GPU-accelerated stain normalization and augmentation
Project description
Torch-StainTools
A fast, GPU-friendly PyTorch toolkit for stain normalization and augmentation of histopathological images.
Torch-StainTools implements GPU-accelerated stain augmentation and normalization algorithms (Reinhard, Macenko, Vahadane) with batch processing and caching for on-the-fly large-scale computational pathology pipelines.
What's New (~ 1.0.7)
-
**Version **: full vectorization support and dynamic shape tracking from Dynamo.
-
Alternative linear concentration solvers:
'qr'(QR Decomposition) and'pinv'(Moore-Penrose inverse) -
Color/Texture-based Hash as cache key if no unique identifiers (e.g., filenames) are available.
What It Does
-
GPU acceleration and vectorized execution for batch inputs .
-
Optional TorchDynamo graph compilation (
torch.compile) for high-throughput execution -
On-the-fly stain normalization and augmentation.
-
Stain matrix caching to avoid redundant computation across tiles.
-
Encapsulation as
nn.Module. Easy to plug into existing neural network pipelines. -
Tissue masking support. Optional and customizable.
Citation
If this toolkit helps you in your publication, please feel free to cite with the following bibtex entry:
@software{zhou_2024_10496083,
author = {Zhou, Yufei},
title = {CielAl/torch-staintools: V1.0.4 Release},
month = jan,
year = 2024,
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {v1.0.4},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.10496083},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10496083}
}
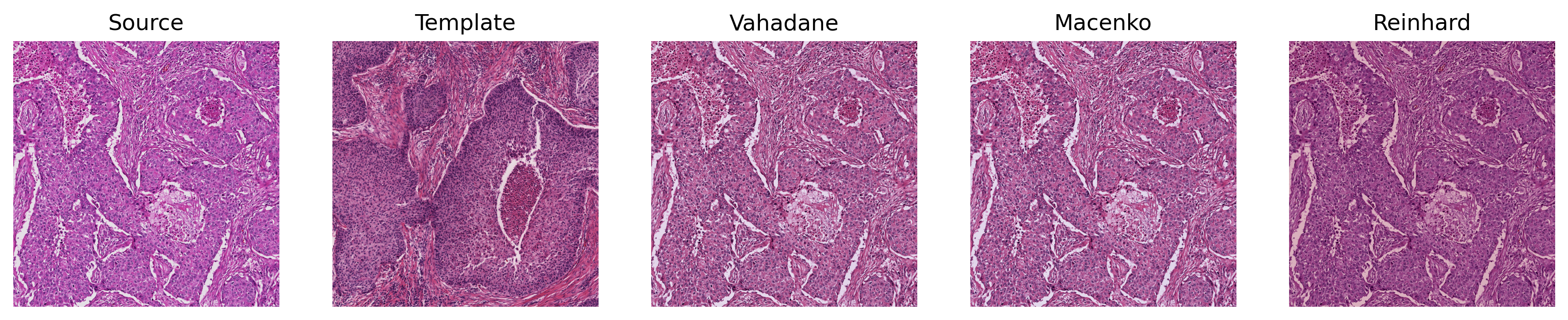
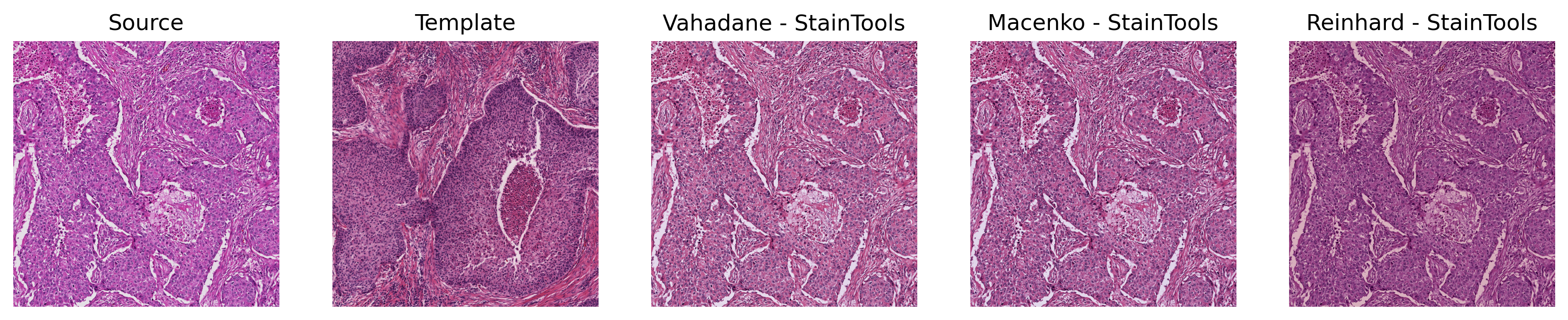
Normalization Showcase
Torch-Staintools
Comparison: StainTools
Augmentation
Torch-Staintools
Comparison: StainTools

Performance Benchmark
Single Large ROI (2500 $\times$ 2500 $\times$ 3; No Caching)
- Representative preprocessing scenario for large tissue ROIs.
- GPU execution with TorchDynamo (
torch.compile) enabled.
Transformation
| Method | CPU [s] | GPU [s] | StainTool [s] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vahadane | 119.00 | 4.60 | 20.90 |
| Macenko | 5.57 | 0.48 | 20.70 |
| Reinhard | 0.84 | 0.02 | 0.41 |
Fitting (Click to Expand)
Fitting (one-time cost)
| Method | CPU [s] | GPU [s] | StainTool [s] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vahadane | 132.00 | 5.20 | 19.10 |
| Macenko | 6.99 | 0.06 | 20.00 |
| Reinhard | 0.42 | 0.01 | 0.08 |
Batched Small Tiles (81 tiles, 256$\times$256$\times$3)
-
Splitting 2500 $\times$ 2500 $\times$ 3 ROI into a batch of 81 smaller patches (256$\times$256$\times$3).
-
Representative on-the-fly processing scenario for training and inference.
-
TorchDynamo (
torch.compile) enabled.
Batch Transformation
| Method | No Cache [s] | Stain Matrix Cached [s] | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vahadane | 6.62 | 0.019 | 348x Faster |
| Macenko | 0.023 | 0.020 | 1.15x Faster |
Batchified Concentration Computation
- Split the sample images under ./test_images (size
2500x2500x3) into 81 non-overlapping256x256x3tiles as a batch. - For the StainTools baseline, a for-loop is implemented to get the individual concentration of each of the numpy array of the 81 tiles.
torch.compileenabled.
| Method | CPU[s] | GPU[s] |
|---|---|---|
FISTA (concentration_solver='fista') |
1.47 | 0.24 |
ISTA (concentration_solver='ista') |
3.12 | 0.31 |
CD (concentration_solver='cd') |
29.30s | 4.87 |
LS (concentration_solver='ls') |
0.22 | 0.097 |
| StainTools (SPAMS) | 16.60 | N/A |
Installation
- From Repository:
pip install git+https://github.com/CielAl/torch-staintools.git
- From PyPI:
pip install torch-staintools
Documentation
Detail documentation regarding the code base can be found in the GitPages.
Minimal Usage and Tips
- For details, follow the example in demo.py
- Normalizers are implemented as
torch.nn.Moduleand can be integrated like a standalone network component. qrandpinvconcentration solvers are on par withlsfor batch concentration computation. Butls(i.e.,torch.linalg.lstsq) may fail on GPU for a single larger input image (width and height). This happens with the defaultcusolverbackend. Try usingmagmainstead:
import torch
torch.backends.cuda.preferred_linalg_library('magma')
Example
# We enable the torch.compile (note this is True by default)
from torch_staintools.normalizer import NormalizerBuilder
# ######### Vahadane
target_tensor = ... # any batch float inputs in B x C x H x W, value range in [0., 1.]
norm_tensor = ... # any batch float inputs in B x C x H x W, value range in [0., 1.]
target_tensor = target_tensor.cuda()
norm_tensor = norm_tensor.cuda()
normalizer_vahadane = NormalizerBuilder.build('vahadane',
concentration_solver='qr',
use_cache=True
)
normalizer_vahadane = normalizer_vahadane.cuda()
normalizer_vahadane.fit(target_tensor)
norm_out = normalizer_vahadane(norm_tensor)
# ###### Augmentation
# augment by: alpha * concentration + beta, while alpha is uniformly randomly sampled from (1 - sigma_alpha, 1 + sigma_alpha),
# and beta is uniformly randomly sampled from (-sigma_beta, sigma_beta).
from torch_staintools.augmentor import AugmentorBuilder
augmentor = AugmentorBuilder.build('vahadane',
use_cache=True,
)
# move augmentor to the corresponding device
augmentor = augmentor.cuda()
num_augment = 5
# multiple copies of different random augmentation of the same tile may be generated
for _ in range(num_augment):
aug_out = augmentor(norm_tensor)
# dump the cache of stain matrices for future usage
augmentor.dump_cache('./cache.pickle')
Stain Matrix Caching
Stain matrix estimation can dominate runtime (especially for Vahadane).
To reduce overhead, Normalizer and Augmentor support an in-memory,
device-specific cache for stain matrices (typically 2×3 for H&E/RGB).
Why it matters: cached stain matrices can be reused across images, yielding substantial speedups in batch and on-the-fly pipelines.
How it works
- Cache contents can be saved and exported for reuse in future.
- Enable with
use_cache=Truewhen constructing aNormalizerorAugmentor - Cached entries are keyed per image (e.g., filename or slide identifier)
- For batched inputs (
B×C×H×W), provide one key per image in the batch
Fallback behavior
- If caching is enabled but no
cache_keyis provided, a texture- and color-based hash is computed automatically. - Visually similar images are likely to reuse stain matrices, while collisions across dissimilar images are minimized.
Enable Cache / Loading
# set `use_cache` to True
# specify `load_path` to read from existing cache data
NormalizerBuilder.build('vahadane',
concentration_solver='qr',
use_cache=True,
load_path='path_to_cache'
)
# Alternatively, read cache manually
normalizer.load_cache('path_to_cach')
If unique identifiers (UID) of images are available
# explicitly set cache_keys in normalization passes.
normalizer(input_batch, cache_keys=list_of_uid)
augmentor(input_batch, cache_keys=list_of_uid)
If cache_keys are not available
# color/texture-based hash keys are internally computed.
normalizer_vahadane(input_batch)
augmentor(input_batch)
#
Export cache
# dump to path
normalizer.dump_cache("/folder/cache.tch")
Load existing cache
Acknowledgments
- Some codes are inspired from torchvahadane, torchstain, and StainTools
- Sample images in the demo and ReadMe.md are selected from The Cancer Genome Atlas Program(TCGA) dataset.
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file torch_staintools-1.0.7.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: torch_staintools-1.0.7.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 54.1 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.10.19
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
ed71f3c9110801eab1fc227b3ab650d542ab215974fbf7c2782d61f3ed26158b
|
|
| MD5 |
a0b1185adc20d8cbfb9cffff93bd5cc5
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
f4040c94826a66330c84b30195d6be1d0f7b487606fad4f94c3934e0a655521a
|
File details
Details for the file torch_staintools-1.0.7-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: torch_staintools-1.0.7-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 67.7 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.2.0 CPython/3.10.19
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
261e74dc13f033f5b167169c26ab0b6471854e5cd1b31a16ddb52f19b74d170d
|
|
| MD5 |
2879c8ae9876f71fe2d22c9733800b55
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
22824c413b57a922625ef8d872851a4c7da00fe638533a2b667b2ad98fd7e1a5
|