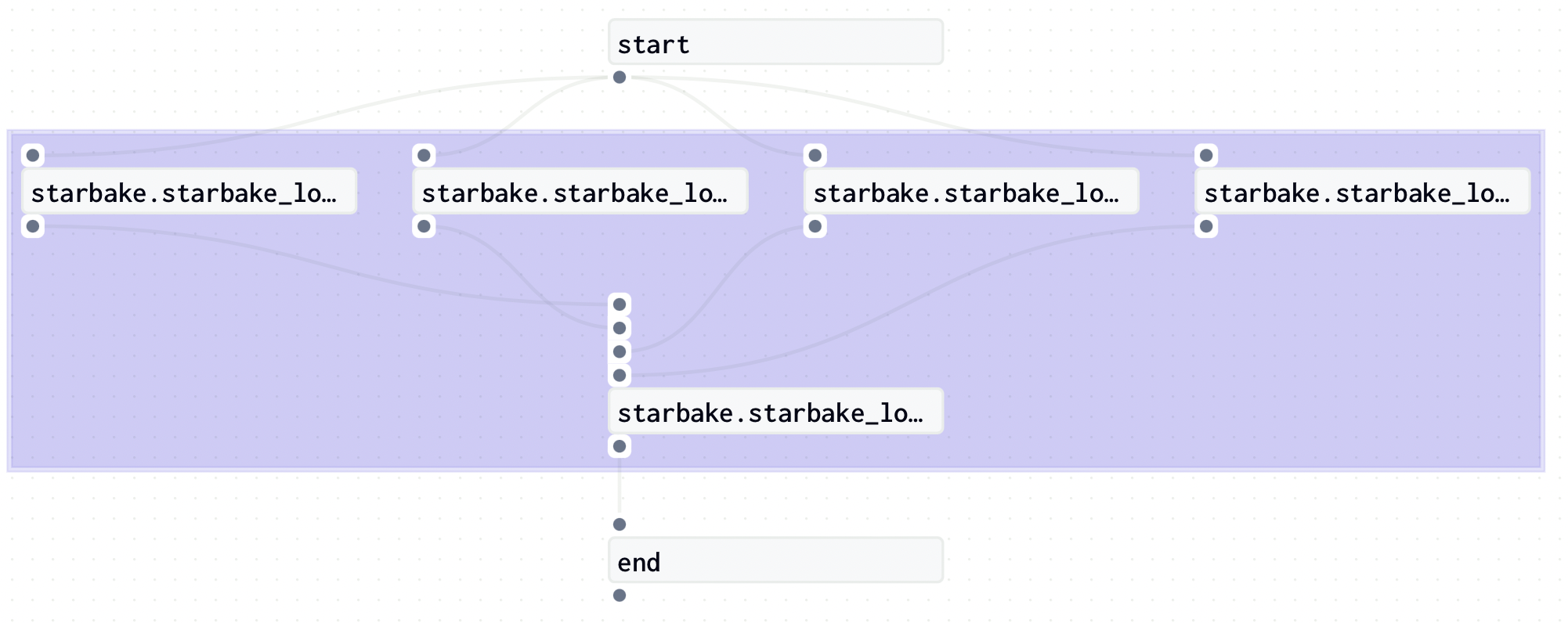
def load_domains(schedule: dict, index) -> GraphDefinition:
dependencies = dict()
nodes = [start]
pre_tasks = sl_job.pre_tasks()
if pre_tasks:
result = list(pre_tasks.output_dict.keys())[0]
if result:
dependencies[start._name] = {
'start': DependencyDefinition(pre_tasks._name, result)
}
nodes.append(pre_tasks)
node_defs = [load_domain(domain) for domain in schedule["domains"]]
ins = dict()
end_dependencies = dict()
for node_def in node_defs:
nodes.append(node_def)
dependencies[node_def._name] = {
'domain': DependencyDefinition(start._name, 'result')
}
result = f"{node_def._name}_result"
ins[result] = In(dagster_type=str)
end_dependencies[result] = DependencyDefinition(node_def._name, 'result')
end = sl_job.dummy_op(task_id="end", ins=ins)
nodes.append(end)
dependencies[end._name] = end_dependencies
post_tasks = sl_job.post_tasks()
if post_tasks:
input = list(post_tasks.input_dict.keys())[0]
if input:
dependencies[post_tasks._name] = {
input: DependencyDefinition(end._name, 'result')
}
nodes.append(post_tasks)
return GraphDefinition(
name=f'schedule_{index}' if len(schedules) > 1 else 'schedule',
node_defs=nodes,
dependencies=dependencies,
)
def job_name(index) -> str:
job_name = os.path.basename(__file__).replace(".py", "").replace(".pyc", "").lower()
return (f"{job_name}_{index}" if len(schedules) > 1 else job_name)
def generate_job(schedule: dict, index) -> JobDefinition:
return JobDefinition(
name=job_name(index),
description=description,
graph_def=load_domains(schedule, index),
)
crons = []
for index, schedule in enumerate(schedules):
cron = schedule['cron']
if(cron):
crons.append(ScheduleDefinition(job_name = job_name(index), cron_schedule = cron))
defs = Definitions(
jobs=[generate_job(schedule, index) for index, schedule in enumerate(schedules)],
schedules=crons,
)
If we want to apply the none pre load strategy instead, we just need to change the pre_load_strategy option to none:
StarlakeDagsterShellJob Transform Example
The following example shows how to use StarlakeDagsterShellJob to generate dynamically transform Jobs using starlake and record corresponding Dagster assets.
description="""example of transform using dagster starlake shell job"""
options = {
# General options
'sl_env_var':'{"SL_ROOT": "/starlake/samples/starbake"}',
# Bash options
'SL_STARLAKE_PATH':'/starlake/starlake.sh',
}
from ai.starlake.dagster.shell import StarlakeDagsterShellJob
sl_job = StarlakeDagsterShellJob(options=options)
from ai.starlake.common import sanitize_id
from ai.starlake.job import StarlakeSparkConfig
import json
import os
import sys
from typing import Set, List
from ai.starlake.dagster import StarlakeDagsterJob
from dagster import AssetKey, MultiAssetSensorDefinition, MultiAssetSensorEvaluationContext, RunRequest, SkipReason, Nothing, In, DependencyDefinition, JobDefinition, GraphDefinition, Definitions, ScheduleDefinition
cron = "None"
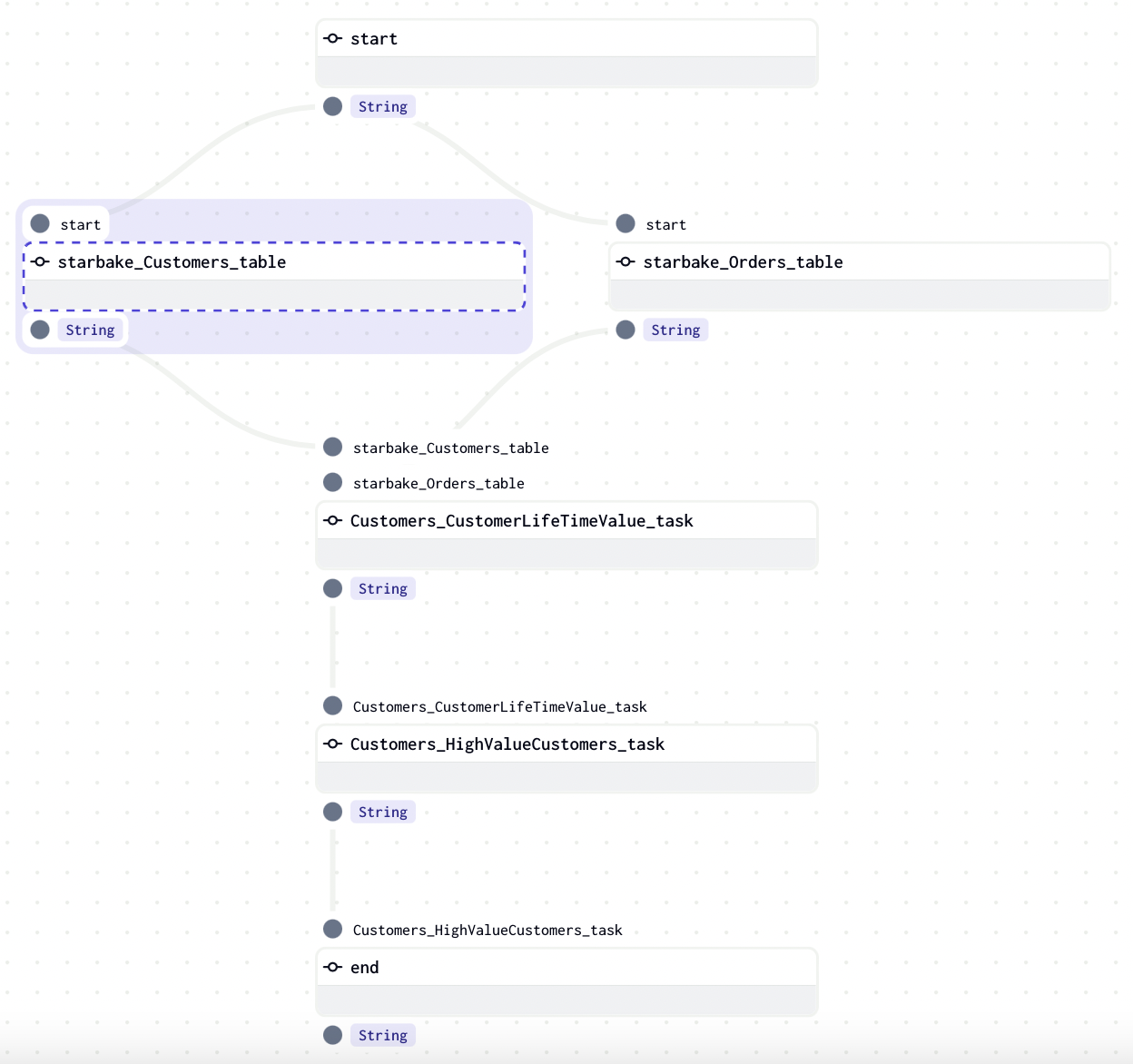
task_deps=json.loads("""[ {
"data" : {
"name" : "Customers.HighValueCustomers",
"typ" : "task",
"parent" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue",
"parentTyp" : "task",
"parentRef" : "CustomerLifetimeValue",
"sink" : "Customers.HighValueCustomers"
},
"children" : [ {
"data" : {
"name" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue",
"typ" : "task",
"parent" : "starbake.Customers",
"parentTyp" : "table",
"parentRef" : "starbake.Customers",
"sink" : "Customers.CustomerLifeTimeValue"
},
"children" : [ {
"data" : {
"name" : "starbake.Customers",
"typ" : "table",
"parentTyp" : "unknown"
},
"task" : false
}, {
"data" : {
"name" : "starbake.Orders",
"typ" : "table",
"parentTyp" : "unknown"
},
"task" : false
} ],
"task" : true
} ],
"task" : true
} ]""")
job_name = os.path.basename(__file__).replace(".py", "").replace(".pyc", "").lower()
# if you want to load dependencies, set load_dependencies to True in the options
load_dependencies: bool = StarlakeDagsterJob.get_context_var(var_name='load_dependencies', default_value='False', options=options).lower() == 'true'
sensor = None
# if you choose to not load the dependencies, a sensor will be created to check if the dependencies are met
if not load_dependencies:
assets: Set[str] = []
def load_assets(task: dict):
if 'children' in task:
for child in task['children']:
assets.append(sanitize_id(child['data']['name']))
load_assets(child)
for task in task_deps:
load_assets(task)
def multi_asset_sensor_with_skip_reason(context: MultiAssetSensorEvaluationContext):
asset_events = context.latest_materialization_records_by_key()
if all(asset_events.values()):
context.advance_all_cursors()
return RunRequest()
elif any(asset_events.values()):
materialized_asset_key_strs = [
key.to_user_string() for key, value in asset_events.items() if value
]
not_materialized_asset_key_strs = [
key.to_user_string() for key, value in asset_events.items() if not value
]
return SkipReason(
f"Observed materializations for {materialized_asset_key_strs}, "
f"but not for {not_materialized_asset_key_strs}"
)
else:
return SkipReason("No materializations observed")
sensor = MultiAssetSensorDefinition(
name = f'{job_name}_sensor',
monitored_assets = list(map(lambda asset: AssetKey(asset), assets)),
asset_materialization_fn = multi_asset_sensor_with_skip_reason,
minimum_interval_seconds = 60,
description = f"Sensor for {job_name}",
job_name = job_name,
)
def compute_task_id(task) -> str:
task_name = task['data']['name']
task_type = task['data']['typ']
task_id = sanitize_id(task_name)
if (task_type == 'task'):
task_id = task_id + "_task"
else:
task_id = task_id + "_table"
return task_id
def create_task(task_id: str, task_name: str, task_type: str, ins: dict={"start": In(Nothing)}):
spark_config_name=StarlakeDagsterJob.get_context_var('spark_config_name', task_name.lower(), options)
if (task_type == 'task'):
return sl_job.sl_transform(
task_id=task_id,
transform_name=task_name,
spark_config=spark_config(spark_config_name, **sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('spark_properties', {})),
ins=ins,
)
else:
load_domain_and_table = task_name.split(".",1)
domain = load_domain_and_table[0]
table = load_domain_and_table[1]
return sl_job.sl_load(
task_id=task_id,
domain=domain,
table=table,
spark_config=spark_config(spark_config_name, **sys.modules[__name__].__dict__.get('spark_properties', {})),
ins=ins,
)
from dagster._core.definitions import NodeDefinition
start = sl_job.dummy_op(task_id="start")
def generate_node_for_task(task, dependencies: dict, nodes: List[NodeDefinition]) -> NodeDefinition :
task_name = task['data']['name']
task_type = task['data']['typ']
task_id = compute_task_id(task)
if (load_dependencies and 'children' in task):
parent_dependencies = dict()
ins = dict()
for child in task['children']:
child_task_id = compute_task_id(child)
ins[child_task_id] = In(Nothing)
parent_dependencies[child_task_id] = DependencyDefinition(child_task_id, 'result')
nodes.append(generate_node_for_task(child, dependencies, nodes))
dependencies[task_id] = parent_dependencies
parent = create_task(task_id=task_id, task_name=task_name, task_type=task_type, ins=ins)
nodes.append(parent)
return parent
else:
node = create_task(task_id=task_id, task_name=task_name, task_type=task_type)
nodes.append(node)
dependencies[task_id] = {
'start': DependencyDefinition(start._name, 'result')
}
return node
def generate_job():
dependencies = dict()
nodes = [start]
pre_tasks = sl_job.pre_tasks()
if pre_tasks:
result = list(pre_tasks.output_dict.keys())[0]
if result:
dependencies[start._name] = {
'start': DependencyDefinition(pre_tasks._name, result)
}
nodes.append(pre_tasks)
ins = dict()
end_dependencies = dict()
for task in task_deps:
node = generate_node_for_task(task, dependencies, nodes)
ins[node._name] = In(Nothing)
end_dependencies[node._name] = DependencyDefinition(node._name, 'result')
end = sl_job.dummy_op(task_id="end", ins=ins)
nodes.append(end)
dependencies[end._name] = end_dependencies
post_tasks = sl_job.post_tasks(ins={"start": In(Nothing)})
if post_tasks:
input = list(post_tasks.input_dict.keys())[0]
if input:
dependencies[post_tasks._name] = {
input: DependencyDefinition(end._name, 'result')
}
nodes.append(post_tasks)
return JobDefinition(
name=job_name,
description=description,
graph_def=GraphDefinition(
name=job_name,
node_defs=nodes,
dependencies=dependencies,
),
)
crons = []
if cron.lower() != 'none':
crons.append(ScheduleDefinition(job_name = job_name, cron_schedule = cron))
defs = Definitions(
jobs=[generate_job()],
schedules=crons,
sensors=[sensor] if sensor else [],
)
If we want to load the dependencies, we just need to set the load_dependencies option to True:
Google Cloud Platform
StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob
This class is a concrete implementation of StarlakeDagsterJob that overrides the sl_job method that will run the starlake command by submitting Dataproc job to the configured Dataproc cluster.
It delegates to an instance of the dagster_gcp.DataprocResource class the responsibility to :
- create the Dataproc cluster
- submit Dataproc job to the latter
- delete the Dataproc cluster
This instance is available through the __dataproc__ property of the StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob class and is configured using the ai.starlake.gcp.StarlakeDataprocClusterConfig class.
The creation of the Dataproc cluster can be performed by calling the pre_tasks method of the StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob.
The deletion of the Dataproc cluster can be performed by calling the post_tasks method of the StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob.
Dataproc cluster configuration
Additional options may be specified to configure the Dataproc cluster.
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| cluster_id | str | the optional unique id of the cluster that will participate in the definition of the Dataproc cluster name (if not specified) |
| dataproc_name | str | the optional dataproc name of the cluster that will participate in the definition of the Dataproc cluster name (if not specified) |
| dataproc_project_id | str | the optional dataproc project id (the project id on which the composer has been instantiated by default) |
| dataproc_region | str | the optional region (europe-west1 by default) |
| dataproc_subnet | str | the optional subnet (the default subnet if not specified) |
| dataproc_service_account | str | the optional service account (service-{self.project_id}@dataproc-accounts.iam.gserviceaccount.com by default) |
| dataproc_image_version | str | the image version of the dataproc cluster (2.2-debian1 by default) |
| dataproc_master_machine_type | str | the optional master machine type (n1-standard-4 by default) |
| dataproc_master_disk_type | str | the optional master disk type (pd-standard by default) |
| dataproc_master_disk_size | int | the optional master disk size (1024 by default) |
| dataproc_worker_machine_type | str | the optional worker machine type (n1-standard-4 by default) |
| dataproc_worker_disk_type | str | the optional worker disk size (pd-standard by default) |
| dataproc_worker_disk_size | int | the optional worker disk size (1024 by default) |
| dataproc_num_workers | int | the optional number of workers (4 by default) |
All of these options will be used by default if no StarlakeDataprocClusterConfig was defined when instantiating StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob.
Dataproc Job configuration
Additional options may be specified to configure the Dataproc job.
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| spark_jar_list | str | the required list of spark jars to be used (using , as separator) |
| spark_bucket | str | the required bucket to use for spark and biqquery temporary storage |
| spark_job_main_class | str | the optional main class of the spark job (ai.starlake.job.Main by default) |
| spark_executor_memory | str | the optional amount of memory to use per executor process (11g by default) |
| spark_executor_cores | int | the optional number of cores to use on each executor (4 by default) |
| spark_executor_instances | int | the optional number of executor instances (1 by default) |
spark_executor_memory, spark_executor_cores and spark_executor_instances options will be used by default if no StarlakeSparkConfig was passed to the sl_load and sl_transform methods.
StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob load Example
The following example shows how to use StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob to generate dynamically DAGs that load domains using starlake and record corresponding outlets.
description="""example to load domain(s) using dagster starlake dataproc job"""
options = {
# General options
'sl_env_var':'{"SL_ROOT": "gcs://starlake/samples/starbake"}',
'pre_load_strategy':'pending',
# Dataproc cluster configuration
'dataproc_project_id':'starbake',
# Dataproc job configuration
'spark_bucket':'my-bucket',
'spark_jar_list':'gcs://artifacts/starlake.jar',
}
from ai.starlake.dagster.gcp import StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob
sl_job = StarlakeDagsterDataprocJob(options=options)
# all the code following the instantiation of the starlake job is exactly the same as that defined for StarlakeDagsterBashJob
#...
StarlakeDagsterCloudRunJob
This class is a concrete implementation of StarlakeDagsterJob that overrides the sl_job method that will run the starlake command by executing Cloud Run job.
Cloud Run job configuration
Additional options may be specified to configure the Cloud Run job.
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| cloud_run_project_id | str | the optional cloud run project id (the project id on which the composer has been instantiated by default) |
| cloud_run_job_name | str | the required name of the cloud run job |
| cloud_run_region | str | the optional region (europe-west1 by default) |
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Hashes for starlake_dagster-0.1.2.1-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | 2563a1e3c66a93724bab50ecd3757bab4c0b164ee5f41ff25688d1d984d039e0 |
|
| MD5 | edfe83c4eb3d12cbcbb2d6d1989cc6e0 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | 51353dd795e9b2e4949f4b3f80a6b1159a4db2674a8b0a1c32bb092efda718ad |