Magnificent app which corrects your previous console command
Project description
The Fuck is a magnificent app, inspired by a [@liamosaur](https://twitter.com/liamosaur/) tweet, that corrects errors in previous console commands.
Is The Fuck too slow? Try the experimental instant mode!
More examples:
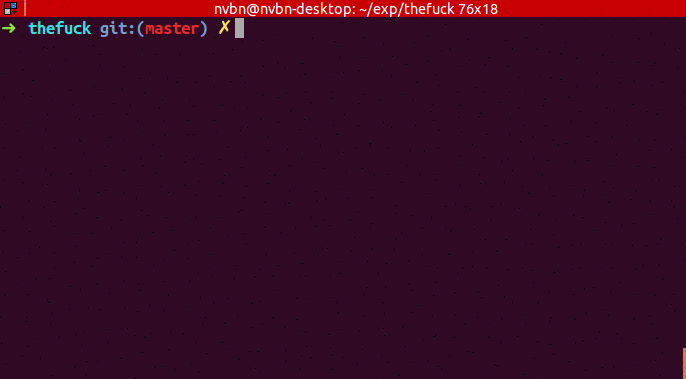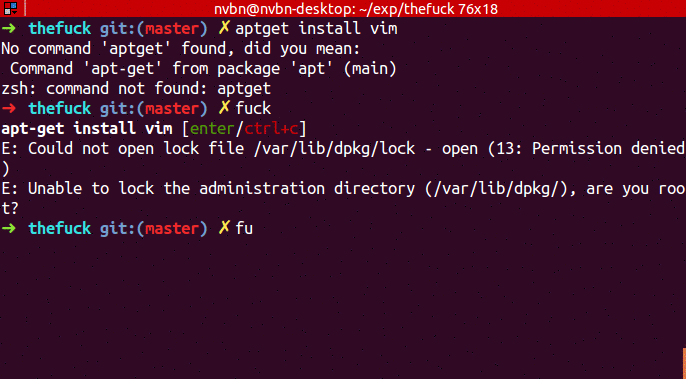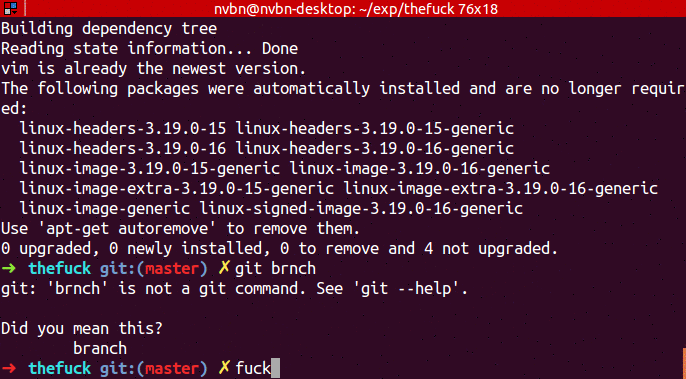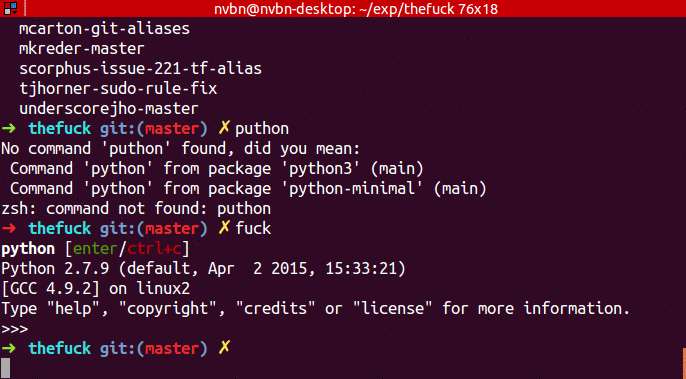
➜ apt-get install vim
E: Could not open lock file /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open (13: Permission denied)
E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/), are you root?
➜ fuck
sudo apt-get install vim [enter/↑/↓/ctrl+c]
[sudo] password for nvbn:
Reading package lists... Done
...➜ git push
fatal: The current branch master has no upstream branch.
To push the current branch and set the remote as upstream, use
git push --set-upstream origin master
➜ fuck
git push --set-upstream origin master [enter/↑/↓/ctrl+c]
Counting objects: 9, done.
...➜ puthon
No command 'puthon' found, did you mean:
Command 'python' from package 'python-minimal' (main)
Command 'python' from package 'python3' (main)
zsh: command not found: puthon
➜ fuck
python [enter/↑/↓/ctrl+c]
Python 3.4.2 (default, Oct 8 2014, 13:08:17)
...➜ git brnch
git: 'brnch' is not a git command. See 'git --help'.
Did you mean this?
branch
➜ fuck
git branch [enter/↑/↓/ctrl+c]
* master➜ lein rpl
'rpl' is not a task. See 'lein help'.
Did you mean this?
repl
➜ fuck
lein repl [enter/↑/↓/ctrl+c]
nREPL server started on port 54848 on host 127.0.0.1 - nrepl://127.0.0.1:54848
REPL-y 0.3.1
...If you’re not afraid of blindly running corrected commands, the require_confirmation settings option can be disabled:
➜ apt-get install vim
E: Could not open lock file /var/lib/dpkg/lock - open (13: Permission denied)
E: Unable to lock the administration directory (/var/lib/dpkg/), are you root?
➜ fuck
sudo apt-get install vim
[sudo] password for nvbn:
Reading package lists... Done
...Contents
Requirements
python (3.4+)
pip
python-dev
Back to Contents
Installation
On macOS or Linux, you can install The Fuck via Homebrew:
brew install thefuckOn Ubuntu / Mint, install The Fuck with the following commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3-dev python3-pip python3-setuptools
pip3 install thefuck --userOn FreeBSD, install The Fuck with the following commands:
pkg install thefuckOn ChromeOS, install The Fuck using chromebrew with the following command:
crew install thefuckOn other systems, install The Fuck by using pip:
pip install thefuckAlternatively, you may use an OS package manager (OS X, Ubuntu, Arch).
# It is recommended that you place this command in your .bash_profile, .bashrc, .zshrc or other startup script:
eval $(thefuck --alias)
# You can use whatever you want as an alias, like for Mondays:
eval $(thefuck --alias FUCK)Or in your shell config (Bash, Zsh, Fish, Powershell, tcsh).
Changes are only available in a new shell session. To make changes immediately available, run source ~/.bashrc (or your shell config file like .zshrc).
To run fixed commands without confirmation, use the --yeah option (or just -y for short, or --hard if you’re especially frustrated):
fuck --yeahTo fix commands recursively until succeeding, use the -r option:
fuck -rBack to Contents
Updating
pip3 install thefuck --upgradeNote: Alias functionality was changed in v1.34 of The Fuck
Uninstall
To remove The Fuck, reverse the installation process: - erase or comment thefuck alias line from your Bash, Zsh, Fish, Powershell, tcsh, … shell config - use your package manager (brew, pip3, pkg, crew, pip) to uninstall the binaries
How it works
The Fuck attempts to match the previous command with a rule. If a match is found, a new command is created using the matched rule and executed. The following rules are enabled by default:
adb_unknown_command – fixes misspelled commands like adb logcta;
ag_literal – adds -Q to ag when suggested;
aws_cli – fixes misspelled commands like aws dynamdb scan;
az_cli – fixes misspelled commands like az providers;
cargo – runs cargo build instead of cargo;
cargo_no_command – fixes wrongs commands like cargo buid;
cat_dir – replaces cat with ls when you try to cat a directory;
cd_correction – spellchecks and correct failed cd commands;
cd_cs – changes cs to cd;
cd_mkdir – creates directories before cd’ing into them;
cd_parent – changes cd.. to cd ..;
chmod_x – add execution bit;
choco_install – append common suffixes for chocolatey packages;
composer_not_command – fixes composer command name;
conda_mistype – fixes conda commands;
cp_create_destination – creates a new directory when you attempt to cp or mv to a non existent one
cp_omitting_directory – adds -a when you cp directory;
cpp11 – adds missing -std=c++11 to g++ or clang++;
dirty_untar – fixes tar x command that untarred in the current directory;
dirty_unzip – fixes unzip command that unzipped in the current directory;
django_south_ghost – adds --delete-ghost-migrations to failed because ghosts django south migration;
django_south_merge – adds --merge to inconsistent django south migration;
docker_login – executes a docker login and repeats the previous command;
docker_not_command – fixes wrong docker commands like docker tags;
docker_image_being_used_by_container ‐ removes the container that is using the image before removing the image;
dry – fixes repetitions like git git push;
fab_command_not_found – fix misspelled fabric commands;
fix_alt_space – replaces Alt+Space with Space character;
fix_file – opens a file with an error in your $EDITOR;
gem_unknown_command – fixes wrong gem commands;
git_add – fixes “pathspec ‘foo’ did not match any file(s) known to git.”;
git_add_force – adds --force to git add <pathspec>... when paths are .gitignore’d;
git_bisect_usage – fixes git bisect strt, git bisect goood, git bisect rset, etc. when bisecting;
git_branch_delete – changes git branch -d to git branch -D;
git_branch_delete_checked_out – changes git branch -d to git checkout master && git branch -D when trying to delete a checked out branch;
git_branch_exists – offers git branch -d foo, git branch -D foo or git checkout foo when creating a branch that already exists;
git_branch_list – catches git branch list in place of git branch and removes created branch;
git_branch_0flag – fixes commands such as git branch 0v and git branch 0r removing the created branch;
git_checkout – fixes branch name or creates new branch;
git_clone_git_clone – replaces git clone git clone ... with git clone ...
git_commit_add – offers git commit -a ... or git commit -p ... after previous commit if it failed because nothing was staged;
git_commit_amend – offers git commit --amend after previous commit;
git_commit_reset – offers git reset HEAD~ after previous commit;
git_diff_no_index – adds --no-index to previous git diff on untracked files;
git_diff_staged – adds --staged to previous git diff with unexpected output;
git_fix_stash – fixes git stash commands (misspelled subcommand and missing save);
git_flag_after_filename – fixes fatal: bad flag '...' after filename
git_help_aliased – fixes git help <alias> commands replacing with the aliased command;
git_hook_bypass – adds --no-verify flag previous to git am, git commit, or git push command;
git_lfs_mistype – fixes mistyped git lfs <command> commands;
git_main_master – fixes incorrect branch name between main and master
git_merge – adds remote to branch names;
git_merge_unrelated – adds --allow-unrelated-histories when required
git_not_command – fixes wrong git commands like git brnch;
git_pull – sets upstream before executing previous git pull;
git_pull_clone – clones instead of pulling when the repo does not exist;
git_pull_uncommitted_changes – stashes changes before pulling and pops them afterwards;
git_push – adds --set-upstream origin $branch to previous failed git push;
git_push_different_branch_names – fixes pushes when local branch name does not match remote branch name;
git_push_pull – runs git pull when push was rejected;
git_push_without_commits – Creates an initial commit if you forget and only git add ., when setting up a new project;
git_rebase_no_changes – runs git rebase --skip instead of git rebase --continue when there are no changes;
git_remote_delete – replaces git remote delete remote_name with git remote remove remote_name;
git_rm_local_modifications – adds -f or --cached when you try to rm a locally modified file;
git_rm_recursive – adds -r when you try to rm a directory;
git_rm_staged – adds -f or --cached when you try to rm a file with staged changes
git_rebase_merge_dir – offers git rebase (--continue | --abort | --skip) or removing the .git/rebase-merge dir when a rebase is in progress;
git_remote_seturl_add – runs git remote add when git remote set_url on nonexistent remote;
git_stash – stashes your local modifications before rebasing or switching branch;
git_stash_pop – adds your local modifications before popping stash, then resets;
git_tag_force – adds --force to git tag <tagname> when the tag already exists;
git_two_dashes – adds a missing dash to commands like git commit -amend or git rebase -continue;
go_run – appends .go extension when compiling/running Go programs;
go_unknown_command – fixes wrong go commands, for example go bulid;
gradle_no_task – fixes not found or ambiguous gradle task;
gradle_wrapper – replaces gradle with ./gradlew;
grep_arguments_order – fixes grep arguments order for situations like grep -lir . test;
grep_recursive – adds -r when you try to grep directory;
grunt_task_not_found – fixes misspelled grunt commands;
gulp_not_task – fixes misspelled gulp tasks;
has_exists_script – prepends ./ when script/binary exists;
heroku_multiple_apps – add --app <app> to heroku commands like heroku pg;
heroku_not_command – fixes wrong heroku commands like heroku log;
history – tries to replace command with the most similar command from history;
hostscli – tries to fix hostscli usage;
ifconfig_device_not_found – fixes wrong device names like wlan0 to wlp2s0;
java – removes .java extension when running Java programs;
javac – appends missing .java when compiling Java files;
lein_not_task – fixes wrong lein tasks like lein rpl;
long_form_help – changes -h to --help when the short form version is not supported
ln_no_hard_link – catches hard link creation on directories, suggest symbolic link;
ln_s_order – fixes ln -s arguments order;
ls_all – adds -A to ls when output is empty;
ls_lah – adds -lah to ls;
man – changes manual section;
man_no_space – fixes man commands without spaces, for example mandiff;
mercurial – fixes wrong hg commands;
missing_space_before_subcommand – fixes command with missing space like npminstall;
mkdir_p – adds -p when you try to create a directory without a parent;
mvn_no_command – adds clean package to mvn;
mvn_unknown_lifecycle_phase – fixes misspelled life cycle phases with mvn;
npm_missing_script – fixes npm custom script name in npm run-script <script>;
npm_run_script – adds missing run-script for custom npm scripts;
npm_wrong_command – fixes wrong npm commands like npm urgrade;
no_command – fixes wrong console commands, for example vom/vim;
no_such_file – creates missing directories with mv and cp commands;
omnienv_no_such_command – fixes wrong commands for goenv, nodenv, pyenv and rbenv (eg.: pyenv isntall or goenv list);
open – either prepends http:// to address passed to open or create a new file or directory and passes it to open;
pip_install – fixes permission issues with pip install commands by adding --user or prepending sudo if necessary;
pip_unknown_command – fixes wrong pip commands, for example pip instatl/pip install;
php_s – replaces -s by -S when trying to run a local php server;
port_already_in_use – kills process that bound port;
prove_recursively – adds -r when called with directory;
python_command – prepends python when you try to run non-executable/without ./ python script;
python_execute – appends missing .py when executing Python files;
python_module_error – fixes ModuleNotFoundError by trying to pip install that module;
quotation_marks – fixes uneven usage of ' and " when containing args’;
path_from_history – replaces not found path with a similar absolute path from history;
rails_migrations_pending – runs pending migrations;
react_native_command_unrecognized – fixes unrecognized react-native commands;
remove_shell_prompt_literal – remove leading shell prompt symbol $, common when copying commands from documentations;
remove_trailing_cedilla – remove trailing cedillas ç, a common typo for European keyboard layouts;
rm_dir – adds -rf when you try to remove a directory;
scm_correction – corrects wrong scm like hg log to git log;
sed_unterminated_s – adds missing ‘/’ to sed’s s commands;
sl_ls – changes sl to ls;
ssh_known_hosts – removes host from known_hosts on warning;
sudo – prepends sudo to the previous command if it failed because of permissions;
sudo_command_from_user_path – runs commands from users $PATH with sudo;
switch_lang – switches command from your local layout to en;
systemctl – correctly orders parameters of confusing systemctl;
terraform_init.py – run terraform init before plan or apply;
test.py – runs py.test instead of test.py;
touch – creates missing directories before “touching”;
tsuru_login – runs tsuru login if not authenticated or session expired;
tsuru_not_command – fixes wrong tsuru commands like tsuru shell;
tmux – fixes tmux commands;
unknown_command – fixes hadoop hdfs-style “unknown command”, for example adds missing ‘-’ to the command on hdfs dfs ls;
unsudo – removes sudo from previous command if a process refuses to run on superuser privilege.
vagrant_up – starts up the vagrant instance;
whois – fixes whois command;
workon_doesnt_exists – fixes virtualenvwrapper env name os suggests to create new.
wrong_hyphen_before_subcommand – removes an improperly placed hyphen (apt-install -> apt install, git-log -> git log, etc.)
yarn_alias – fixes aliased yarn commands like yarn ls;
yarn_command_not_found – fixes misspelled yarn commands;
yarn_command_replaced – fixes replaced yarn commands;
yarn_help – makes it easier to open yarn documentation;
Back to Contents
The following rules are enabled by default on specific platforms only:
apt_get – installs app from apt if it not installed (requires python-commandnotfound / python3-commandnotfound);
apt_get_search – changes trying to search using apt-get with searching using apt-cache;
apt_invalid_operation – fixes invalid apt and apt-get calls, like apt-get isntall vim;
apt_list_upgradable – helps you run apt list --upgradable after apt update;
apt_upgrade – helps you run apt upgrade after apt list --upgradable;
brew_cask_dependency – installs cask dependencies;
brew_install – fixes formula name for brew install;
brew_reinstall – turns brew install <formula> into brew reinstall <formula>;
brew_link – adds --overwrite --dry-run if linking fails;
brew_uninstall – adds --force to brew uninstall if multiple versions were installed;
brew_unknown_command – fixes wrong brew commands, for example brew docto/brew doctor;
brew_update_formula – turns brew update <formula> into brew upgrade <formula>;
dnf_no_such_command – fixes mistyped DNF commands;
nixos_cmd_not_found – installs apps on NixOS;
pacman – installs app with pacman if it is not installed (uses yay or yaourt if available);
pacman_invalid_option – replaces lowercase pacman options with uppercase.
pacman_not_found – fixes package name with pacman, yay or yaourt.
yum_invalid_operation – fixes invalid yum calls, like yum isntall vim;
The following commands are bundled with The Fuck, but are not enabled by default:
git_push_force – adds --force-with-lease to a git push (may conflict with git_push_pull);
rm_root – adds --no-preserve-root to rm -rf / command.
Back to Contents
Creating your own rules
To add your own rule, create a file named your-rule-name.py in ~/.config/thefuck/rules. The rule file must contain two functions:
match(command: Command) -> bool
get_new_command(command: Command) -> str | list[str]Additionally, rules can contain optional functions:
side_effect(old_command: Command, fixed_command: str) -> NoneRules can also contain the optional variables enabled_by_default, requires_output and priority.
Command has three attributes: script, output and script_parts. Your rule should not change Command.
Rules api changed in 3.0: To access a rule’s settings, import it with from thefuck.conf import settings
settings is a special object assembled from ~/.config/thefuck/settings.py, and values from env (see more below).
A simple example rule for running a script with sudo:
def match(command):
return ('permission denied' in command.output.lower()
or 'EACCES' in command.output)
def get_new_command(command):
return 'sudo {}'.format(command.script)
# Optional:
enabled_by_default = True
def side_effect(command, fixed_command):
subprocess.call('chmod 777 .', shell=True)
priority = 1000 # Lower first, default is 1000
requires_output = TrueMore examples of rules, utility functions for rules, app/os-specific helpers.
Back to Contents
Settings
Several The Fuck parameters can be changed in the file $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/thefuck/settings.py ($XDG_CONFIG_HOME defaults to ~/.config):
rules – list of enabled rules, by default thefuck.const.DEFAULT_RULES;
exclude_rules – list of disabled rules, by default [];
require_confirmation – requires confirmation before running new command, by default True;
wait_command – the max amount of time in seconds for getting previous command output;
no_colors – disable colored output;
priority – dict with rules priorities, rule with lower priority will be matched first;
debug – enables debug output, by default False;
history_limit – the numeric value of how many history commands will be scanned, like 2000;
alter_history – push fixed command to history, by default True;
wait_slow_command – max amount of time in seconds for getting previous command output if it in slow_commands list;
slow_commands – list of slow commands;
num_close_matches – the maximum number of close matches to suggest, by default 3.
excluded_search_path_prefixes – path prefixes to ignore when searching for commands, by default [].
An example of settings.py:
rules = ['sudo', 'no_command']
exclude_rules = ['git_push']
require_confirmation = True
wait_command = 10
no_colors = False
priority = {'sudo': 100, 'no_command': 9999}
debug = False
history_limit = 9999
wait_slow_command = 20
slow_commands = ['react-native', 'gradle']
num_close_matches = 5Or via environment variables:
THEFUCK_RULES – list of enabled rules, like DEFAULT_RULES:rm_root or sudo:no_command;
THEFUCK_EXCLUDE_RULES – list of disabled rules, like git_pull:git_push;
THEFUCK_REQUIRE_CONFIRMATION – require confirmation before running new command, true/false;
THEFUCK_WAIT_COMMAND – the max amount of time in seconds for getting previous command output;
THEFUCK_NO_COLORS – disable colored output, true/false;
THEFUCK_PRIORITY – priority of the rules, like no_command=9999:apt_get=100, rule with lower priority will be matched first;
THEFUCK_DEBUG – enables debug output, true/false;
THEFUCK_HISTORY_LIMIT – how many history commands will be scanned, like 2000;
THEFUCK_ALTER_HISTORY – push fixed command to history true/false;
THEFUCK_WAIT_SLOW_COMMAND – the max amount of time in seconds for getting previous command output if it in slow_commands list;
THEFUCK_SLOW_COMMANDS – list of slow commands, like lein:gradle;
THEFUCK_NUM_CLOSE_MATCHES – the maximum number of close matches to suggest, like 5.
THEFUCK_EXCLUDED_SEARCH_PATH_PREFIXES – path prefixes to ignore when searching for commands, by default [].
For example:
export THEFUCK_RULES='sudo:no_command'
export THEFUCK_EXCLUDE_RULES='git_pull:git_push'
export THEFUCK_REQUIRE_CONFIRMATION='true'
export THEFUCK_WAIT_COMMAND=10
export THEFUCK_NO_COLORS='false'
export THEFUCK_PRIORITY='no_command=9999:apt_get=100'
export THEFUCK_HISTORY_LIMIT='2000'
export THEFUCK_NUM_CLOSE_MATCHES='5'Back to Contents
Third-party packages with rules
If you’d like to make a specific set of non-public rules, but would still like to share them with others, create a package named thefuck_contrib_* with the following structure:
thefuck_contrib_foo
thefuck_contrib_foo
rules
__init__.py
*third-party rules*
__init__.py
*third-party-utils*
setup.py
The Fuck will find rules located in the rules module.
Back to Contents
Experimental instant mode
The default behavior of The Fuck requires time to re-run previous commands. When in instant mode, The Fuck saves time by logging output with script, then reading the log.
Currently, instant mode only supports Python 3 with bash or zsh. zsh’s autocorrect function also needs to be disabled in order for thefuck to work properly.
To enable instant mode, add --enable-experimental-instant-mode to the alias initialization in .bashrc, .bash_profile or .zshrc.
For example:
eval $(thefuck --alias --enable-experimental-instant-mode)Back to Contents
Developing
See CONTRIBUTING.md
License MIT
Project License can be found here.
Back to Contents
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file thefuck-3.32.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: thefuck-3.32.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 83.6 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.7.1 importlib_metadata/4.9.0 pkginfo/1.8.2 requests/2.26.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.62.3 CPython/3.9.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
976740b9aa536726fa23cadc9a10bf457e92e335901c61fcff9152c84485ac3d
|
|
| MD5 |
7db2da798dd0c8e3e34295e84c249b6b
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
acd00c256afd3ba1d05882154d16aa0685018f21c60a6769a496558da7d9d8f1
|
File details
Details for the file thefuck-3.32-py2.py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: thefuck-3.32-py2.py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 127.9 kB
- Tags: Python 2, Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.7.1 importlib_metadata/4.9.0 pkginfo/1.8.2 requests/2.26.0 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.62.3 CPython/3.9.9
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9d4604ec4832dae8b3e164969c94e4663052e50906f437ed57419cec76bbca2f
|
|
| MD5 |
7104f47f0011a5b6be9563f219dcdd3e
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
60e2a42cb06f359749003157ab5339db3932641be91c6fa8fc4e36c20b05b628
|