A Python framework for high-performance simulation and graphics programming
Project description
NVIDIA Warp
Warp is a Python framework for writing high-performance simulation and graphics code. Warp takes regular Python functions and JIT compiles them to efficient kernel code that can run on the CPU or GPU.
Warp is designed for spatial computing and comes with a rich set of primitives that make it easy to write programs for physics simulation, perception, robotics, and geometry processing. In addition, Warp kernels are differentiable and can be used as part of machine-learning pipelines with frameworks such as PyTorch, JAX and Paddle.
Please refer to the project Documentation for API and language reference and CHANGELOG.md for release history.
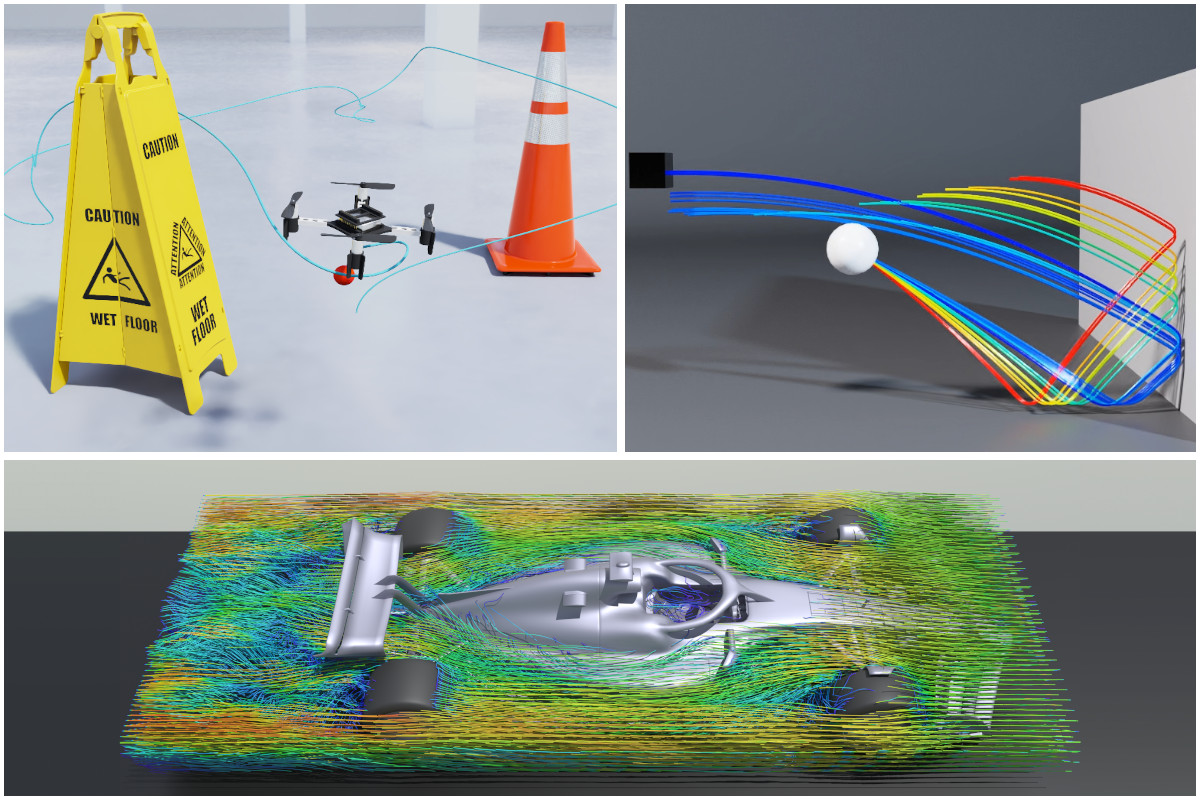
A selection of physical simulations computed with Warp
Installing
Python version 3.9 or newer is required. Warp can run on x86-64 and ARMv8 CPUs on Windows, Linux, and macOS. GPU support requires a CUDA-capable NVIDIA GPU and driver (minimum GeForce GTX 9xx).
The easiest way to install Warp is from PyPI:
pip install warp-lang
You can also use pip install warp-lang[examples] to install additional dependencies for running examples and USD-related features.
The binaries hosted on PyPI are currently built with the CUDA 12 runtime.
We also provide binaries built with the CUDA 13.0 runtime on the GitHub Releases page.
Copy the URL of the appropriate wheel file (warp-lang-{ver}+cu13-py3-none-{platform}.whl) and pass it to
the pip install command, e.g.
| Platform | Install Command |
|---|---|
| Linux aarch64 | pip install https://github.com/NVIDIA/warp/releases/download/v1.11.1/warp_lang-1.11.1+cu13-py3-none-manylinux_2_34_aarch64.whl |
| Linux x86-64 | pip install https://github.com/NVIDIA/warp/releases/download/v1.11.1/warp_lang-1.11.1+cu13-py3-none-manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl |
| Windows x86-64 | pip install https://github.com/NVIDIA/warp/releases/download/v1.11.1/warp_lang-1.11.1+cu13-py3-none-win_amd64.whl |
The --force-reinstall option may need to be used to overwrite a previous installation.
Nightly Builds
Nightly builds of Warp from the main branch are available on the NVIDIA Package Index.
To install the latest nightly build, use the following command:
pip install -U --pre warp-lang --extra-index-url=https://pypi.nvidia.com/
Note that the nightly builds are built with the CUDA 12 runtime and are not published for macOS.
If you plan to install nightly builds regularly, you can simplify future installations by adding NVIDIA's package
repository as an extra index via the PIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URL environment variable. For example:
export PIP_EXTRA_INDEX_URL="https://pypi.nvidia.com"
This ensures the index is automatically used for pip commands, avoiding the need to specify it explicitly.
CUDA Requirements
- Warp packages built with CUDA Toolkit 12.x require NVIDIA driver 525 or newer.
- Warp packages built with CUDA Toolkit 13.x require NVIDIA driver 580 or newer.
This applies to pre-built packages distributed on PyPI and GitHub and also when building Warp from source.
Note that building Warp with the --quick flag changes the driver requirements. The quick build skips CUDA backward compatibility, so the minimum required driver is determined by the CUDA Toolkit version. Refer to the latest CUDA Toolkit release notes to find the minimum required driver for different CUDA Toolkit versions (e.g., this table from CUDA Toolkit 12.6).
Warp checks the installed driver during initialization and will report a warning if the driver is not suitable, e.g.:
Warp UserWarning:
Insufficient CUDA driver version.
The minimum required CUDA driver version is 12.0, but the installed CUDA driver version is 11.8.
Visit https://github.com/NVIDIA/warp/blob/main/README.md#installing for guidance.
This will make CUDA devices unavailable, but the CPU can still be used.
To remedy the situation there are a few options:
- Update the driver.
- Install a compatible pre-built Warp package.
- Build Warp from source using a CUDA Toolkit that's compatible with the installed driver.
Tutorial Notebooks
The NVIDIA Accelerated Computing Hub contains the current, actively maintained set of Warp tutorials:
| Notebook | Colab Link |
|---|---|
| Introduction to NVIDIA Warp |  |
| GPU-Accelerated Ising Model Simulation in NVIDIA Warp |  |
Additionally, several notebooks in the notebooks directory provide additional examples and cover key Warp features:
Running Examples
The warp/examples directory contains a number of scripts categorized under subdirectories
that show how to implement various simulation methods using the Warp API.
Most examples will generate USD files containing time-sampled animations in the current working directory.
Before running examples, users should ensure that the usd-core, matplotlib, and pyglet packages are installed using:
pip install warp-lang[extras]
These dependencies can also be manually installed using:
pip install usd-core matplotlib pyglet
Examples can be run from the command-line as follows:
python -m warp.examples.<example_subdir>.<example>
To browse the example source code, you can open the directory where the files are located like this:
python -m warp.examples.browse
Most examples can be run on either the CPU or a CUDA-capable device, but a handful require a CUDA-capable device. These are marked at the top of the example script.
USD files can be viewed or rendered inside NVIDIA Omniverse, Pixar's UsdView, and Blender. Note that Preview in macOS is not recommended as it has limited support for time-sampled animations.
Built-in unit tests can be run from the command-line as follows:
python -m warp.tests
warp/examples/core
 |
 |
 |
 |
| dem | fluid | graph capture | marching cubes |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| mesh | nvdb | raycast | raymarch |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| sample mesh | sph | torch | wave |
warp/examples/fem
 |
 |
 |
 |
| diffusion 3d | mixed elasticity | apic fluid | streamlines |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| distortion energy | navier stokes | burgers | magnetostatics |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| adaptive grid | nonconforming contact | darcy level-set optimization | elastic shape optimization |
warp/examples/optim
 |
 |
 |
|
| diffray | fluid checkpoint | particle repulsion |
warp/examples/tile
 |
 |
 |
|
| mlp | nbody | mcgp |
Building
For developers who want to build the library themselves, the following tools are required:
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2019 upwards (Windows)
- GCC 9.4 upwards (Linux)
- CUDA Toolkit 12.0 or higher
- Git LFS installed
After cloning the repository, users should run:
python build_lib.py
Upon success, the script will output platform-specific binary files in warp/bin/.
The build script will look for the CUDA Toolkit in its default installation path.
This path can be overridden by setting the CUDA_PATH environment variable. Alternatively,
the path to the CUDA Toolkit can be passed to the build command as
--cuda_path="...". After building, the Warp package should be installed using:
pip install -e .
This ensures that subsequent modifications to the library will be reflected in the Python package.
Learn More
Please see the following resources for additional background on Warp:
- Product Page
- SIGGRAPH 2024 Course Slides
- GTC 2024 Presentation
- GTC 2022 Presentation
- GTC 2021 Presentation
- SIGGRAPH Asia 2021 Differentiable Simulation Course
The underlying technology in Warp has been used in a number of research projects at NVIDIA including the following publications:
- Accelerated Policy Learning with Parallel Differentiable Simulation - Xu, J., Makoviychuk, V., Narang, Y., Ramos, F., Matusik, W., Garg, A., & Macklin, M. (2022)
- DiSECt: Differentiable Simulator for Robotic Cutting - Heiden, E., Macklin, M., Narang, Y., Fox, D., Garg, A., & Ramos, F (2021)
- gradSim: Differentiable Simulation for System Identification and Visuomotor Control - Murthy, J. Krishna, Miles Macklin, Florian Golemo, Vikram Voleti, Linda Petrini, Martin Weiss, Breandan Considine et al. (2021)
Frequently Asked Questions
See the FAQ in the Warp documentation.
Support
Problems, questions, and feature requests can be opened on GitHub Issues.
For inquiries not suited for GitHub Issues, please email warp-python@nvidia.com.
Versioning
Versions take the format X.Y.Z, similar to Python itself:
- Increments in X are reserved for major reworks of the project causing disruptive incompatibility (or reaching the 1.0 milestone).
- Increments in Y are for regular releases with a new set of features.
- Increments in Z are for bug fixes. In principle, there are no new features. Can be omitted if 0 or not relevant.
This is similar to Semantic Versioning but is less strict regarding backward compatibility. Like with Python, some breaking changes can be present between minor versions if well-documented and gradually introduced.
Note that prior to 0.11.0, this schema was not strictly adhered to.
License
Warp is provided under the Apache License, Version 2.0. Please see LICENSE.md for full license text.
This project will download and install additional third-party open source software projects. Review the license terms of these open source projects before use.
Contributing
Contributions and pull requests from the community are welcome. Please see the Contribution Guide for more information on contributing to the development of Warp.
Publications & Citation
Research Using Warp
Our PUBLICATIONS.md file lists academic and research publications that leverage the capabilities of Warp. We encourage you to add your own published work using Warp to this list.
Citing Warp
To cite Warp itself in your own publications, please use the following BibTeX entry:
@misc{warp2022,
title = {Warp: A High-performance Python Framework for GPU Simulation and Graphics},
author = {Miles Macklin},
month = {March},
year = {2022},
note = {NVIDIA GPU Technology Conference (GTC)},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/nvidia/warp}}
}
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distributions
Built Distributions
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file warp_lang-1.11.1-py3-none-win_amd64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: warp_lang-1.11.1-py3-none-win_amd64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 119.0 MB
- Tags: Python 3, Windows x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: uv/0.9.18 {"installer":{"name":"uv","version":"0.9.18","subcommand":["publish"]},"python":null,"implementation":{"name":null,"version":null},"distro":{"name":"Debian GNU/Linux","version":"12","id":"bookworm","libc":null},"system":{"name":null,"release":null},"cpu":null,"openssl_version":null,"setuptools_version":null,"rustc_version":null,"ci":true}
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
15dc10aa51fb0fdbe1ca16d52e5fadca35a47ffd9d0c636826506f96bb2e7c41
|
|
| MD5 |
989b4f4fd2da9efb11d7c688ed203be9
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
252f2713f29bba5800b59835d97e136fa75d65a58b89734ae01de5a5f8f26482
|
File details
Details for the file warp_lang-1.11.1-py3-none-manylinux_2_34_aarch64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: warp_lang-1.11.1-py3-none-manylinux_2_34_aarch64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 136.1 MB
- Tags: Python 3, manylinux: glibc 2.34+ ARM64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: uv/0.9.18 {"installer":{"name":"uv","version":"0.9.18","subcommand":["publish"]},"python":null,"implementation":{"name":null,"version":null},"distro":{"name":"Debian GNU/Linux","version":"12","id":"bookworm","libc":null},"system":{"name":null,"release":null},"cpu":null,"openssl_version":null,"setuptools_version":null,"rustc_version":null,"ci":true}
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
5d0904b0eefcc81f39ba65375427a3de99006088aa43e24a9011263f07d0cd07
|
|
| MD5 |
83570de72ea4aaee9c816f4baa879ca8
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
5bff9ced2d69dc9db6cb6b1d3b80a3d2a81590e11ae368a7864aa5d6089fd820
|
File details
Details for the file warp_lang-1.11.1-py3-none-manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: warp_lang-1.11.1-py3-none-manylinux_2_28_x86_64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 134.8 MB
- Tags: Python 3, manylinux: glibc 2.28+ x86-64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: uv/0.9.18 {"installer":{"name":"uv","version":"0.9.18","subcommand":["publish"]},"python":null,"implementation":{"name":null,"version":null},"distro":{"name":"Debian GNU/Linux","version":"12","id":"bookworm","libc":null},"system":{"name":null,"release":null},"cpu":null,"openssl_version":null,"setuptools_version":null,"rustc_version":null,"ci":true}
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
8b098f41e71d421d80ee7562e38aa8380ff6b0d3b4c6ee866cfbdef733ac5bdc
|
|
| MD5 |
fd4dfe1839fe8ac84f787124e353650d
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
c2bb21e9396a963d50171f539f4a4c9411435e7bb9c5131f4480f882d5e51dc6
|
File details
Details for the file warp_lang-1.11.1-py3-none-macosx_11_0_arm64.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: warp_lang-1.11.1-py3-none-macosx_11_0_arm64.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 24.1 MB
- Tags: Python 3, macOS 11.0+ ARM64
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: uv/0.9.18 {"installer":{"name":"uv","version":"0.9.18","subcommand":["publish"]},"python":null,"implementation":{"name":null,"version":null},"distro":{"name":"Debian GNU/Linux","version":"12","id":"bookworm","libc":null},"system":{"name":null,"release":null},"cpu":null,"openssl_version":null,"setuptools_version":null,"rustc_version":null,"ci":true}
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
1ad11f1fa775269e991a3d55039152c8a504baf86701c849b485cb8e66c49d15
|
|
| MD5 |
6833a5ff8be29c8edacd4a1202320b6e
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
d586507cb6e0534422ff8437f71d676f6366ec907031db54751ad371f07c0b7f
|




















