A powerful and scalable library that can be usedfor a variety of time series data mining tasks
Project description














STUMPY
STUMPY is a powerful and scalable library that efficiently computes something called the matrix profile, which can be used for a variety of time series data mining tasks such as:
pattern/motif (approximately repeated subsequences within a longer time series) discovery
anomaly/novelty (discord) discovery
shapelet discovery
semantic segmentation
density estimation
time series chains (temporally ordered set of subsequence patterns)
Whether you are an academic, data scientist, software developer, or time series enthusiast, STUMPY is straightforward to install and allows you to compute the matrix profile in the most efficient way. Our goal is to allow you to get to your time series insights faster. See documentation for more information.
How to use STUMPY
Typical usage (1-dimensional time series data) with STUMP:
import stumpy
import numpy as np
your_time_series = np.random.rand(10000)
window_size = 50 # Approximately, how many data points might be found in a pattern
matrix_profile = stumpy.stump(your_time_series, m=window_size)Distributed usage for 1-dimensional time series data with Dask Distributed via STUMPED:
import stumpy
import numpy as np
from dask.distributed import Client
dask_client = Client()
your_time_series = np.random.rand(10000)
window_size = 50 # Approximately, how many data points might be found in a pattern
matrix_profile = stumpy.stumped(dask_client, your_time_series, m=window_size)Multi-dimensional time series data with MSTUMP:
import stumpy
import numpy as np
your_time_series = np.random.rand(3, 1000)
window_size = 50 # Approximately, how many data points might be found in a pattern
matrix_profile, matrix_profile_indices = stumpy.mstump(your_time_series, m=window_size)Distributed multi-dimensional time series data analysis with Dask Distributed MSTUMPED:
import stumpy
import numpy as np
from dask.distributed import Client
dask_client = Client()
your_time_series = np.random.rand(3, 1000)
window_size = 50 # Approximately, how many data points might be found in a pattern
matrix_profile, matrix_profile_indices = stumpy.mstumped(dask_client, your_time_series, m=window_size)Time Series Chains:
import stumpy
import numpy as np
your_time_series = np.random.rand(10000)
window_size = 50 # Approximately, how many data points might be found in a pattern
matrix_profile = stumpy.stump(your_time_series, m=window_size)
left_matrix_profile_index = matrix_profile[:, 2]
right_matrix_profile_index = matrix_profile[:, 3]
idx = 10 # Subsequence index for which to retrieve the anchored time series chain for
anchored_chain = stumpy.atsc(left_matrix_profile_index, right_matrix_profile_index, idx)
all_chain_set, longest_unanchored_chain = stumpy.allc(left_matrix_profile_index, right_matrix_profile_index)Dependencies
Where to get it
Conda install (preferred):
conda install -c conda-forge stumpyPyPI install, presuming you have numpy, scipy, and numba installed:
pip install stumpyTo install stumpy from source, see the instructions in the documentation.
Documentation
In order to fully understand and appreciate the underlying algorithms and applications, it is imperative that you read the original publications. For a more detailed example of how to use STUMPY please consult the latest documentation or explore the following tutorials:
Performance
We tested the performance using the Numba JIT compiled version of the code on randomly generated data with various lengths (i.e., np.random.rand(n)).
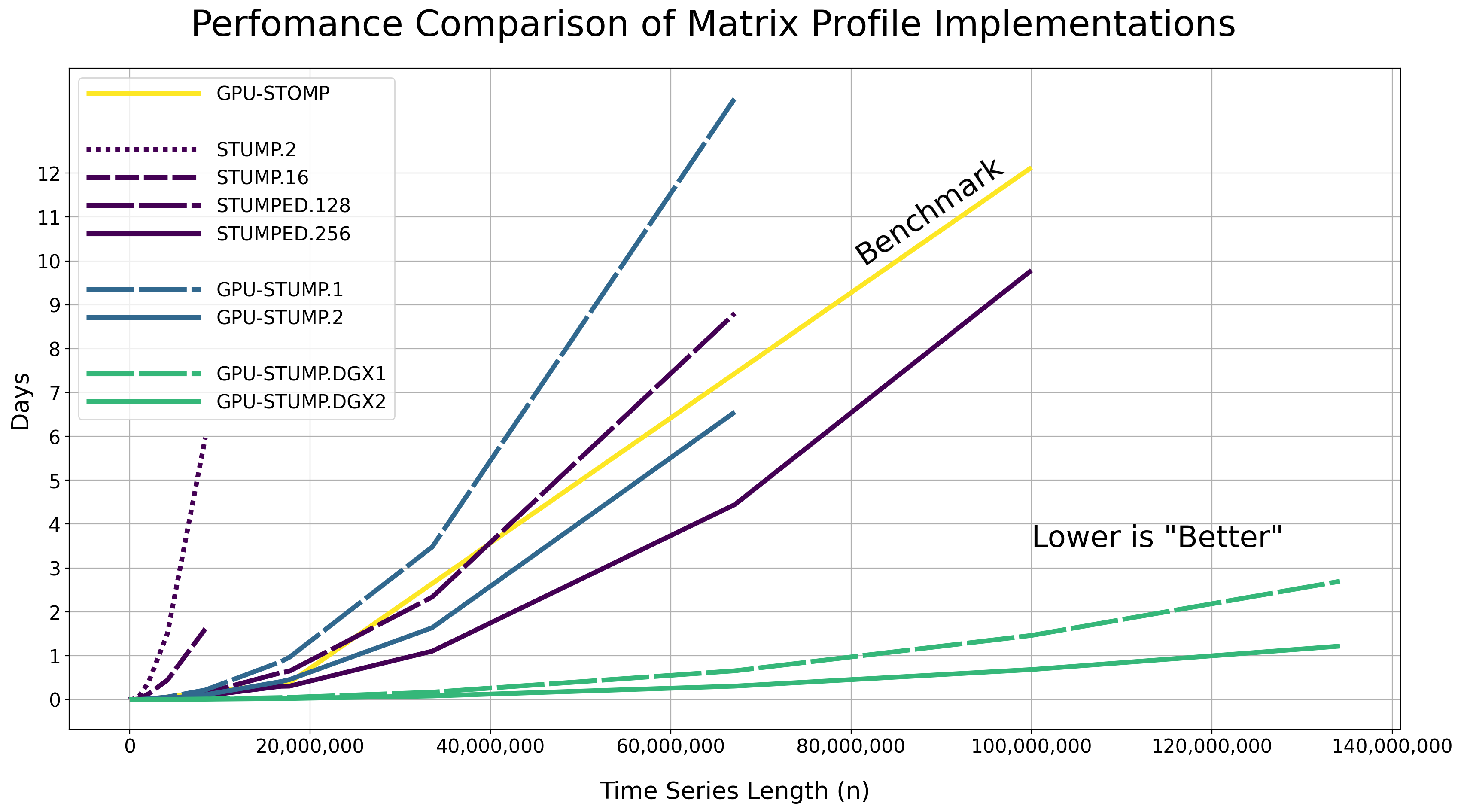
The raw results are displayed below as Hours:Minutes:Seconds.
i |
n = 2i |
GPU-STOMP |
STUMP.16 |
STUMPED.128 |
STUMPED.256 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
6 |
64 |
00:00:10.00 |
00:00:00.00 |
00:00:05.77 |
00:00:06.08 |
7 |
128 |
00:00:10.00 |
00:00:00.00 |
00:00:05.93 |
00:00:07.29 |
8 |
256 |
00:00:10.00 |
00:00:00.01 |
00:00:05.95 |
00:00:07.59 |
9 |
512 |
00:00:10.00 |
00:00:00.02 |
00:00:05.97 |
00:00:07.47 |
10 |
1024 |
00:00:10.00 |
00:00:00.04 |
00:00:05.69 |
00:00:07.64 |
11 |
2048 |
NaN |
00:00:00.09 |
00:00:05.60 |
00:00:07.83 |
12 |
4096 |
NaN |
00:00:00.19 |
00:00:06.26 |
00:00:07.90 |
13 |
8192 |
NaN |
00:00:00.41 |
00:00:06.29 |
00:00:07.73 |
14 |
16384 |
NaN |
00:00:00.99 |
00:00:06.24 |
00:00:08.18 |
15 |
32768 |
NaN |
00:00:02.39 |
00:00:06.48 |
00:00:08.29 |
16 |
65536 |
NaN |
00:00:06.42 |
00:00:07.33 |
00:00:09.01 |
17 |
131072 |
00:00:10.00 |
00:00:19.52 |
00:00:09.75 |
00:00:10.53 |
18 |
262144 |
00:00:18.00 |
00:01:08.44 |
00:00:33.38 |
00:00:24.07 |
19 |
524288 |
00:00:46.00 |
00:03:56.82 |
00:01:35.27 |
00:03:43.66 |
20 |
1048576 |
00:02:30.00 |
00:19:54.75 |
00:04:37.15 |
00:03:01.16 |
21 |
2097152 |
00:09:15.00 |
03:05:07.64 |
00:13:36.51 |
00:08:47.47 |
22 |
4194304 |
NaN |
10:37:51.21 |
00:55:44.43 |
00:32:06.70 |
23 |
8388608 |
NaN |
38:42:51.42 |
03:33:30.53 |
02:00:49.37 |
24 |
16777216 |
NaN |
NaN |
13:03:43.86 |
07:13:47.12 |
NaN |
17729800 |
09:16:12.00 |
NaN |
NaN |
07:18:42.54 |
25 |
33554432 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
26:27:41.29 |
26 |
67108864 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
106:40:17.17 |
NaN |
100000000 |
291:07:12.00 |
NaN |
NaN |
234:51:35.39 |
27 |
134217728 |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
NaN |
GPU-STOMP: Results are reproduced from the original Matrix Profile II paper - NVIDIA Tesla K80 (contains 2 GPUs)
STUMP.16: 16 CPUs in Total - 16x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2650 v4 @ 2.20GHz processors parallelized with Numba on a single server without Dask.
STUMPED.128: 128 CPUs in Total - 8x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2650 v4 @ 2.20GHz processors x 16 servers, parallelized with Numba, and distributed with Dask Distributed.
STUMPED.256: 256 CPUs in Total - 8x Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2650 v4 @ 2.20GHz processors x 32 servers, parallelized with Numba, and distributed with Dask Distributed.
Running Tests
Tests are written in the tests directory and processed using PyTest. and requires coverage.py for code coverage analysis. Tests can be executed with:
./test.shPython Version
STUMPY supports Python 3.6+ and, due to the use of unicode variable names/identifiers, is not compatible with Python 2.x. Given the small dependencies, STUMPY may work on older versions of Python but this is beyond the scope of our support and we strongly recommend that you upgrade to the most recent version of Python.
Getting Help
First, please check the issues on github to see if your question has already been answered there. If no solution is available there feel free to open a new issue and the authors will attempt to respond in a reasonably timely fashion.
Contributing
We welcome contributions in any form! Assistance with documentation, particularly expanding tutorials, is always welcome. To contribute please fork the project, make your changes, and submit a pull request. We will do our best to work through any issues with you and get your code merged into the main branch.
References
Yeh, Chin-Chia Michael, et al. (2016) Matrix Profile I: All Pairs Similarity Joins for Time Series: A Unifying View that Includes Motifs, Discords, and Shapelets. ICDM:1317-1322. Link
Zhu, Yan, et al. (2016) Matrix Profile II: Exploiting a Novel Algorithm and GPUs to Break the One Hundred Million Barrier for TIme Series Motifs and Joins. ICDM:739-748. Link
Yeh, Chin-Chia Michael, et al. (2017) Matrix Profile VI: Meaningful Multidimensional Motif Discovery. ICDM:565-574. Link
Zhu, Yan, et al. (2017) Matrix Profile VII: Time Series Chains: A New Primitive for Time Series Data Mining. ICDM:695-704. Link
Citing
If you have used this codebase in a scientific publication and wish to cite it, please use the Journal of Open Source Software article.
S. M. Law, STUMPY: A Powerful and Scalable Python Library for Time Series Data Mining In: Journal of Open Source Software, The Open Journal, Volume 4, Number 39. 2019
@article{law2017stumpy,
title={{STUMPY: A Powerful and Scalable Python Library for Time Series Data Mining}},
author={Law, Sean M.},
journal={{The Journal of Open Source Software}},
volume={4},
number={39},
pages={1504},
year={2019}
}License & Trademark
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file stumpy-1.1.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: stumpy-1.1.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 25.1 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/1.13.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.22.0 setuptools/41.0.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.32.1 CPython/3.6.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
84c75ee9c1d7f1ec4151b92222b597aa201b1d2e92aa4e1c4d06bfc276b7ce4e
|
|
| MD5 |
959e48965944fed22992241223b157df
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
30b3792f2e136dc5b0a59835a410599a9e7700fc6b8141c94a6b43ad58f73f74
|
File details
Details for the file stumpy-1.1.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: stumpy-1.1.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 29.7 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/1.13.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.22.0 setuptools/41.0.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.32.1 CPython/3.6.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
79a4cc776a30a26a871c33a143b235833950b8d3d3a8d175993828c5cce5d2d4
|
|
| MD5 |
bddb0641a112fd6bc90d688e62c887c6
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
a668971d4ff0f7fc9517b84844fe2956b15196c2ea7a7c6b1a5260194c3a868a
|











