A framework for discrete-time Markov chains analysis.
Project description
PyDTMC is a full-featured, lightweight library for discrete-time Markov chains analysis. It provides classes and functions for creating, manipulating, simulating and visualizing markovian stochastic processes.
| Status: |



|
| Info: |



|
| PyPI: |




|
| Conda: |




|
Requirements
The Python environment must include the following packages:
The package Sphinx is required for building the package documentation. The package pytest is required for performing unit tests. For a better user experience, it's recommended to install Graphviz and pydot before using the plot_graph function.
Installation & Upgrade
PyPI:
$ pip install PyDTMC
$ pip install --upgrade PyDTMC
Git:
$ pip install https://github.com/TommasoBelluzzo/PyDTMC/tarball/master
$ pip install --upgrade https://github.com/TommasoBelluzzo/PyDTMC/tarball/master
$ pip install git+https://github.com/TommasoBelluzzo/PyDTMC.git#egg=PyDTMC
$ pip install --upgrade git+https://github.com/TommasoBelluzzo/PyDTMC.git#egg=PyDTMC
$ conda install -c conda-forge pydtmc
$ conda update -c conda-forge pydtmc
$ conda install -c tommasobelluzzo pydtmc
$ conda update -c tommasobelluzzo pydtmc
Usage
The core element of the library is the MarkovChain class, which can be instantiated as follows:
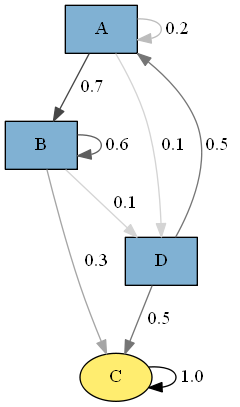
>>> p = [[0.2, 0.7, 0.0, 0.1], [0.0, 0.6, 0.3, 0.1], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0], [0.5, 0.0, 0.5, 0.0]]
>>> mc = MarkovChain(p, ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'])
>>> print(mc)
DISCRETE-TIME MARKOV CHAIN
SIZE: 4
RANK: 4
CLASSES: 2
> RECURRENT: 1
> TRANSIENT: 1
ERGODIC: NO
> APERIODIC: YES
> IRREDUCIBLE: NO
ABSORBING: YES
REGULAR: NO
REVERSIBLE: NO
Below a few examples of MarkovChain properties:
>>> print(mc.is_ergodic)
False
>>> print(mc.recurrent_states)
['C']
>>> print(mc.transient_states)
['A', 'B', 'D']
>>> print(mc.steady_states)
[array([0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0])]
>>> print(mc.is_absorbing)
True
>>> print(mc.fundamental_matrix)
[[1.50943396 2.64150943 0.41509434]
[0.18867925 2.83018868 0.30188679]
[0.75471698 1.32075472 1.20754717]]
>>> print(mc.kemeny_constant)
5.547169811320755
>>> print(mc.entropy_rate)
0.0
Below a few examples of MarkovChain methods:
>>> print(mc.absorption_probabilities())
[1.0 1.0 1.0]
>>> print(mc.expected_rewards(10, [2, -3, 8, -7]))
[-2.76071635, -12.01665113, 23.23460025, -8.45723276]
>>> print(mc.expected_transitions(2))
[[0.085, 0.2975, 0.0, 0.0425]
[0.0, 0.345, 0.1725, 0.0575]
[0.0, 0.0, 0.7, 0.0 ]
[0.15, 0.0, 0.15, 0.0 ]]
>>> print(mc.first_passage_probabilities(5, 3))
[[0.5, 0.0, 0.5, 0.0 ]
[0.0, 0.35, 0.0, 0.05 ]
[0.0, 0.07, 0.13, 0.045 ]
[0.0, 0.0315, 0.1065, 0.03 ]
[0.0, 0.0098, 0.0761, 0.0186]]
>>> print(mc.hitting_probabilities([0, 1]))
[1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.5]
>>> print(mc.mean_absorption_times())
[4.56603774, 3.32075472, 3.28301887]
>>> print(mc.mean_number_visits())
[[0.50943396, 2.64150943, inf, 0.41509434]
[0.18867925, 1.83018868, inf, 0.30188679]
[0.0, 0.0, inf, 0.0 ]
[0.75471698, 1.32075472, inf, 0.20754717]]
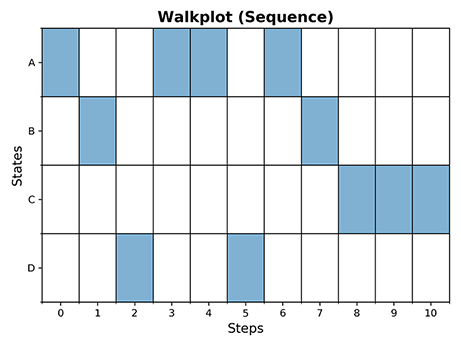
>>> print(mc.walk(10, seed=32))
['D', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C', 'C', 'C', 'C', 'C', 'C']
>>> walk = ["A"]
>>> for _ in range(10):
... current_state = walk[-1]
... next_state = mc.next_state(current_state, seed=32)
... print(f'{current_state} -> {next_state}')
... walk.append(next_state)
A -> B
B -> C
C -> C
C -> C
C -> C
C -> C
C -> C
C -> C
C -> C
C -> C
Plotting functions can provide a visual representation of MarkovChain instances; in order to display the output of plots immediately, the interactive mode of Matplotlib must be turned on:
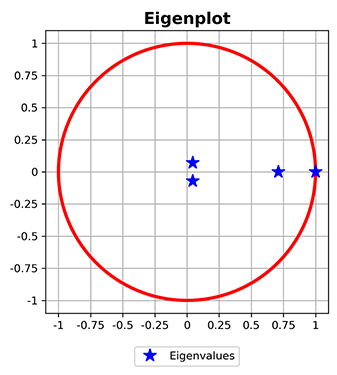
>>> plot_eigenvalues(mc)
>>> plot_graph(mc)
>>> plot_walk(mc, 10, 'sequence')
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file PyDTMC-6.5.0.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: PyDTMC-6.5.0.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 77.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.4.1 importlib_metadata/4.6.1 pkginfo/1.7.1 requests/2.25.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.61.2 CPython/3.9.5
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
33838f14faac69d7ba20482099ac4f98dd4662a7389425eb64119cdde8e5c3c7
|
|
| MD5 |
375592b0c65ee6372ed1f28ddf0b000c
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
315d25b544c8a52242736f48e0a5be6cc8e01c92a31510e6cac9b3d7b35663bd
|
File details
Details for the file PyDTMC-6.5.0-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: PyDTMC-6.5.0-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 47.0 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/3.4.1 importlib_metadata/4.6.1 pkginfo/1.7.1 requests/2.25.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.61.2 CPython/3.9.5
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
8206c6b456f73ed91572957b98442abeae6532a0698b0a7a91f1daa432f479d1
|
|
| MD5 |
03c3640b07e02556909ce4eaf0970649
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
a48988e4d1691a933016c169947637dded1fff72f9808f873d2fae29b716b462
|