Fast Triton-based implementations for RWKV
Project description
This repo aims at providing Triton kernel for RWKV models. RWKV is a brand new network architecture that integrates the advantages of transformers and RNNs, and can be used for a variety of natural language processing tasks. Also, RWKV is the state-of-the-art RNN model.
As rwkv-fla is actively developed now, you should alwayd check for latest version pip install --upgrade rwkv-fla triton
Or you can install if with pip install rwkv-fla[cuda], pip install rwkv-fla[xpu], pip install rwkv-fla[rocm]
If you do need to use fla ops/modules and contemplate further explorations, an alternative way is to install the package from source
pip install -U git+https://github.com/RWKV-Vibe/rwkv-fla
or
pip install -U git+https://gitee.com/rwkv-vibe/rwkv-fla
or manage fla with submodules
git submodule add https://github.com/RWKV-Vibe/rwkv-fla.git 3rdparty/rwkv-fla
ln -s 3rdparty/rwkv-fla/fla fla
This repo aims at providing a collection of efficient Triton-based implementations for state-of-the-art linear attention models. All implementations are written purely in PyTorch and Triton, making them platform-agnostic. Currently verified platforms include NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel. Any pull requests are welcome!

News
- $\texttt{[2025-07]}$: 🐳 Add MLA implementation to
fla(paper). - $\texttt{[2025-07]}$: 🛣️ Added PaTH Attention to fla (paper).
- $\texttt{[2025-06]}$: 🎉 Added MesaNet to fla (paper).
- $\texttt{[2025-06]}$: 🐍 Add Comba implementation to
fla(paper). - $\texttt{[2025-05]}$: 🎉 Add Rodimus* implementation to
fla(paper). - $\texttt{[2025-04]}$: 🎉 Add DeltaProduct implementation to
fla(paper). - $\texttt{[2025-04]}$: 🎉 Add FoX implementation to
fla(paper). - $\texttt{[2025-03]}$:
We have changed the defaultTheinitializer_rangeto the magic 🐳 0.006initializer_rangewas rolled back to the default value of 0.02. For actual training, we recommend trying both. - $\texttt{[2025-02]}$: 🐳 Add NSA implementations to
fla. See kernels here. - $\texttt{[2025-01]}$: 🔥 We are migrating to
torchtitan-based training framework. Check out the flame repo for more details. - $\texttt{[2025-01]}$: 🎉 Add RWKV7 implementations (both kernels and models) to
fla. - $\texttt{[2024-12]}$: Integrated
flash-bidirectional-attentiontofla-org(repo) - $\texttt{[2024-12]}$: :tada: Add Gated DeltaNet implementation to
fla(paper). - $\texttt{[2024-12]}$: :rocket:
flanow officially supports kernels with variable-length inputs. - $\texttt{[2024-11]}$: The inputs are now switched from head-first to seq-first format.
- $\texttt{[2024-11]}$: :boom:
flanow provides a flexible way for training hybrid models. - $\texttt{[2024-10]}$: :fire: Announcing
flame, a minimal and scalable framework for trainingflamodels. Check out the details here. - $\texttt{[2024-09]}$:
flanow includes a fused linear and cross-entropy layer, significantly reducing memory usage during training. - $\texttt{[2024-09]}$: :tada: Add GSA implementation to
fla(paper). - $\texttt{[2024-05]}$: :tada: Add DeltaNet implementation to
fla(paper). - $\texttt{[2024-05]}$: :boom:
flav0.1: a variety of subquadratic kernels/layers/models integrated (RetNet/GLA/Mamba/HGRN/HGRN2/RWKV6, etc., see Models). - $\texttt{[2023-12]}$: :boom: Launched
fla, offering a collection of implementations for state-of-the-art linear attention models.
Models
Roughly sorted according to the timeline supported in fla. The recommended training mode is chunk when available.
Installation
The following requirements should be satisfied
- PyTorch >= 2.5
- Triton >=3.0 (or nightly version, see FAQs)
- einops
- transformers >=4.45.0
- datasets >=3.3.0
- causal-conv1d >=1.4.0
You can install fla with pip:
pip install flash-linear-attention
As fla is actively developed now, for the latest features and updates, an alternative way is to install the package from source
# uninstall `fla` first to ensure a successful upgrade
pip uninstall flash-linear-attention && pip install -U git+https://github.com/fla-org/flash-linear-attention
or manage fla with submodules
git submodule add https://github.com/fla-org/flash-linear-attention.git 3rdparty/flash-linear-attention
ln -s 3rdparty/flash-linear-attention/fla fla
If you have installed triton-nightly and torch pre version, please use the following command:
pip install einops ninja datasets transformers numpy
pip uninstall flash-linear-attention && pip install -U --no-use-pep517 git+https://github.com/fla-org/flash-linear-attention --no-deps
Usage
Token Mixing
We provide ``token mixing'' linear attention layers in fla.layers for you to use.
You can replace the standard multihead attention layer in your model with other linear attention layers.
Example usage is as follows:
>>> import torch
>>> from fla.layers import MultiScaleRetention
>>> batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, hidden_size = 32, 4, 2048, 1024
>>> device, dtype = 'cuda:0', torch.bfloat16
>>> retnet = MultiScaleRetention(hidden_size=hidden_size, num_heads=num_heads).to(device=device, dtype=dtype)
>>> retnet
MultiScaleRetention(
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=2048, bias=False)
(g_proj): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=2048, bias=False)
(o_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=1024, bias=False)
(g_norm_swish_gate): FusedRMSNormSwishGate(512, eps=1e-05)
(rotary): RotaryEmbedding()
)
>>> x = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size).to(device=device, dtype=dtype)
>>> y, *_ = retnet(x)
>>> y.shape
torch.Size([32, 2048, 1024])
We provide the implementations of models that are compatible with 🤗 Transformers library.
Here's an example of how to initialize a GLA model from the default configs in fla:
>>> from fla.models import GLAConfig
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> config = GLAConfig()
>>> config
GLAConfig {
"attn": null,
"attn_mode": "chunk",
"bos_token_id": 1,
"clamp_min": null,
"conv_size": 4,
"elementwise_affine": true,
"eos_token_id": 2,
"expand_k": 0.5,
"expand_v": 1,
"feature_map": null,
"fuse_cross_entropy": true,
"fuse_norm": true,
"fuse_swiglu": true,
"hidden_act": "swish",
"hidden_ratio": 4,
"hidden_size": 2048,
"initializer_range": 0.02,
"intermediate_size": null,
"max_position_embeddings": 2048,
"model_type": "gla",
"norm_eps": 1e-06,
"num_heads": 4,
"num_hidden_layers": 24,
"num_kv_heads": null,
"tie_word_embeddings": false,
"transformers_version": "4.48.2",
"use_cache": true,
"use_gk": true,
"use_gv": false,
"use_output_gate": true,
"use_short_conv": false,
"vocab_size": 32000
}
>>> AutoModelForCausalLM.from_config(config)
GLAForCausalLM(
(model): GLAModel(
(embeddings): Embedding(32000, 2048)
(layers): ModuleList(
(0-23): 24 x GLABlock(
(attn_norm): RMSNorm(2048, eps=1e-06)
(attn): GatedLinearAttention(
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=1024, bias=False)
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=1024, bias=False)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=2048, bias=False)
(g_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=2048, bias=False)
(gk_proj): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=16, bias=False)
(1): Linear(in_features=16, out_features=1024, bias=True)
)
(o_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=2048, bias=False)
(g_norm_swish_gate): FusedRMSNormSwishGate(512, eps=1e-06)
)
(mlp_norm): RMSNorm(2048, eps=1e-06)
(mlp): GatedMLP(
(gate_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=5632, bias=False)
(up_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=5632, bias=False)
(down_proj): Linear(in_features=5632, out_features=2048, bias=False)
)
)
)
(norm): RMSNorm(2048, eps=1e-06)
)
(lm_head): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=32000, bias=False)
)
Fused Modules
We offer a collection of fused modules in fla.modules to facilitate faster training:
Rotary Embedding: rotary positional embeddings as adopted by the Llama architecture, a.k.a., Transformer++.Norm Layers:RMSNorm,LayerNormandGroupNormRMSNormLinear,LayerNormLinearandGroupNormLinearto reduce memory usage of intermediate tensors for improved memory efficiency.
Norm Layers with Gating: combine norm layers with element-wise sigmoid or swish gating, as used by RetNet/GLA.Cross Entropy: faster Triton implementation of cross entropy loss.Linear Cross Entropy: fused linear layer and cross entropy loss to avoid the materialization of large logits tensors. Also refer to implementations by mgmalek and Liger-Kernel.Linear KL Divergence: fused linear layer and KL divergence loss in a similar vein as CE loss.
[!IMPORTANT] You can control using
fuse_linear_cross_entropyin the model configuration to enable/disable the fused linear cross entropy loss.This fused implementation is more memory-efficient but may reduce numerical precision. Due to this trade-off, it is disabled by default. If you enable this feature and encounter training instability (e.g., loss divergence), we recommend disabling it to see if the issue is resolved.
Generation
Upon successfully pretraining a model, it becomes accessible for generating text using the 🤗 text generation APIs. In the following, we give a generation example:
>>> import fla
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> name = 'fla-hub/gla-1.3B-100B'
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(name)
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(name).cuda()
>>> input_prompt = "Power goes with permanence. Impermanence is impotence. And rotation is castration."
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(input_prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids.cuda()
>>> outputs = model.generate(input_ids, max_length=64)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
We also provide a simple script here for benchmarking the generation speed. Simply run it by:
$ python -m benchmarks.benchmark_generation \
--path 'fla-hub/gla-1.3B-100B' \
--repetition_penalty 2. \
--prompt="Hello everyone, I'm Songlin Yang"
Prompt:
Hello everyone, I'm Songlin Yang
Generated:
Hello everyone, I'm Songlin Yang.
I am a 20 year old girl from China who is currently studying in the United States of America for my Master degree and also working as an English teacher at school here on campus since last summer (1st semester). My main goal to be able do well with this course so that we can have
Prompt length: 10, generation length: 64
Total prompt processing + decoding time: 4593ms
All of the pretrained models currently available can be found in fla-hub.
>>> from huggingface_hub import list_models
>>> for model in list_models(author='fla-hub'): print(model.id)
Hybrid Models
fla provides a flexible method to incorporate standard attention layers into existing linear attention models.
This is easily achieved by specifying the attn argument in the model configuration.
For example, to create a 2-layer Samba model with interleaved Mamba and local attention layers, using a sliding window size of 2048:
>>> from fla.models import SambaConfig
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
>>> config = SambaConfig(num_hidden_layers=2)
>>> config.attn = {
'layers': [1],
'num_heads': 18,
'num_kv_heads': 18,
'window_size': 2048
}
>>> config
SambaConfig {
"attn": {
"layers": [
1
],
"num_heads": 18,
"num_kv_heads": 18,
"window_size": 2048
},
"bos_token_id": 1,
"conv_kernel": 4,
"eos_token_id": 2,
"expand": 2,
"fuse_cross_entropy": true,
"fuse_norm": true,
"hidden_act": "silu",
"hidden_ratio": 4,
"hidden_size": 2304,
"initializer_range": 0.02,
"intermediate_size": 4608,
"max_position_embeddings": 2048,
"model_type": "samba",
"norm_eps": 1e-05,
"num_hidden_layers": 2,
"pad_token_id": 0,
"rescale_prenorm_residual": false,
"residual_in_fp32": false,
"state_size": 16,
"tie_word_embeddings": false,
"time_step_floor": 0.0001,
"time_step_init_scheme": "random",
"time_step_max": 0.1,
"time_step_min": 0.001,
"time_step_rank": 144,
"time_step_scale": 1.0,
"transformers_version": "4.45.0",
"use_bias": false,
"use_cache": true,
"use_conv_bias": true,
"vocab_size": 32000
}
>>> AutoModelForCausalLM.from_config(config)
SambaForCausalLM(
(backbone): SambaModel(
(embeddings): Embedding(32000, 2304)
(layers): ModuleList(
(0): SambaBlock(
(mixer_norm): RMSNorm(2304, eps=1e-05)
(mixer): Mamba(
(conv1d): Conv1d(4608, 4608, kernel_size=(4,), stride=(1,), padding=(3,), groups=4608)
(in_proj): Linear(in_features=2304, out_features=9216, bias=False)
(x_proj): Linear(in_features=4608, out_features=176, bias=False)
(dt_proj): Linear(in_features=144, out_features=4608, bias=True)
(out_proj): Linear(in_features=4608, out_features=2304, bias=False)
)
(mlp_norm): RMSNorm(2304, eps=1e-05)
(mlp): SambaMLP(
(gate_proj): Linear(in_features=2304, out_features=12288, bias=False)
(down_proj): Linear(in_features=6144, out_features=2304, bias=False)
(act_fn): SiLU()
)
)
(1): SambaBlock(
(mixer_norm): RMSNorm(2304, eps=1e-05)
(mixer): Attention(
(q_proj): Linear(in_features=2304, out_features=2304, bias=False)
(k_proj): Linear(in_features=2304, out_features=2304, bias=False)
(v_proj): Linear(in_features=2304, out_features=2304, bias=False)
(o_proj): Linear(in_features=2304, out_features=2304, bias=False)
(rotary): RotaryEmbedding()
)
(mlp_norm): RMSNorm(2304, eps=1e-05)
(mlp): SambaMLP(
(gate_proj): Linear(in_features=2304, out_features=12288, bias=False)
(down_proj): Linear(in_features=6144, out_features=2304, bias=False)
(act_fn): SiLU()
)
)
)
(norm_f): RMSNorm(2304, eps=1e-05)
)
(lm_head): Linear(in_features=2304, out_features=32000, bias=False)
)
During inference, you DO NOT need to revise anything for generation! The model will produce output as-is, without any need for additional configurations or modifications.
Training
We provide a minimal framework called :fire: flame built on top of torchtitan, for efficient training of fla models.
Checkout the GLA example for more details.
Evaluation
The lm-evaluation-harness library allows you to easily perform (zero-shot) model evaluations. Follow the steps below to use this library:
-
Install
lm_evalfollowing their instructions. -
Run evaluation with:
$ MODEL='fla-hub/gla-1.3B-100B'
$ python -m evals.harness --model hf \
--model_args pretrained=$MODEL,dtype=bfloat16 \
--tasks wikitext,lambada_openai,piqa,hellaswag,winogrande,arc_easy,arc_challenge,boolq,sciq,copa,openbookqa \
--batch_size 64 \
--num_fewshot 0 \
--device cuda \
--show_config
We've made fla compatible with hf-style evaluations, you can call evals.harness to finish the evaluations.
Running the command above will provide the task results reported in the GLA paper.
- Multi-GPU Evaluation with Hugging Face accelerate 🚀
To perform data-parallel evaluation (where each GPU loads a separate full copy of the model), we leverage the accelerate launcher as follows:
$ MODEL='fla-hub/gla-1.3B-100B'
$ accelerate launch -m evals.harness --model hf \
--model_args pretrained=$MODEL,dtype=bfloat16,trust_remote_code=True \
--tasks wikitext,lambada_openai,piqa,hellaswag,winogrande,arc_easy,arc_challenge,boolq,sciq,copa,openbookqa \
--batch_size 64 \
--num_fewshot 0 \
--device cuda \
--show_config \
--trust_remote_code
- 📏 RULER Benchmark suite
The RULER benchmarks are commonly used for evaluating model performance on long-context tasks.
You can evaluate fla models on RULER directly using lm-evaluation-harness. RULER is only available in a relatively recent version of lm-evaluation-harness, so make sure you have the latest version installed.
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness
cd lm-evaluation-harness
pip install -e .
Then, install the necessary dependencies for RULER:
pip install lm_eval["ruler"]
and run evaluation by (e.g., 32k contexts):
$ accelerate launch -m evals.harness \
--output_path $OUTPUT \
--tasks niah_single_1,niah_single_2,niah_single_3,niah_multikey_1,niah_multikey_2,niah_multikey_3,niah_multiquery,niah_multivalue,ruler_vt,ruler_cwe,ruler_fwe,ruler_qa_hotpot,ruler_qa_squad \
--model_args pretrained=$MODEL,dtype=bfloat16,max_length=32768,trust_remote_code=True \
--metadata='{"max_seq_lengths":[4096,8192,16384,32768]}' \
--batch_size 2 \
--show_config \
--trust_remote_code
If a GPU can't load a full copy of the model, please refer to this link for FSDP settings.
[!Tip] If you are using
lm-evaluation-harnessas an external library and can't find (almost) any tasks available, before callinglm_eval.evaluate()orlm_eval.simple_evaluate(), simply run the following to load the library's stock tasks!
>>> from lm_eval.tasks import TaskManager; TaskManager().initialize_tasks()
Benchmarks
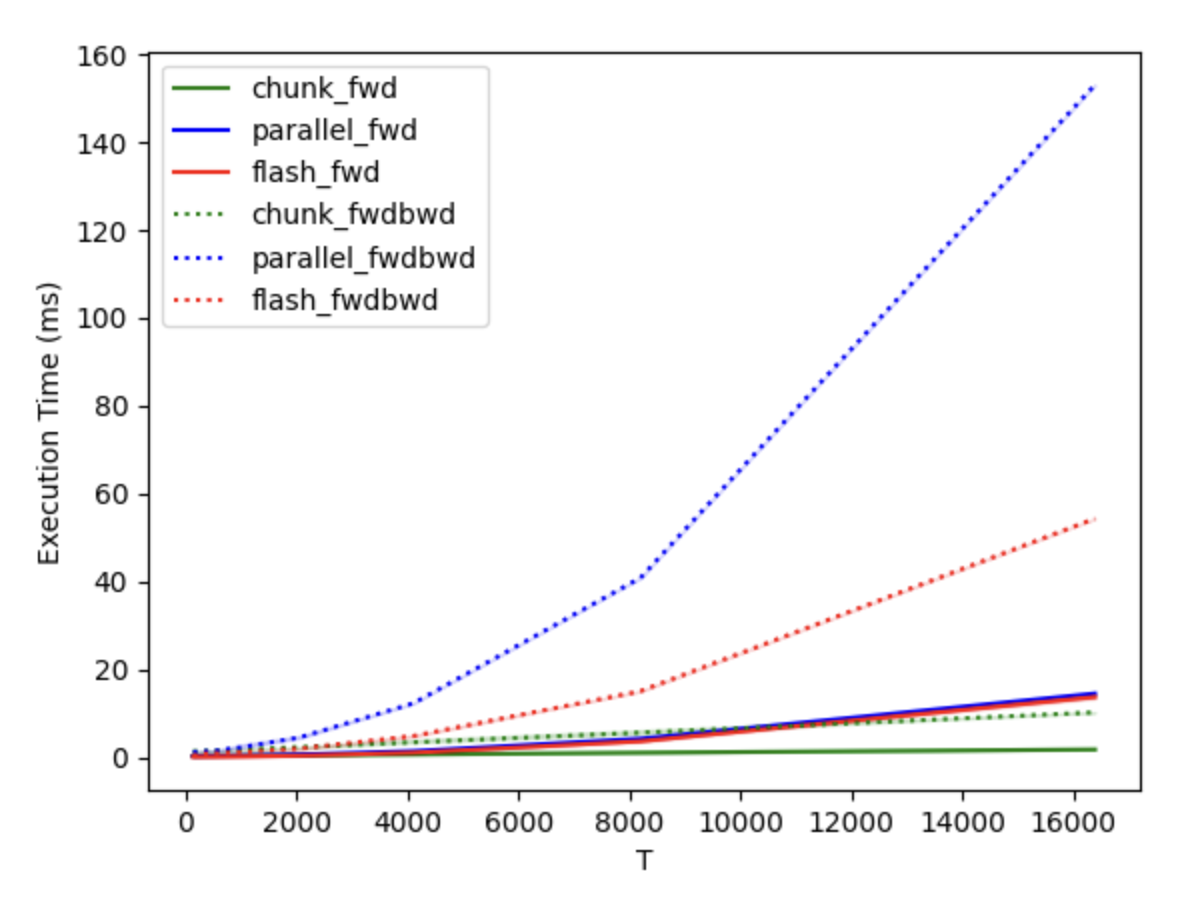
We compared our Triton-based RetNet implementation with CUDA-based FlashAttention2, using a batch size of 8, 32 heads, and a head dimension of 128, across different sequence lengths. These tests were conducted on a single H100 80GB GPU, as illustrated in the following graph
# you might have to first install `fla` to enable its import via `pip install -e .`
$ python benchmark_retention.py
Performance:
T chunk_fwd parallel_fwd flash_fwd chunk_fwdbwd parallel_fwdbwd flash_fwdbwd
0 128.0 0.264032 0.243536 0.083488 1.301856 1.166784 0.320704
1 256.0 0.273472 0.252848 0.094304 1.345872 1.300608 0.807936
2 512.0 0.303600 0.278896 0.098112 1.503168 1.433184 0.857216
3 1024.0 0.357248 0.367360 0.156528 1.773552 2.303424 1.160864
4 2048.0 0.454624 0.605616 0.340928 2.283728 4.483360 1.955936
5 4096.0 0.638960 1.378016 1.004992 3.374720 12.271215 4.813776
6 8192.0 1.012352 4.201344 3.625008 5.581808 40.833618 15.023697
7 16384.0 1.748512 14.489664 13.710080 10.191552 153.093765 54.336864
Citation
If you find this repository helpful, please cite our work:
@software{yang2024fla,
title = {FLA: A Triton-Based Library for Hardware-Efficient Implementations of Linear Attention Mechanism},
author = {Yang, Songlin and Zhang, Yu},
url = {https://github.com/fla-org/flash-linear-attention},
month = jan,
year = {2024}
}
@inproceedings{yang2024gdn,
title = {Gated Delta Networks: Improving Mamba2 with Delta Rule},
author = {Songlin Yang and Jan Kautz and Ali Hatamizadeh},
booktitle = {Proceedings of ICLR},
year = {2025}
}
@inproceedings{yang2024deltanet,
title = {Parallelizing Linear Transformers with the Delta Rule over Sequence Length},
author = {Yang, Songlin and Wang, Bailin and Zhang, Yu and Shen, Yikang and Kim, Yoon},
booktitle = {Proceedings of NeurIPS},
year = {2024}
}
@inproceedings{zhang2024gsa,
title = {Gated Slot Attention for Efficient Linear-Time Sequence Modeling},
author = {Zhang, Yu and Yang, Songlin and Zhu, Ruijie and Zhang, Yue and Cui, Leyang and Wang, Yiqiao and Wang, Bolun and Shi, Freda and Wang, Bailin and Bi, Wei and Zhou, Peng and Fu, Guohong},
booktitle = {Proceedings of NeurIPS},
year = {2024}
}
@inproceedings{qin2024hgrn2,
title = {HGRN2: Gated Linear RNNs with State Expansion},
author = {Qin, Zhen and Yang, Songlin and Sun, Weixuan and Shen, Xuyang and Li, Dong and Sun, Weigao and Zhong, Yiran},
booktitle = {Proceedings of COLM},
year = {2024}
}
@inproceedings{yang2024gla,
title = {Gated Linear Attention Transformers with Hardware-Efficient Training},
author = {Yang, Songlin and Wang, Bailin and Shen, Yikang and Panda, Rameswar and Kim, Yoon},
booktitle = {Proceedings of ICML},
year = {2024}
}
Star History
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to Bitdeer for providing CI server resources that power our infrastructure.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file rwkv_fla-0.7.202508221413.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: rwkv_fla-0.7.202508221413.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 802.7 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.11
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
147ab596ac2c795eb3c9d2ff9f398e8d99a92a6b75b0cd412cc12251d654ff03
|
|
| MD5 |
3e86f01db9fc891f718c1d803cf2383c
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
4b6c36cba6f48efec409923e9524a0c9bd229fc846d7292a9d1f6329392e59b6
|
File details
Details for the file rwkv_fla-0.7.202508221413-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: rwkv_fla-0.7.202508221413-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 1.3 MB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.12.11
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
abf8cbc6aac7e7fec994912014d055c6050fa5605710bce2e36db87f88769fb7
|
|
| MD5 |
e9e9540eacf05f2e903d1099fccb05e1
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
caa9d5857d911cbc499b39fec0003f8c6ead1aa38304ae47c6d5bcffb92a45fa
|



















