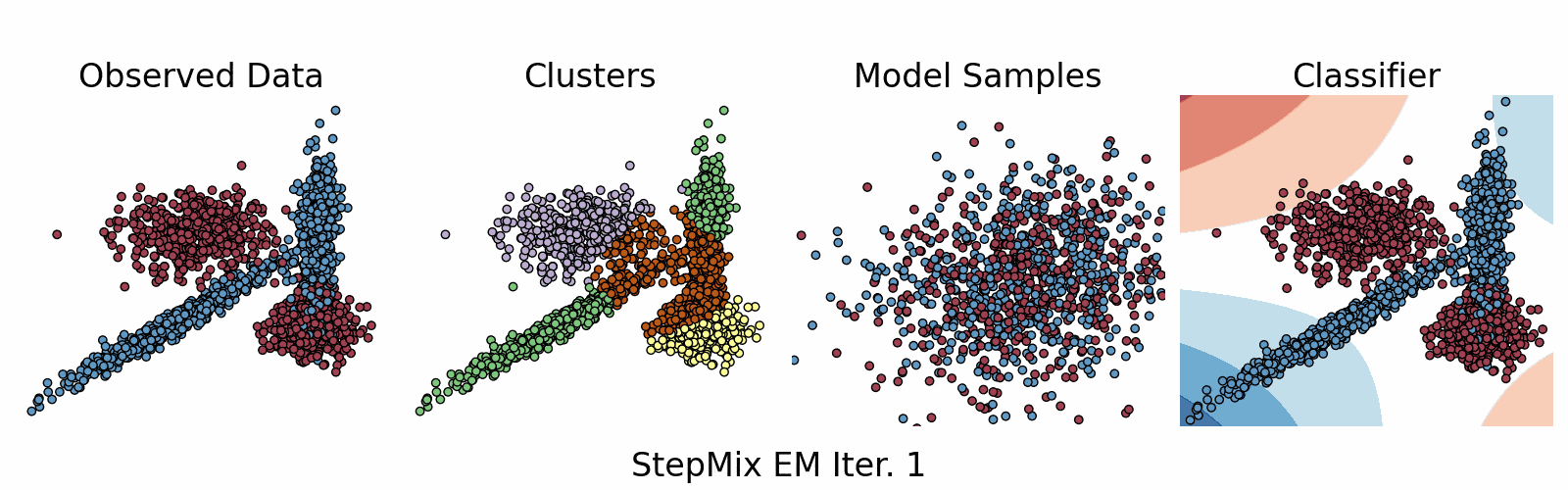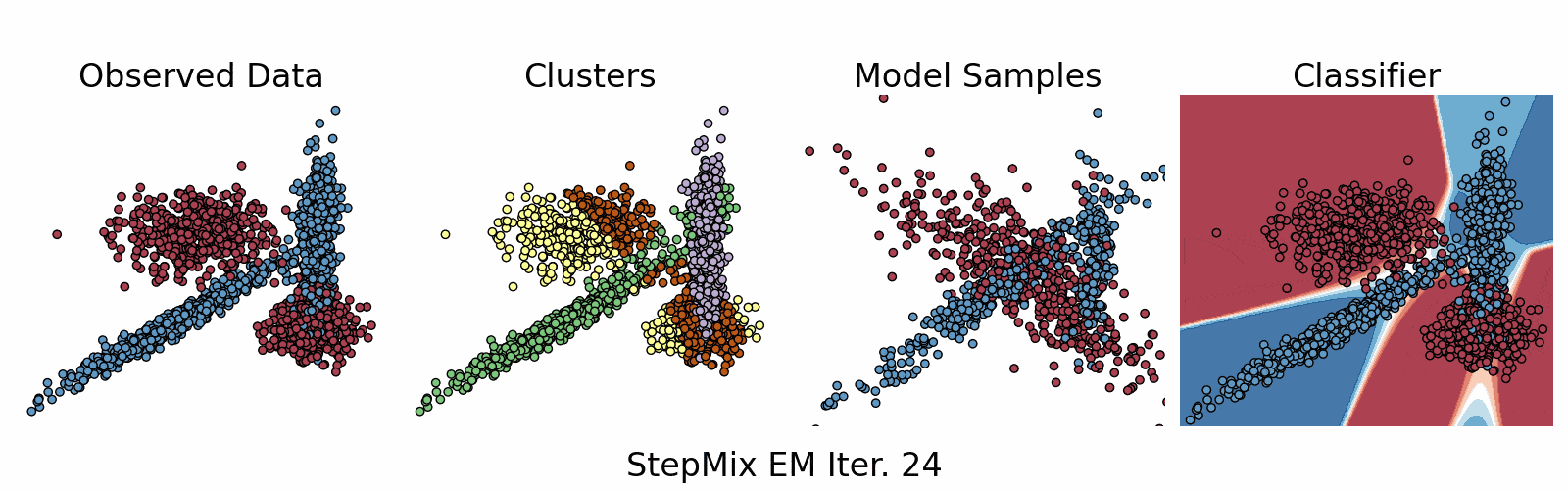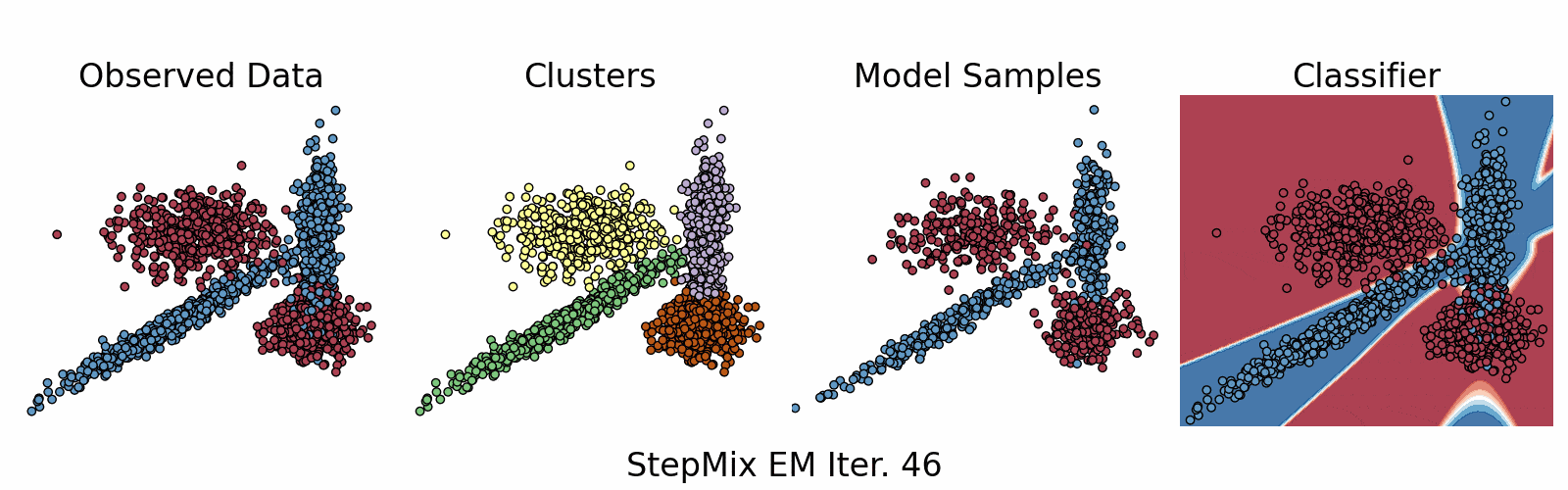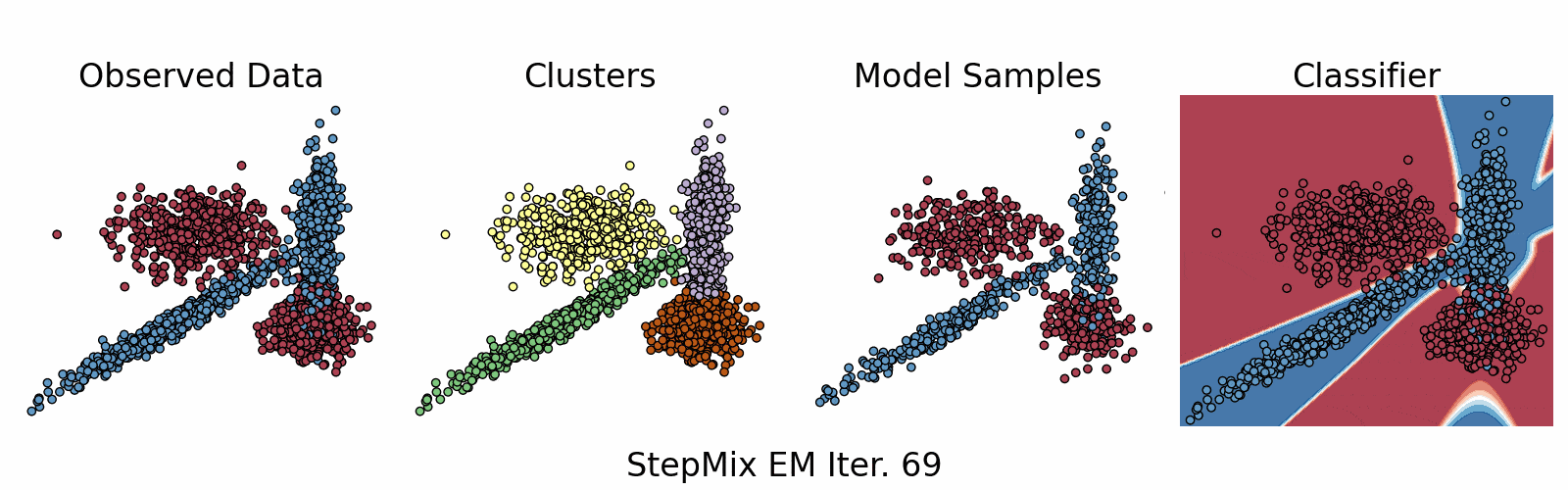
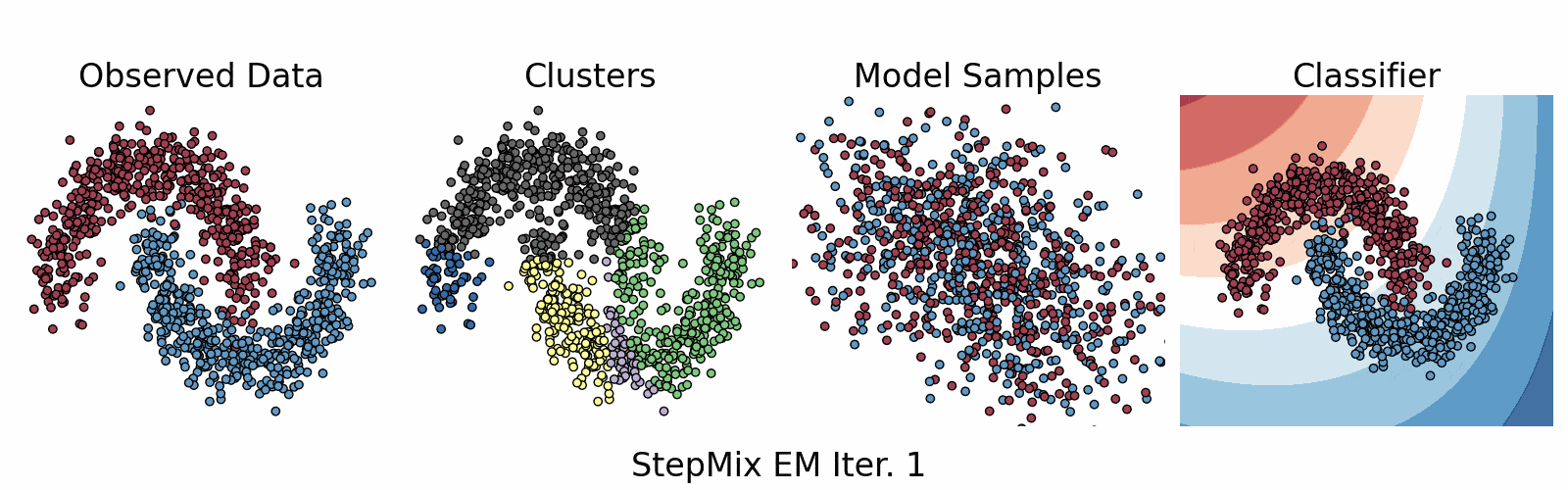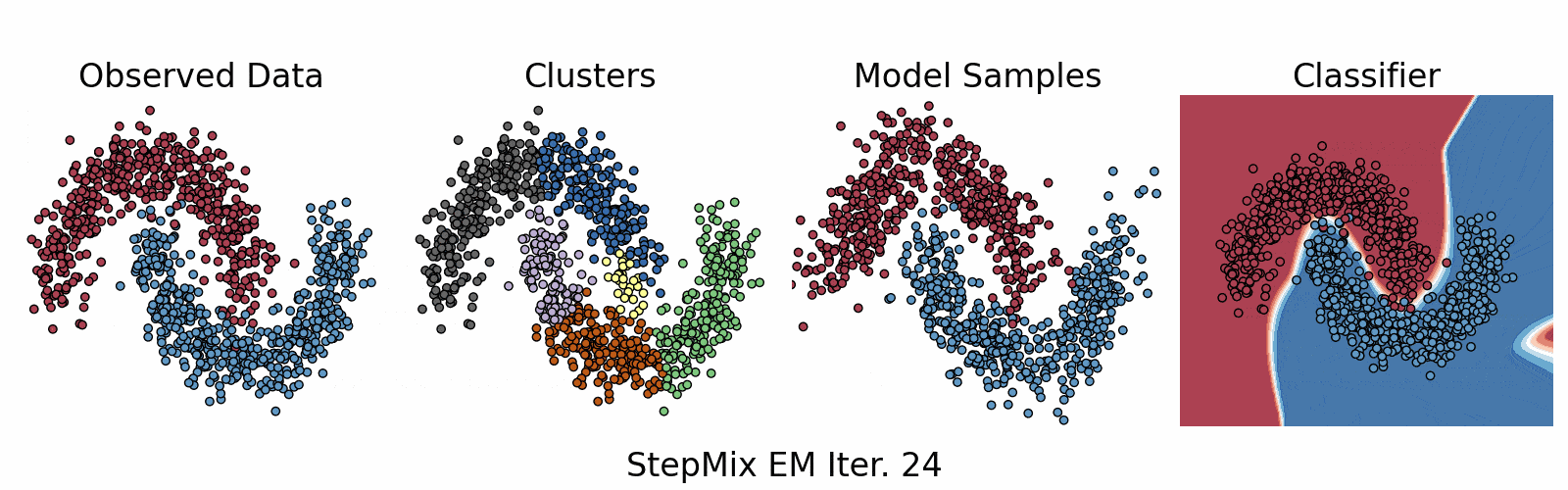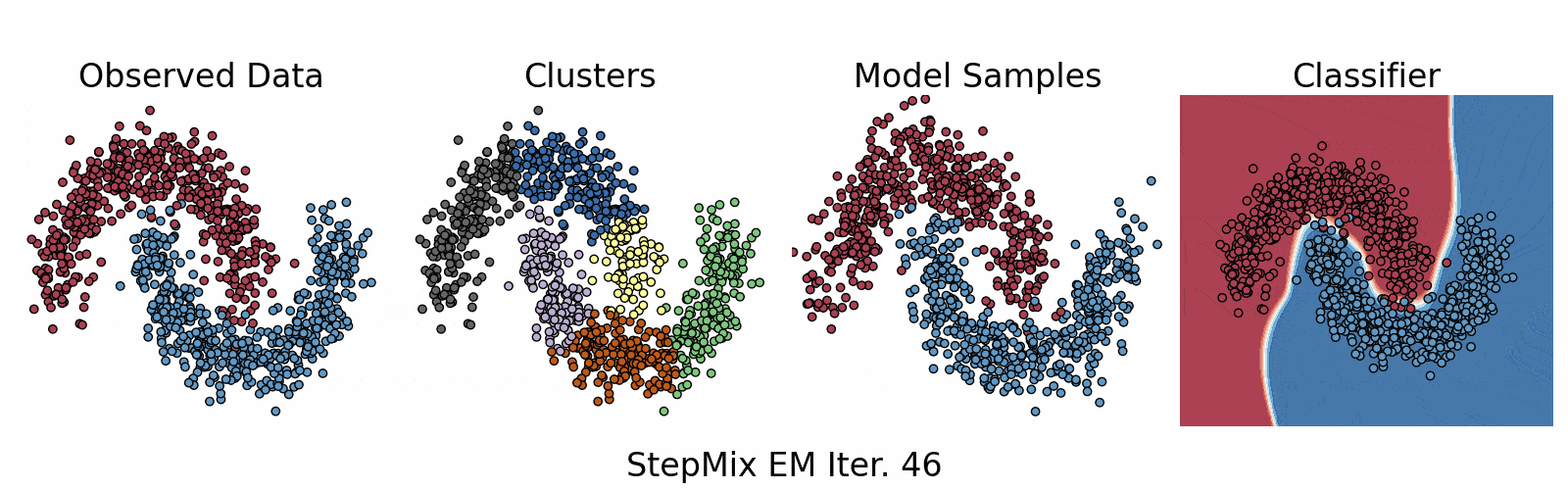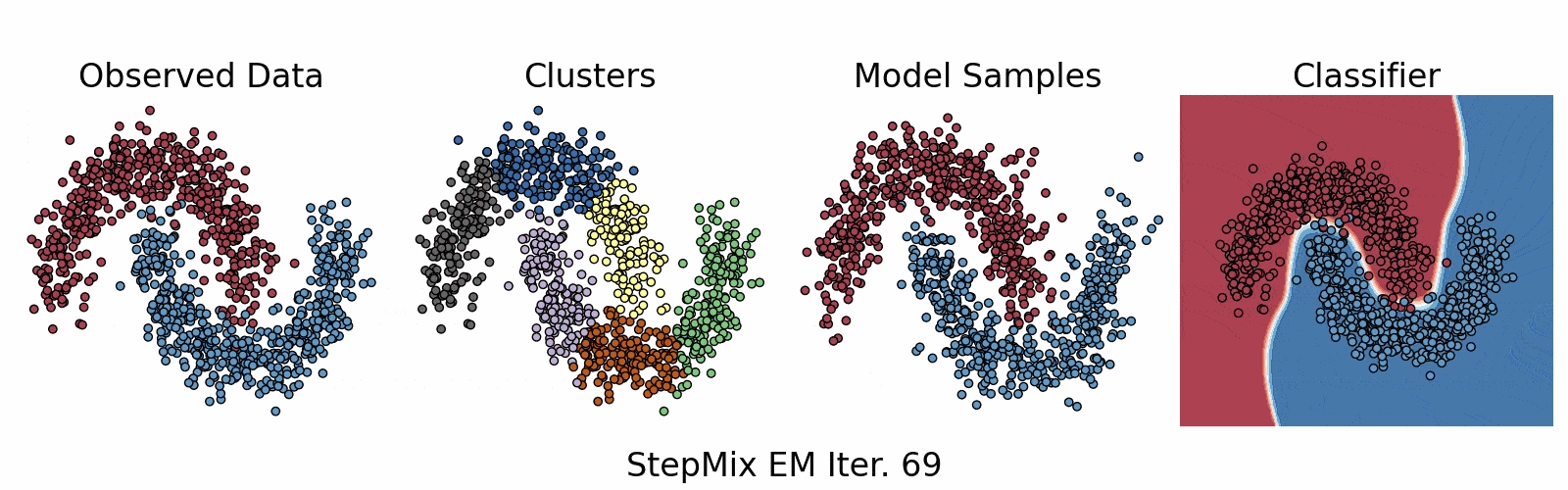
A Python package for stepwise estimation of latent class models with measurement and structural components. The package can also be used to fit mixture models with various observed random variables.
Project description
StepMix
For StepMixR, please refer to this repository.
A Python package following the scikit-learn API for generalized mixture modeling. The package supports categorical data (Latent Class Analysis) and continuous data (Gaussian Mixtures/Latent Profile Analysis). StepMix can be used for both clustering and supervised learning.
Additional features include:
- Support for missing values through Full Information Maximum Likelihood (FIML);
- Multiple stepwise Expectation-Maximization (EM) estimation methods based on pseudolikelihood theory;
- Covariates and distal outcomes;
- Parametric and non-parametric bootstrapping.
Reference
If you find StepMix useful, please leave a ⭐ and consider citing our Journal of Statistical Software paper:
@Article{,
title = {{StepMix}: A {Python} Package for Pseudo-Likelihood
Estimation of Generalized Mixture Models with External
Variables},
author = {Sacha Morin and Robin Legault and F{\'e}lix Lalibert{\'e}
and Zsuzsa Bakk and Charles-{\'E}douard Gigu{\`e}re and Roxane
{de la Sablonni{\`e}re} and {\'E}ric Lacourse},
journal = {Journal of Statistical Software},
year = {2025},
volume = {113},
number = {8},
pages = {1--39},
doi = {10.18637/jss.v113.i08},
}
Install
You can install StepMix with pip, preferably in a virtual environment:
pip install stepmix
Quickstart
A StepMix mixture using categorical variables on a preloaded data matrix. StepMix accepts either numpy.arrayor
pandas.DataFrame. Categories should be integer-encoded and 0-indexed.
from stepmix.stepmix import StepMix
# Categorical StepMix Model with 3 latent classes
model = StepMix(n_components=3, measurement="categorical")
model.fit(data)
# Allow missing values
model_nan = StepMix(n_components=3, measurement="categorical_nan")
model_nan.fit(data_nan)
For binary data you can also use measurement="binary" or measurement="binary_nan". For continuous data, you can fit a Gaussian Mixture with diagonal covariances using measurement="continuous" or measurement="continuous_nan".
Set verbose=1 for a detailed output.
Please refer to the StepMix tutorials to learn how to combine continuous and categorical data in the same model.
Tutorials
Detailed tutorials are available in notebooks:
- Generalized Mixture Models with StepMix:
an in-depth look at how mixture models can be defined with StepMix. The tutorial uses the Iris Dataset as an example
and covers:
- Gaussian Mixtures (Latent Profile Analysis);
- Binary Mixtures (LCA);
- Categorical Mixtures (LCA);
- Mixed Categorical and Continuous Mixtures;
- Missing Values through Full-Information Maximum Likelihood.
- Stepwise Estimation with StepMix:
a tutorial demonstrating how to define measurement and structural models. The tutorial discusses:
- LCA models with distal outcomes;
- LCA models with covariates;
- 1-step, 2-step and 3-step estimation;
- Corrections (BCH or ML) and other options for 3-step estimation;
- Putting it All Together: A Complete Model with Missing Values
- Model Selection:
- Selecting the number of components in a mixture model (
n_components) with cross-validation; - Selecting the number of components with the Parametric Bootstrapped Likelihood Ratio Test (BLRT);
- Fit indices: AIC, BIC and other metrics.
- Selecting the number of components in a mixture model (
- Parameters, Bootstrapping and CI:
a tutorial discussing how to:
- Access StepMix parameters;
- Bootstrap StepMix estimators;
- Quickly plot confidence intervals.
- Supervised and Semi-Supervised Learning with StepMix:
- Binary Classification;
- Multiclass Classification;
- Semi-Supervised Learning;
- Cross-Validation.
- Deriving p-values in StepMix: a tutorial demonstrating how to transform SM parameters into conventional regression coefficients and how to derive p-values.
The tutorial covers models with:
- Continuous covariate;
- Binary covariate;
- Categorical covariate;
- Multiple covariates (different distributions);
- Binary distal outcome;
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file stepmix-2.2.3.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: stepmix-2.2.3.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 61.5 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: python-requests/2.32.4
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
6ddc76f10a40033061812ac16c7d7d2ca7ed2444b62006d9a0f684dee85edc2e
|
|
| MD5 |
70f7bf0701208d2cfa61876f7a52081a
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
d22f69efb0be27540d8ab1fae18edbc778d17b9320aa58b7f5cf42660749d212
|
File details
Details for the file stepmix-2.2.3-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: stepmix-2.2.3-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 44.5 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: python-requests/2.32.4
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
9b38fc5419f317383aca2cabeccade965a69e7f5797d74f6399610329f85e688
|
|
| MD5 |
76625aac071d31b08e40ae7d2cd0ddc2
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
c87aedd784d4686ecf242ceadf49cf44fc82abe9c1a6469387e51f17addb23fa
|