bme280pi: the BME280 Sensor Reader for Raspberry Pi
Project description
bme280pi: the BME280 Sensor Reader for Raspberry Pi
Quickstart
Try in a Jupyter notebook or directly:
from bme280pi import Sensor
sensor = Sensor()
print(sensor.get_data())
How to Install bme280pi
1) Enable the I2C Interface
sudo raspi-config- Select "Interfacing Options"
- Highlight the "I2C" option, and activate "Select" (use tab)
- Answer the question if you'd like the ARM I2C interface to be enabled with "Yes"
- Select "Ok"
- Reboot
For a walk-through with screenshots see the references below.
2) Install Utilities
- Install
python3-smbus2andi2ctools:sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y python3-smbus2 i2c-tools - Then, shut down your Raspberry Pi:
sudo halt. - Disconnect your Raspberry Pi power supply.
- You are now ready to connect the BME280 sensor.
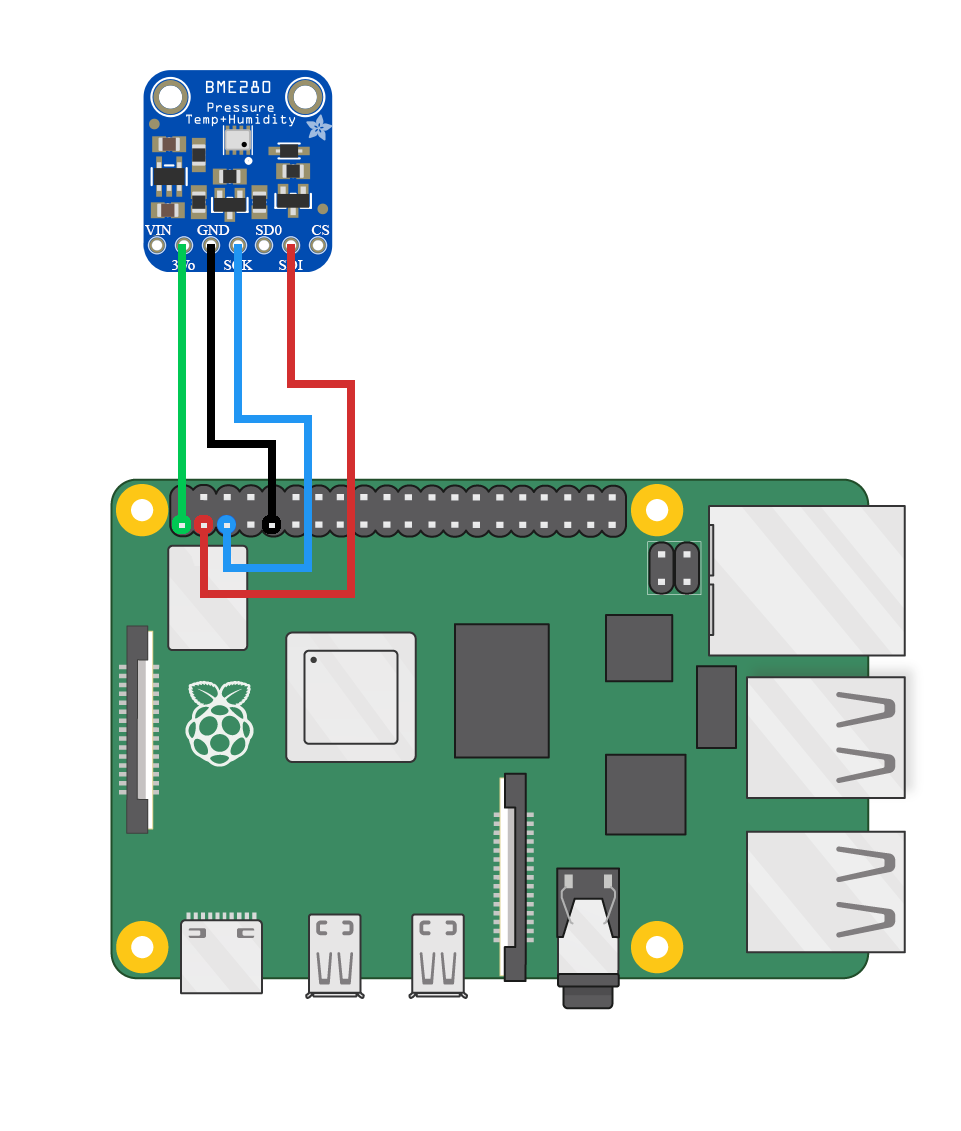
3) Connect the BME280 sensor
4) Install This Module
4a) Installing With pip (Recommended)
You can then install this module by running pip install bme280pi
4b) Installing From Source (alternative to 4a)
If you want the latest version, you can check out the sources and install the package yourself:
git clone https://github.com/MarcoAndreaBuchmann/bme280pi.git
cd bme280pi
pip install .
Troubleshooting
- I2C not working at all? Run
sudo raspi-config nonint get_i2cto see if the port is enabled (0=enabled, 1=disabled). If the result is1(disabled), runsudo raspi-config nonint do_i2c 0to enable it and reboot. - I2C not detected? Run
i2cdetect -y 1and ensure address 0x76/0x77. - Permission error: Add user to
i2cgroup (sudo usermod -aG i2c $USER). - No data: Check connections; try forced mode in init.
How to Use bme280pi In Your Script
You can initialize the sensor class as follows:
from bme280pi import Sensor
sensor = Sensor()
You can then use the sensor object to fetch data, sensor.get_data(), which will return a dictionary
with temperature, humidity, and pressure readings.
You can also just get the temperature (sensor.get_temperature()),
just the pressure (sensor.get_pressure()), or
just the humidity (sensor.get_humidity()).
Note that all commands support user-specified units, e.g. sensor.get_temperature(unit='F'),
or sensor.get_pressure(unit='mmHg').
Using Multiple Sensors
One can also read out multiple sensors using this package. Suppose that the first sensor is located
at 0x76 and the second one at 0x77, then you can initialize two sensors as follows:
from bme280pi import Sensor
sensor1 = Sensor(address=0x76)
sensor2 = Sensor(address=0x77)
data_from_sensor_one = sensor1.get_data()
data_from_sensor_two = sensor2.get_data()
Plotting Data Obtained From Sensor
You can e.g. query the sensor every 10 seconds, and add the results to a dictionary, and then turn that into a pandas DataFrame and plot that (requires matplotlib and pandas):
import time
import datetime
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from bme280pi import Sensor
sensor = Sensor(address=0x76)
measurements = {}
for i in range(20):
measurements[datetime.datetime.now()] = sensor.get_data()
time.sleep(10)
measurements = pd.DataFrame(measurements).transpose()
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
measurements['temperature'].plot()
plt.title("Temperature (C)")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
measurements['pressure'].plot()
plt.title("Pressure (hPa)")
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
measurements['humidity'].plot()
plt.title("Relative Humidity (%)")
plt.savefig("Measurements.png")
Advanced: Build Docs
pip install -r docs/requirements.txt
cd docs && make html
Hosted at ReadTheDocs
Reporting Issues
Please feel free to report any issues you encounter at the issue tracker.
References
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file bme280pi-1.2.1.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: bme280pi-1.2.1.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 23.7 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
09a24077debb39126b9f433b39651491872415a88f80cee3522980f3ff3871d3
|
|
| MD5 |
ed1e2a2cb2ab349a73bc5b22940745c3
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
a8f97c2180174f2a493e870f49f3ba195c6a503d6c8fe25931a6e3277b37d95c
|
File details
Details for the file bme280pi-1.2.1-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: bme280pi-1.2.1-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 24.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.13.7
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
506c75ed597a58b9504c6c33807881f3dc21c6cce38bc92097dadd211ee9aeb2
|
|
| MD5 |
78f3f763d4bc3444283d092ff9aa79b7
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
0ba8e343973d2f50d62ad96487dfaa46308b320d58a13372e0c651c83d24792f
|