Fast, flexible, and advanced augmentation library for deep learning, computer vision, and medical imaging. Albumentations offers a wide range of transformations for both 2D (images, masks, bboxes, keypoints) and 3D (volumes, volumetric masks, keypoints) data, with optimized performance and seamless integration into ML workflows.
Project description
Albumentations
📣 Stay updated! Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest releases, tutorials, and tips directly from the Albumentations team.
Docs | Discord | Twitter | LinkedIn
Albumentations is a Python library for image augmentation. Image augmentation is used in deep learning and computer vision tasks to increase the quality of trained models. The purpose of image augmentation is to create new training samples from the existing data.
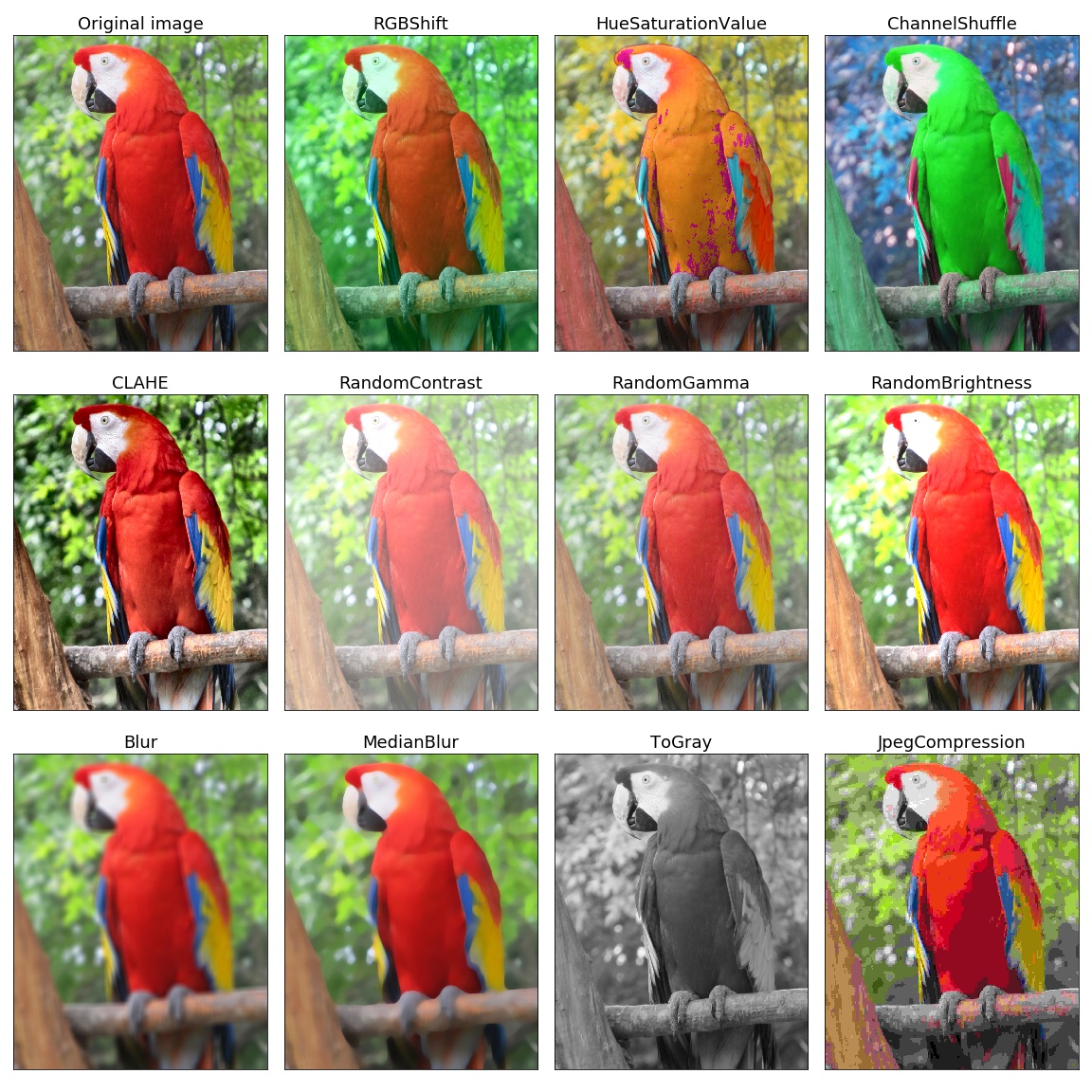
Here is an example of how you can apply some pixel-level augmentations from Albumentations to create new images from the original one:
Why Albumentations
- Complete Computer Vision Support: Works with all major CV tasks including classification, segmentation (semantic & instance), object detection, and pose estimation.
- Simple, Unified API: One consistent interface for all data types - RGB/grayscale/multispectral images, masks, bounding boxes, and keypoints.
- Rich Augmentation Library: 70+ high-quality augmentations to enhance your training data.
- Fast: Consistently benchmarked as the fastest augmentation library also shown below section, with optimizations for production use.
- Deep Learning Integration: Works with PyTorch, TensorFlow, and other frameworks. Part of the PyTorch ecosystem.
- Created by Experts: Built by developers with deep experience in computer vision and machine learning competitions.
Community-Driven Project, Supported By
Albumentations thrives on developer contributions. We appreciate our sponsors who help sustain the project's infrastructure.
| 🟠 Exclusive Partner |
|---|
| Your company could be here |
| 🟡 Integration Partner |
|---|
| Your company could be here |
| 🟢 Community Sponsor |
|---|
 |
💝 Become a Sponsor
Your sponsorship is a way to say "thank you" to the maintainers and contributors who spend their free time building and maintaining Albumentations. Sponsors are featured on our website and README. View sponsorship tiers on our support page
Table of contents
- Albumentations
- Why Albumentations
- Community-Driven Project, Supported By
- Table of contents
- Authors
- Installation
- Documentation
- A simple example
- Getting started
- Who is using Albumentations
- List of augmentations
- A few more examples of augmentations
- Benchmarking results
- Performance Comparison
- Contributing
- Community
- Citing
Authors
Current Maintainer
Vladimir I. Iglovikov | Kaggle Grandmaster
Emeritus Core Team Members
Mikhail Druzhinin | Kaggle Expert
Alexander Buslaev | Kaggle Master
Eugene Khvedchenya | Kaggle Grandmaster
Installation
Albumentations requires Python 3.9 or higher. To install the latest version from PyPI:
pip install -U albumentations
Other installation options are described in the documentation.
Documentation
The full documentation is available at https://albumentations.ai/docs/.
A simple example
import albumentations as A
import cv2
# Declare an augmentation pipeline
transform = A.Compose([
A.RandomCrop(width=256, height=256),
A.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
A.RandomBrightnessContrast(p=0.2),
])
# Read an image with OpenCV and convert it to the RGB colorspace
image = cv2.imread("image.jpg")
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Augment an image
transformed = transform(image=image)
transformed_image = transformed["image"]
Getting started
I am new to image augmentation
Please start with the introduction articles about why image augmentation is important and how it helps to build better models.
I want to use Albumentations for the specific task such as classification or segmentation
If you want to use Albumentations for a specific task such as classification, segmentation, or object detection, refer to the set of articles that has an in-depth description of this task. We also have a list of examples on applying Albumentations for different use cases.
I want to know how to use Albumentations with deep learning frameworks
We have examples of using Albumentations along with PyTorch and TensorFlow.
I want to explore augmentations and see Albumentations in action
Check the online demo of the library. With it, you can apply augmentations to different images and see the result. Also, we have a list of all available augmentations and their targets.
Who is using Albumentations
See also
List of augmentations
Pixel-level transforms
Pixel-level transforms will change just an input image and will leave any additional targets such as masks, bounding boxes, and keypoints unchanged. For volumetric data (volumes and 3D masks), these transforms are applied independently to each slice along the Z-axis (depth dimension), maintaining consistency across the volume. The list of pixel-level transforms:
- AdditiveNoise
- AdvancedBlur
- AutoContrast
- Blur
- CLAHE
- ChannelDropout
- ChannelShuffle
- ChromaticAberration
- ColorJitter
- Defocus
- Downscale
- Emboss
- Equalize
- FDA
- FancyPCA
- FromFloat
- GaussNoise
- GaussianBlur
- GlassBlur
- HEStain
- HistogramMatching
- HueSaturationValue
- ISONoise
- Illumination
- ImageCompression
- InvertImg
- MedianBlur
- MotionBlur
- MultiplicativeNoise
- Normalize
- PixelDistributionAdaptation
- PlanckianJitter
- PlasmaBrightnessContrast
- PlasmaShadow
- Posterize
- RGBShift
- RandomBrightnessContrast
- RandomFog
- RandomGamma
- RandomGravel
- RandomRain
- RandomShadow
- RandomSnow
- RandomSunFlare
- RandomToneCurve
- RingingOvershoot
- SaltAndPepper
- Sharpen
- ShotNoise
- Solarize
- Spatter
- Superpixels
- TextImage
- ToFloat
- ToGray
- ToRGB
- ToSepia
- UnsharpMask
- ZoomBlur
Spatial-level transforms
Spatial-level transforms will simultaneously change both an input image as well as additional targets such as masks, bounding boxes, and keypoints. For volumetric data (volumes and 3D masks), these transforms are applied independently to each slice along the Z-axis (depth dimension), maintaining consistency across the volume. The following table shows which additional targets are supported by each transform:
- Volume: 3D array of shape (D, H, W) or (D, H, W, C) where D is depth, H is height, W is width, and C is number of channels (optional)
- Mask3D: Binary or multi-class 3D mask of shape (D, H, W) where each slice represents segmentation for the corresponding volume slice
| Transform | Image | Mask | BBoxes | Keypoints | Volume | Mask3D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affine | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| AtLeastOneBBoxRandomCrop | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| BBoxSafeRandomCrop | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| CenterCrop | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| CoarseDropout | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ConstrainedCoarseDropout | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Crop | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| CropAndPad | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| CropNonEmptyMaskIfExists | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| D4 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ElasticTransform | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Erasing | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| FrequencyMasking | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| GridDistortion | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| GridDropout | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| GridElasticDeform | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| HorizontalFlip | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Lambda | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| LongestMaxSize | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| MaskDropout | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Morphological | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Mosaic | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| NoOp | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| OpticalDistortion | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| OverlayElements | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Pad | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| PadIfNeeded | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Perspective | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| PiecewiseAffine | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| PixelDropout | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomCrop | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomCropFromBorders | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomCropNearBBox | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomGridShuffle | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomResizedCrop | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomRotate90 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomScale | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomSizedBBoxSafeCrop | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomSizedCrop | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Resize | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Rotate | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SafeRotate | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ShiftScaleRotate | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SmallestMaxSize | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| SquareSymmetry | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ThinPlateSpline | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| TimeMasking | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| TimeReverse | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Transpose | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| VerticalFlip | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| XYMasking | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
3D transforms
3D transforms operate on volumetric data and can modify both the input volume and associated 3D mask.
Where:
- Volume: 3D array of shape (D, H, W) or (D, H, W, C) where D is depth, H is height, W is width, and C is number of channels (optional)
- Mask3D: Binary or multi-class 3D mask of shape (D, H, W) where each slice represents segmentation for the corresponding volume slice
| Transform | Volume | Mask3D | Keypoints |
|---|---|---|---|
| CenterCrop3D | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| CoarseDropout3D | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| CubicSymmetry | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Pad3D | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| PadIfNeeded3D | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| RandomCrop3D | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
A few more examples of augmentations
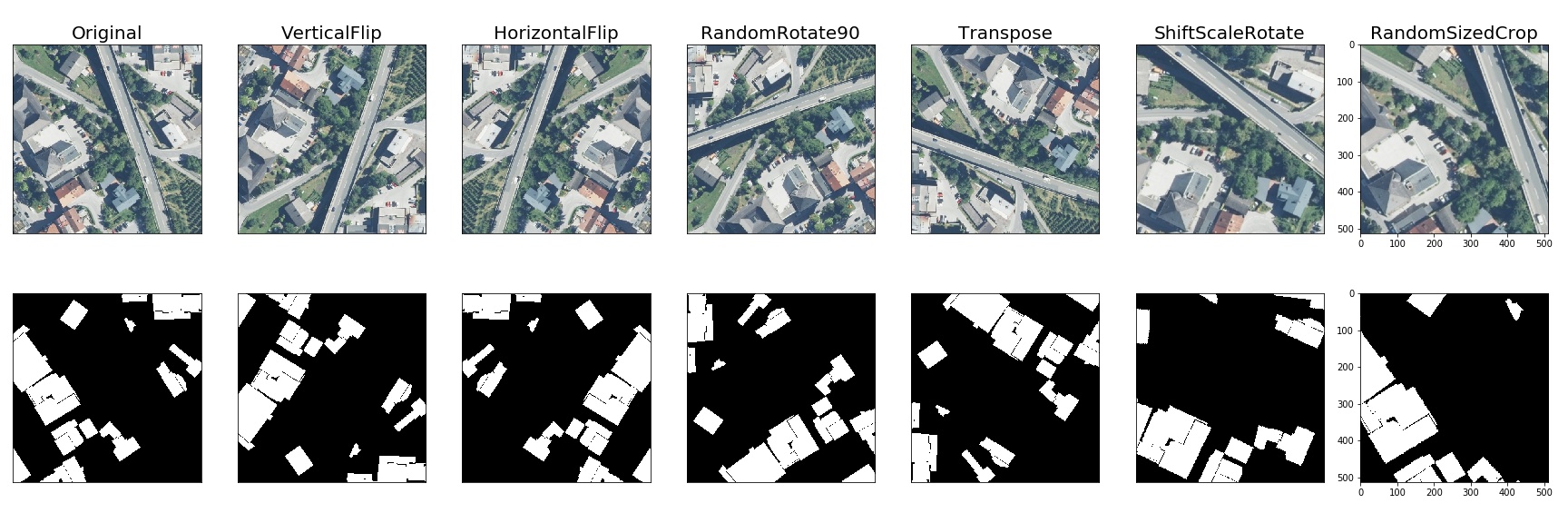
Semantic segmentation on the Inria dataset
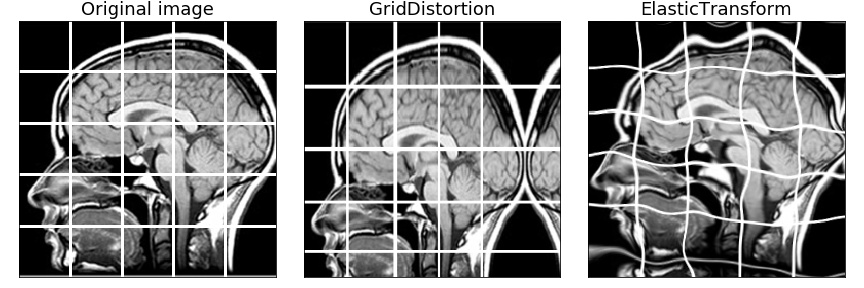
Medical imaging
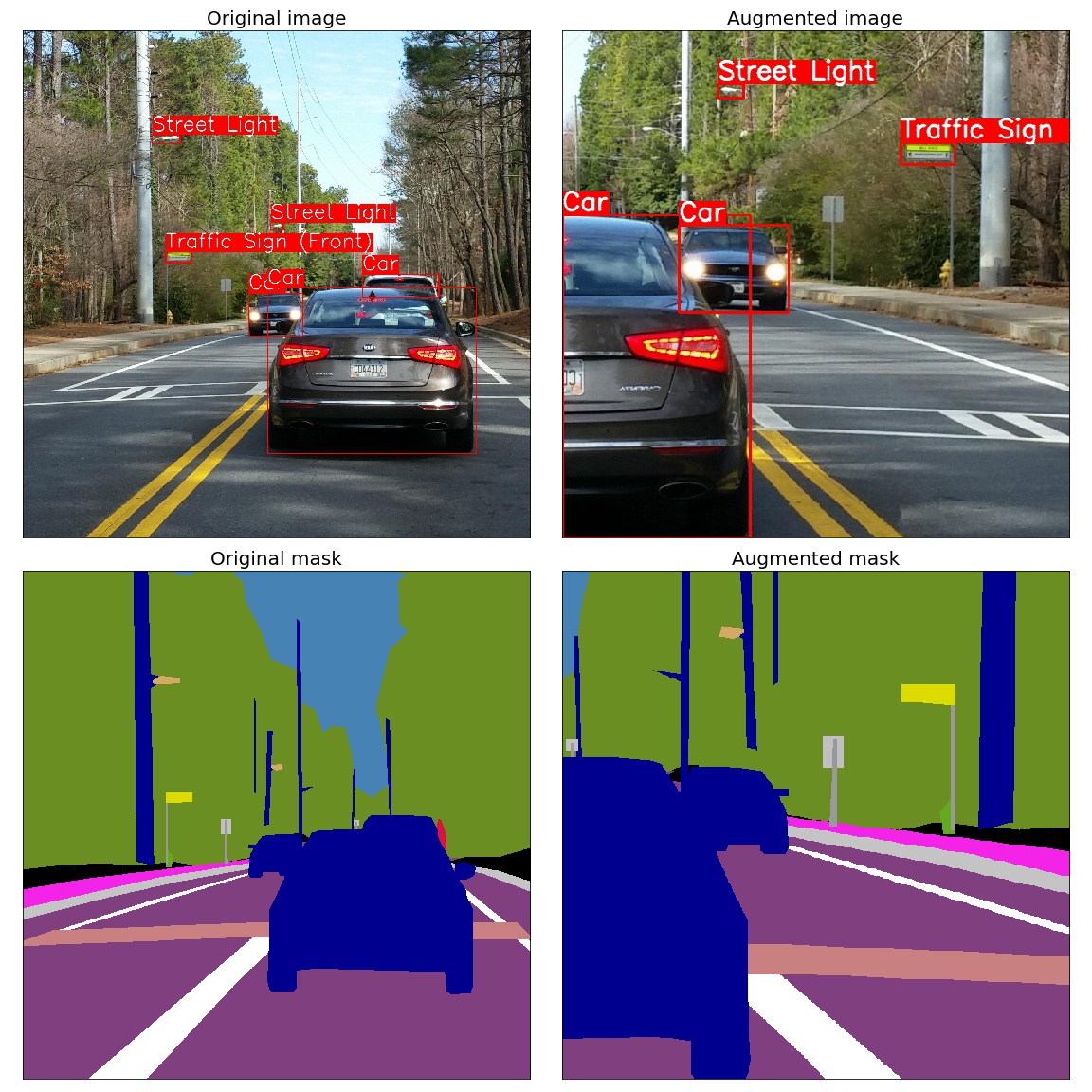
Object detection and semantic segmentation on the Mapillary Vistas dataset
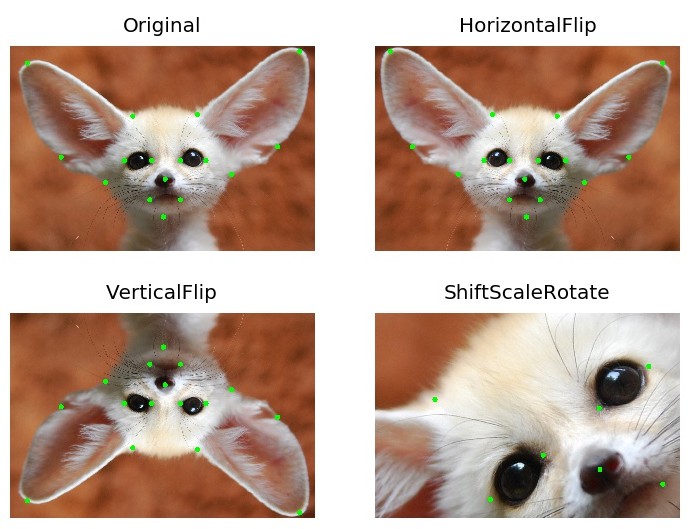
Keypoints augmentation

Benchmark Results
Image Benchmark Results
System Information
- Platform: macOS-15.1-arm64-arm-64bit
- Processor: arm
- CPU Count: 16
- Python Version: 3.12.8
Benchmark Parameters
- Number of images: 2000
- Runs per transform: 5
- Max warmup iterations: 1000
Library Versions
- albumentations: 2.0.4
- augly: 1.0.0
- imgaug: 0.4.0
- kornia: 0.8.0
- torchvision: 0.20.1
Performance Comparison
Number shows how many uint8 images per second can be processed on one CPU thread. Larger is better. The Speedup column shows how many times faster Albumentations is compared to the fastest other library for each transform.
| Transform | albumentations 2.0.4 |
augly 1.0.0 |
imgaug 0.4.0 |
kornia 0.8.0 |
torchvision 0.20.1 |
Speedup (Alb/fastest other) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affine | 1445 ± 9 | - | 1328 ± 16 | 248 ± 6 | 188 ± 2 | 1.09x |
| AutoContrast | 1657 ± 13 | - | - | 541 ± 8 | 344 ± 1 | 3.06x |
| Blur | 7657 ± 114 | 386 ± 4 | 5381 ± 125 | 265 ± 11 | - | 1.42x |
| Brightness | 11985 ± 455 | 2108 ± 32 | 1076 ± 32 | 1127 ± 27 | 854 ± 13 | 5.68x |
| CLAHE | 647 ± 4 | - | 555 ± 14 | 165 ± 3 | - | 1.17x |
| CenterCrop128 | 119293 ± 2164 | - | - | - | - | N/A |
| ChannelDropout | 11534 ± 306 | - | - | 2283 ± 24 | - | 5.05x |
| ChannelShuffle | 6772 ± 109 | - | 1252 ± 26 | 1328 ± 44 | 4417 ± 234 | 1.53x |
| CoarseDropout | 18962 ± 1346 | - | 1190 ± 22 | - | - | 15.93x |
| ColorJitter | 1020 ± 91 | 418 ± 5 | - | 104 ± 4 | 87 ± 1 | 2.44x |
| Contrast | 12394 ± 363 | 1379 ± 25 | 717 ± 5 | 1109 ± 41 | 602 ± 13 | 8.99x |
| CornerIllumination | 484 ± 7 | - | - | 452 ± 3 | - | 1.07x |
| Elastic | 374 ± 2 | - | 395 ± 14 | 1 ± 0 | 3 ± 0 | 0.95x |
| Equalize | 1236 ± 21 | - | 814 ± 11 | 306 ± 1 | 795 ± 3 | 1.52x |
| Erasing | 27451 ± 2794 | - | - | 1210 ± 27 | 3577 ± 49 | 7.67x |
| GaussianBlur | 2350 ± 118 | 387 ± 4 | 1460 ± 23 | 254 ± 5 | 127 ± 4 | 1.61x |
| GaussianIllumination | 720 ± 7 | - | - | 436 ± 13 | - | 1.65x |
| GaussianNoise | 315 ± 4 | - | 263 ± 9 | 125 ± 1 | - | 1.20x |
| Grayscale | 32284 ± 1130 | 6088 ± 107 | 3100 ± 24 | 1201 ± 52 | 2600 ± 23 | 5.30x |
| HSV | 1197 ± 23 | - | - | - | - | N/A |
| HorizontalFlip | 14460 ± 368 | 8808 ± 1012 | 9599 ± 495 | 1297 ± 13 | 2486 ± 107 | 1.51x |
| Hue | 1944 ± 64 | - | - | 150 ± 1 | - | 12.98x |
| Invert | 27665 ± 3803 | - | 3682 ± 79 | 2881 ± 43 | 4244 ± 30 | 6.52x |
| JpegCompression | 1321 ± 33 | 1202 ± 19 | 687 ± 26 | 120 ± 1 | 889 ± 7 | 1.10x |
| LinearIllumination | 479 ± 5 | - | - | 708 ± 6 | - | 0.68x |
| MedianBlur | 1229 ± 9 | - | 1152 ± 14 | 6 ± 0 | - | 1.07x |
| MotionBlur | 3521 ± 25 | - | 928 ± 37 | 159 ± 1 | - | 3.79x |
| Normalize | 1819 ± 49 | - | - | 1251 ± 14 | 1018 ± 7 | 1.45x |
| OpticalDistortion | 661 ± 7 | - | - | 174 ± 0 | - | 3.80x |
| Pad | 48589 ± 2059 | - | - | - | 4889 ± 183 | 9.94x |
| Perspective | 1206 ± 3 | - | 908 ± 8 | 154 ± 3 | 147 ± 5 | 1.33x |
| PlankianJitter | 3221 ± 63 | - | - | 2150 ± 52 | - | 1.50x |
| PlasmaBrightness | 168 ± 2 | - | - | 85 ± 1 | - | 1.98x |
| PlasmaContrast | 145 ± 3 | - | - | 84 ± 0 | - | 1.71x |
| PlasmaShadow | 183 ± 5 | - | - | 216 ± 5 | - | 0.85x |
| Posterize | 12979 ± 1121 | - | 3111 ± 95 | 836 ± 30 | 4247 ± 26 | 3.06x |
| RGBShift | 3391 ± 104 | - | - | 896 ± 9 | - | 3.79x |
| Rain | 2043 ± 115 | - | - | 1493 ± 9 | - | 1.37x |
| RandomCrop128 | 111859 ± 1374 | 45395 ± 934 | 21408 ± 622 | 2946 ± 42 | 31450 ± 249 | 2.46x |
| RandomGamma | 12444 ± 753 | - | 3504 ± 72 | 230 ± 3 | - | 3.55x |
| RandomResizedCrop | 4347 ± 37 | - | - | 661 ± 16 | 837 ± 37 | 5.19x |
| Resize | 3532 ± 67 | 1083 ± 21 | 2995 ± 70 | 645 ± 13 | 260 ± 9 | 1.18x |
| Rotate | 2912 ± 68 | 1739 ± 105 | 2574 ± 10 | 256 ± 2 | 258 ± 4 | 1.13x |
| SaltAndPepper | 629 ± 6 | - | - | 480 ± 12 | - | 1.31x |
| Saturation | 1596 ± 24 | - | 495 ± 3 | 155 ± 2 | - | 3.22x |
| Sharpen | 2346 ± 10 | - | 1101 ± 30 | 201 ± 2 | 220 ± 3 | 2.13x |
| Shear | 1299 ± 11 | - | 1244 ± 14 | 261 ± 1 | - | 1.04x |
| Snow | 611 ± 9 | - | - | 143 ± 1 | - | 4.28x |
| Solarize | 11756 ± 481 | - | 3843 ± 80 | 263 ± 6 | 1032 ± 14 | 3.06x |
| ThinPlateSpline | 82 ± 1 | - | - | 58 ± 0 | - | 1.41x |
| VerticalFlip | 32386 ± 936 | 16830 ± 1653 | 19935 ± 1708 | 2872 ± 37 | 4696 ± 161 | 1.62x |
Contributing
To create a pull request to the repository, follow the documentation at CONTRIBUTING.md
Community
Citing
If you find this library useful for your research, please consider citing Albumentations: Fast and Flexible Image Augmentations:
@Article{info11020125,
AUTHOR = {Buslaev, Alexander and Iglovikov, Vladimir I. and Khvedchenya, Eugene and Parinov, Alex and Druzhinin, Mikhail and Kalinin, Alexandr A.},
TITLE = {Albumentations: Fast and Flexible Image Augmentations},
JOURNAL = {Information},
VOLUME = {11},
YEAR = {2020},
NUMBER = {2},
ARTICLE-NUMBER = {125},
URL = {https://www.mdpi.com/2078-2489/11/2/125},
ISSN = {2078-2489},
DOI = {10.3390/info11020125}
}
📫 Stay Connected
Never miss updates, tutorials, and tips from the Albumentations team! Subscribe to our newsletter.
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distribution
Built Distribution
Filter files by name, interpreter, ABI, and platform.
If you're not sure about the file name format, learn more about wheel file names.
Copy a direct link to the current filters
File details
Details for the file albumentations-2.0.8.tar.gz.
File metadata
- Download URL: albumentations-2.0.8.tar.gz
- Upload date:
- Size: 354.5 kB
- Tags: Source
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.9.22
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
4da95e658e490de3c34af8fcdffed09e36aa8a4edd06ca9f9e7e3ea0b0b16856
|
|
| MD5 |
6d7f25f1868850fc401c746a222fece8
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
f4f485eb56c3217b53bcfc2d12e840a0b18ca60902086321cafa5a730f9c0470
|
File details
Details for the file albumentations-2.0.8-py3-none-any.whl.
File metadata
- Download URL: albumentations-2.0.8-py3-none-any.whl
- Upload date:
- Size: 369.4 kB
- Tags: Python 3
- Uploaded using Trusted Publishing? No
- Uploaded via: twine/6.1.0 CPython/3.9.22
File hashes
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 |
c4c4259aaf04a7386ad85c7fdcb73c6c7146ca3057446b745cc035805acb1017
|
|
| MD5 |
950bd8cc13241b04c659a7e4602a1960
|
|
| BLAKE2b-256 |
8e64013409c451a44b61310fb757af4527f3de57fc98a00f40448de28b864290
|