A Hermite function series module.
Project description
Hermite Function Series
A Hermite function series package.
from HermiteFunction import HermiteFunction
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
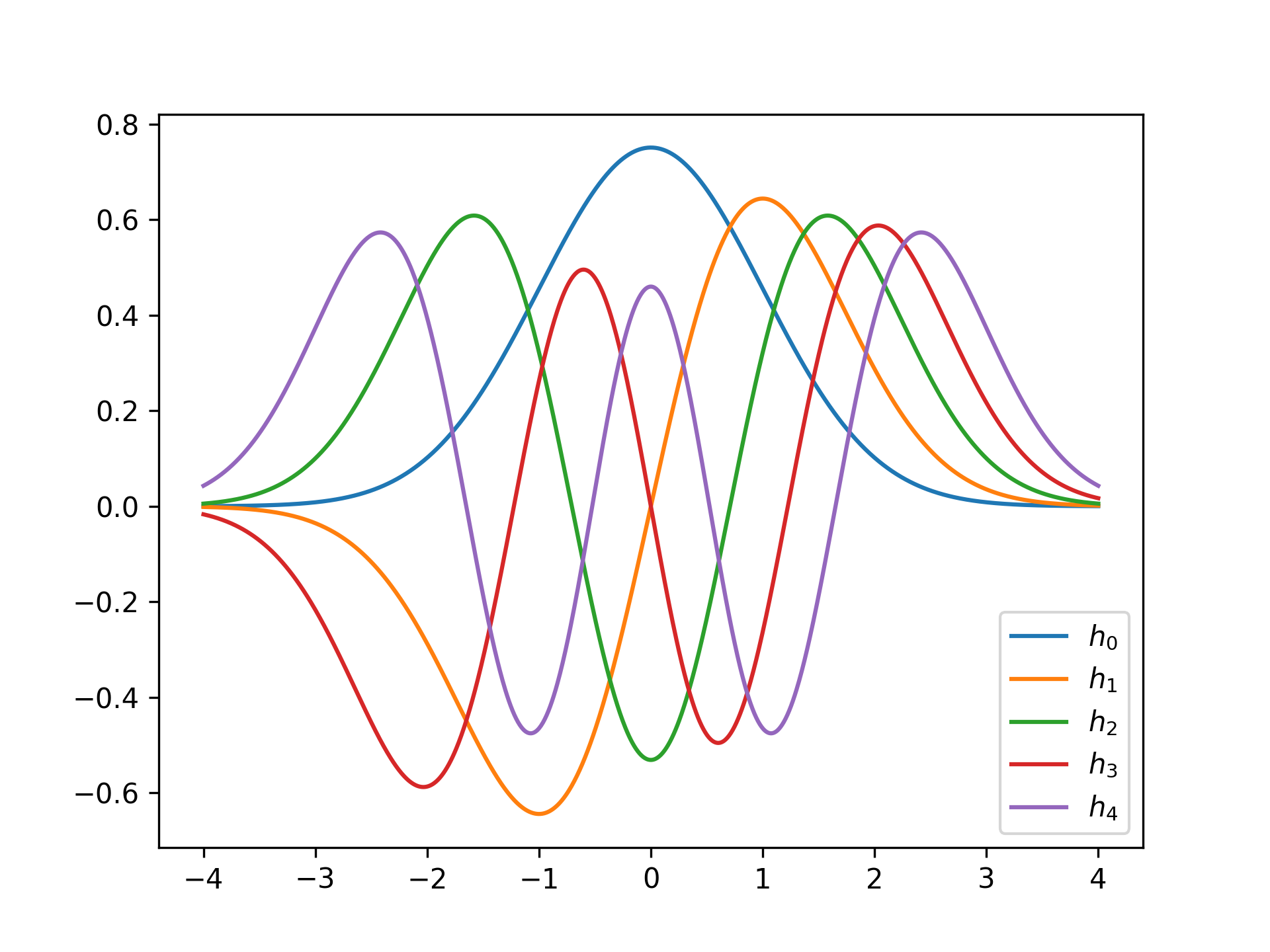
x = np.linspace(-4, +4, 1000)
for n in range(5):
poly = HermiteFunction(n)
plt.plot(x, poly(x), label='$h_{}$'.format(n))
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
Installation
pip install hermite-function
Usage
This package provides a single class, HermiteFunction, to handle Hermite function series.
A series can be initialized in three ways:
- With the constructor, that takes an non-negative integer to create a pure Hermite function with the given index, or an array-like of coefficients to create a Hermite function series.
- With the random factory for a Hermite series with random indices up to a given degree.
- By fitting a data set.
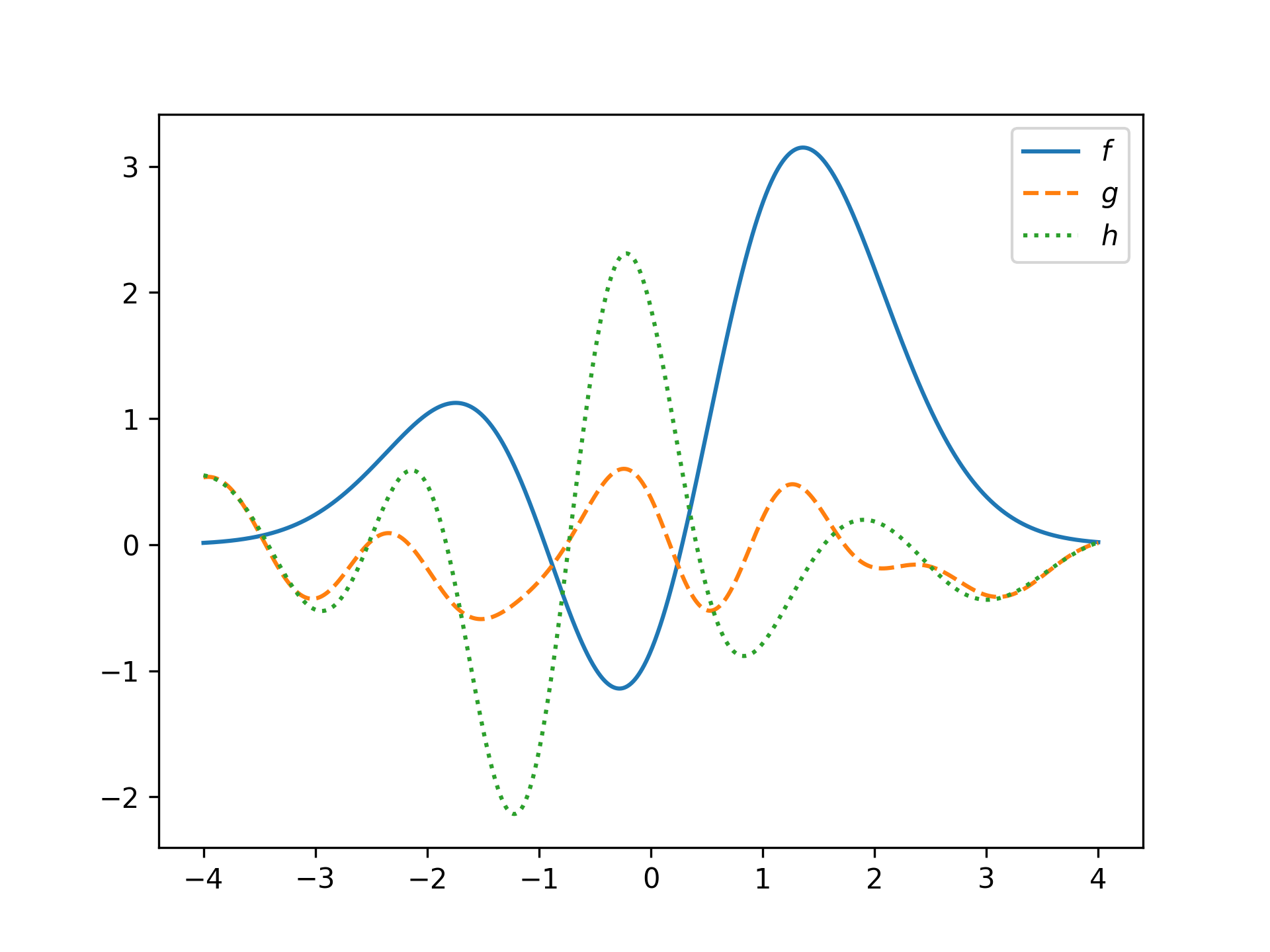
f = HermiteFunction((1, 2, 3))
g = HermiteFunction.random(15)
h = HermiteFunction.fit(x, g(x), 10)
plt.plot(x, f(x), label='$f$'), plt.plot(x, g(x), '--', label='$g$'), plt.plot(x, h(x), ':', label='$h$')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
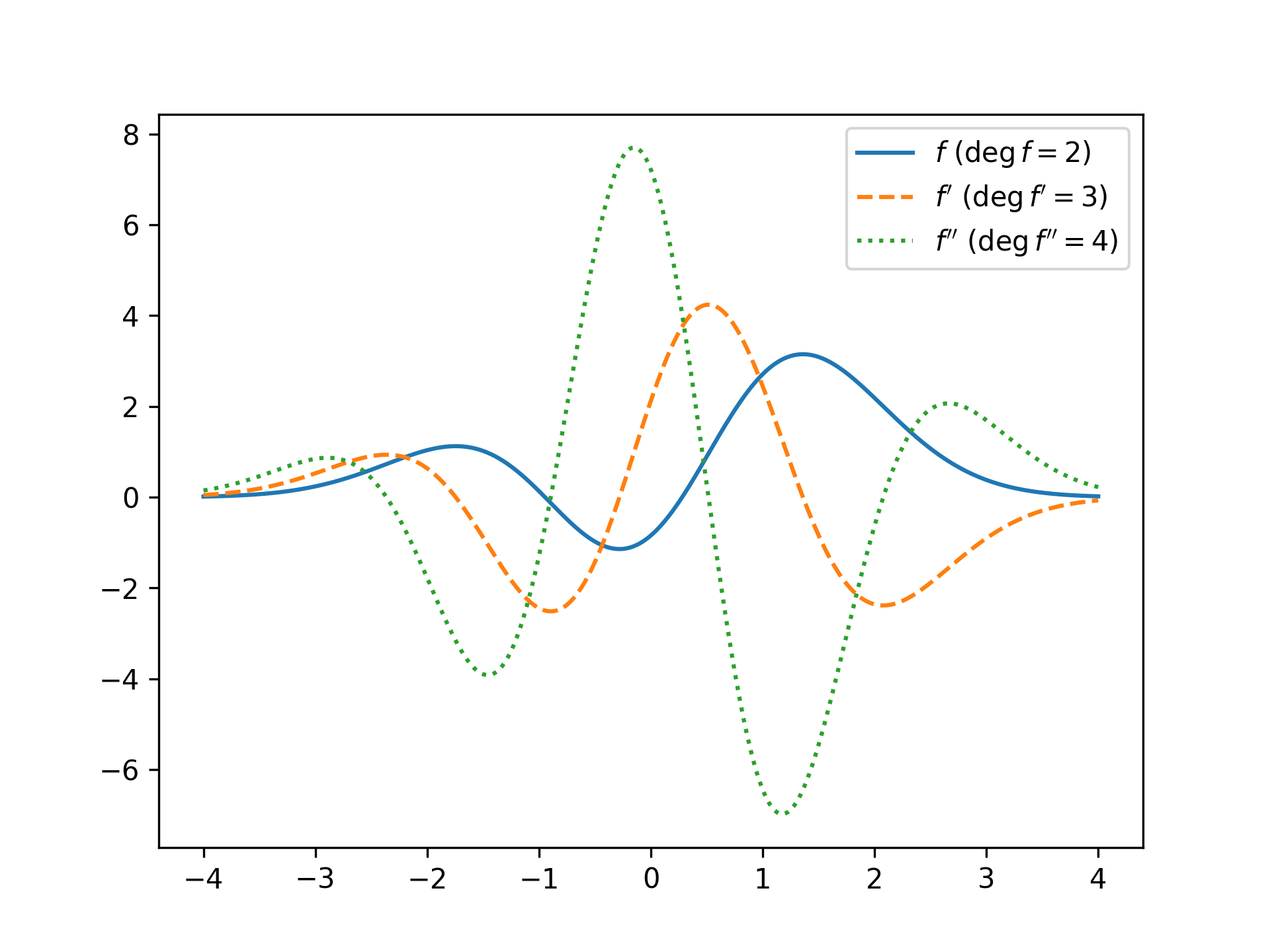
Methods for functions, simple evaluation and differentiation to an arbitrary degree, are implemented.
f_p = f.der()
f_pp = f.der(2)
plt.plot(x, f(x), label='$f$'), plt.plot(x, f_p(x), '--', label='$f\'$'), plt.plot(x, f_pp(x), ':', label='$f\'\'$')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Hilbert space operations are also provided, where the Hermite functions are used as an orthonormal basis of the $L_\mathbb{R}^2$ space. Like vector addition, scalar (or elementwise) multiplication, inner product and norm.
g = HermiteFunction(4)
h = f + g
i = 0.5 * f
plt.plot(x, f(x), label='$f$'), plt.plot(x, g(x), '--', label='$g$'), plt.plot(x, h(x), ':', label='$h$'), plt.plot(x, i(x), '-.', label='$i$')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
f.dot(h), f.norm()
(14, 3.7416573867739413)
But also the more exotic methods, the evaluation of the kinetic energy and finding $h$ to fulfill $fg=h_0h$ for a given $f, g$ (so $h=\frac{fg}{h_0}$).
f.kin(), str(f.prod_reorder(g))
(12.378679656440358,
'0.0 h_0 + 0.0 h_1 + 7.3 h_2 + 4.0 h_3 + 18.0 h_4 + 4.5 h_5 + 11.6 h_6')
Proofs
Note: Githubs Latex rendering is buggy, therefore better have a look at the notebook that generated this markdown you are reading right now.
In the following let $$ f=\sum_{k=0}^\infty f_k h_k, \ g=\sum_{k=0}^\infty g_k h_k. $$ where $h_k$ are the Hermite functions, defined by the Hermite polynomials $H_k$: $$ h_k(x) = \frac{e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}}{\sqrt{2^kk!\sqrt{\pi}}} H_k(x) $$ from Wikipedia - Hermite functions.
Hilbert space operations
Nothing unusual. All the standard $L_\mathbb{R}^2$ operations.
Scalar product
$$ \langle f|g\rangle_{L_\mathbb{R}^2} = \sum_{k=0}^\infty f_k^*g_k $$
Norm
$$ ||f||{L\mathbb{R}^2} = \sqrt{\sum_{k=0}^\infty |f_k|^2} $$
Scalar multiplication
$$ af = \sum_{k=0}^\infty af_kh_k $$
Addition
$$ f+g = \sum_{k=0}^\infty (f_k+g_k)h_k $$
Function operations
Evaluation
$$ f(x) = \sum_{k=0}^\infty f_kh_k(x) $$
Differentiation
$$ \begin{aligned} f' &= \sum_k f_k h_k' &&\mid h'k = \sqrt{\frac{k}{2}}h{k-1} - \sqrt{\frac{k+1}{2}}h_{k+1} \ &= \sum_k f_k \left( \sqrt{\frac{k}{2}}h_{k-1} - \sqrt{\frac{k+1}{2}}h_{k+1} \right) \ &= \sum_{k=0}^\infty f_k\sqrt{\frac{k}{2}} h_{k-1} - \sum_{k=0}^\infty f_k\sqrt{\frac{k+1}{2}} h_{k+1} &&\mid k-1 \to k, \ k+1 \to k \ &= \sum_{k=-1}^\infty \sqrt{\frac{k+1}{2}}f_{k+1} h_k - \sum_{k=1}^\infty \sqrt{\frac{k}{2}}f_{k-1} h_k &&\mid -0+0 = -\sqrt{\frac{-1+1}{2}}f_{-1+1}h_{-1} + \sqrt{\frac{0}{2}}f_{0-1} h_0 \ &= \sum_{k=0}^\infty \sqrt{\frac{k+1}{2}}f_{k+1} h_k - \sum_{k=0}^\infty \sqrt{\frac{k}{2}}f_{k-1} h_k \ &= \sum_k \left( \sqrt{\frac{k+1}{2}}f_{k+1} - \sqrt{\frac{k}{2}}f_{k-1} \right) h_k \end{aligned} \ \begin{pmatrix} f'_0 \ f'_1 \ f'_2 \ f'3 \ \vdots \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} 0 & \sqrt{\frac{1}{2}} & 0 & 0 & \ -\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}} & 0 & \sqrt{\frac{2}{2}} & 0 & \cdots \ 0 & -\sqrt{\frac{2}{2}} & 0 & \sqrt{\frac{3}{2}} & \ 0 & 0 & -\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}} & 0 & \ & \vdots & & & \ddots \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} f_0 \ f_1 \ f_2 \ f_3 \ \vdots \end{pmatrix} $$ With $h'k=\sqrt{\frac{k}{2}}h{k+1}-\sqrt{\frac{k+1}{2}}h{k-1}$ from Wikipedia-Hermite functions.
Integration
TODO
Kinetic energy
$$ T = -\frac{1}{2}\int_{\mathbb{R}}f^*(x)f''(x)dx = +\frac{1}{2}\int_{\mathbb{R}}|f'(x)|^2dx = \frac{1}{2}||f'||{L{\mathbb{R}}^2}^2 $$
''Multiplication''
The product of two Hermite functions is $$ \begin{aligned} &h_i(x) h_j(x) &&\mid h_j(x) = \frac{e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}}{\sqrt{2^jj!\sqrt{\pi}}}H_j(x) \ &= \frac{e^{-x^2}}{\sqrt{2^{i+j}i!j!\pi}} H_i(x)H_j(x) &&\mid H_j(x) = 2^\frac{j}{2}\tilde{H}j(\sqrt{2}x) \ &= \frac{e^{-x^2}}{\sqrt{2^{i+j} i!j! \pi}} 2^\frac{i+j}{2} \tilde{H}i(\sqrt{2}x) \tilde{H}j(\sqrt{2}x) &&\mid \tilde{H}i\tilde{H}j = \sum{k=0}^{\min{i, j}}k!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k}\tilde{H}{i+j-2k} \ &= \frac{e^{-x^2}}{\sqrt{2^{i+j}i!j!\pi}} 2^\frac{i+j}{2} \sum{k=0}^{\min{i, j}} k!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k} \tilde{H}{i+j-2k}(\sqrt{2}x) &&\mid \cdot1=2^{k-k} \ &= \frac{e^{-x^2}}{\sqrt{2^{i+j}i!j!\pi}}\sum{j=0}^{\min{i, j}} 2^kk!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k}2^\frac{i+j-2k}{2} \tilde{H}{i+j-2k}(\sqrt{2}x) &&\mid H_j(x)=2^\frac{j}{2} \tilde{H}j(\sqrt{2}x) \ &= \frac{e^{-x^2}}{\sqrt{2^{i+j}i!j!\pi}}\sum{k=0}^{\min{i, j}} 2^kk!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k} H{i+j-2k}(x) &&\mid h_j(x)=\frac{e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}}{\sqrt{2^jj!\sqrt{\pi}}} H_j(x) \ &= \frac{e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}}{\sqrt{i!j! \sqrt{\pi}}}\sum_{j=0}^{\min{i, j}} k!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k}\sqrt{(i+j-2k)!} h_{i+j-2k}(x) &&\mid h_0(x) = \frac{e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}}{\sqrt[4]{\pi}} \ &= h_0(x)\sum_{k=0}^{\min{i,j}} k!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k}\sqrt{\frac{(i+j-2k)!}{i!j!}} h_{i+j-2k}(x) \ &= h_0(x)\sum_{k=0}^{\min{i,j}} \frac{\sqrt{i!j!(i+j-2k)!}}{k!(i-k)!(j-k)!} h_{i+j-2k}(x) \end{aligned} $$ With
- $h_j(x)=\frac{e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}}{\sqrt{2^jj!\sqrt{\pi}}}H_j(x)$, $H_j(x)=2^\frac{j}{2} \tilde{H}_j(\sqrt{2}x)$ and $h_0(x)=\frac{e^{-\frac{x^2}{2}}}{\sqrt[4]{\pi}}$ from Wikipedia-Hermite functions,
- $H_j(x)=2^\frac{j}{2}\tilde{H}_j(\sqrt{2}x)$ from Wikipedia-Hermite polynomials,
- $\tilde{H}i\tilde{H}j=\sum{k=0}^{\min{i, j}}k!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k}\tilde{H}{i+j-2k}$ from some file I found on the internet eq. A.8.
Therefore follows for the products of Hermite series: $$ \begin{aligned} fg &= \sum_if_ih_i \sum_jg_jh_j = \sum_{i, j}f_ig_j h_ih_j \ &\qquad\mid h_ih_j = h_0\sum_{k=0}^{\min{i,j}} k!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k}\sqrt{\frac{(i+j-2k)!}{i!j!}} h_{i+j-2k} \ &= h_0 \sum_{i, j} f_ig_j \sum_{k=0}^{\min{i,j}} k!\binom{i}{k}\binom{j}{k}\sqrt{\frac{(i+j-2k)!}{i!j!}} h_{i+j-2k} \ &\vdots \ &\text{(some steps I am not able to prove)} \ &\vdots \ &= h_0 \sum_{b=0}^\infty \sum_{n=b}^\infty \sum_{d=-b, 2}^{+b} f_{\frac{n-d}{2}}g_{\frac{n+d}{2}} \left(\frac{n-b}{2}\right)!\binom{\frac{n-d}{2}}{\frac{n-b}{2}}\binom{\frac{n+d}{2}}{\frac{n-b}{2}}\sqrt{\frac{\left(\frac{n-b}{2}\right)!}{\left(\frac{n-d}{2}\right)!\left(\frac{n+d}{2}\right)!}} h_b \ &= h_0 \sum_{b=0}^\infty \sum_{n=b}^\infty \sum_{d=0}^b f_{\frac{n+b}{2}-d}g_{\frac{n-b}{2}+d} \left(\frac{n-b}{2}\right)!\binom{\frac{n+b}{2}-d}{\frac{n-b}{2}}\binom{\frac{n-b}{2}+d}{\frac{n-b}{2}}\sqrt{\frac{\left(\frac{n-b}{2}\right)!}{\left(\frac{n+b}{2}-d\right)!\left(\frac{n-b}{2}+d\right)!}} h_b \end{aligned} $$
Trivial tests
# Addition
for n in range(100):
f = HermiteFunction.random(20)
g = HermiteFunction.random(np.random.randint(0, 20)) #test different sized
assert np.allclose((f+g)(x), f(x)+g(x))
# Scalar multiplication
for n in range(100):
f = HermiteFunction.random(20)
c = np.random.rand()
assert np.allclose((c*f)(x), c*(f(x)))
Derivative
def der_num(x, y, n=1):
"""Nummerical differentiation."""
for _ in range(n):
y = np.diff(y) / np.diff(x)
x = (x[1:] + x[:-1]) / 2
return x, y
for i in range(100):
f = HermiteFunction(20)
assert np.allclose(f.der()(der_num(x, f(x))[0]), der_num(x, f(x))[1], atol=1e-3)
Products
from math import sqrt
from scipy.special import binom
for _ in range(100):
f, g = HermiteFunction.random(11), HermiteFunction.random(14)
assert np.allclose(f(x)*g(x), HermiteFunction(0)(x)*((f.prod_reorder(g))(x)), atol=1e-4)
Kinetic energy
def kin_num(x, y):
'''Nummeric kinetic energy.'''
x, y_lapl = der_num(x, y, 2)
y = (y[2:] + 2*y[1:-1] + y[:-2]) / 4 #mid y twice to broadcast to y_lapl
return -np.trapz(y*y_lapl, x) / 2
for _ in range(100):
f = HermiteFunction.random(5)
assert np.allclose(f.kin(), kin_num(x, f(x)), atol=1e-2)
Fitting
for _ in range(100):
f = HermiteFunction.random(20)
y = f(x)
fit = HermiteFunction.fit(x, y, 20)
assert np.allclose(f.coef, fit.coef)
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file hermite-function-0.9.2.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: hermite-function-0.9.2.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 6.8 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.10.0
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
7035942fcb64446b48552f1f4143580c6343fc7a510fa74019190b49c56ab60d
|
|
| MD5 |
4c68ed8fa0cf7d7ee80e69af37589e81
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
1c6af1bcfc8611880a7d96c242dab795856c8f96007bea0db4aa862713450f2a
|
File details
Details for the file hermite_function-0.9.2-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: hermite_function-0.9.2-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 7.0 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/4.0.2 CPython/3.10.0
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
77406739a77b8b378a4fb8b04cb06af6ca1e46be5b7928e51a76fa443bbe93fe
|
|
| MD5 |
12868bb5f192d42951841184a9df9906
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
03aa779cab4d86fd8d8c10467f19e81e4e031eb7a1852c394c96de8ccefeb64d
|