'docker run' and 'docker exec' with useful defaults
Project description

docker-run – docker run and docker exec with useful defaults
docker-run is a CLI tool for simplified interaction with Docker images. Use it to easily start and attach to Docker containers with useful predefined arguments.
[!IMPORTANT]
This repository is open-sourced and maintained by the Institute for Automotive Engineering (ika) at RWTH Aachen University.
DevOps, Containerization and Orchestration of Software-Defined Vehicles are some of many research topics within our Vehicle Intelligence & Automated Driving domain.
If you would like to learn more about how we can support your advanced driver assistance and automated driving efforts, feel free to reach out to us!
:email: opensource@ika.rwth-aachen.de
While docker-run can be used with any Docker image, we recommend to also check out our other tools for Docker and ROS.
- docker-ros automatically builds minimal container images of ROS applications
- docker-ros-ml-images provides machine learning-enabled ROS Docker images
Quick Demo
The following quickly launches the GUI application xeyes to demonstrate how docker-run takes care of X11 forwarding from container to host. The --verbose flag prints the underlying docker run command that is run under the hood.
docker-run --verbose 607qwq/xeyes
Functionality
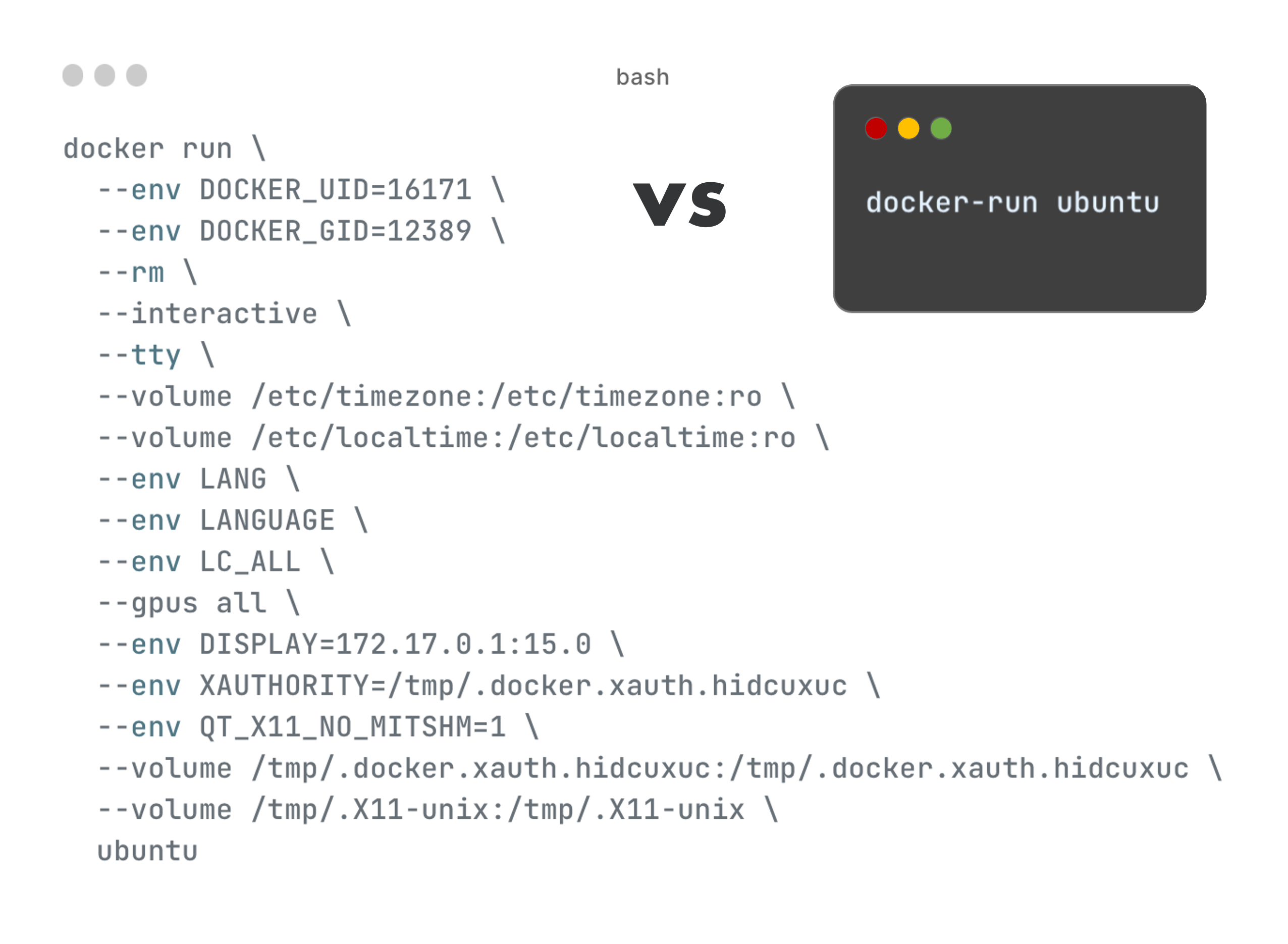
docker-run is designed to be used the same way as the official docker run and docker exec commands.
In general, you can pass the same arguments to docker-run as you would pass to docker run, e.g.
docker-run --volume $(pwd):/volume ubuntu ls /volume
In addition to the arguments you are passing, docker-run however also enables the following features by default. Most of these default features can be disabled, see Usage.
- container removal after exit (
--rm) - interactive tty (
--interactive --tty) - current directory name as container name (
--name) - relative bind mounts (
--volume [./RELATIVE_PATH>]:[TARGET_PATH]) - GPU support (
--gpus all/--runtime nvidia) - X11 GUI forwarding
If a container with matching name is already running, docker-run will execute a command in that container via docker exec instead. This lets you quickly attach to a running container without passing any command, e.g.
docker-run --name my-running-container
Unlike with docker run, you can also set the Docker image via the --image arguments, see Usage. This may be required for more complex use cases.
Installation
pip install docker-run-cli
# (optional) shell auto-completion
source $(activate-python-docker-run-shell-completion 2> /dev/null)
[!WARNING]
Outside of a virtual environment, pip may default to a user-site installation of executables to~/.local/bin, which may not be present in your shell'sPATH. If runningdocker-runerrors withdocker-run: command not found, add the directory to your path. (More information)echo "export PATH=\$HOME/.local/bin:\$PATH" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
Usage
usage: docker-run [--help] [--image IMAGE] [--loc] [--mwd] [--name NAME]
[--no-gpu] [--no-it] [--no-name] [--no-rm] [--no-tz]
[--no-x11] [--verbose] [--version]
Executes `docker run` with the following features enabled by default, each of
which can be disabled individually: container removal after exit, interactive
tty, current directory name as container name, GPU support, X11 GUI
forwarding. Passes any additional arguments to `docker run`. Executes `docker
exec` instead if a container with the specified name (`--name`) is already
running.
options:
--help show this help message and exit
--image IMAGE image name (may also be specified without --image as last
argument before command)
--loc enable automatic locale
--mwd mount current directory at same path
--name NAME container name; generates `docker exec` command if already
running
--no-gpu disable automatic GPU support
--no-it disable automatic interactive tty
--no-name disable automatic container name (current directory)
--no-rm disable automatic container removal
--no-tz disable automatic timezone
--no-x11 disable automatic X11 GUI forwarding
--verbose print generated command
--version show program's version number and exit
Plugins
docker-run can be extended through plugins. Plugins are installed as optional dependencies.
# install specific plugin <PLUGIN_NAME>
pip install docker-run-cli[<PLUGIN_NAME>]
# install all plugins
pip install docker-run-cli[plugins]
| Plugin | Description |
|---|---|
docker-ros |
extra functionality for Docker images built by docker-ros |
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file docker_run_cli-0.10.2.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: docker_run_cli-0.10.2.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 15.5 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9ad94533e887cafabda19fa393b4633b299d62e68a7e302bed9c1439003d0b35
|
|
| MD5 |
8bb80f86157735e8cef4464760a756af
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
c4eff88bf16c05ca0c4bd233e382b097c46c535fae49a6dd54bc16caf48eec7c
|
File details
Details for the file docker_run_cli-0.10.2-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: docker_run_cli-0.10.2-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 15.2 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
8fe6641cd7c18c78ace88a044c5a74d9950e840290d05c9a7b4b618d2c557c4c
|
|
| MD5 |
a0b2de6061659057d879ce709198a05a
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
17686e13d5b2bf39f1b18729862f19e2a34f8583b8d785abf30b482dd1565165
|



















