A library for augmenting text for natural language processing applications.
Project description
TextAugment: Improving short text classification through global augmentation methods
TextAugment is a Python 3 library for augmenting text for natural language processing applications. TextAugment stands on the giant shoulders of NLTK, Gensim, and TextBlob and plays nicely with them.
Citation Paper
Improving short text classification through global augmentation methods published to MLDM 2019
Requirements
- Python 3
The following software packages are dependencies and will be installed automatically.
$ pip install numpy nltk gensim textblob googletrans
The following code downloads NLTK corpus for wordnet.
nltk.download('wordnet')
The following code downloads NLTK tokenizer. This tokenizer divides a text into a list of sentences by using an unsupervised algorithm to build a model for abbreviation words, collocations, and words that start sentences.
nltk.download('punkt')
The following code downloads default NLTK part-of-speech tagger model. A part-of-speech tagger processes a sequence of words, and attaches a part of speech tag to each word.
nltk.download('averaged_perceptron_tagger')
Use gensim to load a pre-trained word2vec model. Like Google News from Google drive.
import gensim
model = gensim.models.Word2Vec.load_word2vec_format('./GoogleNews-vectors-negative300.bin', binary=True)
Or training one from scratch using your data or the following public dataset:
Installation
Install from pip [Recommended]
$ pip install textaugment
or install latest release
$ pip install git+git@github.com:dsfsi/textaugment.git
Install from source
$ git clone git@github.com:dsfsi/textaugment.git
$ cd textaugment
$ python setup.py install
How to use
There are three types of augmentations which can be used:
- word2vec
from textaugment import Word2vec
- wordnet
from textaugment import Wordnet
- translate (This will require internet access)
from textaugment import Translate
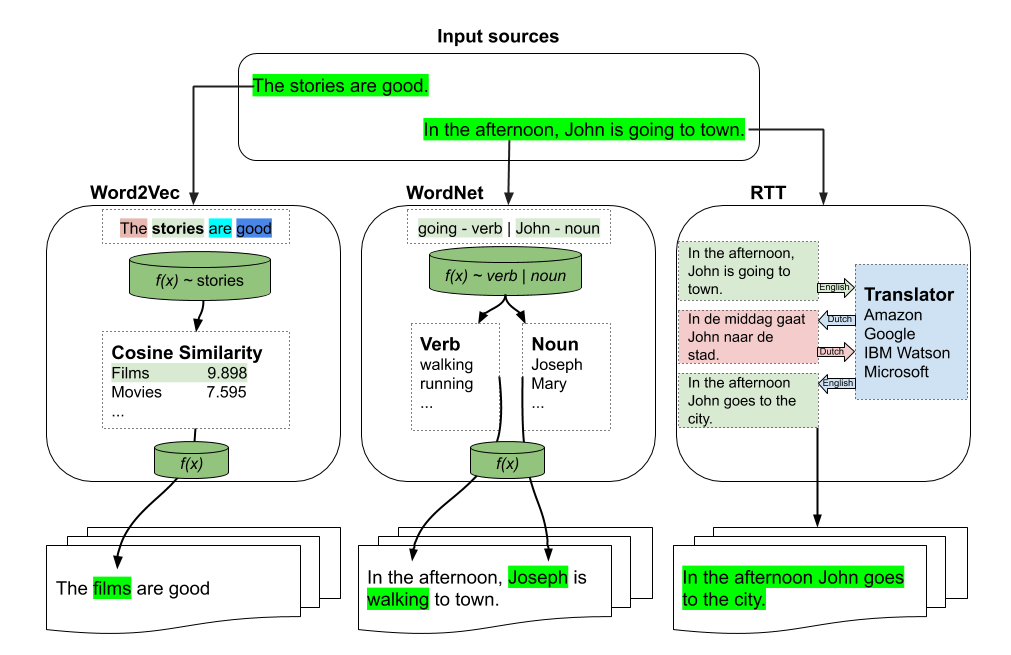
Word2vec-based augmentation
Basic example
>>> from textaugment import Word2vec
>>> t = Word2vec(model='path/to/gensim/model'or 'gensim model itself')
>>> t.augment('The stories are good')
The films are good
Advanced example
>>> runs = 1 # By default.
>>> v = False # verbose mode to replace all the words. If enabled runs is not effective. Used in this paper (https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~diyiy/docs/emnlp_wang_2015.pdf)
>>> p = 0.5 # The probability of success of an individual trial. (0.1<p<1.0), default is 0.5. Used by Geometric distribution to selects words from a sentence.
>>> t = Word2vec(model='path/to/gensim/model'or'gensim model itself', runs=5, v=False, p=0.5)
>>> t.augment('The stories are good')
The movies are excellent
WordNet-based augmentation
Basic example
>>> import nltk
>>> nltk.download('punkt')
>>> nltk.download('wordnet')
>>> from textaugment import Wordnet
>>> t = Wordnet()
>>> t.augment('In the afternoon, John is going to town')
In the afternoon, John is walking to town
Advanced example
>>> v = True # enable verbs augmentation. By default is True.
>>> n = False # enable nouns augmentation. By default is False.
>>> runs = 1 # number of times to augment a sentence. By default is 1.
>>> p = 0.5 # The probability of success of an individual trial. (0.1<p<1.0), default is 0.5. Used by Geometric distribution to selects words from a sentence.
>>> t = Wordnet(v=False ,n=True, p=0.5)
>>> t.augment('In the afternoon, John is going to town')
In the afternoon, Joseph is going to town.
RTT-based augmentation
Example
>>> src = "en" # source language of the sentence
>>> to = "fr" # target language
>>> from textaugment import Translate
>>> t = Translate(src="en", to="fr")
>>> t.augment('In the afternoon, John is going to town')
In the afternoon John goes to town
Built with ❤ on
Authors
Acknowledgements
Cite this paper when using this library.
Licence
MIT licensed. See the bundled LICENCE file for more details.
Project details
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file textaugment-1.1.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: textaugment-1.1.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 10.4 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/1.13.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.21.0 setuptools/41.0.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.29.1 CPython/3.6.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
6d0ecca10cafc6e73d3f0b3b78beeb62b4db8f1527f026feeaa8e19ca986f7c6
|
|
| MD5 |
7b5ef3c9efd1a78259788015ffb455c7
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
7e421f7b29274fed9242080fcb31dc52d5b67cf9578370fd8d783959f7cfbd4e
|
File details
Details for the file textaugment-1.1-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: textaugment-1.1-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 11.1 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/1.13.0 pkginfo/1.5.0.1 requests/2.21.0 setuptools/41.0.1 requests-toolbelt/0.9.1 tqdm/4.29.1 CPython/3.6.8
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
65c2d014dab8f4457f5998c0b2f3e04a7ae0e717cb81d0ab5f0f59b760133e1b
|
|
| MD5 |
f6d4ce092f907799dcfe6419a264e6cb
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
8da0c48647d04668f3b7cec8e9504058a959709251f2cc5dd4a8df4d62b2a638
|